Depuraciones y configuraciones de ejemplo de IPSec sobre cable
Contenido
Introducción
La seguridad de protocolos en Internet (IPSec) es un marco de los estándares abiertos que asegura las comunicaciones privadas seguras sobre las redes del IP. De acuerdo con los estándares desarrollados por la Fuerza de tareas de ingeniería en Internet (IETF) (IETF), el IPSec asegura la confidencialidad, la integridad, y la autenticidad de las comunicaciones de datos a través de una red IP pública. El IPSec proporciona a un componente necesario para un basado en estándares, solución flexible para desplegar una política de seguridad de toda la red.
Este documento proporciona un ejemplo de configuración del IPSec entre dos cables módem de Cisco. Esta configuración crea un túnel de encripción a través de una red de cable entre dos routeres de cable módem de las uBR9xx Series de Cisco. Todo el tráfico entre las dos redes se cifra. Pero el tráfico destinado para otras redes se permite pasar unencrypted. Para los usuarios del oficina pequeña, oficina en el hogar (SOHO), esto permite la creación del Redes privadas virtuales (VPN) a través de una red de cable.
prerrequisitos
Requisitos
No hay requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
Los módems deben ajustarse a estos requisitos de configurar el IPSec en dos Cable módems:
-
Cisco uBR904, uBR905, o uBR924 en el modo de ruteo
-
Conjunto de características del IPSec 56
-
Software Release 12.0(5)T o Posterior de Cisco IOS®
Además, usted debe tener un Sistema de terminación del cablemódem (CMTS), que es cualquier Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) - de cabecera compatible con router del cable, tal como uBR7246VXR del Cisco uBR7246, del Cisco uBR7223, o de Cisco.
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si la red está funcionando, asegúrese de haber comprendido el impacto que puede tener cualquier comando.
Convenciones
Consulte Convenciones de Consejos TécnicosCisco para obtener más información sobre las convenciones del documento.
Teoría Precedente
El ejemplo en este documento utiliza un módem de cable del uBR904, un módem de cable del uBR924, y un uBR7246VXR CMTS. El Cable módems funciona con el Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(6), y el CMTS funciona con el Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(4)EC.
Nota: Este ejemplo se hace con la configuración manual en el Cable módems a través del puerto de la consola. Si un proceso automatizado se realiza a través del archivo de configuración de DOCSIS (el script ios.cfg se crea con las Listas de acceso de la configuración IPSec) entonces 100 y 101 no puede ser utilizado. Esto es porque la implementación de Cisco de la tabla de los docsDevNmAccess del Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) utiliza las Listas de acceso del Cisco IOS. Crea una lista de acceso por la interfaz. En el uBR904, 924, y 905, las primeras dos Listas de acceso se utilizan generalmente (100 y 101). En un módem de cable que soporte el Bus serie universal (USB), como el CVA120, tres Listas de acceso se utilizan (100, 101, y 102).
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Utilice la herramienta de búsqueda de comandos (clientes registrados solamente) para encontrar la información adicional sobre los comandos en este documento.
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
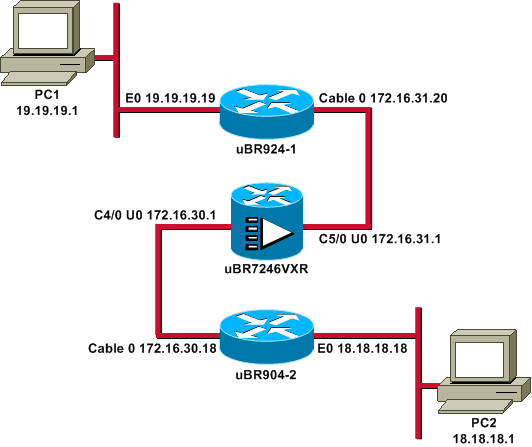
Nota: Todos los IP Addresses en este diagrama tienen una máscara 24-bit.
Configuraciones
En este documento, se utilizan estas configuraciones:
| uBR924-1 |
|---|
service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname ubr924-1 ! enable password ww ! ! ! ! clock timezone - -8 ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ! ! crypto isakmp policy 10 !--- Creates an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) policy with the specified priority !--- number of 10. The range for the priority is 1 to 10000, where 1 is the !--- highest priority. This command also enters Internet Security Association !--- and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) policy configuration command mode. hash md5 !--- Specifies the MD5 (HMAC variant) hash algorithm for packet authentication. authentication pre-share !--- Specifies that the authentication keys are pre-shared, as opposed to !--- dynamically negotiated using Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman (RSA) public !--- key signatures. group 2 !--- Diffie-Hellman group for key negotiation. lifetime 3600 !--- Defines how long, in seconds, each security association should exist before !--- it expires. Its range is 60 to 86400, and in this case, it is 1 hour. crypto isakmp key mykey address 18.18.18.18 !--- Specifies the pre-shared key that should be used with the peer at the !--- specific IP address. The key can be any arbitrary alphanumeric key up to !--- 128 characters. The key is case-sensitive and must be entered identically !--- on both routers. In this case, the key is mykey and the peer is the !--- Ethernet address of uBR904-2 . ! crypto IPSec transform-set TUNNELSET ah-md5-hmac esp-des !--- Establishes the transform set to use for IPsec encryption. As many as !--- three transformations can be specified for a set. Authentication Header !--- and ESP are in use. Another common transform set used in industry is !--- esp-des esp-md5-hmac. ! crypto map MYMAP local-address Ethernet0 !--- Creates the MYMAP crypto map and applies it to the Ethernet0 interface. crypto map MYMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp !--- Creates a crypto map numbered 10 and enters crypto map configuration mode. set peer 18.18.18.18 !--- Identifies the IP address for the destination peer router. In this case, !--- the Ethernet interface of the remote cable modem (ubr904-2) is used. set transform-set TUNNELSET !--- Sets the crypto map to use the transform set previously created. match address 101 !--- Sets the crypto map to use the access list that specifies the type of !--- traffic to be encrypted. !--- Do not use access lists 100, 101, and 102 if the IPsec config is !--- downloaded through the ios.cfg in the DOCSIS configuration file. ! ! ! ! voice-port 0 input gain -2 output attenuation 0 ! voice-port 1 input gain -2 output attenuation 0 ! ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 19.19.19.19 255.255.255.0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface cable-modem0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache cable-modem downstream saved channel 525000000 39 1 cable-modem mac-timer t2 40000 no cable-modem compliant bridge crypto map MYMAP !--- Applies the previously created crypto map to the cable interface. ! router rip version 2 network 19.0.0.0 network 172.16.0.0 ! ip default-gateway 172.16.31.1 ip classless ip http server ! access-list 101 permit ip 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 !--- Access list that identifies the traffic to be encrypted. In this case, !--- it is setting traffic from the local Ethernet network to the remote !--- Ethernet network. snmp-server manager ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 password ww login ! end |
La configuración del otro módem de cable es muy similar, tan la mayor parte de los comentarios en la configuración previa se omite.
| uBR904-2 |
|---|
version 12.1 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname ubr904-2 ! enable password ww ! ! ! ! ! clock timezone - -8 ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! ! ! crypto isakmp policy 10 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 lifetime 3600 crypto isakmp key mykey address 19.19.19.19 ! ! crypto IPSec transform-set TUNNELSET ah-md5-hmac ESP-Des ! crypto map MYMAP local-address Ethernet0 crypto map MYMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 19.19.19.19 !--- Identifies the IP address for the destination peer router. In this case, !--- the Ethernet interface of the remote cable modem (uBR924-1) is used. set transform-set TUNNELSET match address 101 ! ! ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 18.18.18.18 255.255.255.0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 ! interface cable-modem0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 no keepalive cable-modem downstream saved channel 555000000 42 1 cable-modem Mac-timer t2 40000 no cable-modem compliant bridge crypto map MYMAP ! router rip version 2 network 18.0.0.0 network 172.16.0.0 ! ip default-gateway 172.16.30.1 ip classless no ip http server ! access-list 101 permit ip 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 snmp-server manager ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 password ww login ! end |
El uBR7246VXR CMTS también funciona con la versión 2 del Routing Information Protocol (RIP), de modo que la encaminamiento trabaje. Ésta es la configuración de RIP usada en el CMTS:
| uBR7246VXR |
|---|
router rip version 2 network 172.16.0.0 no auto-summary |
Verificación
Use esta sección para confirmar que su configuración funciona correctamente.
Para verificar que el IPSec trabaje:
-
Verifique estas cosas:
-
El Cisco IOS Software soporta el IPSec.
-
La configuración corriente está correcta.
-
Las interfaces están para arriba.
-
Rutear los trabajos.
-
La lista de acceso definida para cifrar el tráfico está correcta.
-
-
Cree el tráfico y mire el cifrar y el Decrypt, para ver la cantidad que está aumentando.
-
Gire los debugs para crypto.
La herramienta Output Interpreter Tool (clientes registrados solamente) (OIT) soporta ciertos comandos show. Utilice la OIT para ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
Publique el comando show version en ambo Cable módems.
ubr924-1#show version Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) 920 Software (UBR920-K1O3SV4Y556I-M), Version 12.1(6), RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Copyright (c) 1986-2000 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Wed 27-Dec-00 16:36 by kellythw Image text-base: 0x800100A0, data-base: 0x806C1C20 ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 12.0(6r)T3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) ubr924-1 uptime is 1 hour, 47 minutes System returned to ROM by reload at 10:39:05 - Fri Feb 9 2001 System restarted at 10:40:05 - Fri Feb 9 2001 System image file is "flash:ubr920-k1o3sv4y556i-mz.121-6" cisco uBR920 CM (MPC850) processor (revision 3.e) with 15872K/1024K bytes of memory. Processor board ID FAA0422Q04F Bridging software. 1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 1 Cable Modem network interface(s) 3968K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write) 1536K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write) Configuration register is 0x2102
UBR924-1 funciona con el Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(6) con el conjunto de características del VALUE SMALL OFFICE/VOICE/FW IPSEC 56.
ubr904-2#show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (TM) 900 Software (UBR900-K1OY556I-M), Version 12.1(6),
RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Copyright (c) 1986-2000 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 27-DEC-00 11:06 by kellythw
Image text-base: 0x08004000, database: 0x085714DC
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.2(19980518:195057), RELEASED SOFTWARE
ROM: 900 Software (UBR900-RBOOT-M), Version 11.3(11)NA,
EARLY DEPLOYMENT RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
ubr904-2 uptime is 1 hour, 48 minutes
System returned to ROM by reload at 10:38:44 - Fri Feb 9 2001
System restarted at 10:40:37 - Fri Feb 9 2001
System image file is "flash:ubr900-k1oy556i-mz.121-6"
cisco uBR900 CM (68360) processor (revision D)
with 8192K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FAA0235Q0ZS
Bridging software.
1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
1 Cable Modem network interface(s)
4096K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)
2048K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write)
Configuration register is 0x2102
UBR904-2 funciona con el Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(6) con el PEQUEÑO conjunto de características del IPSec 56 OFFICE/FW.
ubr924-1#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet0 19.19.19.19 YES NVRAM up up cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 YES unset up up ubr904-2#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet0 18.18.18.18 YES NVRAM up up cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 YES unset up up
Del comando más reciente, usted puede ver que las interfaces de Ethernet están para arriba. Los IP Addresses de las interfaces de Ethernet fueron ingresados manualmente. Las interfaces del cable son también ascendentes y aprendieron sus IP Addresses con el DHCP. Porque asignan estas direcciones del cable dinámicamente, no pueden ser utilizadas como pares en la configuración IPSec.
ubr924-1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - ISIS level-1, L2 - ISIS level-2, ia - ISIS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.31.1 to network 0.0.0.0
19.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 19.19.19.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0
R 18.0.0.0/8 [120/2] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 3 masks
R 172.16.135.0/25 [120/1] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
R 172.16.29.0/27 [120/1] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
R 172.16.30.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
C 172.16.31.0/24 is directly connected, cable-modem0
R 192.168.99.0/24 [120/3] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:24, cable-modem0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 10.10.10.0 [120/2] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:24, cable-modem0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.31.1
Usted puede ver de esta salida que uBR924-1 esté aprendiendo sobre la ruta 18.18.18.0, que es la interfaz de Ethernet de uBR904-2.
ubr904-2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - ISIS, L1 - ISIS level-1, L2 - ISIS level-2, IA - ISIS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.30.1 to network 0.0.0.0
R 19.0.0.0/8 [120/2] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
18.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 18.18.18.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 3 masks
R 172.16.135.0/25 [120/1] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
R 172.16.29.224/27 [120/1] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
C 172.16.30.0/24 is directly connected, cable-modem0
R 172.16.31.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
R 192.168.99.0/24 [120/3] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:18, cable-modem0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 10.10.10.0 [120/2] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:18, cable-modem0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.30.1
De la tabla de ruteo de uBR904-2, usted puede ver que la red para los Ethernetes de uBR924-1 está en la tabla de ruteo.
Nota: Pudo haber los casos donde usted no puede funcionar con un Routing Protocol entre el dos Cable módems. En estos casos, usted debe agregar las Static rutas en el CMTS al tráfico directo para las interfaces de Ethernet del Cable módems.
La cosa siguiente a marcar es la certificación de la lista de acceso; publique el comando show access-lists en ambo Routers.
ubr924-1#show access-lists
Extended IP access list 101
permit ip 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 (2045 matches)
ubr904-2#show access-lists
Extended IP access list 101
permit ip 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 (2059 matches)
La lista de acceso fijó sesión IPSec cuando el LAN detrás de uBR924-1 (19.19.19.0) envía el tráfico IP al LAN detrás de uBR904-2 (18.18.18.0), y vice versa. No utilice “ningunos” en las Listas de acceso, porque crea los problemas. Refiera a configurar el IPSec Network Security para más detalles.
No hay tráfico IPSec. Publique el comando show crypto engine connection active.
ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0
No hay conexiones del IPSec porque ningún tráfico ha correspondido con las Listas de acceso.
Nota: Consulte Información Importante sobre Comandos de Debug antes de usar un comando debug.
El siguiente paso es girar algunos debugs crypto para generar el tráfico interesante.
En este ejemplo, se giran estos debugs:
-
debug crypto engine
-
debug crypto ipsec
-
debug crypto key-exchange
Usted debe primero generar un cierto tráfico interesante para ver la salida de los debugs. Publique un ping extendido del acceso de Ethernet de uBR904-2 al PC en uBR924-1 (dirección IP 19.19.19.1).
ubr904-2#ping ip Target IP address: 19.19.19.1 !--- IP address of PC1 behind the Ethernet of uBR924-1. Repeat count [5]: 100 !--- Sends 100 pings. Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 18.18.18.18 !--- IP address of the Ethernet behind uBR904-2. Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 100, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 19.19.19.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
El uBR924-2 muestra esta salida de los debugs:
ubr904-2#
01:50:37: IPSec(sa_request): ,
(key eng. msg.) src= 18.18.18.18, dest= 19.19.19.19,
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x19911A16(428939798), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4004
01:50:37: IPSec(sa_request): ,
(key Eng. msg.) src= 18.18.18.18, dest= 19.19.19.19,
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x7091981(118036865), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4004
01:50:37: ISAKMP: received ke message (1/2)
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): sitting IDLE. Starting QM immediately (QM_IDLE)
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): beginning Quick Mode exchange, M-ID of 1108017901
01:50:37: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP (1): sending packet to 19.19.19.19 (I) QM_IDLE
01:50:37: ISAKMP (1): received packet from 19.19.19.19 (I) QM_IDLE
01:50:37: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): processing SA payload. message ID = 1108017901
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: transform 1, AH_MD5
01:50:37: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:3.!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!7: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:37: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5
01:50:37: validate proposal 0
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DES
01:50:37: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:37: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:37: validate proposal 0
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:37: IPSec(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.1!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 99 percent (99/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 30/40/70 ms
ubr904-2#
Note que el primer ping falló. Esto es porque necesita establecer la conexión.
UBR924-1 muestra esta salida de los debugs:
ubr924-1#
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): received packet from 18.18.18.18 (R) QM_IDLE
01:50:24: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing SA payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: transform 1, AH_MD5
01:50:24: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:24: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:24: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5
01:50:24: validate proposal 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DES
01:50:24: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:24: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:24: validate proposal 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:24: IPSec(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:24: IPSec(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #2,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:24: validate proposal request 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing NONCE payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing ID payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET src 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0
prot 0 Port 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing ID payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET dst 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0
prot 0 Port 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): asking for 2 spis from IPSec
01:50:24: IPSec(key_engine): got a queue event...
01:50:24: IPSec(spi_response): getting spi 393021796 for SA
from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19 for prot 2
01:50:24: IPSec(spi_response): getting spi 45686884 for SA
from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19 for prot 3
01:50:24: ISAKMP: received ke message (2/2)
01:50:24: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): sending packet to 18.18.18.18 (R) QM_IDLE
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): received packet from 18.18.18.18 (R) QM_IDLE
01:50:24: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:24: IPSec allocate flow 0
01:50:24: IPSec allocate flow 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Creating IPSec SAs
01:50:24: inbound SA from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19
(proxy 18.18.18.0 to 19.19.19.0)
01:50:24: has spi 393021796 and conn_id 2000 and flags 4
01:50:24: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:24: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:24: outbound SA from 19.19.19.19 to 18.18.18.18
(proxy 19.19.19.0 to 18.18.18.0)
01:50:24: has spi 428939798 and conn_id 2001 and flags 4
01:50:24: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:24: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Creating IPSec SAs
01:50:24: inbound SA from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19
(proxy 18.18.18.0 to 19.19.19.0)
01:50:24: has spi 45686884 and conn_id 2002 and flags 4
01:50:24: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:24: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:24: outbound SA from 19.19.19.19 to 18.18.18.18
(proxy 19.19.19.0 to 18.18.18.0)
01:50:24: has spi 118036865 and conn_id 2003 and flags 4
01:50:25: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:25: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:25: ISAKMP (0:1): deleting node 1108017901 error FALSE reason
"quick mode done (await()"
01:50:25: IPSec(key_engine): got a queue event...
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x176D0964(393021796), conn_id= 2000, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) src= 19.19.19.19, dest= 18.18.18.18,
src_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x19911A16(428939798), conn_id= 2001, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x2B92064(45686884), conn_id= 2002, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) src= 19.19.19.19, dest= 18.18.18.18,
src_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x7091981(118036865), conn_id= 2003, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 19.19.19.19, sa_prot= 51,
sa_spi= 0x176D0964(393021796),
sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2000
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 18.18.18.18, sa_prot= 51,
sa_spi= 0x19911A16(428939798),
sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2001
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 19.19.19.19, sa_prot= 50,
sa_spi= 0x2B92064(45686884),
sa_trans= ESP-Des , sa_conn_id= 2002
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 18.18.18.18, sa_prot= 50,
sa_spi= 0x7091981(118036865),
sa_trans= ESP-Des , sa_conn_id= 2003
ubr924-1#
Una vez que se crea el túnel IPsec, usted puede ver la conexión y los paquetes encriptados y desencriptados.
ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 0 99 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 99 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 0 99 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 99 0
La primera línea 200x muestra los 99 paquetes recibidos. Tiene que desencriptar los paquetes para enviarlos al PC1. La segunda línea muestra 99 paquetes enviados. Tiene que cifrar los paquetes antes de que los envíe a uBR904-2. Las terceras y cuartas líneas hacen el mismo proceso, pero con el ESP-DES lo transforman en vez del AH-MD5-HMAC.
Nota: Si la transformación fijó que se configura en el módem de cable es ESP-DES ESP-MD5-HMAC, usted considera solamente dos sistemas autónomos (AS), en comparación con los cuatro mostrados en el comando show anterior.
ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 0 99 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 99 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 0 99 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 99 0
Publique un ping extendido al PC2 de uBR924-1 para ver si los contadores incrementan para los paquetes encriptados y desencriptados.
ubr924-1#ping ip Target IP address: 18.18.18.1 Repeat count [5]: 50 Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 19.19.19.19 Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 50, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 18.18.18.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (50/50), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/30/33 ms ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 0 149 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 149 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 0 149 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 149 0 ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 0 149 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 149 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 0 149 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 149 0
Otro ping extendido se puede publicar, para considerar que los contadores incrementan otra vez. Esta vez, envía un ping 500-packet de uBR904-2 a la interfaz de Ethernet de uBR924-1 (19.19.19.19).
ubr904-2#ping ip Target IP address: 19.19.19.19 Repeat count [5]: 500 Datagram size [100]: 1000 Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 18.18.18.18 Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 500, 1000-byte ICMP Echos to 19.19.19.19, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 01:59:06: IPSec(encapsulate): encaps area too small, moving to new buffer: idbtype 0, encaps_size 26, header size 60, avail 84!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (500/500), round-trip min/avg/max = 98/135/352 ms ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 0 649 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 649 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 0 649 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 649 0 ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 0 649 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 649 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 0 649 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 649 0
Usted puede publicar los comandos clear crypto isakmp y clear crypto sa de borrar las conexiones. También, si no hay tráfico a través del túnel IPsec durante el vencimiento, el IPSec reajusta la conexión automáticamente.
Troubleshooting
No hay actualmente información disponible específica para resolver problemas esta configuración.
Información Relacionada
- Comandos del IPSec Network Security
- Una Introducción al encripción de seguridad IP (IPSec) - Información del debug
- Ejemplos de la configuración IPSec
- Configurar el IPSec Network Security
- Configurar el Cisco Universal Broadband Routers (uBR) de la serie 900
- Descargas del cable Cisco/de la Banda ancha (clientes registrados solamente)
- Soporte de tecnología de la Banda ancha por cable
- Soporte Técnico y Documentación - Cisco Systems
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios