Acquisire dati per il traffico USA-T con il router serie 8000
Opzioni per il download
Linguaggio senza pregiudizi
La documentazione per questo prodotto è stata redatta cercando di utilizzare un linguaggio senza pregiudizi. Ai fini di questa documentazione, per linguaggio senza di pregiudizi si intende un linguaggio che non implica discriminazioni basate su età, disabilità, genere, identità razziale, identità etnica, orientamento sessuale, status socioeconomico e intersezionalità. Le eventuali eccezioni possono dipendere dal linguaggio codificato nelle interfacce utente del software del prodotto, dal linguaggio utilizzato nella documentazione RFP o dal linguaggio utilizzato in prodotti di terze parti a cui si fa riferimento. Scopri di più sul modo in cui Cisco utilizza il linguaggio inclusivo.
Informazioni su questa traduzione
Cisco ha tradotto questo documento utilizzando una combinazione di tecnologie automatiche e umane per offrire ai nostri utenti in tutto il mondo contenuti di supporto nella propria lingua. Si noti che anche la migliore traduzione automatica non sarà mai accurata come quella fornita da un traduttore professionista. Cisco Systems, Inc. non si assume alcuna responsabilità per l’accuratezza di queste traduzioni e consiglia di consultare sempre il documento originale in inglese (disponibile al link fornito).
Introduzione
In questo documento viene descritto come acquisire il traffico per utenti non autorizzati nel router Cisco serie 8000.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Familiarità con i router Cisco serie 8000 e il software Cisco IOS® XR.
Componenti usati
Le informazioni di questo documento si basano sui router Cisco serie 8000 e non sono limitate a una versione software e hardware specifica.
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Premesse
Durante le attività di risoluzione dei problemi, in alcuni casi è necessario verificare il traffico che viene trasferito all'unità di elaborazione centrale (CPU ) per l'ulteriore elaborazione o gestione.
In questo documento viene spiegato come acquisire il traffico sui router Cisco serie 8000.
Procedura
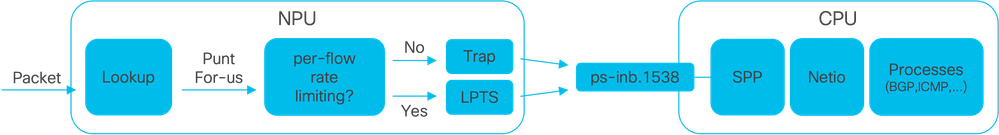
Immagine1 - Router Cisco serie 8000: diagramma NPU e CPU semplificato.
Quando si riceve un pacchetto Nel router Cisco 8000, l'unità di elaborazione di rete (NPU) esegue una ricerca che determina una decisione di inoltro.
In alcuni casi, è possibile che la decisione sia quella di puntare il pacchetto, ossia di passare il pacchetto alla CPU per un'ulteriore elaborazione o gestione.
La ricerca NPU determina anche se è necessaria la limitazione della velocità per flusso quando si passa il pacchetto alla CPU.
- Se è richiesta la limitazione per la velocità del flusso, il pacchetto viene inviato alla CPU tramite il servizio Local Packet Transport Service (LPTS), ad esempio un pacchetto del protocollo di routing.
- Se non è richiesta una limitazione per la velocità del flusso, viene generata una trap e il pacchetto viene trasferito alla CPU, ad esempio un pacchetto con TTL (Time-to-Live) scaduto.
I pacchetti, se non hanno limitazioni di velocità, vengono trasferiti alla CPU tramite una VLAN interna dedicata con ID 1538.
È possibile verificare sia le voci della tabella LPTS che quelle della tabella Traps utilizzando il comando show lpts pifib hardware entry brief e il comando show controllers npu status traps-all.
Il comando show lpts pifib hardware entry brief visualizza le voci della tabella LPTS.
In questo caso, l'output è limitato alle voci associate al Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8202#show lpts pifib hardware entry brief location 0/rp0/cpu0 | include "Type|BGP"
Type DestIP SrcIP Interface vrf L4 LPort/Type RPort npu Flowtype DestNode PuntPrio Accept Drop
IPv4 10.4.11.2 10.4.11.3 any 0 6 Port:20656 179 0 BGP-known Dlvr RP0 CRITICAL 32339 0
IPv4 10.4.11.2 10.4.11.3 any 0 6 Port:179 0 0 BGP-cfg-peer Dlvr RP0 MEDIUM 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 6 Port:any 179 0 BGP-default Dlvr RP0 LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 6 Port:179 0 0 BGP-default Dlvr RP0 LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 6 Port:any 179 0 BGP-default Dlvr RP0 LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 6 Port:179 0 0 BGP-default Dlvr RP0 LOW 0 0
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8202#
Il comando show controller npu status traps-all elenca tutte le voci di trap e i contatori associati.
In questo caso, l'output è limitato alle voci con corrispondenze di pacchetti, escludendo tutte le voci che mostrano zero nelle colonne Pacchetti accettati e Pacchetti scartati.
Tutte le trap sono limitate in termini di velocità.
show controllers npu stats traps-all instance 0 location 0/rp0/cpu0 | exclude "0 0"
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8202#show controllers npu stats traps-all instance 0 location 0/rp0/cpu0 | exclude "0 0"
Traps marked (D*) are punted (post policing) to the local CPU internal VLAN 1586 for debugging
They can be read using "show captured packets traps" CLI
Traps marked (D) are dropped in the NPU
Traps punted to internal VLAN 1538 are processed by the process "spp" on the "Punt Dest" CPU
They can also be read using "show captured packets traps" CLI
"Configured Rate" is the rate configured by user (or default setting) in pps at the LC level
"Hardware Rate" is the actual rate in effect after hardware adjustments
Policer Level:
NPU: Trap meter is setup per NPU in packets per second
IFG: Trap meter is setup at every IFG in bits per second
The per IFG meter is converted from the user configured/default rate (pps)
based on the "Avg-Pkt Size" into bps.
Due to hardware adjustments, the "Configured Rate" and
"Hardware Rate" differ in values.
NOTE:The displayed stats are NOT real-time and are updated every 30 SECONDS from the hardware.
Trap Type NPU Trap Punt Punt Punt Punt Configured Hardware Policer Avg-Pkt Packets Packets
ID ID Dest VoQ VLAN TC Rate(pps) Rate(pps) Level Size Accepted Dropped
====================================================================================================================================================================
ARP 0 3 RPLC_CPU 271 1538 7 542 533 IFG 1520 136 0
NOT_MY_MAC(D*) 0 4 RPLC_CPU 264 1586 0 67 150 IFG 64 0 1691165
DHCPV4_SERVER 0 8 RPLC_CPU 265 1538 1 542 523 NPU N/A 63898 0
LLDP 0 26 RPLC_CPU 270 1538 6 4000 3862 IFG 1520 132247 0
ONLINE_DIAG 0 31 RPLC_CPU 271 1538 7 4000 3922 IFG 64 50977 0
V4_MCAST_DISABLED(D*) 0 69 RPLC_CPU 269 1586 5 67 150 IFG 64 0 37613
V6_MCAST_DISABLED(D*) 0 80 RPLC_CPU 264 1586 0 67 150 IFG 64 0 118051
L3_IP_MULTICAST_NOT_FOUND(D*) 0 125 RPLC_CPU 264 1586 0 67 150 IFG 64 0 3
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8202#
L'utility di shell spp_platform_cap può essere utilizzata per acquisire pacchetti che attraversano questa VLAN interna dedicata tra la NPU e la CPU. La stessa utility consente anche di acquisire il traffico inviato o ricevuto tramite l'interfaccia di gestione del router.
L'utilità spp_platform_pcap shell viene eseguita dall'interno della shell e offre diverse opzioni di utilizzo. Per accedere o accedere alla shell, eseguire il comando run. Per disconnettersi dalla shell, digitare exit.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8202#run
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$spp_platform_pcap -h
Usage: spp_platform_pcap options
Use Ctrl-C to stop anytime
-h --help Display this usage information.
-D --Drop capture Drops in SPP.
-i --interface Interface-name
Available from the output of
"show ipv4 interface brief"
-Q --direction direction of the packet
Options: IN | OUT |
Mandatory option
(when not using the -d option)
-s --source Originator of the packet.
Options: ANY | CPU | NPU | NSR | MGMT | PTP | LC_PKTIO | LC_REDIR
-d --destination destination of the packet
Options: ANY | CPU | NPU | MGMT | PTP | LC_PKTIO | LC_REDIR |
-l --l4protocol IANA-L4-protocol-number
(use with Address family (-a)
Interface (-i) and direction (-Q)
Options: min:0 Max:255
-a --addressFamily address Family used with l4protocol (-l)
Interface (-i) and direction (-Q)
Options: ipv4 | ipv6 |
-x --srcIp Src-IP (v4 or v6)
Used with -a, -i and -Q only
-X --dstIp Dst-IP (v4 or v6)
Used with -a, -i and -Q only
-y --srcPort Src-Port
Used with -a, -l, -i and -Q only
Options: min:0 Max:65535
-Y --dstPort Dst-Port
Used with -a, -l, -i and -Q only
Options: min:0 Max:65535
-P --l2Packet Based on L2 packet name/etype
Interface (-i) and direction (-Q) needed
Use for non-L3 packets
Options:ether-type (in hex format)
ARP | ISIS | LACP | SYNCE | PTP | LLDP | CDP |
-w --wait Wait time(in seconds)
Use Ctrl-C to abort
-c --count Count of packets to collect
min:1; Max:1024
-t --trapNameOrId Trap-name(in quotes) or number(in decimal)
(direction "in" is a MUST).
Refer to "show controllers npu stats traps-all instance all location <LC|RP>
Note: Trap names with (D*) in the display are not punted to SPP.
They are punted to ps-inb.1586
-S --puntSource Punt-sources
Options: LPTS_FORWARDING | INGRESS_TRAP | EGRESS_TRAP | INBOUND_MIRROR |
NPUH |
-p --pcap capture packets in pcap file.
-v --verbose Print the filter offsets.
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$
Notare l'opzione -Q della direzione di acquisizione, dove il valore IN indica che vengono acquisiti i pacchetti puntiformi (i pacchetti ricevuti dalla CPU). Il valore OUT indica che acquisisce i pacchetti iniettati (i pacchetti inviati dalla CPU). L'opzione -p consente di acquisire i pacchetti in un file pcap.
Considerare che, per impostazione predefinita, la cattura spp_platform_pcap:
- Viene eseguito per 60 secondi.
- Acquisisce un massimo di 100 pacchetti.
- Tronca tutti i pacchetti acquisiti a 214 byte.
Ad esempio, per avviare un'acquisizione non filtrata di tutto il traffico ricevuto dalla CPU, digitare il comando spp_platform_pcap -Q IN -p:
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$spp_platform_pcap -Q IN -p
All trace-enabled SPP nodes will be traced.
Node "socket/rx" set for trace filtering. Index: 1
Wait time is 60 seconds. Use Ctrl-C to stop
Collecting upto 100 packets (within 60 seconds)
^CSignal handling initiated <<<<<<<< Here: 'Ctrl-C' was used to stop the capture.
Tracing stopped with 10 outstanding...
Wrote 90 traces to /tmp/spp_bin_pcap
All trace-enabled SPP nodes will be traced.
pcap: Captured pcap file for packets saved at "/tmp/spp_pcap_capture_0_RP0_CPU0.pcap"
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$
Al termine della cattura, il file risultante viene reso disponibile sul disco locale.
Copiare il file dal router al computer locale e verificarne il contenuto utilizzando l'applicazione di decodifica dei pacchetti preferita.
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ls -la /tmp
total 44
<snip>
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8516 Aug 7 06:58 spp_pcap_capture_0_RP0_CPU0.pcap
<snip>
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$cp /tmp/spp_pcap_capture_0_RP0_CPU0.pcap /harddisk:/
[node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$exit
logout
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8202#dir harddisk: | include spp_pcap
16 -rw-r--r--. 1 8516 Aug 8 07:01 spp_pcap_capture_0_RP0_CPU0.pcap
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8202#
È possibile essere più specifici per quanto riguarda l'intento della cattura. Ad esempio, è possibile utilizzare le funzionalità dei filtri delle utility per acquisire il traffico per l'uso relativo a un'interfaccia router specifica, a un indirizzo IP o a un determinato protocollo.
Ad esempio, utilizzando questo comando, è possibile acquisire il traffico BGP da un peer specifico su un'interfaccia specifica:
spp_platform_pcap -Q IN -a ipv4 -l 6 -i HundredGigE0/0/0/1 -x 10.100.0.1 -Y 179 -p
È inoltre possibile utilizzare spp_platform_cap per acquisire il traffico inviato o ricevuto tramite l'interfaccia di gestione del router.
Ad esempio, utilizzando questo comando, è possibile acquisire il traffico ricevuto dall'interfaccia di gestione.
spp_platform_pcap -Q IN -p -i MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0
Tutti gli esempi precedenti sono stati eseguiti su un router Cisco serie 8000 standalone. Se si utilizza un router Cisco serie 8000 distribuito, considerare in quale nodo, processore di routing o scheda di linea si desidera eseguire l'acquisizione.
È possibile che il traffico a cui si è interessati venga gestito da una determinata CPU della scheda di linea. Sia il show controller npu status traps-all che il show lpts pifib hardware entry brief possono aiutare a identificare la destinazione del punt.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8808#show controllers npu stats traps-all instance 0 location 0/0/cpu0 | include "Type|Accepted|==|ARP|ISIS L3"
Trap Type NPU Trap Punt Punt Punt Punt Configured Hardware Policer Avg-Pkt Packets Packets
ID ID Dest VoQ VLAN TC Rate(pps) Rate(pps) Level Size Accepted Dropped
====================================================================================================================================================================
ARP 0 10 LC_CPU 239 1538 7 542 531 NPU N/A 15 0
ISIS/L3 0 129 BOTH_RP-CPU 239 1538 7 10000 9812 IFG 1520 0 0
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8808#
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8808#show lpts pifib hardware entry brief location 0/0/cpu0 | include "Type|--|Fragment|OSPF"
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Type DestIP SrcIP Interface vrf L4 LPort/Type RPort npu Flowtype DestNode PuntPrio Accept Drop
---- -------------------- -------------------- -------------- ----- --- ------------ ------ ---- ------------------ -------- ------------ ------ ------
IPv4 any any any 0 0 any 0 0 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 0 any 0 0 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 0 any 0 1 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 0 any 0 1 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 0 any 0 2 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 0 any 0 2 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 0 OSPF-mc-known Dlvr BothRP HIGH 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 0 OSPF-mc-default Dlvr BothRP LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 1 OSPF-mc-default Dlvr BothRP LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 2 OSPF-mc-default Dlvr BothRP LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 0 OSPF-uc-known Dlvr BothRP MEDIUM 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 0 OSPF-uc-default Dlvr RP1 LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 1 OSPF-uc-default Dlvr RP1 LOW 0 0
IPv4 any any any 0 89 any 0 2 OSPF-uc-default Dlvr RP1 LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 0 any 0 0 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 0 any 0 1 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 0 any 0 2 Fragment Local LC LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 89 any 0 0 OSPF-mc-default Dlvr BothRP LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 89 any 0 1 OSPF-mc-default Dlvr BothRP LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 89 any 0 2 OSPF-mc-default Dlvr BothRP LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 89 any 0 0 OSPF-uc-default Dlvr RP1 LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 89 any 0 1 OSPF-uc-default Dlvr RP1 LOW 0 0
IPv6 any any any 0 89 any 0 2 OSPF-uc-default Dlvr RP1 LOW 0 0
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8808#
Una volta identificata, collegarsi alla scheda di linea specifica ed eseguire l'utilità spp_platform_pcap come mostrato in precedenza.
attach location 0/0/cpu0
spp_platform_pcap -Q IN -p
! --- execute 'Ctrl-C' to stop the capture
Informazioni correlate
Video su Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC)
Cisco serie 8000 - Acquisire dati per il traffico in transito, video
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
12-Aug-2024 |
Versione iniziale |
Contributo dei tecnici Cisco
- Ricardo LourencoResponsabile tecnico del Customer Delivery Engineering
 Feedback
Feedback