Configurazione di IPSec dinamico-statico da router a router con NAT
Sommario
Introduzione
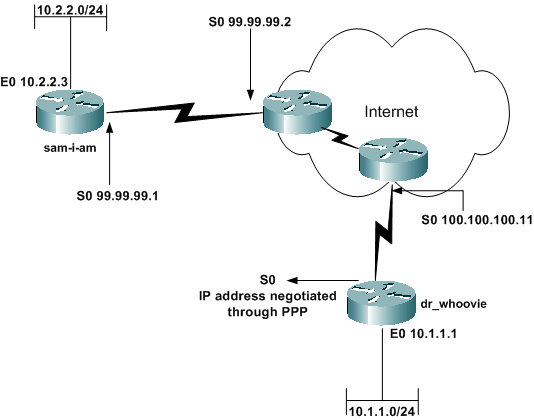
In questa configurazione di esempio, un router remoto riceve un indirizzo IP tramite una parte del protocollo PPP denominata IP Control Protocol (IPCP). Il router remoto utilizza l'indirizzo IP per connettersi a un router hub. Questa configurazione consente al router hub di accettare connessioni IPSec dinamiche. Il router remoto utilizza NAT (Network Address Translation) per "collegare" i dispositivi con indirizzo privato alla rete con indirizzo privato dietro il router hub. Il router remoto conosce l'endpoint e può avviare connessioni al router hub. Il router hub, tuttavia, non conosce l'endpoint e pertanto non può avviare connessioni con il router remoto.
In questo esempio, dr_whoovie è il router remoto e sam-i-am è il router hub. Un elenco degli accessi specifica il traffico da crittografare, in modo che dr_whoovie sappia quale traffico crittografare e dove si trova l'endpoint sam-i-am. Il router remoto deve avviare la connessione. Entrambe le parti stanno facendo un sovraccarico NAT.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Questo documento richiede una conoscenza di base del protocollo IPSec. Per ulteriori informazioni su IPSec, vedere Introduzione alla crittografia IPSec (IP Security).
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
-
Software Cisco IOS® versione 12.2(24a)
-
Cisco serie 2500 Router
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Convenzioni
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni usate, consultare il documento Cisco sulle convenzioni nei suggerimenti tecnici.
Configurazione
In questa sezione vengono presentate le informazioni necessarie per configurare le funzionalità descritte più avanti nel documento.
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi menzionati in questo documento, usare lo strumento di ricerca dei comandi (solo utenti registrati).
Esempio di rete
Il documento usa la seguente configurazione di rete:
Configurazioni
In questo documento vengono usate le seguenti configurazioni:
| sam-i-am |
|---|
Current configuration: ! version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log up time no service password-encryption ! hostname sam-i-am ! ip subnet-zero ! !--- These are the IKE policies. crypto isakmp policy 1 !--- Defines an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) policy. !--- Use the crypto isakmp policy command !--- in global configuration mode. !--- IKE policies define a set of parameters to be used !--- during the IKE phase I negotiation. hash md5 authentication pre-share !--- Specifies pre-shared keys as the authentication method. crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 !--- Configures a pre-shared authentication key, !--- used in global configuration mode. ! !--- These are the IPSec policies. crypto ipsec transform-set rtpset esp-des esp-md5-hmac !--- A transform set is an acceptable combination !--- of security protocols and algorithms. !--- This command defines a transform set !--- that has to be matched on the peer router. crypto dynamic-map rtpmap 10 !--- Use dynamic crypto maps to create policy templates !--- that can be used to process negotiation requests !--- for new security associations (SA) from a remote IPSec peer, !--- even if you do not know all of the crypto map parameters !--- required to communicate with the remote peer, !--- such as the IP address of the peer. set transform-set rtpset !--- Configure IPSec to use the transform set "rtpset" !--- that was defined previously. match address 115 !--- Assign an extended access list to a crypto map entry !--- that is used by IPSec to determine which traffic !--- should be protected by crypto and which traffic !--- does not need crypto protection. crypto map rtptrans 10 ipsec-isakmp dynamic rtpmap !--- Specifies that this crypto map entry is to reference !--- a preexisting dynamic crypto map. ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.2.2.3 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip nat inside !--- This indicates that the interface is connected to the !--- inside network, which is subject to NAT translation. no mop enabled ! interface Serial0 ip address 99.99.99.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip nat outside !--- This indicates that the interface is connected !--- to the outside network. crypto map rtptrans !--- Use the crypto map interface configuration command !--- to apply a previously defined crypto map set to an interface. ! ip nat inside source route-map nonat interface Serial0 overload !--- Except the private network from the NAT process. ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0 no ip http server ! access-list 115 permit ip 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 115 deny ip 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 any !--- Include the private-network-to-private-network traffic !--- in the encryption process. access-list 120 deny ip 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 120 permit ip 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 any !--- Except the private network from the NAT process. route-map nonat permit 10 match ip address 120 ! line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password ww login ! end |
| dr_whoovie |
|---|
Current configuration: ! version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname dr_whoovie ! ip subnet-zero ! !--- These are the IKE policies. crypto isakmp policy 1 !--- Defines an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) policy. !--- Use the crypto isakmp policy command !--- in global configuration mode. !--- IKE policies define a set of parameters to be used !--- during the IKE phase I negotiation. hash md5 authentication pre-share !--- Specifies pre-shared keys as the authentication method. crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 99.99.99.1 !--- Configures a pre-shared authentication key, !--- used in global configuration mode. ! !--- These are the IPSec policies. crypto ipsec transform-set rtpset esp-des esp-md5-hmac !--- A transform set is an acceptable combination !--- of security protocols and algorithms. !--- This command defines a transform set !--- that has to be matched on the peer router. ! crypto map rtp 1 ipsec-isakmp !--- Creates a crypto map and indicates that IKE will be used !--- to establish the IPSec SAs for protecting !--- the traffic specified by this crypto map entry. set peer 99.99.99.1 !--- Use the set peer command to specify an IPSec peer in a crypto map entry. set transform-set rtpset !--- Configure IPSec to use the transform set "rtpset" !--- that was defined previously. match address 115 !--- Include the private-network-to-private-network traffic !--- in the encryption process. ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip nat inside !--- This indicates that the interface is connected to the !--- inside network, which is subject to NAT translation. no mop enabled ! interface Serial0 ip address negotiated !--- Specifies that the IP address for this interface !--- is obtained via PPP/IPCP address negotiation. !--- This example was set up in a lab with an IP address !--- assigned with IPCP. no ip directed-broadcast ip nat outside !--- This indicates that the interface is connected !--- to the outside network. encapsulation ppp no ip mroute-cache no ip route-cache crypto map rtp !--- Use the crypto map interface configuration command !--- to apply a previously defined crypto map set to an interface. ip nat inside source route-map nonat interface Serial0 overload !--- Except the private network from the NAT process. ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0 no ip http server ! access-list 115 permit ip 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 115 deny ip 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 any !--- Include the private-network-to-private-network traffic !--- in the encryption process. access-list 120 deny ip 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 120 permit ip 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 any !--- Except the private network from the NAT process. dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit dialer-list 1 protocol ipx permit route-map nonat permit 10 match ip address 120 ! line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password ww login ! end |
Verifica
Le informazioni contenute in questa sezione permettono di verificare che la configurazione funzioni correttamente.
Alcuni comandi show sono supportati dallo strumento Output Interpreter (solo utenti registrati); lo strumento permette di visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show.
-
ping: utilizzato per diagnosticare la connettività di rete di base
Nell'esempio viene mostrato un ping tra l'interfaccia Ethernet 10.1.1.1 su dr_whoovie e l'interfaccia Ethernet 10.2.2.3 su sam-i-am.
dr_whoovie# ping Protocol [ip]: Target IP address: 10.2.2.3 Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 10.1.1.1 Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.2.2.3, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.1.1.1 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/38/40 ms
-
show crypto ipsec sa: visualizza le associazioni di sicurezza (SA) della fase 2.
-
show crypto isakmp sa: visualizza le associazioni di protezione della fase 1.
Output di esempio
Questo output viene generato dal comando show crypto ipsec sa emesso sul router hub.
sam-i-am# show crypto ipsec sa
interface: Serial0
Crypto map tag: rtptrans, local addr. 99.99.99.1
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (10.2.2.0/255.255.255.0/0/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (10.1.1.0/255.255.255.0/0/0)
current_peer: 100.100.100.1
PERMIT, flags={}
#pkts encaps: 6, #pkts encrypt: 6, #pkts digest 6
#pkts decaps: 6, #pkts decrypt: 6, #pkts verify 6
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0,
#pkts decompress failed: 0, #send errors 0, #recv errors 0
local crypto endpt.: 99.99.99.1, remote crypto endpt.: 100.100.100.1
path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu interface Serial0
current outbound spi: 52456533
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0x6462305C(1684156508)
transform: esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
slot: 0, conn id: 2000, flow_id: 1, crypto map: rtptrans
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4607999/3510)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
inbound ah sas:
inbound pcp sas:
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0x52456533(1380279603)
transform: esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
slot: 0, conn id: 2001, flow_id: 2, crypto map: rtptrans
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4607999/3510)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
outbound ah sas:
outbound pcp sas:
Con questo comando vengono visualizzate le associazioni di protezione IPSec create tra i dispositivi peer. Il tunnel crittografato connette l'interfaccia 100.100.100.1 su dr_whoovie e l'interfaccia 99.99.99.1 su sam-i-am. Questo tunnel comporta il traffico tra le reti 10.2.2.3 e 10.1.1.1. Due associazioni di sicurezza ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) vengono create in entrata e in uscita. Il tunnel viene stabilito anche se sam-i-am non conosce l'indirizzo IP del peer (100.100.100.1). Le associazioni di protezione (SA) per le intestazioni di autenticazione non vengono utilizzate perché non è configurato alcun account AH.
Gli esempi di output mostrano che l'interfaccia seriale 0 su dr_whoovie riceve un indirizzo IP di 100.100.100.1 tramite IPCP.
-
Prima della negoziazione dell'indirizzo IP:
dr_whoovie#show interface serial0 Serial0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is HD64570 Internet address will be negotiated using IPCP MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1544 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, loopback not set -
Dopo la negoziazione dell'indirizzo IP:
dr_whoovie#show interface serial0 Serial0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is HD64570 Internet address is 100.100.100.1/32 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1544 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, loopback not set
Questo esempio è stato impostato in un'esercitazione con il comando peer default ip address per assegnare un indirizzo IP all'estremità remota dell'interfaccia 0 seriale su dr_whoovie. Il pool IP è definito con il comando ip local pool sull'estremità remota.
Risoluzione dei problemi
In questa sezione vengono fornite informazioni utili per risolvere i problemi di configurazione.
Comandi per la risoluzione dei problemi
Lo strumento Output Interpreter (solo utenti registrati) (OIT) supporta alcuni comandi show. Usare OIT per visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show.
Nota: consultare le informazioni importanti sui comandi di debug prima di usare i comandi di debug.
-
debug crypto ipsec: visualizza le negoziazioni IPSec della fase 2.
-
debug crypto isakmp: visualizza le negoziazioni ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol) della fase 1.
-
debug crypto engine: visualizza il traffico crittografato.
-
debug ip nat detail: (facoltativo) verifica il funzionamento della funzione NAT visualizzando le informazioni su ogni pacchetto convertito dal router.
 Attenzione: questo comando genera una grande quantità di output. Utilizzare questo comando solo quando il traffico sulla rete IP è basso.
Attenzione: questo comando genera una grande quantità di output. Utilizzare questo comando solo quando il traffico sulla rete IP è basso. -
clear crypto isakmp: cancella le SA correlate alla fase 1.
-
clear crypto sa: cancella le SA correlate alla fase 2.
-
clear ip nat translation - Cancella le traduzioni NAT dinamiche dalla tabella di traduzione.
Informazioni correlate
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
11-Dec-2001 |
Versione iniziale |
 Attenzione: questo comando genera una grande quantità di output. Utilizzare questo comando solo quando il traffico sulla rete IP è basso.
Attenzione: questo comando genera una grande quantità di output. Utilizzare questo comando solo quando il traffico sulla rete IP è basso.  Feedback
Feedback