Esempio di configurazione NEAT con Cisco Identity Services Engine
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento viene descritto la configurazione e il comportamento della topologia NEAT (Network Edge Authentication Topology) in uno scenario semplice. NEAT utilizza il protocollo CISP (Client Information Signaling Protocol) per propagare gli indirizzi MAC dei client e le informazioni sulla VLAN tra gli switch supplicant e autenticator.
In questo esempio di configurazione, sia lo switch autenticatore (detto anche autenticatore) che lo switch supplicant (detto anche supplicant) eseguono l'autenticazione 802.1x; l'autenticatore autentica il supplicant, che a sua volta autentica il PC di prova.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Cisco raccomanda la conoscenza dello standard di autenticazione IEEE 802.1x.
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
- Due switch Cisco Catalyst serie 3560 con software Cisco IOS®, versione 12.2(55)SE8; uno switch funge da autenticatore e l'altro da supplicant.
- Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), versione 1.2.1
- PC con Microsoft Windows XP, Service Pack 3.
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Configurazione
In questo esempio vengono illustrate configurazioni di esempio per:
- Switch di autenticazione
- Switch supplicant
- Cisco ISE
Le configurazioni rappresentano il minimo necessario per eseguire questa esercitazione; potrebbero non essere ottimali per altre esigenze o soddisfarle.
Esempio di rete
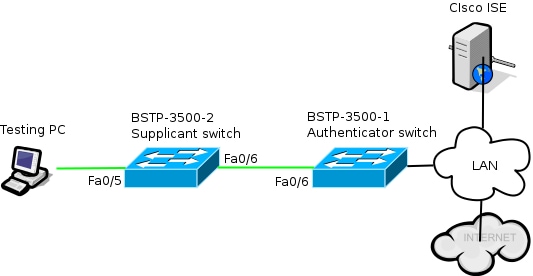
Nel diagramma della rete viene illustrata la connettività utilizzata nell'esempio. Le linee nere indicano la connettività logica o fisica, mentre le linee verdi indicano i collegamenti autenticati tramite l'utilizzo di 802.1x.
Configurazione switch autenticatore
L'autenticatore contiene gli elementi di base necessari per dot1x. Nell'esempio, i comandi specifici di NEAT o CISP sono visualizzati in grassetto.
Questa è la configurazione di autenticazione, autorizzazione e accounting (AAA) di base:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
aaa authorization network default group radius
aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group radius
radius-server host 10.48.66.107 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco
! Enable authenticator switch to authenticate the supplicant switch.
dot1x system-auth-control
! Enable CISP framework.
cisp enable
! configure uplink port as access and dot1x authentication.
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport mode access
authentication port-control auto
dot1x pae authenticator
spanning-tree portfast
CISP è abilitato a livello globale e la porta di interconnessione è configurata in modalità di autenticazione e accesso.
Configurazione switch supplicant
L'accurata configurazione del supplicant è fondamentale affinché l'intera configurazione funzioni come previsto. Questa configurazione di esempio contiene una configurazione AAA e dot1x tipica.
Questa è la configurazione AAA di base:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
aaa authorization network default group radius
aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group radius
radius-server host 10.48.66.107 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco
! Enable supplicant switch to authenticate devices connected
dot1x system-auth-control
! Forces the switch to send only multicast EAPOL packets when it receives either
unicast or multicast packets, which allows NEAT to work on the supplicant
switch in all host modes.
dot1x supplicant force-multicast
! Enable CISP framework operation.
cisp enable
Il supplicant deve avere le credenziali configurate e deve fornire un metodo EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) da utilizzare.
Il richiedente può utilizzare l'autenticazione EAP-Message Digest 5 (MD5) e EAP-Flexible Authentication via Secure Protocol (FAST) (tra gli altri tipi di EAP) per l'autenticazione in caso di CISP. Per ridurre al minimo la configurazione ISE, in questo esempio viene usato EAP-MD5 per autenticare il richiedente e inviare l'autenticazione. L'impostazione predefinita prevede l'uso di EAP-FAST, che richiede la preparazione delle credenziali di accesso protetto (PAC); questo documento non copre tale scenario.
! configure EAP mode used by supplicant switch to authenticate itself to
authenticator switch eap profile EAP_PRO
method md5
! Configure credentials use by supplicant switch during that authentication.
dot1x credentials CRED_PRO
username bsnsswitch
password 0 C1sco123
La connessione del richiedente all'autenticatore è già configurata come porta trunk (diversamente dalla configurazione della porta di accesso sull'autenticatore). In questa fase, la configurazione cambia in modo dinamico quando ISE restituisce l'attributo corretto.
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk
dot1x pae supplicant
dot1x credentials CRED_PRO
dot1x supplicant eap profile EAP_PRO
La porta che si connette al PC Windows ha una configurazione minima ed è mostrata qui solo come riferimento.
interface FastEthernet0/5
switchport access vlan 200
switchport mode access
authentication port-control auto
dot1x pae authenticator
Configurazione di ISE
In questa procedura viene descritto come configurare una configurazione ISE di base.
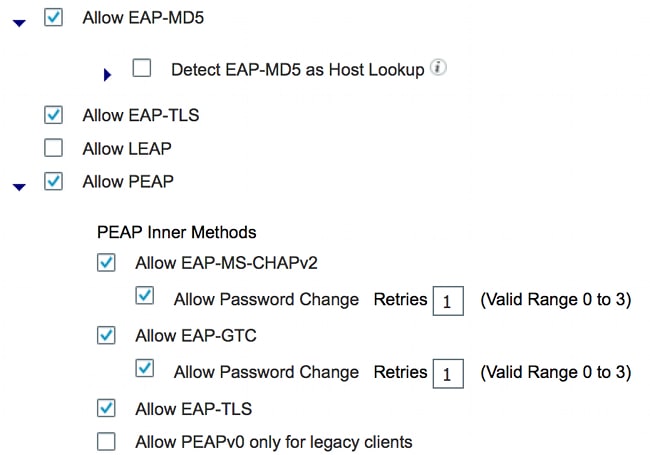
- Abilitare i protocolli di autenticazione richiesti.
In questo esempio, il dot1x cablato consente a EAP-MD5 di autenticare il richiedente all'autenticatore e a MSCHAPv2 (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol)-Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol versione 2 di autenticare il PC Windows al richiedente.
Selezionare Criterio > Risultati > Autenticazione > Protocolli consentiti, selezionare l'elenco dei servizi di protocollo utilizzati dal punto 1x cablato e verificare che i protocolli in questo passaggio siano abilitati.
- Creare un criterio di autorizzazione. Passare a Criterio > Risultati > Autorizzazione > Criterio di autorizzazione e creare o aggiornare un criterio in modo che contenga NEAT come attributo restituito. Questo è un esempio di tale politica:
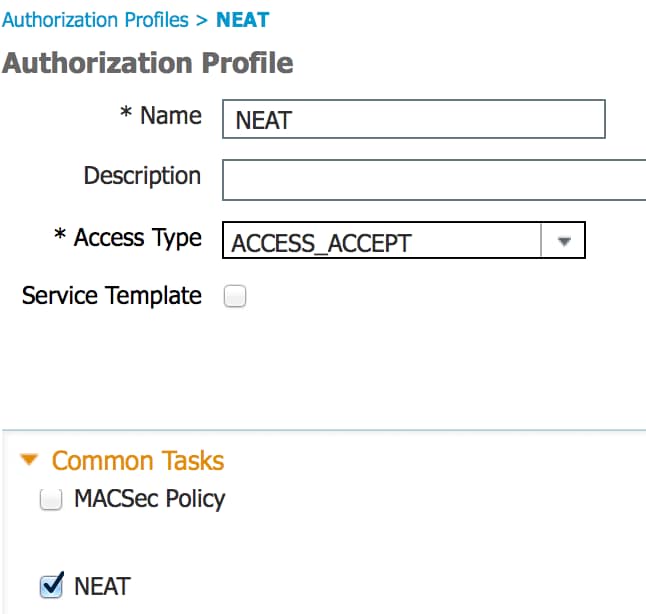
Quando l'opzione NEAT è attivata, ISE restituisce device-traffic-class=switch come parte dell'autorizzazione. Questa opzione è necessaria per modificare la modalità della porta dell'autenticatore da accesso a trunk. - Creare una regola di autorizzazione per utilizzare questo profilo. Passare a Criteri > Autorizzazione e creare o aggiornare una regola.
In questo esempio, viene creato un gruppo di dispositivi speciale denominato Authenticator_switches e tutti i supplicant inviano un nome utente che inizia con bsnswitch.

- Aggiungere gli switch al gruppo appropriato. Selezionare Amministrazione > Risorse di rete > Dispositivi di rete, quindi fare clic su Aggiungi.

Nell'esempio, il BSTP-3500-1 (l'autenticatore) fa parte del gruppo Authenticator_switches; il BSTP-3500-2 (il supplicant) non deve necessariamente far parte di questo gruppo.
Verifica
Per verificare che la configurazione funzioni correttamente, consultare questa sezione. In questa sezione vengono descritti due comportamenti:
- Autenticazione tra switch
- Autenticazione tra il PC Windows e il richiedente
Vengono inoltre illustrate tre ulteriori situazioni:
- Rimozione di un client autenticato dalla rete
- Rimozione di un supplicante
- Porte senza dot1x su un supplicant
Switch supplicant da autenticazione a autenticazione switch
In questo esempio, il supplicant esegue l'autenticazione dell'autenticatore. Le fasi del processo sono le seguenti:
- Il richiedente è configurato e collegato alla porta fastethernet0/6. Lo scambio dot1x fa sì che il supplicant utilizzi EAP per inviare un nome utente e una password preconfigurati all'autenticatore.
- L'autenticatore esegue uno scambio RADIUS e fornisce le credenziali per la convalida ISE.
- Se le credenziali sono corrette, ISE restituisce gli attributi richiesti da NEAT (device-traffic-class=switch) e l'autenticatore cambia la modalità switchport da access a trunk.
Nell'esempio viene mostrato come scambiare le informazioni CISP tra gli switch:
bstp-3500-1#debug cisp all
Oct 15 13:51:03.672: %AUTHMGR-5-START: Starting 'dot1x' for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID 0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: %DOT1X-5-SUCCESS: Authentication successful for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: %AUTHMGR-7-RESULT: Authentication result 'success' from
'dot1x' for client (001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID
0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: Applying command... 'no switchport access vlan 1' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.739: Applying command... 'no switchport nonegotiate' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.748: Applying command... 'switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q'
at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.756: Applying command... 'switchport mode trunk' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.756: Applying command... 'switchport trunk native vlan 1' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.764: Applying command... 'spanning-tree portfast trunk' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: %AUTHMGR-5-SUCCESS: Authorization succeeded for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID 0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Start in
state Not Running
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Waiting
link UP
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 13:51:05.669: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/6, changed state to
up
Oct 15 13:51:06.793: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:06.793: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Start in
state Waiting link UP (no-op)
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/6, changed state to up
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Link UP in
state Waiting link UP
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Idle
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT: Received action Start Tick Timer
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT: Started CISP tick timer
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:28.377: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:28.377: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:29.400: CISP-EVENT: Stopped CISP tick timer
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x22 Length:0x001C
Type:REGISTRATION
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: Payload: 0200E84B
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposed CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Negotiated CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 59467
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x22 Length:0x001C
Type:REGISTRATION
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: Payload: 01000000
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x23 Length:0x003A
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: Payload: 010011020009001B0D5521C10300050 ...
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
to authenticator list
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about new
downstream client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client info at Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
to authenticator list
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about new
downstream client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client info at Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x23 Length:0x0018
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Una volta completata l'autenticazione e l'autorizzazione, si verifica lo scambio CISP. Ogni scambio ha una REQUEST, inviata dal supplicant, e una RESPONSE, che funge da risposta e conferma da parte dell'autenticatore.
Vengono eseguiti due scambi distinti: REGISTRATION e ADD_CLIENT. Durante lo scambio REGISTRATION, il supplicant informa l'autenticatore che è compatibile con CISP e l'autenticatore riconosce questo messaggio. Lo scambio ADD_CLIENT viene utilizzato per informare l'autenticatore dei dispositivi connessi alla porta locale del richiedente. Come per REGISTRATION, ADD-CLIENT viene avviato sul supplicant e riconosciuto dall'autenticatore.
Immettere questi comandi show per verificare la comunicazione, i ruoli e gli indirizzi:
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
bstp-3500-1#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/6
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
Nell'esempio, il ruolo di Authenticator viene assegnato correttamente all'interfaccia corretta (fa0/6) e vengono registrati due indirizzi MAC. Gli indirizzi MAC sono quelli supplicant sulla porta fa0/6 sulla VLAN1 e sulla VLAN200.
È ora possibile eseguire la verifica delle sessioni di autenticazione dot1x. La porta fa0/6 sullo switch a monte è già autenticata. Questo è lo scambio dot1x che viene attivato quando BSTP-3500-2 (il supplicant) è collegato:
bstp-3500-1#show authentication sessions
Interface MAC Address Method Domain Status Session ID
Fa0/6 001b.0d55.2187 dot1x DATA Authz Success 0A3039E10000000700FB3259
Come previsto in questa fase, non vi sono sessioni sul richiedente:
bstp-3500-2#show authentication sessions
No Auth Manager contexts currently exist
Switch da autenticazione PC Windows a supplicant
In questo esempio, il PC Windows esegue l'autenticazione al supplicant. Le fasi del processo sono le seguenti:
- Il PC Windows è collegato alla porta FastEthernet 0/5 del BSTP-3500-2 (il supplicant).
- Il supplicant esegue l'autenticazione e l'autorizzazione con l'ISE.
- Il richiedente informa l'autenticatore che un nuovo client è connesso alla porta.
Questa è la comunicazione del ricorrente:
Oct 15 14:19:37.207: %AUTHMGR-5-START: Starting 'dot1x' for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID 0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:37.325: %DOT1X-5-SUCCESS: Authentication successful for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID
Oct 15 14:19:37.325: %AUTHMGR-7-RESULT: Authentication result 'success' from
'dot1x' for client (c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID
0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Received action Add Client
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to supplicant list
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant received event Add Client in
state Idle
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to the ADD list
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to ADD CLIENT req
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x24 Length:0x0029
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: Payload: 010011020009C46413B429C30300050 ...
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'retransmit' timer (30s)
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT: Started CISP tick timer
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant state changed to Request
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x24 Length:0x0018
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant received event Receive Packet
in state Request
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Stopped 'retransmit' timer
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): All Clients implicitly ACKed
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant state changed to Idle
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: %AUTHMGR-5-SUCCESS: Authorization succeeded for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID 0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Authenticator received event Start in
state Not Running
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Authenticator state changed to Waiting
link UP
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 14:19:38.373: CISP-EVENT: Stopped CISP tick timer
Oct 15 14:19:39.162: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/5, changed state to
up
Viene eseguito uno scambio ADD_CLIENT, ma non è necessario alcuno scambio REGISTRATION.
Per verificare il comportamento del richiedente, immettere il comando show cisp registrations:
bstp-3500-2#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/5
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
Fa0/6
802.1x Sup (Supplicant)
Il supplicant ha il ruolo di supplicant nei confronti dell'autenticatore (interfaccia fa0/6) e il ruolo di autenticatore nei confronti del PC Windows (interfaccia fa0/5).
Per verificare il comportamento dell'autenticatore, immettere il comando show cisp clients:
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
c464.13b4.29c3 200 Fa0/6
Un nuovo indirizzo MAC viene visualizzato sull'autenticatore nella VLAN 200. È l'indirizzo MAC osservato nelle richieste AAA sul supplicant.
Le sessioni di autenticazione devono indicare che lo stesso dispositivo è collegato sulla porta fa0/5 del richiedente:
bstp-3500-2#show authentication sessions
Interface MAC Address Method Domain Status Session ID
Fa0/5 c464.13b4.29c3 dot1x DATA Authz Success 0A3039E20000001501018B58
Rimozione del client autenticato dalla rete
Quando un client viene rimosso (ad esempio, se una porta viene chiusa), l'autenticatore riceve una notifica tramite lo scambio DELETE_CLIENT.
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x25 Length:0x0029
Type:DELETE_CLIENT
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: Payload: 010011020009C46413B429C30300050 ...
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client c464.13b4.29c3
(vlan: 200) from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x25 Length:0x0018
Type:DELETE_CLIENT
Rimozione dello switch supplicant
Quando un richiedente viene scollegato o rimosso, l'autenticatore ripristina la configurazione originale sulla porta per evitare problemi di sicurezza.
Oct 15 15:57:31.257: Applying command... 'no switchport nonegotiate' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.273: Applying command... 'switchport mode access' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.273: Applying command... 'no switchport trunk encapsulation
dot1q' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.290: Applying command... 'no switchport trunk native vlan 1' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.299: Applying command... 'no spanning-tree portfast trunk' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.307: Applying command... 'switchport access vlan 1' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.315: Applying command... 'spanning-tree portfast' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/6, changed state to down
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Link DOWN
in state Idle
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client 001b.0d55.21c1
(vlan: 200) from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Not
Running
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 15:57:33.262: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/6, changed state
to down
Allo stesso tempo, il supplicant rimuove i client che rappresentano il supplicant dalla tabella CISP e disattiva CISP su tale interfaccia.
Porte senza dot1x su switch supplicant
Le informazioni CISP propagate dal supplicant all'autenticatore servono solo come un altro livello di imposizione. Il supplicant informa l'autenticatore di tutti gli indirizzi MAC consentiti ad esso connessi.
Uno scenario generalmente frainteso è questo: se un dispositivo è collegato a una porta su cui non è abilitato dot1x, l'indirizzo MAC viene appreso e propagato allo switch a monte tramite CISP.
L'autenticatore consente la comunicazione che proviene da tutti i client appresi tramite CISP.
In sostanza, il ruolo del richiedente è quello di limitare l'accesso dei dispositivi, tramite il dot1x o altri metodi, e di propagare l'indirizzo MAC e le informazioni sulla VLAN all'autenticatore. L'autenticatore agisce da esecutore delle informazioni fornite in tali aggiornamenti.
Ad esempio, è stata creata una nuova VLAN (VLAN300) su entrambi gli switch e un dispositivo è stato collegato alla porta fa0/4 sul dispositivo supplicant. La porta fa0/4 è una porta di accesso semplice che non è configurata per dot1x.
Questo output del supplicant visualizza una nuova porta registrata:
bstp-3500-2#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/4
Fa0/5
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
Fa0/6
802.1x Sup (Supplicant)
Sull'autenticatore, un nuovo indirizzo MAC è visibile sulla VLAN 300.
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c2 300 Fa0/6
c464.13b4.29c3 200 Fa0/6
68ef.bdc7.13ff 300 Fa0/6
Risoluzione dei problemi
Le informazioni contenute in questa sezione permettono di risolvere i problemi relativi alla configurazione.
Questi comandi aiutano a risolvere i problemi relativi a NEAT e CISP; nel presente documento sono riportati alcuni esempi per la maggior parte di essi:
- debug cisp all: visualizza lo scambio di informazioni CISP tra gli switch.
- show cisp summary: visualizza un riepilogo dello stato dell'interfaccia CISP sullo switch.
- show cisp registrations: indica le interfacce che partecipano agli scambi CISP, i ruoli di tali interfacce e se le interfacce fanno parte di NEAT.
- show cisp clients: visualizza una tabella di indirizzi MAC client noti e la loro posizione (VLAN e interfaccia). Questo è utile principalmente dall'autenticatore.
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
18-Oct-2013 |
Versione iniziale |
 Feedback
Feedback