Exemple de configuration de tunnel IPSec LAN à LAN entre un Catalyst 6500 avec le module de service VPN et un pare-feu PIX
Contenu
Introduction
Ce document décrit comment créer un tunnel IPSec LAN à LAN entre un commutateur de la gamme Cisco Catalyst 6500 avec le module de service VPN IPSec (W) et un pare-feu Cisco PIX.
Conditions préalables
Conditions requises
Aucune spécification déterminée n'est requise pour ce document.
Components Used
Les informations contenues dans ce document sont basées sur les versions de matériel et de logiciel suivantes :
-
Logiciel Cisco IOS® Version 12.2(14)SY2 pour Supervisor Engine de la gamme Catalyst 6000, avec module de service VPN IPSec
-
Logiciel Cisco PIX Firewall Version 6.3(3)
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Informations générales
Le module de service VPN Catalyst 6500 est équipé de deux ports Gigabit Ethernet (GE) sans connecteurs externes visibles. Ces ports sont adressables uniquement à des fins de configuration. Le port 1 est toujours le port interne. Ce port gère tout le trafic en provenance et à destination du réseau interne. Le second port (port 2) gère tout le trafic en provenance et à destination du WAN ou des réseaux externes. Ces deux ports sont toujours configurés en mode d’agrégation 802.1Q. Le module de service VPN utilise une technique appelée Bump In The Wire (BITW) pour le flux de paquets.
Les paquets sont traités par une paire de VLAN, une couche 3 à l’intérieur du VLAN et une couche 2 à l’extérieur du VLAN. Les paquets, de l'intérieur vers l'extérieur, sont acheminés via une méthode appelée Encoded Address Recognition Logic (EARL) vers le VLAN interne. Après avoir chiffré les paquets, le module de service VPN utilise le VLAN externe correspondant. Dans le processus de déchiffrement, les paquets de l'extérieur vers l'intérieur sont pontés au module de service VPN à l'aide du VLAN externe. Une fois que le module de service VPN déchiffre le paquet et mappe le VLAN au VLAN interne correspondant, EARL achemine le paquet vers le port LAN approprié. Les VLAN internes de couche 3 et les VLAN externes de couche 2 sont associés à la commande crypto connect vlan. Il existe trois types de ports dans les commutateurs de la gamme Catalyst 6500 :
-
Routed ports - Par défaut, tous les ports Ethernet sont des ports routés dans Cisco IOS. Ces ports sont associés à un VLAN masqué.
-
Ports d'accès - Ces ports sont associés à un VLAN externe ou VTP (VLAN Trunk Protocol). Vous pouvez associer plusieurs ports à un VLAN défini.
-
Ports agrégés - Ces ports transportent de nombreux VLAN externes ou VTP, sur lesquels tous les paquets sont encapsulés avec un en-tête 802.1Q.
Configuration
Cette section vous fournit des informations pour configurer les fonctionnalités décrites dans ce document.
Remarque : Utilisez l’outil de recherche de commandes (clients inscrits seulement) pour en savoir plus sur les commandes figurant dans le présent document.
Diagramme du réseau
Ce document utilise la configuration réseau suivante :
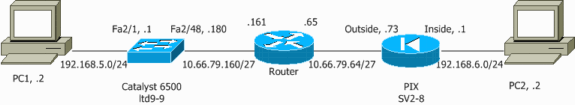
Configuration d'IPSec à l'aide d'un port d'accès ou de liaison de couche 2
Procédez comme suit pour configurer IPSec à l'aide d'un port d'accès ou de liaison de couche 2 pour l'interface physique externe.
-
Ajoutez les VLAN internes au port interne du module de service VPN.
Supposez que le module de service VPN se trouve sur le logement 4. Utilisez VLAN 100 comme VLAN interne et VLAN 209 comme VLAN externe. Configurez les ports GE du module de service VPN comme suit :
interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk
-
Ajoutez l'interface VLAN 100 et l'interface où le tunnel est terminé (qui, dans ce cas, est l'interface Vlan 209, comme indiqué ici).
interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 interface Vlan209 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100
-
Configurez le port physique externe en tant que port d'accès ou de liaison (dans ce cas, FastEthernet 2/48, comme indiqué ici).
!--- This is the configuration that uses an access port. interface FastEthernet2/48 no ip address switchport switchport access vlan 209 switchport mode access !--- This is the configuration that uses a trunk port. interface FastEthernet2/48 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk
-
Créez la NAT de contournement. Ajoutez ces entrées à l'instruction no nat afin d'exempter la liaison entre ces réseaux :
access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
-
Créez votre configuration de chiffrement et la liste de contrôle d'accès (ACL) qui définit le trafic à chiffrer.
-
Créez une liste de contrôle d’accès Crypto (dans ce cas, la liste de contrôle d’accès 100 - Trafic intéressant) qui définit le trafic du réseau interne 192.168.5.0/24 vers le réseau distant 192.168.6.0/24, comme ceci :
access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
-
Définissez vos propositions de politique ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol), comme suit :
crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2
-
Émettez cette commande (dans cet exemple) pour utiliser et définir des clés pré-partagées :
crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.73
-
Définissez vos propositions IPSec, comme suit :
crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
-
Créez votre instruction crypto map, comme ceci :
crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.73 set transform-set cisco match address 100
-
-
Appliquez la crypto-carte à l'interface VLAN 100, comme ceci :
interface vlan100 crypto map cisco
Ces configurations sont utilisées :
| Catalyst 6500 |
|---|
!--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.73 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. !--- This indicates that Internet Key Exchange (IKE) !--- is used to establish the IPSec !--- security associations (SAs) to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.73 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! no spanning-tree vlan 100 ! ! ! interface FastEthernet2/1 ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 ! !--- This is the outside Layer 2 port that allows !--- VLAN 209 traffic to enter. interface FastEthernet2/48 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk ! interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- VLAN 100 is defined as the Interface VLAN (IVLAN). switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable ! interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- The Port VLAN (PVLAN) configuration is handled transparently by !--- the VPN service module without user configuration !--- or involvement. It also is not shown in the configuration. !--- Note: For every IVLAN, a corresponding PVLAN exists. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! !--- This is the IVLAN that is configured to intercept the traffic !--- destined to the secure port on which the inside port !--- of the VPN service module is the only port present. interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 crypto map cisco !--- This is the secure port that is a virtual Layer 3 interface. !--- This interface purposely does not have a Layer 3 IP address !--- configured. This is normal for the BITW process. !--- The IP address is moved from this interface to the VLAN 100 to !--- accomplish BITW. This brings the VPN service module into !--- the packet path. interface Vlan209 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100 ! ip classless global (outside) 1 interface !--- NAT 0 prevents NAT for networks specified in the ACL inside_nat0_outbound. nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.161 !--- This access list (inside_nat0_outbound) is used with the nat zero command. !--- This prevents traffic which matches the access list from undergoing !--- network address translation (NAT). The traffic specified by this ACL is !--- traffic that is to be encrypted and !--- sent across the VPN tunnel. This ACL is intentionally !--- the same as (100). !--- Two separate access lists should always be used in this configuration. access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 |
| Pare-feu PIX |
|---|
SV2-8(config)# show run : Saved : PIX Version 6.3(3) interface ethernet0 auto interface ethernet1 auto interface ethernet2 auto shutdown interface ethernet3 auto shutdown interface ethernet4 auto shutdown interface ethernet5 auto shutdown interface ethernet6 auto shutdown nameif ethernet0 outside security0 nameif ethernet1 inside security100 nameif ethernet2 intf2 security10 nameif ethernet3 intf3 security15 nameif ethernet4 intf4 security20 nameif ethernet5 intf5 security25 nameif ethernet6 intf6 security30 enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted hostname SV2-8 domain-name cisco.com fixup protocol dns maximum-length 512 fixup protocol ftp 21 fixup protocol h323 h225 1720 fixup protocol h323 ras 1718-1719 fixup protocol http 80 fixup protocol ils 389 fixup protocol rsh 514 fixup protocol rtsp 554 fixup protocol sip 5060 fixup protocol sip udp 5060 fixup protocol skinny 2000 fixup protocol smtp 25 fixup protocol sqlnet 1521 fixup protocol tftp 69 names !--- This is the traffic to the router. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 access-list nonat permit ip 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 pager lines 24 mtu outside 1500 mtu inside 1500 mtu intf2 1500 mtu intf3 1500 mtu intf4 1500 mtu intf5 1500 mtu intf6 1500 ip address outside 10.66.79.73 255.255.255.224 ip address inside 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0 ip address intf2 127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 no ip address intf3 no ip address intf4 no ip address intf5 no ip address intf6 ip audit info action alarm ip audit attack action alarm no failover failover timeout 0:00:00 failover poll 15 no failover ip address outside no failover ip address inside no failover ip address intf2 no failover ip address intf3 no failover ip address intf4 no failover ip address intf5 no failover ip address intf6 pdm history enable arp timeout 14400 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list nonat nat (inside) 1 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 0 0 route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.65 1 timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 rpc 0:10:00 h225 1:00:00 timeout h323 0:05:00 mgcp 0:05:00 sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+ aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius aaa-server LOCAL protocol local no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server community public no snmp-server enable traps floodguard enable !--- These are IPSec policies. sysopt connection permit-ipsec crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp crypto map cisco 10 match address 100 crypto map cisco 10 set peer 10.66.79.180 crypto map cisco 10 set transform-set cisco crypto map cisco interface outside !--- These are IKE policies. isakmp enable outside isakmp key ******** address 10.66.79.180 netmask 255.255.255.255 isakmp policy 1 authentication pre-share isakmp policy 1 encryption des isakmp policy 1 hash md5 isakmp policy 1 group 2 isakmp policy 1 lifetime 86400 telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 terminal width 80 Cryptochecksum:244c86c9beab00bda8f790502ca74db9 : end |
Configuration d'IPSec à l'aide d'un port routé
Procédez comme suit pour configurer IPSec à l'aide d'un port routé de couche 3 pour l'interface physique externe.
-
Ajoutez les VLAN internes au port interne du module de service VPN.
Supposez que le module de service VPN se trouve sur le logement 4. Utilisez VLAN 100 comme VLAN interne et VLAN 209 comme VLAN externe. Configurez les ports GE du module de service VPN comme suit :
interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk
-
Ajoutez l'interface VLAN 100 et l'interface où le tunnel est terminé (qui, dans ce cas, est FastEthernet2/48, comme indiqué ici).
interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 interface FastEthernet2/48 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100
-
Créez la NAT de contournement. Ajoutez ces entrées à l'instruction no nat afin d'exempter la liaison entre ces réseaux :
access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
-
Créez votre configuration de chiffrement et la liste de contrôle d’accès qui définit le trafic à chiffrer.
-
Créez une liste de contrôle d’accès (dans ce cas, la liste de contrôle d’accès 100) qui définit le trafic du réseau interne 192.168.5.0/24 vers le réseau distant 192.168.6.0/24, comme suit :
access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
-
Définissez vos propositions de politique ISAKMP, comme ceci :
crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2
-
Émettez cette commande (dans cet exemple) pour utiliser et définir des clés pré-partagées :
crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.73
-
Définissez vos propositions IPSec, comme suit :
crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
-
Créez votre instruction crypto map, comme ceci :
crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.73 set transform-set cisco match address 100
-
-
Appliquez la crypto-carte à l'interface VLAN 100, comme ceci :
interface vlan100 crypto map cisco
Ces configurations sont utilisées :
| Catalyst 6500 |
|---|
!--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.73 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. !--- This indicates that IKE is used to establish the !--- IPSec SAs to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.73 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! no spanning-tree vlan 100 ! ! ! interface FastEthernet2/1 ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 ! !--- This is the secure port that is configured in routed port mode. !--- This routed port mode does not have a Layer 3 IP address !--- configured. This is normal for the BITW process. !--- The IP address is moved from this interface to the VLAN 100 to !--- accomplish BITW. This brings the VPN service module into !--- the packet path. This is the Layer 2 port VLAN on which the !--- outside port of the VPN service module also belongs. ! interface FastEthernet2/48 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100 ! interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- VLAN 100 is defined as the IVLAN. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable ! interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- The PVLAN configuration is handled transparently by the !--- VPN service module without user configuration !--- or involvement. It also is not shown in the configuration. !--- Note: For every IVLAN, a corresponding PVLAN exists. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! !--- This is the IVLAN that is configured to intercept the traffic !--- destined to the secure port on which the inside port of the !--- VPN service module is the only port present. interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 crypto map cisco !--- This is the secure port that is a virtual Layer 3 interface. !--- This interface purposely does not have a Layer 3 IP address !--- configured. This is normal for the BITW process. !--- The IP address is moved from this interface to the VLAN 100 to !--- accomplish BITW. This brings the VPN service module into !--- the packet path. ! ip classless global (outside) 1 interface !--- NAT 0 prevents NAT for networks specified in the ACL inside_nat0_outbound. nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.161 ! !--- This access list (inside_nat0_outbound) is used with the nat zero command. !--- This prevents traffic which matches the access list from undergoing !--- network address translation (NAT). The traffic specified by this ACL is !--- traffic that is to be encrypted and !--- sent across the VPN tunnel. This ACL is intentionally !--- the same as (100). !--- Two separate access lists should always be used in this configuration. access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 |
| Pare-feu PIX |
|---|
SV2-8(config)# show run : Saved : PIX Version 6.3(3) interface ethernet0 auto interface ethernet1 auto interface ethernet2 auto shutdown interface ethernet3 auto shutdown interface ethernet4 auto shutdown interface ethernet5 auto shutdown interface ethernet6 auto shutdown nameif ethernet0 outside security0 nameif ethernet1 inside security100 nameif ethernet2 intf2 security10 nameif ethernet3 intf3 security15 nameif ethernet4 intf4 security20 nameif ethernet5 intf5 security25 nameif ethernet6 intf6 security30 enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted hostname SV2-8 domain-name cisco.com fixup protocol dns maximum-length 512 fixup protocol ftp 21 fixup protocol h323 h225 1720 fixup protocol h323 ras 1718-1719 fixup protocol http 80 fixup protocol ils 389 fixup protocol rsh 514 fixup protocol rtsp 554 fixup protocol sip 5060 fixup protocol sip udp 5060 fixup protocol skinny 2000 fixup protocol smtp 25 fixup protocol sqlnet 1521 fixup protocol tftp 69 names !--- This is the traffic to the router. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 access-list nonat permit ip 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 pager lines 24 mtu outside 1500 mtu inside 1500 mtu intf2 1500 mtu intf3 1500 mtu intf4 1500 mtu intf5 1500 mtu intf6 1500 ip address outside 10.66.79.73 255.255.255.224 ip address inside 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0 ip address intf2 127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 no ip address intf3 no ip address intf4 no ip address intf5 no ip address intf6 ip audit info action alarm ip audit attack action alarm no failover failover timeout 0:00:00 failover poll 15 no failover ip address outside no failover ip address inside no failover ip address intf2 no failover ip address intf3 no failover ip address intf4 no failover ip address intf5 no failover ip address intf6 pdm history enable arp timeout 14400 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list nonat nat (inside) 1 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 0 0 route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.65 1 timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 rpc 0:10:00 h225 1:00:00 timeout h323 0:05:00 mgcp 0:05:00 sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+ aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius aaa-server LOCAL protocol local no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server community public no snmp-server enable traps floodguard enable !--- These are IPSec policies. sysopt connection permit-ipsec crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp crypto map cisco 10 match address 100 crypto map cisco 10 set peer 10.66.79.180 crypto map cisco 10 set transform-set cisco crypto map cisco interface outside !--- These are IKE policies. isakmp enable outside isakmp key ******** address 10.66.79.180 netmask 255.255.255.255 isakmp policy 1 authentication pre-share isakmp policy 1 encryption des isakmp policy 1 hash md5 isakmp policy 1 group 2 isakmp policy 1 lifetime 86400 telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 terminal width 80 Cryptochecksum:244c86c9beab00bda8f790502ca74db9 : end |
Vérification
Cette section fournit les informations pour confirmer que votre configuration fonctionne correctement.
L'Outil Interpréteur de sortie (clients enregistrés uniquement) (OIT) prend en charge certaines commandes show. Utilisez l'OIT pour afficher une analyse de la sortie de la commande show .
-
show crypto ipsec sa - Affiche les paramètres utilisés par les SA IPSec actuelles.
-
show crypto isakmp sa — Affiche toutes les SA IKE en cours au niveau d'un homologue.
-
show crypto vlan - Affiche le VLAN associé à la configuration de chiffrement.
-
show crypto eli - Affiche les statistiques du module de service VPN.
Pour plus d'informations sur la vérification et le dépannage d'IPSec, référez-vous à Dépannage de la sécurité IP - Compréhension et utilisation des commandes de débogage.
Dépannage
Cette section fournit les informations nécessaires au dépannage de votre configuration.
Dépannage des commandes
Remarque : Avant d'émettre des commandes debug, reportez-vous à Informations importantes sur les commandes de débogage.
-
debug crypto ipsec : Cette commande affiche les négociations IPSec de la phase 2.
-
debug crypto isakmp - Affiche les négociations ISAKMP de la phase 1.
-
debug crypto engine - Montre le trafic crypté.
-
clear crypto isakmp : efface les SA liées à la phase 1.
-
clear crypto sa : efface les SA liées à la phase 2.
Pour plus d'informations sur la vérification et le dépannage d'IPSec, référez-vous à Dépannage de la sécurité IP - Compréhension et utilisation des commandes de débogage.
Informations connexes
Contacter Cisco
- Ouvrir un dossier d’assistance

- (Un contrat de service de Cisco est requis)
 Commentaires
Commentaires