Configuration de la fonction MPLS VPN sur POS, SRP et ATM sur des GSR Cisco
Contenu
Introduction
Ce document fournit un exemple de configuration pour le réseau privé virtuel (VPN) MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) sur ATM, Packet over SONET/SDH (POS) et le protocole de réutilisation spatiale (SRP) sur les routeurs de commutation Gigabit Cisco 12000 (GSR).
Ces acronymes sont utilisés dans ce document.
-
CE - Routeur de périphérie client
-
PE - Routeur de périphérie du fournisseur
-
P - Routeur principal du fournisseur
-
VRF - Routage et transfert virtuels
Conditions préalables
Conditions requises
Avant de tenter cette configuration, assurez-vous que les conditions suivantes sont remplies :
-
Connaissance de base de MPLS et de la fonctionnalité VPN MPLS.
Components Used
Les informations contenues dans ce document sont basées sur les versions de matériel et de logiciel suivantes :
-
P et Routeurs de PE
-
Logiciel Cisco IOS® Version 12.0(28)S sur tous les routeurs
-
Routeurs de la gamme Cisco GSR 12000
-
-
Routeurs CE
-
Logiciel Cisco IOS Version 12.0(28)S sur tous les routeurs
-
Routeurs Cisco 7200VXR
-
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Produits connexes
Cette configuration peut également être utilisée avec les plates-formes de routeur prises en charge au coeur du fournisseur (P) :
-
Cisco 7200
-
Cisco 7500
-
Cisco 7600
-
Cisco 8500
-
Cisco 10000
-
Cisco 10700
-
Cisco 12000
Cette configuration peut également être utilisée avec les plates-formes de routeur prises en charge à la périphérie du fournisseur (PE) :
-
Cisco 3600
-
Cisco 3700
-
Cisco 7200
-
Cisco 7500
-
Cisco 7600
-
Cisco 8500
-
Cisco 10000
-
Cisco 10700
-
Cisco 12000
Remarque : les routeurs Cisco 3700/3600 ne prennent pas en charge les modules POS et SRP. Toute plate-forme située sous le 3600 ne prend pas en charge la configuration MPLS.
Conventions
Pour plus d'informations sur les conventions des documents, référez-vous aux Conventions utilisées pour les conseils techniques de Cisco.
Informations générales
MPLS est disponible pour prendre en charge plusieurs interfaces physiques. Ces interfaces incluent ATM, POS et SRP. Ces interfaces sont généralement utilisées pour les connexions de backbone en raison de leur haut débit. La fonctionnalité VPN MPLS permet aux fournisseurs de services d'interconnecter plusieurs sites sans avoir à utiliser ATM, POS ou SRP du côté du client.
Il existe deux implémentations de MPLS sur ATM. L'une est l'utilisation de l'identificateur de chemin virtuel (VPI) et du canal virtuel identifié (VCI) comme étiquette, également appelée MPLS basé sur des cellules sur ATM. Cette mise en oeuvre est documentée dans la RFC 3035 ![]() . La deuxième mise en oeuvre ATM est l’utilisation de l’en-tête « shim » MPLS, également appelé MPLS par paquets sur ATM. Cet en-tête est inséré entre les en-têtes de couche 2 et de couche 3. Le format de l'en-tête shim est documenté dans la RFC 3032
. La deuxième mise en oeuvre ATM est l’utilisation de l’en-tête « shim » MPLS, également appelé MPLS par paquets sur ATM. Cet en-tête est inséré entre les en-têtes de couche 2 et de couche 3. Le format de l'en-tête shim est documenté dans la RFC 3032 ![]() . Cet exemple de configuration est basé sur l'implémentation de l'en-tête shim pour l'interface ATM.
. Cet exemple de configuration est basé sur l'implémentation de l'en-tête shim pour l'interface ATM.
Packet over Synchronous Optical Network/Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET/SDH) est une technologie qui place la couche IP directement au-dessus de la couche SONET. Il élimine la surcharge nécessaire pour exécuter IP sur ATM sur SONET. POS prend en charge le format d’encapsulation multiple. Il s’agit de PPP, HDLC et Frame Relay. L'en-tête shim est utilisé pour fournir la prise en charge MPLS. Cet exemple de configuration utilise l'encapsulation HDLC par défaut sur les interfaces Cisco POS.
Le protocole SRP (Spatial Reuse Protocol) est une technologie de couche 2 qui fournit une résilience au niveau de la couche 2. Il fonctionne également sur SONET/SDH. La prise en charge MPLS est assurée par l'implémentation de l'en-tête shim.
Configuration
Cette section vous fournit des informations pour configurer les fonctionnalités décrites dans ce document.
Remarque : Pour en savoir plus sur les commandes utilisées dans le présent document, utilisez l’outil de recherche de commandes (clients inscrits seulement).
Diagramme du réseau
Ce document utilise la configuration réseau suivante :
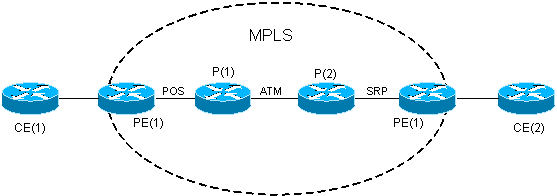
Configurations
Voici quelques considérations relatives à l'exemple de configuration :
-
L'exemple de configuration du service VPN MPLS EIGRP route depuis les CE. L'ID de bogue Cisco CSCds09932 (clients enregistrés uniquement) a introduit la prise en charge du protocole EIGRP pour MPLS VPN avec le logiciel Cisco IOS Version 12.0(22)S. Ceci a été porté vers le logiciel Cisco IOS Version 12.2T via l'ID de bogue Cisco CSCdx26186 (clients enregistrés uniquement) à partir de la version 12.2(15)T du logiciel Cisco IOS. L'application du même VRF à plusieurs instances EIGRP n'est pas prise en charge et peut interrompre le routeur. Une vérification de ce problème a été ultérieurement intégrée à l'ID de bogue Cisco CSCdz40426 (clients enregistrés uniquement). Référez-vous à Support VPN MPLS pour EIGRP entre la périphérie du fournisseur et la périphérie du client pour en savoir plus sur la prise en charge VPN MPLS pour EIGRP.
-
Le système autonome EIGRP est identique sur les deux routeurs CE. Le système autonome BGP est identique sur les deux routeurs PE.
-
Le réseau fédérateur MPLS est basé sur des interfaces POS, ATM et SRP et configuré avec OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) et MP-BGP. La connexion entre PE et CE est Fast Ethernet.
Ce document utilise les configurations suivantes :
| CE(1) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ip cef !--- CEF is not required on the CE because there is no MPLS configuration. !--- CEF is the fastest switching algorithm on Cisco routers !--- and it is best to leave it enabled. ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 11.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 11.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.252 ! router eigrp 100 network 11.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 no auto-summary ! ip classless |
| PE 1 |
|---|
!
version 12.0
!
!--- CEF is enabled by default on GSR.
.
!
ip vrf Customer_A
rd 100:1
route-target export 100:1
route-target import 100:1
!--- Enables the VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) routing table.
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip vrf forwarding Customer_A
!--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface.
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.252
!
interface POS4/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!--- Enables dynamic Label Switching of IPv4 packets on an interface. !--- At minimum, this is all you need to configure MPLS over POS. !--- Note the default encapsulation of POS interfaces is HDLC. !--- An mpls ip command can also be used instead of tag-switching ip.
crc 32
clock source internal
!
!
router eigrp 1
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A
redistribute bgp 100 metric 10000 1 255 1 1500
network 192.168.2.0
no auto-summary
autonomous-system 100
!--- The autonomous-system 100 must match the AS used on the CE. !--- The bgp must be redistributed with metric. The default-metric !--- command can also be used.
exit-address-family
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 send-community both
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A
redistribute eigrp 100
!--- The EIGRP AS 100 must be redistributed to the BGP vrf instance.
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
ip classless |
| P(1) |
|---|
!
version 12.0
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface POS2/0
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!--- This enables MPLS over POS.
crc 32
!
!
interface ATM6/0
no ip address
!
interface ATM6/0.100 point-to-point
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
pvc 0/100
!
!--- This enables "packet-based" MPLS over ATM.
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
ip classless |
| P 2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 ! interface ATM4/0 no ip address ! interface ATM4/0.100 point-to-point ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 tag-switching ip pvc 0/100 !--- This enables "packet-based" MPLS over ATM. ! ! interface SRP5/0 ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast tag-switching ip !--- This enables MPLS over SRP. ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.1.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.2.2.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! ip classless |
| PE 2 |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ! ip vrf Customer_A rd 100:1 route-target export 100:1 route-target import 100:1 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 ! interface SRP4/0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.252 tag-switching ip !--- This enables MPLS over SRP. ! interface FastEthernet6/0 ip vrf forwarding Customer_A !--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface. ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252 ! ! router eigrp 1 ! address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A redistribute bgp 100 metric 10000 1 255 1 1500 network 192.168.1.0 no auto-summary autonomous-system 100 exit-address-family !--- The autonomous-system 100 must match the AS used on the CE. !--- The bgp must be redistributed with metric. The default-metric !--- command can also be used. ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router bgp 100 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A redistribute eigrp 100 !--- The EIGRP AS 100 must be redistributed to the BGP vrf instance. no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family ! ip classless |
| CE(2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ip cef !--- CEF is not required on the CE because there is no MPLS configuration. !--- CEF is the fastest switching algorithm on Cisco routers so it is !--- best to leave it enabled. ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 22.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 22.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 22.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252 ! ! router eigrp 100 network 22.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 no auto-summary ! |
Vérification
Cette section présente des informations que vous pouvez utiliser pour vous assurer que votre configuration fonctionne correctement.
Certaines commandes show sont prises en charge par l'Output Interpreter Tool (clients enregistrés uniquement), qui vous permet de voir une analyse de la sortie de la commande show.
-
show ip vrf - Vérifie que le VRF correct existe.
-
show ip route vrf Customer_A - Vérifie les informations de routage sur les routeurs de PE.
-
ping vrf Customer_A <ip address> : vérifie la connectivité en envoyant des paquets ICMP.
-
traceroute vrf Customer_A <ip address> : vérifie les informations de routage sur les routeurs PE.
-
show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A neighbors - Vérifie le voisin EIGRP à l'intérieur de l'instance VRF.
-
show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A topology - Vérifie la topologie EIGRP à l'intérieur de l'instance VRF.
-
show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf Customer_A - Vérifie la table BGP à l'intérieur de l'instance VRF.
-
show ip cef vrf Customer_A <ip address> detail - Vérifie la table CEF dans l'instance VRF.
-
show tag-switching forwarding-table : vérifie s'il existe une route/étiquette pour le préfixe de destination.
-
show ip route : vérifie que les CE échangent des routes.
PE 1
PE(1)#show ip vrf
Name Default RD Interfaces
Customer_A 100:1 FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#show ip route vrf Customer_A
Routing Table: Customer_A
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
B 22.3.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
B 22.2.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
B 22.1.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 11.2.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
D 11.3.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
D 11.1.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 192.168.1.0 [200/0] via 4.4.4.4, 01:16:14
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#ping vrf Customer_A 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
D-GSR-12012-2A#ping vrf Customer_A ip ?
WORD Ping destination address or hostname
<cr>
PE(1)#ping vrf Customer_A ip
Target IP address: 192.168.1.2
Repeat count [5]: 100
Datagram size [100]: 1500
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]:
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 100, 1500-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (100/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
PE(1)#traceroute vrf Customer_A 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 192.168.1.2
1 10.0.0.2 [MPLS: Labels 18/28 Exp 0] 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec
2 10.1.1.2 [MPLS: Labels 19/28 Exp 0] 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec
3 192.168.1.1 4 msec 0 msec 0 msec
4 192.168.1.2 4 msec 0 msec *
PE(1)#show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 100
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq Type
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 192.168.2.2 Fa0/0 11 10:51:41 10 200 0 8
PE(1)#show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(100)/ID(192.168.2.1) Routing Table: Customer_A
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - Reply status
P 11.2.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 11.3.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 11.1.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 22.3.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 22.2.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 22.1.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 192.168.1.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via VPNv4 Sourced (28160/0)
P 192.168.2.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Connected, FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf Customer_A
BGP table version is 17, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 100:1 (default for vrf Customer_A)
*> 11.1.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*> 11.2.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*> 11.3.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*>i22.1.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i22.2.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i22.3.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i192.168.1.0/30 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 ?
*> 192.168.2.0/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
PE(1)#show ip cef vrf Customer_A
Prefix Next Hop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 drop Null0 (default route handler entry)
0.0.0.0/32 receive
11.1.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
11.2.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
11.3.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
22.1.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
22.2.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
22.3.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
192.168.1.0/30 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
192.168.2.0/30 attached FastEthernet0/0
192.168.2.0/32 receive
192.168.2.1/32 receive
192.168.2.2/32 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
192.168.2.3/32 receive
224.0.0.0/4 drop
224.0.0.0/24 receive
255.255.255.255/32 receive
PE(1)#show ip cef vrf Customer_A 11.1.1.0 detail
11.1.1.0/24, version 16, epoch 0, cached adjacency 192.168.2.2
0 packets, 0 bytes
tag information set, all rewrites owned
local tag: 27
via 192.168.2.2, FastEthernet0/0, 0 dependencies
next hop 192.168.2.2, FastEthernet0/0
valid cached adjacency
tag rewrite with Fa0/0, 192.168.2.2, tags imposed {}
PE(1)#show tag-switching forwarding-table
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
16 Pop tag 2.2.2.2/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
17 17 3.3.3.3/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
18 18 4.4.4.4/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
19 19 10.2.2.0/30 0 PO4/0 point2point
20 Pop tag 10.1.1.0/30 0 PO4/0 point2point
22 Untagged 11.2.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
26 Untagged 11.3.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
27 Untagged 11.1.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
28 Aggregate 192.168.2.0/30[V] 255132
PE(1)#show tag-switching forwarding-table vrf Customer_A
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
22 Untagged 11.2.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
26 Untagged 11.3.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
27 Untagged 11.1.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
28 Aggregate 192.168.2.0/30[V] 255132
P(1)
P(1)A#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 Pop tag 1.1.1.1/32 260843 PO2/0 point2point 17 Pop tag 3.3.3.3/32 0 AT6/0.100 point2point 18 19 4.4.4.4/32 269131 AT6/0.100 point2point 19 Pop tag 10.2.2.0/30 0 AT6/0.100 point2point
P 2)
P(2)#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 Pop tag 10.0.0.0/30 0 AT4/0.100 point2point 17 Pop tag 2.2.2.2/32 0 AT4/0.100 point2point 18 16 1.1.1.1/32 269930 AT4/0.100 point2point 19 Pop tag 4.4.4.4/32 276490 SR5/0 10.2.2.2
PE 2
PE(2)#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 18 1.1.1.1/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 17 17 2.2.2.2/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 18 Pop tag 3.3.3.3/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 19 16 10.0.0.0/30 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 20 Pop tag 10.1.1.0/30 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 25 Untagged 22.1.1.0/24[V] 2280 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 26 Untagged 22.2.1.0/24[V] 570 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 27 Untagged 22.3.1.0/24[V] 570 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 28 Aggregate 192.168.1.0/30[V] 251808
CE(1)
CE(1)#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 22.3.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
D 22.2.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
D 22.1.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 11.2.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback1
C 11.3.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 11.1.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.1.0 [90/30720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:46, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
CE(1)#ping 22.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 22.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
CE(2)
D-R7206-5A#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 22.3.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 22.2.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback1
C 22.1.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 11.2.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
D 11.3.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
D 11.1.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.2.0 [90/30720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:33, FastEthernet2/0
CE(2)#ping 11.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 11.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Dépannage
Il n'existe actuellement aucune information de dépannage spécifique pour cette configuration.
Informations connexes
Historique de révision
| Révision | Date de publication | Commentaires |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
05-Jun-2005 |
Première publication |
Contacter Cisco
- Ouvrir un dossier d’assistance

- (Un contrat de service de Cisco est requis)
 Commentaires
Commentaires