Configurazione di BRI-to-BRI Dialup con mappe dialer DDR
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento viene descritto come configurare il routing DDR (dial-on-demand routing) tra due router con interfacce BRI. In questa configurazione, un router SOHO (Small Office Home Office) compone il numero del router del sito centrale ogni volta che deve passare il traffico alla rete centrale. La connessione viene interrotta automaticamente se non viene effettuato traffico per un periodo di tempo definito dall'utente. Questa rete utilizza anche il protocollo di routing Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) con il comando ip ospf demand-circuit per impedire che eventuali route per la rete lato remoto vengano rimosse quando il collegamento DDR viene interrotto. Tuttavia, non è necessario un protocollo di routing per l'esecuzione su questo collegamento.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
I punti seguenti descrivono diversi fattori di progettazione su cui è necessario decidere prima di configurare un collegamento DDR.
-
Implementazione DDR: È possibile utilizzare mappe dialer (DDR legacy) o profili dialer. Per ulteriori informazioni sulle differenze tra queste due implementazioni, consultare il documento sulla configurazione del DDR ISDN con profili dialer. In questa configurazione vengono utilizzate le mappe dialer.
-
Composizione singola o bidirezionale: È possibile configurare ciascun router in modo che avvii il collegamento DDR componendo l'altro lato oppure fare in modo che la connessione venga avviata solo dal lato (normalmente il SOHO). Esaminare i modelli di traffico e prendere in considerazione le informazioni mostrate di seguito prima di decidere quale metodo di composizione usare:
-
Se vengono chiamati entrambi i router:
-
Entrambi i siti possono avviare un collegamento quando è presente traffico destinato alla rete dell'altro router.
-
Entrambi i router potrebbero comporre il numero contemporaneamente. Il messaggio potrebbe essere occupato.
-
-
Se la composizione è limitata al router SOHO:
-
Il traffico proveniente dal sito centrale e destinato al router SOHO fallirebbe se il collegamento non è attivo.
-
Eviterai messaggi occupati a causa di chiamate in conflitto.
-
Nota: nell'esempio, solo il router SOHO avvia il collegamento DDR.
-
-
Protocollo di routing: È possibile scegliere di eseguire un protocollo di routing sul collegamento, ma è necessario assicurarsi che gli aggiornamenti periodici, ad esempio i collegamenti, non siano contrassegnati come interessanti, in modo che il collegamento non rimanga attivo per un periodo di tempo indefinito. Inoltre, il protocollo di routing deve mantenere intatta la tabella di routing e non eliminare i percorsi quando il collegamento non funziona. A tale scopo, è possibile usare il comando ip ospf demand-circuit o il routing delle istantanee. Se non si desidera utilizzare un protocollo di routing, è possibile configurare una route statica su ciascun router in cui l'hop successivo punta all'interfaccia BRI dell'altro router.
-
Traffico interessante: È necessario prestare attenzione quando si definisce il traffico interessante DDR. Il traffico interessante definito in modo errato su entrambi i lati può impedire che il collegamento venga attivato quando desiderato, venga disconnesso prematuramente o addirittura non venga disconnesso affatto. È ad esempio possibile contrassegnare tutto il traffico del protocollo di routing come non interessante, in modo che gli aggiornamenti periodici non mantengano il collegamento indefinitamente.
Componenti usati
Questa configurazione è stata sviluppata e testata utilizzando le seguenti versioni software e hardware:
-
Router Cisco 1604 SOHO con un'interfaccia BRI-U con software Cisco IOS® versione 12.1(5)T
-
Router Cisco 3640 con NM-4B-U (quattro interfacce BRI-U) e Cisco IOS 12.1(2)
Convenzioni
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni usate, consultare il documento Cisco sulle convenzioni nei suggerimenti tecnici.
Configurazione
In questa sezione vengono presentate le informazioni necessarie per configurare le funzionalità descritte più avanti nel documento.
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi menzionati in questo documento, usare lo strumento di ricerca dei comandi di IOS
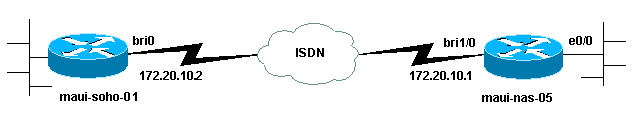
Esempio di rete
Questo documento utilizza le impostazioni di rete mostrate nel diagramma sottostante.
Configurazioni
Questo documento utilizza le configurazioni mostrate di seguito.
Nota: le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a un ambiente lab isolato. valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi sulla rete.
| maui-soho-01 (1600) |
|---|
maui-soho-01#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1656 bytes ! version 12.1 no service single-slot-reload-enable service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! hostname maui-soho-01 ! logging rate-limit console 10 except errors aaa new-model aaa authentication login default local aaa authentication login NO_AUTHEN none aaa authentication ppp default local !--- basic AAA configuration for PPP calls enable secret 5 <deleted> ! username admin password <deleted> username maui-nas-05 password cisco !--- username for remote router (maui-nas-05) and shared secret !--- (used for CHAP authentication) !--- Shared secret must be the same on both sides. ip subnet-zero ! isdn switch-type basic-ni ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.17.1.1 255.255.255.0 !--- The loopback address will be used by OSPF for the router ID. ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0 no ip address shutdown no fair-queue ! interface BRI0 !--- BRI interface used for DDR dialout ip address 172.20.10.2 255.255.255.0 !--- IP address !--- The remote address is in the same subnet. encapsulation ppp ip ospf demand-circuit !--- This forces OSPF to keep the routing table intact when the DDR link !--- is down. This should only be configured on one router for a !--- point-to-point circuit. dialer idle-timeout 900 !--- Idle timeout is set to 900 seconds (15 minutes). !--- The link will be disconnected if there is no interesting traffic !--- for 900 secs. dialer map ip 172.20.10.1 name maui-nas-05 broadcast 5551111 dialer map ip 172.20.10.1 name maui-nas-05 broadcast 5551112 !--- dialer map statements for the remote router !--- The name must match the one used by the remote router to identify !--- itself. The broadcast keyword is required to send broadcast traffic !--- over the link(for OSPF). The two different phone numbers correspond !--- to the b-channels of the remote side. The multiple statements allow !--- the router to dial the second number if the first number is busy. dialer load-threshold 80 outbound !--- This set the load level for traffic at which additional connections !--- will be added to the Multilink PPP bundle. !--- Load level values range from 1 (unloaded) to 255 (fully loaded). !--- The threshold in this case is 80/255 = 32%. dialer-group 1 !--- apply interesting traffic definition from dialer-list 1 isdn switch-type basic-ni isdn spid1 51255522220101 5552222 isdn spid2 51255522230101 5552223 ppp authentication chap !--- Use chap authentication. ppp multilink !--- Use multilink to bring up both BRI channels. ! router ospf 5 log-adjacency-changes network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 172.17.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 172.20.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! ip classless ip route 172.20.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.20.10.0 no ip http server ! access-list 101 remark Define Interesting Traffic access-list 101 deny ospf any any !--- mark OSPF as uninteresting !--- This will prevent OSPF hellos from keeping the link up. access-list 101 permit ip any any dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 101 !--- Interesting traffic is defined by access-list 101. !--- This is applied to BRI0 using dialer-group 1. ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 login authentication NO_AUTHEN transport input none line vty 0 4 ! end |
| maui-nas-05 (3640) |
|---|
maui-nas-05#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! version 12.1 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! hostname maui-nas-05 ! aaa new-model aaa authentication login default local aaa authentication login NO_AUTHEN none aaa authentication ppp default local !--- basic AAA configuration for PPP calls enable secret 5 <deleted> ! username admin password 7 <deleted> username maui-soho-01 password 7 cisco !--- username for remote router (maui-soho-01) and shared secret !--- (used for CHAP authentication) !--- Shared secret must be the same on both sides. ip subnet-zero ! isdn switch-type basic-ni ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.22.1.1 255.255.255.0 !--- The loopback address is used by OSPF for the router ID. ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.22.53.105 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 no ip address shutdown ! interface BRI1/0 !--- BRI interface used to accept dialin ip address 172.20.10.1 255.255.255.0 !--- IP address !--- The remote address is in the same subnet. encapsulation ppp dialer idle-timeout 900 !--- Idle timeout is set to 900 seconds (15 minutes). !--- Set this value to be equal to or higher than the idle-timeout on the !--- client side. A higher idle-timeout permits the client side to !--- determine when to bring down the link. ! dialer map ip 172.20.10.2 name maui-soho-01 broadcast !--- dialer map statement for the BRI interface of the remote router !--- The name must be the one used by the remote router to identify !--- itself. The broadcast keyword is required to send broadcast traffic !--- over the link(for OSPF). Note: There is no phone number, as we are !--- not configuring this side to dial. If you want this router to dial, !--- add the remote side phone number to the dialer map statement dialer-group 1 !--- apply interesting traffic definition from dialer-list 1 isdn switch-type basic-ni isdn spid1 51255511110101 5551111 isdn spid2 51255511120101 5551112 ppp authentication chap ppp multilink !--- allow multilink connections ! ! <<--unused interface configurations have been removed. ! router ospf 5 network 172.20.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 172.22.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 172.22.53.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 default-information originate always !--- transmit OSPF default information !--- This may be required for remote router to use the BRI DDR link. ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Ethernet0/0 ip route 172.22.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.22.53.0 no ip http server ! dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit !--- All IP traffic is defined interesting. !--- This is applied to BRI0 using dialer-group 1. ! line con 0 login authentication NO_AUTHEN transport input none line 97 102 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end |
Nota: se il router fa parte di una topologia point-to-point OSPF (2 router), solo un'estremità del circuito di richiesta deve essere configurata con il comando ip ospf demand-circuit. Tuttavia, tutti i router devono avere questa funzione caricata all'interno dell'area e devono supportare il comando ip ospf demand-circuit. Se il router fa parte di una topologia punto-multipunto OSPF (ad esempio, hub e spoke), solo l'estremità multipunto deve essere configurata con questo comando.
Output di esempio
Comandi show
Alcuni comandi show sono supportati dallo strumento Output Interpreter, che consente di visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show.
-
show dialer interface [ type number ] - Visualizza le informazioni di diagnostica generali relative alle interfacce configurate per DDR e visualizza la configurazione del timer e il tempo prima del timeout della connessione. Verificare i messaggi seguenti:
-
"Lo stato del dialer è un livello di collegamento dati verso l'alto" - Il dialer è apparso correttamente.
-
"Physical layer up" (Livello fisico verso l'alto) - È apparso il protocollo di linea, ma il Network Control Protocol (NCP) no.
-
"Dial REASON" (Motivo composizione) Visualizza gli indirizzi di origine e di destinazione del pacchetto da cui è stata avviata la composizione.
-
-
show isdn status: verificare che il router comunichi correttamente con lo switch ISDN. Questo comando visualizza anche il numero di chiamate attive. È necessario verificare i seguenti messaggi:
-
"Lo stato del layer 1 è ATTIVO",
-
"Stato livello 2 = MULTIPLE_FRAME_DEFINED"
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni, vedere Utilizzo del comando show isdn status per la risoluzione dei problemi BRI.
-
-
show caller user username detail: visualizza i parametri LCP negoziati dettagliati.
Output di esempio
Il comando show ip route visualizza la tabella di routing sullo switch dopo l'attivazione del collegamento DDR. Si noti che sono installate le route OSPF dal sito remoto.
maui-soho-01#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - ISIS level-1, L2 - ISIS level-2, ia - ISIS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 172.20.10.1 to network 0.0.0.0
172.17.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.17.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0
172.20.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks
C 172.20.10.0/24 is directly connected, BRI0
C 172.20.10.1/32 is directly connected, BRI0
S 172.20.0.0/16 [1/0] via 172.20.10.0
172.22.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
O 172.22.53.0/24 [110/1572] via 172.20.10.1, 00:01:37, BRI0
O 172.22.1.1/32 [110/1563] via 172.20.10.1, 00:01:37, BRI0
O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 172.20.10.1, 00:01:37, BRI0
Nota: le route OSPF (in particolare la route predefinita) dal lato remoto vengono aggiunte alla tabella di routing. In questo modo, il client (maui-soho-01) potrà chiamare il collegamento BRI ogni volta che sarà necessario inviare traffico attraverso il collegamento. Poiché si tratta di un circuito di richiesta OSPF, le voci OSPF nella tabella di routing non vengono rimosse (invecchiate) quando il collegamento diventa inattivo a causa del timeout di inattività del dialer scaduto.
Nell'output show caller user username detail si noti il timeout di inattività per la connessione.
maui-soho-01#show caller user maui-nas-05 detail
User: maui-nas-05, line BR0:1, service PPP
Active time 00:02:33, Idle time 00:00:00
Timeouts: Absolute Idle
Limits: - -
Disconnect in: - -
PPP: LCP Open, multilink Open, CHAP (AAA <--> AAA)
LCP: -> peer, AuthProto, MagicNumber, MRRU, EndpointDisc
<- peer, AuthProto, MagicNumber, MRRU, EndpointDisc
NCP: Closed IPCP, CDPCP
Dialer: Connected to 5551111, outbound
Type is ISDN, group BR0
Cause: ip (s=172.20.10.2, d=172.20.10.1)
IP: Local 172.20.10.2/24
Bundle: Member of maui-nas-05, last input 00:00:00
Counts: 945 packets input, 147302 bytes, 0 no buffer
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun
972 packets output, 150964 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
User: maui-nas-05, line Vi1, service PPP Bundle
Active time 00:02:32, Idle time 00:02:32
Timeouts: Absolute Idle
Limits: - 00:15:00
Disconnect in: - 00:12:26
!--- time after which this call will be disconnected unless it receives !--- interesting traffic
PPP: LCP Open, multilink Open, IPCP, CDPCP
LCP: -> peer, MagicNumber, MRRU, EndpointDisc
<- peer
NCP: Open IPCP, CDPCP
IPCP: <- peer, Address
-> peer, Address
Dialer: Connected to 5551111, outbound
Idle timer 900 secs, idle 153 secs
Type is IN-BAND SYNC, group BR0
IP: Local 172.20.10.2/24, remote 172.20.10.1
Bundle: First link of maui-nas-05, 1 link, last input 00:02:33
Counts: 20 packets input, 2916 bytes, 0 no buffer
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun
23 packets output, 2683 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
Risoluzione dei problemi
Comandi debug
Nota: prima di usare i comandi di debug, consultare le informazioni importanti sui comandi di debug.
-
debug isdn q931 - Visualizza la configurazione delle chiamate e la disattivazione della connessione di rete ISDN (layer 3).
-
debug isdn q921: visualizza i messaggi del livello di collegamento dati (livello 2) sul canale D tra il router e lo switch ISDN. Utilizzare questo debug se il comando show isdn status non visualizza i livelli 1 e 2 verso l'alto.
-
debug dialer [eventi] | packets] - Visualizza le informazioni di debug DDR relative ai pacchetti ricevuti su un'interfaccia dialer.
-
debug ppp negotiation: visualizza le informazioni sul traffico e gli scambi PPP durante la negoziazione dei componenti PPP, inclusi il protocollo LCP (Link Control Protocol), l'autenticazione e il protocollo NCP. Una negoziazione PPP riuscita aprirà innanzitutto lo stato LCP, quindi eseguirà l'autenticazione e infine la negoziazione NCP (generalmente IPCP).
-
debug ppp authentication: visualizza i messaggi del protocollo di autenticazione PPP, inclusi gli scambi di pacchetti Challenge Authentication Protocol (CHAP) e gli scambi del protocollo PAP (Password Authentication Protocol).
-
debug ppp error: visualizza gli errori di protocollo e le statistiche sugli errori associate alla negoziazione e al funzionamento della connessione PPP.
Per ulteriori informazioni, fare riferimento al documento sulla tecnologia di accesso remoto: Tecniche di risoluzione dei problemi per ulteriori informazioni sulla risoluzione dei problemi di questa connessione DDR.
Output di esempio del comando debug
L'output del comando debug visualizza la chiamata DDR attivata da un ping ICMP all'interfaccia BRI dei router remoti. I debug mostrano la composizione del router Soho, la connessione al sito centrale, la negoziazione del protocollo ppp e l'esecuzione dell'autenticazione CHAP.
maui-soho-01#debug dialer Dial on demand events debugging is on maui-soho-01#debug ppp negotiation PPP protocol negotiation debugging is on maui-soho-01#debug ppp authentication PPP authentication debugging is on maui-soho-01#debug isdn q931 ISDN Q931 packets debugging is on maui-soho-01# maui-soho-01# maui-soho-01# maui-soho-01#ping 172.20.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.20.10.1, timeout is 2 seconds: *Mar 1 21:57:42.625: BR0 DDR: Dialing cause ip (s=172.20.10.2, d=172.20.10.1) !--- The ping destined for 172.20.10.1 dials the BRI. *Mar 1 21:57:42.629: BR0 DDR: Attempting to dial 5551111 !--- phone number of the remote router that is dialed *Mar 1 21:57:42.653: ISDN BR0: TX -> SETUP pd = 8 callref = 0x09 *Mar 1 21:57:42.661: Bearer Capability i = 0x8890 *Mar 1 21:57:42.669: Channel ID i = 0x83 *Mar 1 21:57:42.677: Keypad Facility i = '5551111' *Mar 1 21:57:43.002: ISDN BR0: RX <- CALL_PROC pd = 8 callref = 0x89 *Mar 1 21:57:43.010: Channel ID i = 0x89 *Mar 1 21:57:43.189: ISDN BR0: RX <- CONNECT pd = 8 callref = 0x89 *Mar 1 21:57:43.216: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface BRI0:1, changed state to up *Mar 1 21:57:43.236: BR0:1 PPP: Treating connection as a callout !--- PPP negotiation begins. *Mar 1 21:57:43.236: BR0:1 PPP: Phase is ESTABLISHING, Active Open [0 sess, 1 load] *Mar 1 21:57:43.248: BR0:1 LCP: O CONFREQ [Closed] id 10 len 34 *Mar 1 21:57:43.252: BR0:1 LCP: AuthProto CHAP (0x0305C22305) *Mar 1 21:57:43.256: BR0:1 LCP: MagicNumber 0x153BEFE7 (0x0506153BEFE7) *Mar 1 21:57:43.260: BR0:1 LCP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) *Mar 1 21:57:43.268: BR0:1 LCP: EndpointDisc 1 Local (0x130F016D6175692D736F686F2D3031) *Mar 1 21:57:43.280: ISDN BR0: TX -> CONNECT_ACK pd = 8 callref = 0x09 *Mar 1 21:57:43.300: BR0:1 LCP: I CONFREQ [REQsent] id 7 Len 33 *Mar 1 21:57:43.304: BR0:1 LCP: AuthProto CHAP (0x0305C22305) *Mar 1 21:57:43.308: BR0:1 LCP: MagicNumber 0x354AAC53 (0x0506354AAC53) *Mar 1 21:57:43.312: BR0:1 LCP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) *Mar 1 21:57:43.320: BR0:1 LCP: EndpointDisc 1 Local (0x130E016D6175692D6E61732D3035) *Mar 1 21:57:43.327: BR0:1 LCP: O CONFACK [REQsent] id 7 Len 33 *Mar 1 21:57:43.331: BR0:1 LCP: AuthProto CHAP (0x0305C22305) *Mar 1 21:57:43.335: BR0:1 LCP: MagicNumber 0x354AAC53 (0x0506354AAC53) *Mar 1 21:57:43.339: BR0:1 LCP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) *Mar 1 21:57:43.347: BR0:1 LCP: EndpointDisc 1 Local (0x130E016D6175692D6E61732D3035) *Mar 1 21:57:43.359: BR0:1 LCP: I CONFACK [ACKsent] id 10 Len 34 *Mar 1 21:57:43.363: BR0:1 LCP: AuthProto CHAP (0x0305C22305) *Mar 1 21:57:43.367: BR0:1 LCP: MagicNumber 0x153BEFE7 (0x0506153BEFE7) *Mar 1 21:57:43.371: BR0:1 LCP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) *Mar 1 21:57:43.379: BR0:1 LCP: EndpointDisc 1 Local (0x130F016D6175692D736F686F2D3031) *Mar 1 21:57:43.383: BR0:1 LCP: State is Open *Mar 1 21:57:43.383: BR0:1 PPP: Phase is AUTHENTICATING, by both [0 sess, 1 load] !--- PPP Authentication begins. *Mar 1 21:57:43.391: BR0:1 CHAP: O CHALLENGE id 6 Len 33 from "maui-soho-01" !--- outgoing challenge for the remote router !--- This username should be configured in the dialer map statement !--- at the remote router. *Mar 1 21:57:43.399: BR0:1 CHAP: I CHALLENGE id 6 Len 32 from "maui-nas-05" !--- incoming challenge from remote router !--- This username should be configured in the dialer map statement. *Mar 1 21:57:43.415: BR0:1 CHAP: O RESPONSE id 6 Len 33 from "maui-soho-01" *Mar 1 21:57:43.443: BR0:1 CHAP: I SUCCESS id 6 Len 4 !--- Incoming CHAP Authentication is successful. *Mar 1 21:57:43.450: BR0:1 CHAP: I RESPONSE id 6 Len 32 from "maui-nas-05" *Mar 1 21:57:43.466: BR0:1 CHAP: O SUCCESS id 6 Len 4 !--- Outgoing CHAP Authentication is successful. *Mar 1 21:57:43.474: BR0:1 PPP: Phase is VIRTUALIZED [0 sess, 1 load] *Mar 1 21:57:43.581: Vi1 PPP: Phase is DOWN, Setup [0 sess, 1 load] *Mar 1 21:57:43.601: BR0:1 IPCP: Packet buffered while building MLP bundle interface *Mar 1 21:57:43.605: BR0:1 CDPCP: Packet buffered while building MLP bundle interface *Mar 1 21:57:43.609: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Virtual-Access1, changed state to up !--- Virtual access interface is automatically created (needed for multilink). *Mar 1 21:57:43.613: Vi1 DDR: Dialer statechange to up *Mar 1 21:57:43.617: Vi1 DDR: Dialer call has been placed *Mar 1 21:57:43.625: Vi1 PPP: Treating connection as a callout *Mar 1 21:57:43.625: Vi1 PPP: Phase is ESTABLISHING, Active Open [0 sess, 1 load] *Mar 1 21:57:43.637: Vi1 LCP: O CONFREQ [Closed] id 1 Len 34 *Mar 1 21:57:43.641: Vi1 LCP: AuthProto CHAP (0x0305C22305) *Mar 1 21:57:43.645: Vi1 LCP: MagicNumber 0x153BF171 (0x0506153BF171) *Mar 1 21:57:43.649: Vi1 LCP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) *Mar 1 21:57:43.653: Vi1 LCP: EndpointDisc 1 Local (0x130F016D6175692D736F686F2D3031) *Mar 1 21:57:43.665: Vi1 PPP: Phase is UP [0 sess, 1 load] *Mar 1 21:57:43.677: Vi1 IPCP: O CONFREQ [Closed] id 1 Len 10 *Mar 1 21:57:43.681: Vi1 IPCP: Address 172.20.10.2 (0x0306AC140A02) *Mar 1 21:57:43.693: Vi1 CDPCP: O CONFREQ [Closed] id 1 Len 4 *Mar 1 21:57:43.697: BR0:1 MLP: maui-nas-05, multilink up, first link *Mar 1 21:57:43.700: Vi1 PPP: Pending ncpQ size is 2 *Mar 1 21:57:43.700: BR0:1 IPCP: Redirect packet to Vi1 *Mar 1 21:57:43.708: Vi1 IPCP: I CONFREQ [REQsent] id 1 Len 10 *Mar 1 21:57:43.712: Vi1 IPCP: Address 172.20.10.1 (0x0306AC140A01) *Mar 1 21:57:43.716: Vi1 IPCP: O CONFACK [REQsent] id 1 Len 10 *Mar 1 21:57:43.724: Vi1 IPCP: Address 172.20.10.1 (0x0306AC140A01) *Mar 1 21:57:43.728: BR0:1 CDPCP: Redirect packet to Vi1 *Mar 1 21:57:43.732: Vi1 CDPCP: I CONFREQ [REQsent] id 1 Len 4 *Mar 1 21:57:43.736: Vi1 CDPCP: O CONFACK [REQsent] id 1 Len 4 *Mar 1 21:57:43.744: Vi1 IPCP: I CONFACK [ACKsent] id 1 Len 10 *Mar 1 21:57:43.752: Vi1 IPCP: Address 172.20.10.2 (0x0306AC140A02) *Mar 1 21:57:43.756: Vi1 IPCP: State is Open !--- IPCP state is open. *Mar 1 21:57:43.764: Vi1 CDPCP: I CONFACK [ACKsent] id 1 Len 4 *Mar 1 21:57:43.768: Vi1 CDPCP: State is Open *Mar 1 21:57:43.772: Vi1 DDR: dialer protocol up *Mar 1 21:57:43.784: BR0 IPCP: Install route to 172.20.10.1 !--- Install route to remote side. *Mar 1 21:57:44.462: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface BRI0:1, changed state to up *Mar 1 21:57:44.657: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual-Access1, changed state to up *Mar 1 21:57:49.180: %ISDN-6-CONNECT: Interface BRI0:1 is now connected to 5551111 maui-nas-05 !--- BRI Dial on Demand Routing (DDR) Link is operational. maui-soho-01#
Informazioni correlate
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
16-Dec-2005 |
Versione iniziale |
 Feedback
Feedback