Configuración de IPv6 Black-Holing a través de la Interfaz Null0
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento describe cómo configurar Black-Holing en IPv6 a través de la interfaz Null0. Black Hole Routing es un método que permite al administrador bloquear el tráfico no deseado, como el tráfico de fuentes ilegales o el tráfico generado por un ataque de denegación de servicio (DoS), mediante el enrutamiento dinámico del tráfico a una interfaz muerta o a un host diseñado para recopilar información para su investigación, lo que mitiga el impacto del ataque en la red.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Asegúrese de cumplir estos requisitos antes de realizar esta configuración:
-
Conocer el protocolo de ruteo BGP y su funcionamiento
-
Conocer el esquema de direccionamiento IPv6
Componentes Utilizados
La información de este documento se basa en el Cisco 7200 Series Router con Cisco IOS® Software Release 15.0(1).
Convenciones
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Use la Command Lookup Tool (sólo para clientes registrados) para encontrar más información sobre los comandos usados en este documento.
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
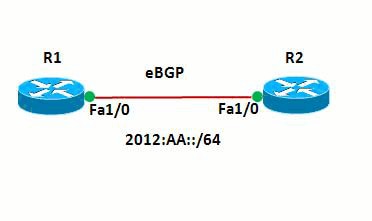
En esta red, los routers y R1 y R2 forman una relación eBGP entre sí. Los routers utilizan OSPFv3 para comunicarse internamente. En el router R1, la retención en negro se logra mediante la configuración de Null0 de tal manera que cualquier paquete con dirección de origen 20:20::20/128 se dirige a Null0. En otras palabras, todo el tráfico ruteado a Null0 se descarta.
Configuraciones de Ejemplo
En este documento, se utilizan estas configuraciones:
| Router R1 |
|---|
! hostname R1 ! no ip domain lookup ip cef ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef ! ! interface Loopback1 no ip address ipv6 address AA::1/128 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! interface Loopback10 no ip address ipv6 address AA:10::10/128 ipv6 enable ! interface FastEthernet1/0 no ip address speed auto duplex auto ipv6 address 2012:AA::1/64 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! router bgp 6501 bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor BB::1 remote-as 6502 neighbor BB::1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor BB::1 update-source Loopback1 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 redistribute static network AA:10::10/128 neighbor BB::1 activate exit-address-family ! ipv6 route 20:20::20/128 Null0 ipv6 router ospf 10 router-id 1.1.1.1 ! end |
| Router R2 |
|---|
! hostname R2 ! ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef ! ! interface Loopback1 no ip address ipv6 address BB::1/128 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! interface Loopback20 no ip address ipv6 address 20:20::20/128 ipv6 enable ! interface FastEthernet1/0 no ip address speed auto duplex auto ipv6 address 2012:AA::2/64 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! router bgp 6502 bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor AA::1 remote-as 6501 neighbor AA::1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor AA::1 update-source Loopback1 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 network 20:20::20/128 neighbor AA::1 activate exit-address-family ! ipv6 router ospf 10 router-id 2.2.2.2 ! end |
Verificación
Use esta sección para confirmar que su configuración funciona correctamente.
La herramienta Output Interpreter Tool (clientes registrados solamente) (OIT) soporta ciertos comandos show. Utilice la OIT para ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
Para verificar la configuración de eBGP, utilice los comandos show ipv6 route bgp y show bgp ipv6 unicast en el router R1.
| Router R1 |
|---|
show ipv6 route R1#show ipv6 route bgp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 7 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, HA - Home Agent, MR - Mobile Router, R - RIP
I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, ND - Neighbor Discovery
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
!--- The router R2 advertises the network 20:20::20/128, !--- but still the routing table is empty.
Para verificar cuáles son las rutas recibidas por BGP, utilice el comando show bgp ipv6 unicast. R1#show bgp ipv6 unicast
BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 20:20::20/128 BB::1 0 0 6502 I
*> :: 0 32768 ?
*> AA:10::10/128 :: 0 32768 I
!--- Note that the route 20:20::20/128 is received, !--- but it is not installed in the routing table.
|
Utilice el origen como interfaz de loopback 20 para intentar hacer ping al router R1 desde el router R2.
R2#ping ipv6 AA:10::10 source lo20 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to AA:10::10, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 20:20::20 ..... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) !--- The reason is the ICMP packet reaches !--- router R1 with source address as !--- 20:20::20/128 and therefore gets dropped.
Intente hacer ping al router R1 desde el router R2 sin el uso de la interfaz de loopback como origen.
R2#ping AA:10::10 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to AA:10::10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/61/180 ms !--- In this case, the ICMP packet has !--- the source address as BB::1.
Si se quita la instrucción ipv6 route 20:20::20/128 Null0 del router R1, la ruta 20:20::20/128 anunciada por el router R2 se instala en la tabla de ruteo del router R1. Este es el ejemplo de salida:
| En el router R1 |
|---|
R1(config)#no ipv6 route 20:20::20/128 Null0
!--- The Null0 command in removed from router R1.
R1#show bgp ipv6 unicast
BGP table version is 7, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 20:20::20/128 :: 0 32768 ?
* BB::1 0 0 6502 I
*> AA:10::10/128 :: 0 32768 I
!--- After the removal of the statement, !--- the route 20:20::20/128 is shown as best route.
R1#show ipv6 route bgp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 7 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, HA - Home Agent, MR - Mobile Router, R - RIP
I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, ND - Neighbor Discovery
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
B 20:20::20/128 [20/0]
via BB::1
!--- You can see that the route is displayed in routing table.
|
Ahora intente hacer ping al router R1 desde el router R2 con el origen como la interfaz Loopback Lo 20.
R2#ping ipv6 AA:10::10 source lo20 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to AA:10::10, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 20:20::20 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/54/140 ms !--- You can see that the ping is successful.
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
30-Jul-2012 |
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios