Ejemplo de configuración de NEAT con Cisco Identity Services Engine
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento describe la configuración y el comportamiento de Network Edge Authentication Topology (NEAT) en un escenario simple. NEAT utiliza el protocolo de señalización de información del cliente (CISP) para propagar las direcciones MAC del cliente y la información de VLAN entre los switches del solicitante y del autenticador.
En este ejemplo de configuración, tanto el switch autenticador (también denominado autenticador) como el switch suplicante (también denominado suplicante) realizan la autenticación 802.1x; el autenticador autentica al suplicante, que, a su vez, autentica el equipo de prueba.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recomienda que conozca el estándar de autenticación IEEE 802.1x.
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las siguientes versiones de software y hardware.
- Dos switches Catalyst de Cisco serie 3560 con Cisco IOS® Software, versión 12.2(55)SE8; un switch actúa como autenticador y el otro como solicitante.
- Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), versión 1.2.
- PC con Microsoft Windows XP, Service Pack 3.
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configurar
Este ejemplo cubre configuraciones de ejemplo para:
- Switch autenticador
- Switch suplicante
- ISE de Cisco
Las configuraciones son las mínimas necesarias para realizar este ejercicio de laboratorio; es posible que no sean óptimas para otras necesidades o que no las satisfagan.
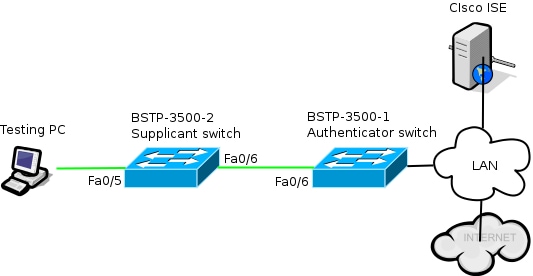
Diagrama de la red
Este diagrama de red ilustra la conectividad utilizada en este ejemplo. Las líneas negras indican conectividad lógica o física, y las líneas verdes indican enlaces autenticados mediante el uso de 802.1x.
Configuración del switch autenticador
El autenticador contiene los elementos básicos necesarios para dot1x. En este ejemplo, los comandos específicos de NEAT o CISP aparecen en negrita.
Esta es la configuración básica de autenticación, autorización y contabilidad (AAA):
aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
aaa authorization network default group radius
aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group radius
radius-server host 10.48.66.107 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco
! Enable authenticator switch to authenticate the supplicant switch.
dot1x system-auth-control
! Enable CISP framework.
cisp enable
! configure uplink port as access and dot1x authentication.
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport mode access
authentication port-control auto
dot1x pae authenticator
spanning-tree portfast
El CISP se habilita globalmente y el puerto de interconexión se configura en el modo de acceso y autenticador.
Configuración del switch suplicante
Una configuración precisa del suplicante es crucial para que toda la configuración funcione según lo esperado. Este ejemplo de configuración contiene una configuración típica AAA y dot1x.
Esta es la configuración AAA básica:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
aaa authorization network default group radius
aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group radius
radius-server host 10.48.66.107 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco
! Enable supplicant switch to authenticate devices connected
dot1x system-auth-control
! Forces the switch to send only multicast EAPOL packets when it receives either
unicast or multicast packets, which allows NEAT to work on the supplicant
switch in all host modes.
dot1x supplicant force-multicast
! Enable CISP framework operation.
cisp enable
El solicitante debe tener credenciales configuradas y debe proporcionar un método de protocolo de autenticación extensible (EAP) que se utilizará.
El solicitante puede utilizar EAP-Message Digest 5 (MD5) y EAP-Flexible Authentication mediante protocolo seguro (FAST) (entre otros tipos de EAP) para la autenticación en caso de CISP. Para mantener la configuración de ISE al mínimo, este ejemplo utiliza EAP-MD5 para la autenticación del solicitante con el autenticador. (El valor predeterminado forzaría el uso de EAP-FAST, que requiere el aprovisionamiento de credenciales de acceso protegido [PAC]; este documento no cubre ese escenario.)
