Esempio di configurazione del software di sistema EtherChannel tra gli switch Catalyst serie 3550/3560/3750 e gli switch Catalyst con Cisco IOS
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento viene fornita una configurazione di esempio per come configurare EtherChannel tra uno switch Catalyst 3550 e uno switch Catalyst 6500/6000 con software di sistema Cisco IOS®. EtherChannel può essere chiamato Fast EtherChannel o Gigabit EtherChannel, a seconda della velocità delle interfacce o delle porte utilizzate per formare EtherChannel.
Nota: i comandi EtherChannel applicati allo switch Catalyst 3550 in questo documento possono essere applicati anche agli switch Catalyst serie 3750.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Nessun requisito specifico previsto per questo documento.
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
-
Switch Catalyst 3550 con software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(14)EA
-
Switch Catalyst 6500/6000 con software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(13)E1
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Convenzioni
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni usate, consultare il documento Cisco sulle convenzioni nei suggerimenti tecnici.
Nozioni di base
In questo documento, due interfacce Gigabit Ethernet su uno switch Catalyst 3550 - l'interfaccia Gigabit Ethernet sullo switch 3500 è un'interfaccia Ethernet negoziata 10/100/1000 - sono state integrate in un Fast EtherChannel con due interfacce Fast Ethernet da uno switch Catalyst 6500/6000 con software Cisco IOS per formare un EtherChannel di layer 2 (L2).
Nota: in questo documento, Fast EtherChannel, Gigabit EtherChannel, port channel e channel group fanno tutti riferimento a EtherChannel.
La configurazione dello switch Catalyst descritta in questo documento è valida su tutti gli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000 o Catalyst serie 4500/4000 con software di sistema Cisco IOS.
Questo documento mostra i file di configurazione solo per gli switch, nonché l'output dei relativi comandi show di esempio. Per i dettagli su come configurare EtherChannel, fare riferimento a questi documenti:
-
Sezione Configurazione di EtherChannel di layer 2 in Configurazione di EtherChannel (switch Catalyst 3550)
-
Sezione Configurazione di EtherChannel di layer 3 in Configurazione di EtherChannel (switch Catalyst 3560)
-
Sezione Configurazione di EtherChannel di layer 2 in Configurazione di EtherChannel (switch Catalyst 3750)
-
Configurazione di EtherChannel di layer 3 e layer 2 (Catalyst 6500/6000 con software di sistema Cisco IOS)
-
Sezione Configurazione di EtherChannel di layer 2 in Descrizione e configurazione di EtherChannel (Catalyst 4500/4000 con software di sistema Cisco IOS)
Note importanti
EtherChannel può essere configurato manualmente con i comandi appropriati. Inoltre, è possibile configurare EtherChannel automaticamente con il protocollo PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol) in modo che lo switch negozi il canale con l'altro lato del collegamento. Per maggiori informazioni sul PAgP, fare riferimento a questi documenti:
-
Informazioni sulla sezione Port Aggregation Protocol in Configurazione di EtherChannel (switch Catalyst 3550)
-
Informazioni sulla sezione Port Aggregation Protocol in Configurazione di EtherChannel (switch Catalyst 3560)
-
Sezione Port Aggregation Protocol in Configurazione di EtherChannel (switch Catalyst 3750)
-
Informazioni sulla sezione Port Aggregation Protocol in Configurazione di EtherChannel (Catalyst 6500/6000 con software di sistema Cisco IOS)
-
Sezione Informazioni sul protocollo Port Aggregation in Descrizione e configurazione di EtherChannel (Catalyst 4500/4000 con software di sistema Cisco IOS)
Le configurazioni descritte in questo documento vengono implementate utilizzando la modalità desiderata. Se si intende configurare EtherChannel manualmente, seguire le istruzioni fornite per creare un canale porta. In questo modo si evitano problemi con lo Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) durante il processo di configurazione. STP può disattivare alcune porte, con uno stato della porta di errore-disabled [errdisable], se un lato è configurato come canale prima che l'altro lato possa essere configurato come canale.
Per creare un canale di porta, effettuare le seguenti operazioni:
-
Lasciare le interfacce da utilizzare nel channeling delle porte come chiuse a livello amministrativo.
-
Creare il canale della porta (gruppo di canali) sullo switch Catalyst 6500/6000.
Accertarsi di impostare la modalità del canale su on, ad esempio la modalità del gruppo di canali 1 su on.
-
Creazione di canali delle porte sullo switch Catalyst 3550, 3560 o 3750.
Assicurarsi di impostare la modalità canale su on.
-
Riattivare le interfacce disabilitate in precedenza sullo switch Catalyst 6500/6000 con il comando no shut.
Configurazione
In questa sezione vengono presentate le informazioni necessarie per configurare le funzionalità descritte più avanti nel documento.
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi menzionati in questo documento, usare lo strumento di ricerca dei comandi ![]() (solo utenti registrati).
(solo utenti registrati).
Esempio di rete
Nel documento viene usata l'impostazione di rete mostrata nel diagramma:
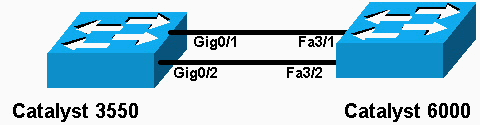
Nota: l'interfaccia Gigabit Ethernet sullo switch Catalyst 3550 è un'interfaccia Ethernet negoziata 10/100/1000 Mbps. La porta Gigabit dello switch Catalyst 3550 può essere collegata anche a una porta FastEthernet (100 Mbps) su uno switch Catalyst 6500/6000.
Nota: gli switch Catalyst serie 3750 supportano EtherChannel tra stack, che consente alle interfacce di switch diversi dello stack di essere membri dello stesso gruppo EtherChannel. Per ulteriori informazioni su EtherChannel in un ambiente di switch in stack, fare riferimento alla sezione EtherChannel and Switch Stack della documentazione Configurazione di EtherChannel per gli switch Catalyst serie 3750.
Configurazioni
Nel documento vengono usate queste configurazioni:
| Catalyst 3550 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 1610 bytes ! version 12.1 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Cat3550 ! enable password ww ! ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! ! ! ! !--- A logical port-channel interface is automatically created !--- when ports are grouped into a channel group. interface Port-channel 1 !--- In this example, the L2 EtherChannel is configured. !--- A Layer 3 (L3) EtherChannel can also be configured on the Catalyst 3550 switches. !--- For more information, refer to the document Configuring EtherChannel. switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status! !--- Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interface on the Catalyst 3550 is a !--- 10/100/1000 Mbps negotiated Ethernet interface. The Gigabit port on the Catalyst 3550 is !--- connected to a FastEthernet (100 Mbps) port on the Catalyst 6500/6000. !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status channel-group 1 mode desirable ! !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface GigabitEthernet0/3 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status ! !--- Output suppressed. interface GigabitEthernet0/12 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status !--- Interface VLAN1 is required for management purposes. interface Vlan1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! ip classless ip http server ! ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 5 15 ! end |
| Catalyst 6500/6000 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 5869 bytes ! version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname cat6500 ! boot buffersize 126968 boot bootldr bootflash:c6msfc-boot-mz.121-4.E1 enable password ww ! redundancy main-cpu auto-sync standard ip subnet-zero ! ! no ip finger ! ! ! ! !--- A logical port-channel interface is automatically created !--- when ports are grouped into a channel group. interface Port-channel 1 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/2 no ip address shutdown ! !--- Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interface on the Catalyst 3550 is a !--- 10/100/1000 Mbps negotiated Ethernet interface. The Gigabit port on the Catalyst 3550 is !--- connected to a FastEthernet (100 Mbps) port on the Catalyst 6500/6000. interface FastEthernet3/1 no ip address !--- In this example, the L2 EtherChannel is configured. !--- An L3 EtherChannel can also be configured on the Catalyst 6500/6000 running !--- Cisco IOS System Software. For more details, refer to the document !--- Configuring EtherChannel. !--- On a Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport !--- command once, without any keywords, in order to configure the interface as an L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default; !--- no additional command is required. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet3/2 no ip address !--- On a Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport !--- command once, without any keywords, in order to configure the interface as an L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default; !--- no additional command is required. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet3/3 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! !--- Output suppressed. ! interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! !--- Interface VLAN1 is required for management purposes. interface Vlan1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 ! end |
Nota: questo esempio di configurazione mostra una configurazione EtherChannel con collegamenti di accesso. La stessa configurazione si applica ai collegamenti trunk EtherChannel. Eseguire il comando switchport mode trunk o consentire agli switch di negoziare la modalità con la modalità dinamica desiderabile. Per ulteriori informazioni su come configurare il trunking, consultare la sezione Configurazione dei trunking VLAN nel documento sulla configurazione delle VLAN.
Configurazione Port-Channel Sub Interface
Un altro esempio di configurazione del canale della porta con l'interfaccia secondaria nello switch Catalyst 3560 con software Cisco IOS versione 12.2(25).
| Catalyst 3560 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 2480 bytes ! version 12.2 ! interface Port-channel5 no switchport no ip address ! interface Port-channel5.690 ! interface Port-channel10 no switchport no ip address ! interface Port-channel10.1 ! interface Port-channel10.690 ! interface Port-channel11 no switchport no ip address |
Verifica
Alcuni comandi show sono supportati dallo strumento Output Interpreter (solo utenti registrati); lo strumento permette di visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show. ![]()
Per verificare il canale della porta negli switch Catalyst 6500/6000 e Catalyst 3500 con software di sistema Cisco IOS, eseguire questi comandi:
Per controllare lo stato STP sugli switch Catalyst 6500/6000 e Catalyst 3500 con software di sistema Cisco IOS, eseguire questo comando:
Catalyst 3550
Cat3550#show interface port-channel 1
Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 0002.4b28.db02 (bia 0002.4b28.db02)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 200000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is off
Members in this channel: Gi0/1 Gi0/2
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:03:27, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
26 packets input, 5344 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 17 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
59 packets output, 5050 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Cat3550#show spanning-tree vlan 1 detail
VLAN1 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
We are the root of the spanning tree
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 1 last change occurred 00:00:38 ago
from Port-channel1
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 0
Port 65 (Port-channel1) of VLAN1 is forwarding
Port path cost 12, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.65.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated port id is 128.65, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 34, received 0
Cat3550# show etherchannel 1 summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
U - port-channel in use
Group Port-channel Ports
-----+------------+-----------------------------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) Gi0/1(P) Gi0/2(P)
Cat3550# ping 10.1.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Catalyst 6500/6000
Cat6500# show interface port-channel 1
Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 0002.7ef1.36e1 (bia 0002.7ef1.36e1)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 200000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
Members in this channel: Fa3/1 Fa3/2
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/2000, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 1000 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
407 packets input, 34994 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 311 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
93 packets output, 16598 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Cat6500# show spanning-tree vlan 1 detail
VLAN1 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 00d0.024f.6001
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Current root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Root port is 833 (Port-channel1), cost of root path is 12
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:02:13 ago
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300
Port 833 (Port-channel1) of VLAN1 is forwarding
Port path cost 12, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 131.65.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated port id is 128.65, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 1, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 0, received 66
Cat6500# show etherchannel 1 summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
Group Port-channel Ports
-----+------------+-----------------------------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) Fa3/1(P) Fa3/2(P)
Cat6500# ping 10.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Risoluzione dei problemi
Stato err-disabled
Un problema comune durante la configurazione di EtherChannel è che le interfacce passano alla modalità err-disabled. Questa condizione si può verificare quando Etherchannel viene portato in modalità ON su uno switch e l'altro switch non viene configurato immediatamente. Se questo stato viene lasciato per qualche minuto, il comando STP sullo switch su cui EtherChannel è abilitato interpreta questa condizione come un loop. In questo modo, le porte raggruppate nel canale vengono messe nello stato err-disabled. Per ulteriori informazioni su come determinare se le interfacce EtherChannel sono in stato err-disabled, vedere l'esempio:
%SPANTREE-2-CHNL_MISCFG: Detected loop due to etherchannel misconfiguration of Gi0/9 %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: channel-misconfig error detected on Po10, putting Gi0/9 in err-disable state %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: channel-misconfig error detected on Po10, putting Gi0/10 in err-disable state
Switch1#show etherchannel summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
u - unsuitable for bundling
U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
d - default port
Number of channel-groups in use: 1
Number of aggregators: 1
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------
10 Po10(SD) - Gi0/9(D) Gi0/10(D)
Switch1#show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/9 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi0/9 err-disabled 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTX
Switch1#show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/10 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi0/10 err-disabled 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTX
Il messaggio di errore indica che EtherChannel ha rilevato un loop nello spanning tree. Per risolvere il problema, impostare la modalità del canale su desiderati su entrambi i lati della connessione, quindi riattivare le interfacce:
Switch1#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch1(config)#interface gi0/9 Switch1(config-if)#channel-group 10 mode desirable
In questo modo, ciascun dispositivo formerà un canale solo se concordato da entrambi. Se la negoziazione per formare il canale non ha esito positivo, le porte continueranno comunque a funzionare come porte normali.
Dopo aver impostato la modalità canale su entrambi i lati della connessione, usare i comandi shutdown e no shutdown sull'interfaccia associata per riattivare manualmente le porte:
Switch1(config-if)#shutdown Switch1(config-if)#no shutdown
Il comando "speed nonegotiate" non viene visualizzato nella configurazione in esecuzione
Il comando speed nonegotiate configurato su un canale porta non sempre viene visualizzato nella configurazione in esecuzione. Questo si verifica perché la non negoziazione sull'interfaccia del canale della porta dipende da quella delle porte incluse. Viene inserito quando il canale della porta è attivo e in base alla configurazione delle singole porte del canale.
Informazioni correlate
- Requisiti di sistema per implementare EtherChannel sugli switch Catalyst
- Configurazione di esempio: EtherChannel tra gli switch Catalyst con software di sistema CatOS e Cisco IOS
- Switch - Supporto dei prodotti
- Supporto della tecnologia di switching LAN
- Documentazione e supporto tecnico – Cisco Systems
 Feedback
Feedback