Dépannage de DLSw à l'aide de commandes de débogage
Contenu
Introduction
Ce document fournit des informations sur la façon de dépanner DLSw (Data Link Switching) avec les commandes debug.
Conditions préalables
Conditions requises
Aucune spécification déterminée n'est requise pour ce document.
Components Used
Ce document n'est pas limité à des versions de matériel ou de logiciel spécifiques.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Déboguages
Avant d'essayer l'une des commandes debug de ce document, référez-vous à Informations importantes sur les commandes Debug.
Lorsque vous dépannez le démarrage d'une session, exécutez la commande debug dlsw et observez :
-
La configuration initiale de la session
-
Indique si le circuit est en cours d'activation
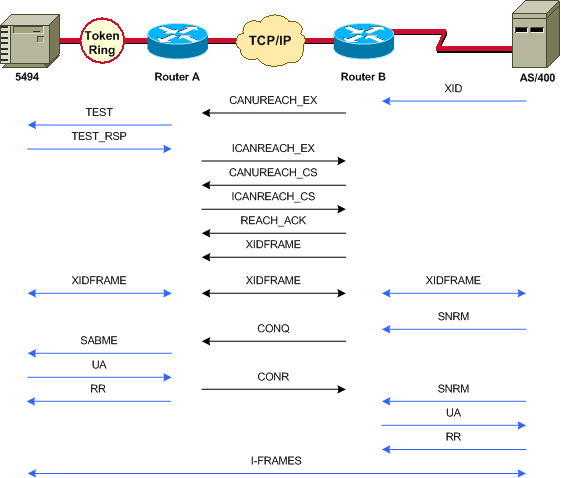
Ce schéma montre le flux d'un contrôleur de communication Cisco 3174 vers l'hôte via Data-Link Switching Plus (DLSw+) :
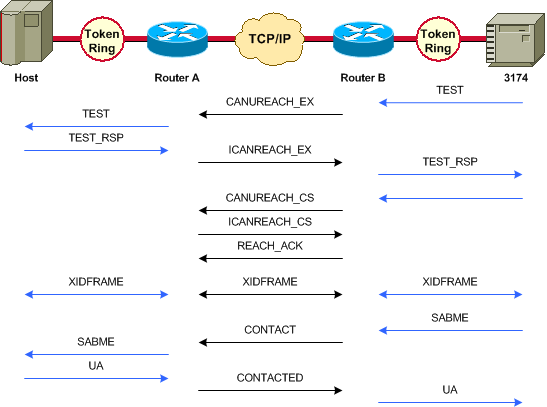
L'exemple suivant de la commande debug dlsw montre le flux d'une session correcte lorsqu'elle est activée.
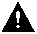 Attention : La commande debug dlsw peut entraîner une grave dégradation des performances, en particulier lorsqu'elle est exécutée sur un routeur dont plusieurs circuits sont connectés à plusieurs homologues configurés.
Attention : La commande debug dlsw peut entraîner une grave dégradation des performances, en particulier lorsqu'elle est exécutée sur un routeur dont plusieurs circuits sont connectés à plusieurs homologues configurés.
ibu-7206# debug dlsw DLSw reachability debugging is on at event level for all protocol traffic DLSw peer debugging is on DLSw local circuit debugging is on DLSw core message debugging is on DLSw core state debugging is on DLSw core flow control debugging is on DLSw core xid debugging is on ibu-7206# DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : UDATA_STN.Ind dlen: 208 CSM: Received CLSI Msg : UDATA_STN.Ind dlen: 208 from TokenRing3/0 CSM: smac 8800.5a49.1e38, dmac c000.0000.0080, ssap F0, dsap F0 CSM: Received frame type NETBIOS DATAGRAM from 0800.5a49.1e38, To3/0 DLSw: peer_put_bcast() to non-grouped peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSw: Keepalive Request sent to peer 5.5.5.1(2065)) DLSw: Keepalive Response from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Ind dlen: 41 CSM: Received CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Ind dlen: 41 from TokenRing3/0 CSM: smac c001.68ff.0001, dmac 4000.0000.0001, ssap 4 , dsap 0
Notez la trame de test qui provient du LAN (localement) de la station c001.68ff.0001 à l’adresse MAC 4000.0000.0001. Chaque fois que vous voyez un .Ind, il s’agit d’un paquet provenant du réseau local. Chaque fois qu'un paquet est envoyé au réseau local, vous devez voir un .RSP.
DLSw: peer_put_bcast() to non-grouped peer 5.5.5.1(2065) %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 4( ICR ) -explorer from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Rsp dlen: 44
Notez la diffusion qui est envoyée à l'homologue distant et la réponse ICR (I Can Reach). Cela signifie que le routeur distant a identifié la station comme étant accessible. Remarquez ensuite la réponse de test TEST_STN.Rsp, qui est la réponse de test du routeur ? ? à la station.
DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID_STN.Ind dlen: 54 pfinCSM: Received CLSI Msg : ID_STN.Ind dlen: 54 from TokenRing3/0 CSM: smac c001.68ff.0001, dmac 4000.0000.0001, ssap 4 , dsap 4
Une fois que la station a reçu la réponse au test, la première identification Exchange (XID) est envoyée au routeur Cisco ; ceci peut être vu avec l'ID_STN.Ind. Le routeur se tient sur cette trame jusqu’à ce que les détails soient effacés entre les deux routeurs DLSw.
DLSw: new_ckt_from_clsi(): TokenRing3/0 4001.68ff.0001:4->4000.0000.0001:4 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:DLC-Id state:DISCONNECTED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_a() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Req dlen: 108 DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:DISCONNECTED->LOCAL_RESOLVE DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 108 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:DLC-ReqOpnStn.Cnf state:LOCAL_RESOLVE DLSw: core: dlsw_action_b() CORE: Setting lf size to 30 %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 3( CUR ) to peer 5.5.5.1(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:LOCAL_RESOLVE->CKT_START %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 4( ICR ) from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSw: 1622182940 recv FCI 0 - s:0 so:0 r:0 ro:0 DLSw: recv RWO DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:WAN-ICR state:CKT_START DLSw: core: dlsw_action_e() DLSw: sent RWO DLSw: 1622182940 sent FCI 80 on ACK - s:20 so:1 r:20 ro:1 %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 5( ACK ) to peer 5.5.5.1(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CKT_START->CKT_ESTABLISHED
Notez le flux interne de DLSw entre les deux homologues. Ces paquets sont normaux pour chaque démarrage de session.
La première étape de ce processus consiste à passer d'un état déconnecté à un état CKT_ESTABLISHED ; cette séquence se produit :
-
Les deux routeurs transmettent une trame CUR pour le circuit lui-même, appelée CUR_cs (Can You Reach circuit setup).
-
Lorsque l'homologue qui initie la trame CUR_cs reçoit une trame ICR_cs, il envoie un accusé de réception et se déplace pour établir un circuit.
-
Les deux routeurs DLSw sont prêts pour le traitement XID.
DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:DLC-Id state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_f() DLSw: 1622182940 sent FCA on XID %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) to peer 5.5.5.1(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED
Après réception d’un XID, la réponse de test est envoyée à la station et est conservée par le routeur. Le routeur transmet ensuite ce XID à son homologue à travers ce circuit, ce qui signifie que des paquets sont envoyés à et depuis l'homologue avec l'ID de circuit marqué sur lui.
De cette manière, DLSw sait ce qui se passe entre deux stations, car DLSw met fin à la session LLC2 de chaque côté du cloud.
gnb%DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSw: 1622182940 recv FCA on XID - s:20 so:0 r:20 ro:0 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:WAN-XID state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_g() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 12 DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 39 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:DLC-Id state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_f() %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) to peer 5.5.5.1(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED
Initialement, il y a une réponse au premier XID qui a été envoyé auparavant.
Notez que, dans ID.Rsp, le XID est envoyé à la station, qui répond avec un ID.Ind (qui est un autre XID envoyé à l'homologue DLSw).
%DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 8( CONQ ) from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:WAN-CONQ state:CKT_ESTABLISHED
La station de l'autre côté répond par un SABME (CONQ) au XID ; par conséquent, la négociation XID s'est terminée et la session est prête à démarrer.
DLSw: core: dlsw_action_i() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Req dlen: 16 !--- CONNECT.Req means that a SABME has been sent. DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CONTACT_PENDING DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 8 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:DLC-Connect.Cnf state:CONTACT_PENDING DLSw: core: dlsw_action_j() %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 9( CONR ) to peer 5.5.5.1(2065) success DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : FLOW.Req dlen: 0 DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CONTACT_PENDING->CONNECTED
Le routeur reçoit maintenant l'UA de la station, ce qui est visible dans le message CONNECT.Cfm. Ceci est envoyé à l'homologue distant via un CONR.
%DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 10( INFO ) from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSw: 1622182940 decr r - s:20 so:0 r:19 ro:0 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:WAN-INFO state:CONNECTED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_m() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : DATA.Req dlen: 34 DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CONNECTED->CONNECTED DLSw: 1622182940 decr s - s:19 so:0 r:19 ro:0 DLSW Received-disp : CLSI Msg : DATA.Ind dlen: 35 DLSw: sent RWO DLSw: 1622182940 sent FCI 80 on INFO - s:19 so:0 r:39 ro:1 %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 10( INFO ) to peer 5.5.5.1(2065) success %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 10( INFO ) from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSw: 1622182940 decr r - s:19 so:0 r:38 ro:1 DLSw: 1622182940 recv FCA on INFO - s:19 so:0 r:38 ro:0 DLSw: 1622182940 recv FCI 0 - s:19 so:0 r:38 ro:0 DLSw: recv RWO DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:WAN-INFO state:CONNECTED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_m() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : DATA.Req dlen: 28 DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CONNECTED->CONNECTED
Le fichier DATA.Req indique qu'une trame I a été transmise ; DATA.Ind indique qu'une trame I a été reçue. Celles-ci sont très utiles pour déterminer quels paquets circulent sur les routeurs DLSw.
DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : DISCONNECT.Ind dlen: 8 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:DLC-Disc.Ind state:CONNECTED
Ce résultat montre un fichier DISCONNECT.Ind ; comme précédemment, any .Ind provient du réseau local. Cela signifie que la station a envoyé une déconnexion. Le routeur commence alors à démonter le circuit.
DLSw: core: dlsw_action_n() %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 14( HLTQ ) to peer 5.5.5.1(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CONNECTED->DISC_PENDING %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 15( HLTR ) from peer 5.5.5.1(2065) DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:WAN-HLTR state:DISC_PENDING
Une fois la déconnexion reçue, le routeur envoie un HALT à l’homologue distant et attend sa réponse. Une fois la réponse reçue, le routeur envoie un UA à la station et ferme le circuit. Ceci est indiqué comme DISCONNECT.Rsp :
DLSw: core: dlsw_action_q() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : DISCONNECT.Rsp dlen: 4 DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : CLOSE_STN.Req dlen: 4 DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:DISC_PENDING->CLOSE_PEND DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : CLOSE_STN.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 8 DLSw: START-FSM (1622182940): event:DLC-CloseStn.Cnf state:CLOSE_PEND DLSw: core: dlsw_action_y() DLSw: 1622182940 to dead queue DLSw: END-FSM (1622182940): state:CLOSE_PEND->DISCONNECTED
DLSw place ensuite le circuit dans la file d'attente morte. À partir de la file d'attente inactive, les pointeurs sont nettoyés et prêts pour un nouveau circuit.
Pour une session avec NetBIOS, la manière dont DLSw gère la négociation est modifiée ; mais les débogages sont très similaires. La seule différence dans SNA et NetBIOS est que les XID ne circulent pas pour les stations NetBIOS et que les routeurs DLSw échangent à la place des trames NetBIOS Name Query et NetBIOS Name Reconnzed.
Traduction multimédia DLSw
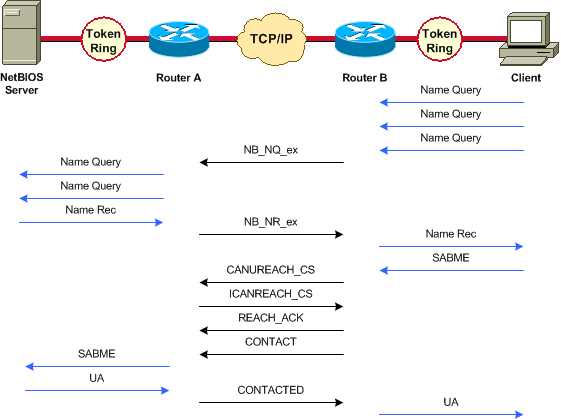
Une fois l’interface activée, le routeur démarre le processus : il détermine l'emplacement du contrôleur distant.
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial4, changed state to up DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID_STN.Ind dlen: 46 CSM: Received CLSI Msg : ID_STN.Ind dlen: 46 from Serial4 CSM: smac 4000.5494.00dd, dmac 4000.9404.0001, ssap 4 , dsap 4 %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 4( ICR ) -explorer from peer 10.17.2.198(2065) DLSw: new_ckt_from_clsi(): Serial4 4000.5494.00dd:4-4000.9404.0001:4
Une fois la trame ICR reçue, le DLSw démarre la machine à état fini (FSM) pour cette session. Cela est fait par REQ_OPNSTN.Req et REQ_OPNSTN.Cfm qui vont entre DLSw et l'interface de services de liaison Cisco (CLSI).
DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:DLC-Id state:DISCONNECTED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_a() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Req dlen: 106 DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:DISCONNECTED->LOCAL_RESOLVE DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 106 DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:DLC-ReqOpnStn.Cnf state:LOCAL_RESOLVE DLSw: core: dlsw_action_b() CORE: Setting lf size to FF
Après avoir discuté avec CLSI, le routeur envoie ensuite des trames CUR de démarrage de session au routeur distant. Ces trames CUR se trouvent uniquement entre les deux routeurs.
%DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 3( CUR ) to peer 10.17.2.198(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:LOCAL_RESOLVE->CKT_START %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 4( ICR ) from peer 10.17.2.198(2065) DLSw: 488636 recv FCI 0 - s:0 so:0 r:0 ro:0 DLSw: recv RWO DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:WAN-ICR state:CKT_START DLSw: core: dlsw_action_e() DLSw: sent RWO DLSw: 488636 sent FCI 80 on ACK - s:20 so:1 r:20 ro:1 %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 5( ACK ) to peer 10.17.2.198(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_START->CKT_ESTABLISHED
Une fois le circuit établi, il envoie le XID stocké et commence l'échange XID.
Il est très important de comprendre d'où viennent les XID. Dans cette situation, il y a deux résultats importants :
-
DLC-Id ? ? signifie que le XID provient de la station DLC locale.
-
WAN-XID ? ? signifie que le XID provient du routeur distant (la station distante).
DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:DLC-Id state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_f() DLSw: 488636 sent FCA on XID %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) to peer 10.17.2.198(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) from peer 10.17.2.198(2065) DLSw: 488636 recv FCA on XID - s:20 so:0 r:20 ro:0 DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:WAN-XID state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_g() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 12 DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) from peer 10.17.2.198(2065) DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:WAN-XID state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_g() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Req dlen: 88 DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 82 DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:DLC-Id state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_f() %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) to peer 10.17.2.198(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) from peer 10.17.2.198(2065) DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:WAN-XID state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_g() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 88 DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 82 DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:DLC-Id state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_f() %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) to peer 10.17.2.198(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED %DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) from peer 10.17.2.198(2065) DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:WAN-XID state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_g() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 88 DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 82 DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:DLC-Id state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_f() %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 7( XID ) to peer 10.17.2.198(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CKT_ESTABLISHED
Le routeur reçoit ensuite le CONQ de l'AS/400 (SABME) qui est traduit en ligne série sous la forme d'un SNRM (Set Normal Response). Lorsque l'UA apparaît sur la ligne série (CONNECT.Cfm), le routeur envoie le CONR de l'autre côté et déplace la session vers CONNECTED.
%DLSWC-3-RECVSSP: SSP OP = 8( CONQ ) from peer 10.17.2.198(2065) DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:WAN-CONQ state:CKT_ESTABLISHED DLSw: core: dlsw_action_i() DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Req dlen: 16 DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CKT_ESTABLISHED->CONTACT_PENDING DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 8 DLSw: START-FSM (488636): event:DLC-Connect.Cnf state:CONTACT_PENDING DLSw: core: dlsw_action_j() %DLSWC-3-SENDSSP: SSP OP = 9( CONR ) to peer 10.17.2.198(2065) success DLSw: END-FSM (488636): state:CONTACT_PENDING->CONNECTED
DLSw Conduite d'une traduction de support inverse
Une autre configuration courante est appelée LLC (Logical Link Control) SDLC (Synchronous Data Link Control) ; SDLLC), c’est-à-dire lorsque la station principale est connectée au routeur via une ligne SDLC. Ceci est généralement observé dans les environnements hôtes qui migrent l’hôte vers une pièce jointe Token Ring. Cette configuration modifie la manière dont DLSw gère la ligne SDLC, car il existe généralement un degré élevé d'incertitude quant à l'activité ou non de l'unité de traitement distante.
Étant donné que l'AS/400 est principal ou est défini sur négociable dans le rôle, il doit démarrer la session. Lorsque cela se produit, cette séquence se produit :
-
La ligne série devient opérationnelle.
-
L'AS/400 envoie le premier XID.
-
Le processus de recherche du contrôleur distant démarre.
-
La configuration du circuit est terminée.
-
La négociation XID commence dans la ligne.
Traduction multimédia DLSw locale
Une fois la négociation XID terminée, l'AS/400 envoie un SNRM au routeur Cisco. Cela entraîne l’envoi d’un CONQ par le routeur et l’attente d’un CONR du routeur distant. Mais l'UA n'est envoyé qu'après la réception du CONR.
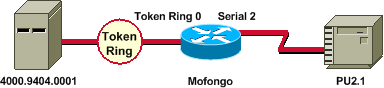
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial2, changed state to up %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID_STN.Ind dlen: 46 CSM: Received CLSI Msg : ID_STN.Ind dlen: 46 from Serial2
Comme il s'agit d'un local DLSw, le comportement est un peu différent. La première chose qui est vue est le XID du côté série. Le XID du côté série doit être stocké jusqu'à ce que les trames de test LLC et les réponses soient terminées.
CSM: smac 4000.5494.00dd, dmac 4000.9404.0001, ssap 4 , dsap 4 DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Req dlen: 46 DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Req dlen: 46 DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Req dlen: 46 CSM: Write to all peers not ok - PEER_NO_CONNECTIONS DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Ind dlen: 43 CSM: Received CLSI Msg : TEST_STN.Ind dlen: 43 from TokenRing0 CSM: smac c000.9404.0001, dmac 4000.5494.00dd, ssap 0 , dsap 4
La station de test quitte le routeur et la réponse revient de l'AS/400. Le FSM local peut maintenant être créé. (N'oubliez pas qu'il s'agit d'une session locale.)
DLSw: csm_to_local(): Serial2-->TokenRing0 4000.5494.00dd:4->4000.9404.0001:4 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:ADMIN-START DLSw: LFSM-A: Opening DLC station DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Req dlen: 106 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:DISCONNECTED ->OPN_STN_PEND DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:ADMIN-START DLSw: LFSM-A: Opening DLC station DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Req dlen: 106 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:DISCONNECTED ->OPN_STN_PEND DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 106 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:DLC-ReqOpnStn.Cnf DLSw: LFSM-B: DLC station opened DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:OPN_STN_PEND ->ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : REQ_OPNSTN.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 106 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-ReqOpnStn.Cnf DLSw: LFSM-B: DLC station opened DLSw: processing saved clsi message
Après confirmation locale que le FSM est prêt, le routeur envoie le XID (ID.Req) au partenaire, qui est l'AS/400 dans ce scénario.
DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Req dlen: 12 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:OPN_STN_PEND ->ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 32 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 12 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED
Un XID provient de la Token Ring. Cet ID.Ind a une longueur de 108 et doit être transféré au partenaire dans ce scénario, qui est la ligne SDLC. Ceci peut être vu avec l'ID.Req qui a été envoyé. Notez que, chaque fois qu'un paquet est reçu, un LFSM doit être démarré.
DLSw Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 108 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Req dlen: 88 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED
Notez la réponse XID de la ligne série et lors de son transfert au partenaire (dans ce cas, la station Token Ring). Cela dure un certain temps, jusqu'à ce que l'échange XID pour ce périphérique PU 2.1 soit terminé.
DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 82 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 80 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 108 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 88 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 82 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 80 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 108 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 88 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial2, changed state to up DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : ID.Ind dlen: 82 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-Id DLSw: LFSM-X: forward XID to partner DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : ID.Rsp dlen: 80 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:ESTABLISHED ->ESTABLISHED
Après l'échange XID, un SABME est reçu de l'AS/400 via CONNECT.Ind. Ceci indique au routeur d'envoyer un fichier CONNECT.Req à la ligne SDLC, qui est le SNRM. Ensuite, un fichier CONNECT.Cfm (UA) est reçu de la ligne série, ce qui fait que le code DLSw envoie un fichier CONNECT.Rsp (UA) à l'AS/400.
DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Ind dlen: 8 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:DLC-Connect.Ind DLSw: LFSM-C: starting local partner DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:ADMIN-CONN DLSw: LFSM-D: sending connect request to station DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Req dlen: 16 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:ESTABLISHED ->CONN_OUT_PEND DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:ESTABLISHED ->CONN_IN_PEND DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 8 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-Connect.Cnf DLSw: LFSM-E: station accepted the connection DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:ADMIN-CONN DLSw: LFSM-F: accept incoming connection DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : CONNECT.Rsp dlen: 20 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:CONN_IN_PEND ->CONNECTED DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : FLOW.Req dlen: 0 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:CONN_OUT_PEND->CONNECTED
Il s'agit de la session qui se produit lorsque le contrôleur (SDLC) est arrêté :
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial2, changed state to down %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial2, changed state to administratively down DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : DISCONNECT.Ind dlen: 8 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-Disc.Ind DLSw: LFSM-Q: acknowledge disconnect DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : DISCONNECT.Rsp dlen: 4
Ici, un DISQUE est envoyé à l'AS/400 (DISCONNECT.Rsp). Le circuit local est ensuite désactivé.
DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:ADMIN-STOP DLSw: LFSM-Z: close dlc station request DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : CLOSE_STN.Req dlen: 4 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:ESTABLISHED ->CLOSE_PEND DISP Sent : CLSI Msg : CLOSE_STN.Req dlen: 4 DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:ESTABLISHED ->CLOSE_PEND DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : CLOSE_STN.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 8 DLSw: START-LFSM TokenRing0 (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd) event:DLC-CloseStn.Cnf DLSw: LFSM-Y: driving partner to close circuit DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:ADMIN-STOP DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:CLOSE_PEND ->CLOSE_PEND DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.9404.0001->4000.5494.00dd): state:CLOSE_PEND ->DISCONNECTED DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : DISCONNECT.Ind dlen: 8 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-Disc.Ind DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:CLOSE_PEND ->CLOSE_PEND DLSW Received-ctlQ : CLSI Msg : CLOSE_STN.Cfm CLS_OK dlen: 8 DLSw: START-LFSM Serial2 (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001) event:DLC-CloseStn.Cnf DLSw: LFSM-Y: removing local switch entity DLSw: END-LFSM (4000.5494.00dd->4000.9404.0001): state:CLOSE_PEND ->DISCONNECTED
Une fois que DISCONNECT.Ind (UA) a été reçu de l'AS/400, la session est nettoyée et est déplacée à un état de déconnexion.
Problèmes de performances
Pour plus d'informations sur les problèmes de performances, reportez-vous à la section Gestion et mise en file d'attente de bande passante dans Data-Link Switching Plus (DLSw+), ou reportez-vous à Techniques de filtrage SAP/MAC DLSw+.
 Commentaires
Commentaires