! configure EAP mode used by supplicant switch to authenticate itself to
authenticator switch eap profile EAP_PRO
method md5
! Configure credentials use by supplicant switch during that authentication.
dot1x credentials CRED_PRO
username bsnsswitch
password 0 C1sco123
La conexión del solicitante al autenticador ya está configurada como puerto troncal (a diferencia de la configuración del puerto de acceso en el autenticador). En esta etapa, esto es lo esperado; la configuración cambiará dinámicamente cuando ISE devuelva el atributo correcto.
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk
dot1x pae supplicant
dot1x credentials CRED_PRO
dot1x supplicant eap profile EAP_PRO
El puerto que se conecta al PC con Windows tiene una configuración mínima y se muestra aquí sólo como referencia.
interface FastEthernet0/5
switchport access vlan 200
switchport mode access
authentication port-control auto
dot1x pae authenticator
Configuración de ISE
Este procedimiento describe cómo configurar una configuración básica de ISE.
- Active los protocolos de autenticación necesarios.
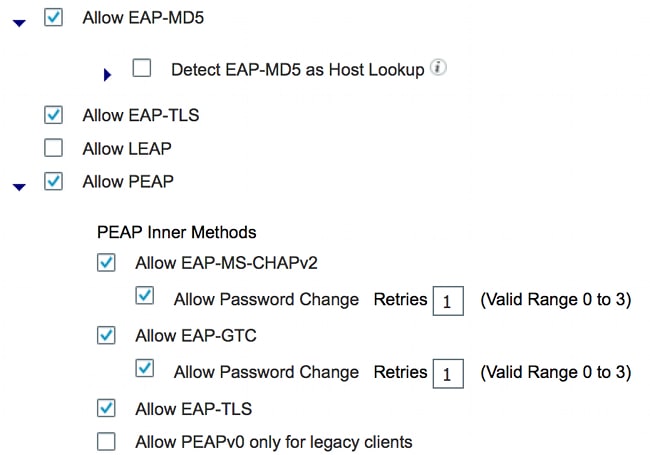
En este ejemplo, el dot1x cableado permite que EAP-MD5 autentique al solicitante en el autenticador y permite que el Protocolo de autenticación extensible protegido (PEAP)-Protocolo de autenticación por desafío mutuo de Microsoft versión 2 (MSCHAPv2) autentique el PC con Windows en el solicitante.
Navegue hasta Policy > Results > Authentication > Allowed protocols, seleccione la lista de servicios de protocolo utilizada por wired dot1x, y asegúrese de que los protocolos en este paso estén habilitados.
- Cree una directiva de autorización. Navegue hasta Policy > Results > Authorization > Authorization Policy, y cree o actualice una política para que contenga NEAT como un atributo devuelto. Este es un ejemplo de tal política:
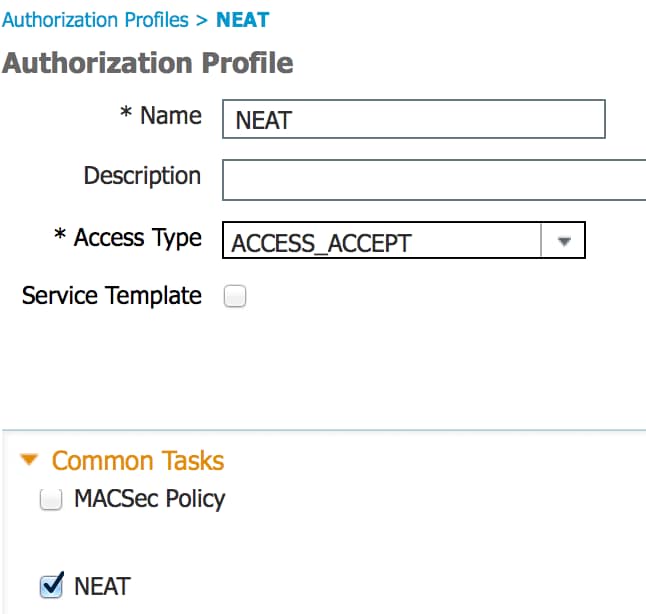
Cuando la opción NEAT está activada, ISE devuelve device-traffic-class=switch como parte de la autorización. Esta opción es necesaria para cambiar el modo de puerto del autenticador del acceso al tronco. - Cree una regla de autorización para utilizar este perfil. Navegue hasta Policy > Authorization, y cree o actualice una regla.
En este ejemplo, se crea un grupo de dispositivos especial llamado Authenticator_switches, y todos los suplicantes envían un nombre de usuario que comienza con bsnsswitch.

- Agregue los switches al grupo apropiado. Navegue hasta Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices, y haga clic en Add.

En este ejemplo, BSTP-3500-1 (el autenticador) es parte del grupo Authenticator_switches; BSTP-3500-2 (el solicitante) no necesita ser parte de este grupo.
Verificación
Use esta sección para confirmar que su configuración funciona correctamente. En esta sección se describen dos comportamientos:
- Autenticación entre switches
- Autenticación entre el PC con Windows y el solicitante
También explica tres situaciones adicionales:
- Eliminación de un cliente autenticado de la red
- Retirada de un solicitante
- Puertos sin dot1x en un suplicante
Autenticación del switch suplicante al switch autenticador
En este ejemplo, el solicitante se autentica ante el autenticador. Los pasos del proceso son:
- El suplicante está configurado y conectado al puerto fastethernet0/6. El intercambio dot1x hace que el solicitante utilice EAP para enviar un nombre de usuario y contraseña preconfigurados al autenticador.
- El autenticador realiza un intercambio RADIUS y proporciona credenciales para la validación de ISE.
- Si las credenciales son correctas, ISE devuelve los atributos requeridos por NEAT (device-traffic-class=switch) y el autenticador cambia su modo de puerto de switch de acceso a troncal.
Este ejemplo muestra el intercambio de información CISP entre switches:
bstp-3500-1#debug cisp all
Oct 15 13:51:03.672: %AUTHMGR-5-START: Starting 'dot1x' for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID 0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: %DOT1X-5-SUCCESS: Authentication successful for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: %AUTHMGR-7-RESULT: Authentication result 'success' from
'dot1x' for client (001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID
0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: Applying command... 'no switchport access vlan 1' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.739: Applying command... 'no switchport nonegotiate' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.748: Applying command... 'switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q'
at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.756: Applying command... 'switchport mode trunk' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.756: Applying command... 'switchport trunk native vlan 1' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.764: Applying command... 'spanning-tree portfast trunk' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: %AUTHMGR-5-SUCCESS: Authorization succeeded for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID 0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Start in
state Not Running
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Waiting
link UP
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 13:51:05.669: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/6, changed state to
up
Oct 15 13:51:06.793: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:06.793: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Start in
state Waiting link UP (no-op)
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/6, changed state to up
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Link UP in
state Waiting link UP
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Idle
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT: Received action Start Tick Timer
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT: Started CISP tick timer
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:28.377: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:28.377: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:29.400: CISP-EVENT: Stopped CISP tick timer
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x22 Length:0x001C
Type:REGISTRATION
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: Payload: 0200E84B
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposed CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Negotiated CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 59467
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x22 Length:0x001C
Type:REGISTRATION
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: Payload: 01000000
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x23 Length:0x003A
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: Payload: 010011020009001B0D5521C10300050 ...
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
to authenticator list
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about new
downstream client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client info at Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
to authenticator list
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about new
downstream client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client info at Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x23 Length:0x0018
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Una vez que la autenticación y la autorización se realizan correctamente, se produce el intercambio CISP. Cada intercambio tiene una SOLICITUD, que envía el solicitante, y una RESPUESTA, que sirve como respuesta y confirmación del autenticador.
Se realizan dos intercambios distintos: REGISTRATION y ADD_CLIENT. Durante el intercambio REGISTRATION, el solicitante informa al autenticador que es compatible con CISP y el autenticador reconoce este mensaje. El intercambio ADD_CLIENT se utiliza para informar al autenticador sobre los dispositivos conectados al puerto local del solicitante. Al igual que con REGISTRATION, ADD-CLIENT se inicia en el solicitante y es reconocido por el autenticador.
Ingrese estos comandos show para verificar la comunicación, los roles y las direcciones:
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
bstp-3500-1#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/6
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
En este ejemplo, el rol de Authenticator se asigna correctamente a la interfaz correcta (fa0/6) y se registran dos direcciones MAC. Las direcciones MAC son el suplicante en el puerto fa0/6 en VLAN1 y en VLAN200.
Ahora se puede realizar la verificación de las sesiones de autenticación dot1x. El puerto fa0/6 en el switch ascendente ya está autenticado. Este es el intercambio dot1x que se activa cuando se conecta BSTP-3500-2 (el solicitante):
bstp-3500-1#show authentication sessions
Interface MAC Address Method Domain Status Session ID
Fa0/6 001b.0d55.2187 dot1x DATA Authz Success 0A3039E10000000700FB3259
Como se esperaba en esta etapa, no hay sesiones sobre el solicitante:
bstp-3500-2#show authentication sessions
No Auth Manager contexts currently exist
Autenticación de PC de Windows en switch suplicante
En este ejemplo, la PC con Windows se autentica ante el solicitante. Los pasos del proceso son:
- El PC con Windows está conectado al puerto FastEthernet 0/5 en BSTP-3500-2 (el solicitante).
- El solicitante realiza la autenticación y la autorización con ISE.
- El solicitante informa al autenticador que un nuevo cliente está conectado en el puerto.
Esta es la comunicación del solicitante:
Oct 15 14:19:37.207: %AUTHMGR-5-START: Starting 'dot1x' for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID 0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:37.325: %DOT1X-5-SUCCESS: Authentication successful for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID
Oct 15 14:19:37.325: %AUTHMGR-7-RESULT: Authentication result 'success' from
'dot1x' for client (c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID
0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Received action Add Client
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to supplicant list
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant received event Add Client in
state Idle
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to the ADD list
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to ADD CLIENT req
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x24 Length:0x0029
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: Payload: 010011020009C46413B429C30300050 ...
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'retransmit' timer (30s)
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT: Started CISP tick timer
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant state changed to Request
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x24 Length:0x0018
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant received event Receive Packet
in state Request
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Stopped 'retransmit' timer
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): All Clients implicitly ACKed
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant state changed to Idle
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: %AUTHMGR-5-SUCCESS: Authorization succeeded for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID 0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Authenticator received event Start in
state Not Running
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Authenticator state changed to Waiting
link UP
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 14:19:38.373: CISP-EVENT: Stopped CISP tick timer
Oct 15 14:19:39.162: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/5, changed state to
up
Se produce un intercambio ADD_CLIENT, pero no se necesita ningún intercambio REGISTRATION.
Para verificar el comportamiento en el solicitante, ingrese el comando show cisp registrations:
bstp-3500-2#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/5
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
Fa0/6
802.1x Sup (Supplicant)
El solicitante tiene la función de un solicitante hacia el autenticador (interfaz fa0/6) y la función de un autenticador hacia la PC con Windows (interfaz fa0/5).
Para verificar el comportamiento en el autenticador, ingrese el comando show cisp clients:
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
c464.13b4.29c3 200 Fa0/6
Una nueva dirección MAC aparece en el autenticador bajo VLAN 200. Es la dirección MAC que se observó en las solicitudes AAA del solicitante.
Las sesiones de autenticación deben indicar que el mismo dispositivo está conectado en el puerto fa0/5 del solicitante:
bstp-3500-2#show authentication sessions
Interface MAC Address Method Domain Status Session ID
Fa0/5 c464.13b4.29c3 dot1x DATA Authz Success 0A3039E20000001501018B58
Eliminación del cliente autenticado de la red
Cuando se elimina un cliente (por ejemplo, si se apaga un puerto), se notifica al autenticador a través del intercambio DELETE_CLIENT.
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x25 Length:0x0029
Type:DELETE_CLIENT
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: Payload: 010011020009C46413B429C30300050 ...
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client c464.13b4.29c3
(vlan: 200) from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x25 Length:0x0018
Type:DELETE_CLIENT
Desmontaje del interruptor del suplicante
Cuando un suplicante es desconectado o removido, el autenticador introduce la configuración original nuevamente en el puerto para evitar problemas de seguridad.
Oct 15 15:57:31.257: Applying command... 'no switchport nonegotiate' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.273: Applying command... 'switchport mode access' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.273: Applying command... 'no switchport trunk encapsulation
dot1q' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.290: Applying command... 'no switchport trunk native vlan 1' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.299: Applying command... 'no spanning-tree portfast trunk' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.307: Applying command... 'switchport access vlan 1' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.315: Applying command... 'spanning-tree portfast' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/6, changed state to down
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Link DOWN
in state Idle
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client 001b.0d55.21c1
(vlan: 200) from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Not
Running
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 15:57:33.262: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/6, changed state
to down
Al mismo tiempo, el suplicante quita los clientes que representan al suplicante de la tabla CISP y desactiva el CISP en esa interfaz.
Puertos sin dot1x en switch suplicante
La información CISP que se propaga desde el solicitante al autenticador sólo sirve como otra capa de aplicación. El solicitante informa al autenticador acerca de todas las direcciones MAC permitidas que están conectadas a él.
Un escenario que normalmente se malinterpreta es el siguiente: si un dispositivo está conectado a un puerto que no tiene dot1x habilitado, la dirección MAC se aprende y se propaga al switch ascendente a través de CISP.
El autenticador permite la comunicación que proviene de todos los clientes aprendidos a través de CISP.
Básicamente, es la función del suplicante restringir el acceso de los dispositivos, a través de dot1x u otros métodos, y propagar la dirección MAC y la información VLAN al autenticador. El autenticador actúa como ejecutor de la información proporcionada en esas actualizaciones.
Por ejemplo, se creó una nueva VLAN (VLAN300) en ambos switches y se conectó un dispositivo al puerto fa0/4 en el solicitante. El puerto fa0/4 es un puerto de acceso simple que no está configurado para dot1x.
Este resultado del suplicante muestra un nuevo puerto registrado:
bstp-3500-2#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/4
Fa0/5
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
Fa0/6
802.1x Sup (Supplicant)
En el autenticador, una nueva dirección MAC es visible en la VLAN 300.
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c2 300 Fa0/6
c464.13b4.29c3 200 Fa0/6
68ef.bdc7.13ff 300 Fa0/6
Troubleshoot
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para solucionar problemas de configuración.
Estos comandos le ayudan a resolver problemas de NEAT y CISP; este documento incluye ejemplos para la mayoría de ellos:
- debug cisp all - muestra el intercambio de información CISP entre los switches.
- show cisp summary - muestra un resumen del estado de la interfaz CISP en el switch.
- show cisp registrations - indica las interfaces que participan en los intercambios CISP, las funciones de esas interfaces y si las interfaces son parte de NEAT.
- show cisp clients - muestra una tabla de direcciones MAC de clientes conocidas y su ubicación (VLAN e interfaz). Esto es útil principalmente del autenticador.
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
18-Oct-2013 |
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios