Configurazione di un tunnel VPN site-to-site con ASA e Strongswan
Opzioni per il download
Linguaggio senza pregiudizi
La documentazione per questo prodotto è stata redatta cercando di utilizzare un linguaggio senza pregiudizi. Ai fini di questa documentazione, per linguaggio senza di pregiudizi si intende un linguaggio che non implica discriminazioni basate su età, disabilità, genere, identità razziale, identità etnica, orientamento sessuale, status socioeconomico e intersezionalità. Le eventuali eccezioni possono dipendere dal linguaggio codificato nelle interfacce utente del software del prodotto, dal linguaggio utilizzato nella documentazione RFP o dal linguaggio utilizzato in prodotti di terze parti a cui si fa riferimento. Scopri di più sul modo in cui Cisco utilizza il linguaggio inclusivo.
Informazioni su questa traduzione
Cisco ha tradotto questo documento utilizzando una combinazione di tecnologie automatiche e umane per offrire ai nostri utenti in tutto il mondo contenuti di supporto nella propria lingua. Si noti che anche la migliore traduzione automatica non sarà mai accurata come quella fornita da un traduttore professionista. Cisco Systems, Inc. non si assume alcuna responsabilità per l’accuratezza di queste traduzioni e consiglia di consultare sempre il documento originale in inglese (disponibile al link fornito).
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento viene descritto come configurare il tunnel IPSec Internet Key Exchange versione 1 da sito a sito tramite la CLI tra un'ASA e un server strongSwan.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Cisco raccomanda la conoscenza dei seguenti argomenti:
- Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA)
- Comandi di base di Linux
- Concetti generali su IPSec
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni:
- Cisco ASAv con versione 9.12(3)9
- Ubuntu 20.04 con strongSwan U5.8.2
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Configurazione
Questa sezione descrive come completare le configurazioni di ASA e strongSwan.
Scenario
In questa configurazione, il PC1 nella LAN-A desidera comunicare con il PC2 nella LAN-B. Il traffico deve essere crittografato e inviato tramite un tunnel Internet Key Exchange versione 1 (IKEv1) tra l'ASA e il server strongSwan. Entrambi i peer eseguono l'autenticazione reciproca con una chiave precondivisa (PSK).
Esempio di rete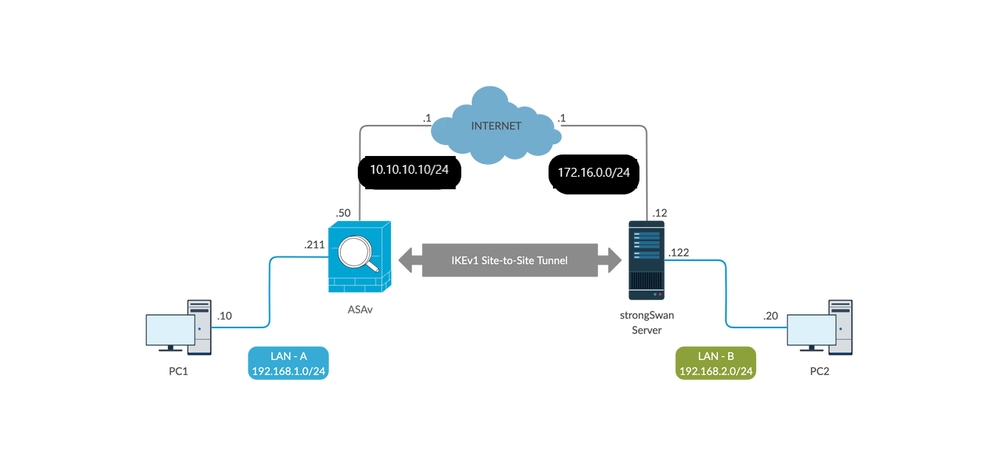
Nota: per stabilire un tunnel VPN da sito a sito, verificare che sia disponibile una connettività sia alle reti interne che a quelle esterne, in particolare al peer remoto. È possibile usare un comando ping per verificare la connettività di base.
Configurazione ASA
!Configure the ASA interfaces
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.1.211 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.0
!
!Configure the ACL for the VPN traffic of interest
!
object-group network local-network
network-object 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
!
object-group network remote-network
network-object 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
!
access-list asa-strongswan-vpn extended permit ip object-group local-network object-group remote-network
!
!Enable IKEv1 on the 'Outside' interface
!
crypto ikev1 enable outside
!
!Configure how ASA identifies itself to the peer
!
crypto isakmp identity address
!
!Configure the IKEv1 policy
!
crypto ikev1 policy 10
authentication pre-share
encryption aes-256
hash sha
group 5
lifetime 3600
!
!Configure the IKEv1 transform-set
!
crypto ipsec ikev1 transform-set tset esp-aes-256 esp-sha-hmac
!
!Configure a crypto map and apply it to outside interface
!
crypto map outside_map 10 match address asa-strongswan-vpn
crypto map outside_map 10 set peer 172.16.0.0
crypto map outside_map 10 set ikev1 transform-set tset
crypto map outside_map 10 set security-association lifetime seconds 28800
crypto map outside_map interface outside
!
!Configure the Tunnel group (LAN-to-LAN connection profile)
!
tunnel-group 172.16.0.0 type ipsec-l2l
tunnel-group 172.16.0.0 ipsec-attributes
ikev1 pre-shared-key cisco
!
Nota: Esiste una corrispondenza dei criteri IKEv1 quando entrambi i criteri dei due peer contengono gli stessi valori di autenticazione, crittografia, hash e parametro Diffie-Hellman. Per IKEv1, il criterio peer remoto deve inoltre specificare una durata minore o uguale alla durata del criterio inviato dall'iniziatore. Se le durate non sono identiche, l'appliance ASA usa una durata più breve. Inoltre, se non si specifica un valore per un determinato parametro di criterio, viene applicato il valore predefinito.
Nota: un ACL per il traffico VPN usa gli indirizzi IP di origine e di destinazione dopo il protocollo NAT (Network Address Translation).
Esenzione NAT (facoltativa):
In genere, non deve essere eseguito alcun NAT sul traffico VPN. Per escludere il traffico, è necessario creare una regola NAT di identità. La regola NAT di identità traduce semplicemente un indirizzo nello stesso indirizzo.
nat (inside,outside) source static local-network local-network destination static remote-network remote-network no-proxy-arp route-lookup
Configurazione strongSwan
Su Ubuntu, modificare questi due file con i parametri di configurazione da utilizzare nel tunnel IPsec. È possibile utilizzare l'editor preferito per modificarli.
/etc/ipsec.conf
/etc/ipsec.secrets
# /etc/ipsec.conf - strongSwan IPsec configuration file
# basic configuration
config setup
strictcrlpolicy=no
uniqueids = yes
charondebug = "all"
# VPN to ASA
conn vpn-to-asa
authby=secret
left=%defaultroute
leftid=172.16.0.0
leftsubnet=192.168.2.0/24
right=10.10.10.10
rightid=10.10.10.10
rightsubnet=192.168.1.0/24
ike=aes256-sha1-modp1536
esp=aes256-sha1
keyingtries=%forever
leftauth=psk
rightauth=psk
keyexchange=ikev1
ikelifetime=1h
lifetime=8h
dpddelay=30
dpdtimeout=120
dpdaction=restart
auto=start
# config setup - Defines general configuration parameters.
# strictcrlpolicy - Defines if a fresh CRL must be available in order for the peer authentication based on RSA
signatures to succeed.
# uniqueids - Defines whether a particular participant ID must be kept unique, with any new IKE_SA using an ID
deemed to replace all old ones using that ID.
# charondebug - Defines how much charon debugging output must be logged.
# conn- Defines a connection.
# authby - Defines how the peers must authenticate; acceptable values are secret or psk, pubkey, rsasig, ecdsasig.
# left - Defines the IP address of the strongSwan's interface paricipating in the tunnel.
# lefid - Defines the identity payload for the strongSwan.
# leftsubnet - Defines the private subnet behind the strongSwan, expressed as network/netmask.
# right - Defines the public IP address of the VPN peer.
# rightid - Defines the identity payload for the VPN peer.
# rightsubnet - Defines the private subnet behind the VPN peer, expressed as network/netmask.
# ike - Defines the IKE/ISAKMP SA encryption/authentication algorithms. You can add a comma-separated list.
# esp - Defines the ESP encryption/authentication algorithms. You can add a comma-separated list.
# keyingtries - Defines the number of attempts that must be made to negotiate a connection.
# keyexchange - Defines the method of key exchange, whether IKEv1 or IKEv2.
# ikelifetime - Defines the duration of an established phase-1 connection.
# lifetime - Defines the duration of an established phase-2 connection.
# dpddelay - Defines the time interval with which R_U_THERE messages/INFORMATIONAL exchanges are sent to the peer.
These are only sent if no other traffic is received.
# dpdtimeout - Defines the timeout interval, after which all connections to a peer are deleted in case of inactivity.
# dpdaction - Defines what action needs to be performed on DPD timeout. Takes three values as paramters : clear, hold, and restart.
With clear the connection is closed with no further actions taken, hold installs a trap policy, which catches
matching traffic and tries to re-negotiate the connection on demand and restart immediately triggers an attempt
to re-negotiate the connection. The default is none which disables the active sending of DPD messages.
# auto - Defines what operation, if any, must be done automatically at IPsec startup (start loads a connection and brings
it up immediately).
/etc/ipsec.secrets - This file holds shared secrets or RSA private keys for authentication.
# RSA private key for this host, authenticating it to any other host which knows the public part.
172.16.0.0 10.10.10.10 : PSK "cisco"
Comandi utili (strongSwan)
Avvio/Arresto/Stato:
$ sudo ipsec up <nome-connessione>
$ sudo ipsec up vpn-to-asa
generating QUICK_MODE request 656867907 [ HASH SA No ID ID ]
sending packet: from 172.16.0.0[500] to 10.10.10.10[500] (204 bytes)
received packet: from 10.10.10.10[500] to 172.16.0.0[500] (188 bytes)
parsed QUICK_MODE response 656867907 [ HASH SA No ID ID N((24576)) ]
selected proposal: ESP:AES_CBC_256/HMAC_SHA1_96/NO_EXT_SEQ
detected rekeying of CHILD_SA vpn-to-asa{2}
CHILD_SA vpn-to-asa{3} established with SPIs c9080c93_i 3f570a23_o and TS 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24
connection 'vpn-to-asa' established successfully
$ sudo ipsec down <nome-connessione>
$ sudo ipsec down vpn-to-asa
generating QUICK_MODE request 656867907 [ HASH SA No ID ID ]
sending packet: from 172.16.0.0[500] to 10.10.10.10[500] (204 bytes)
received packet: from 10.10.10.10[500] to 172.16.0.0[500] (188 bytes)
parsed QUICK_MODE response 656867907 [ HASH SA No ID ID N((24576)) ]
selected proposal: ESP:AES_CBC_256/HMAC_SHA1_96/NO_EXT_SEQ
detected rekeying of CHILD_SA vpn-to-asa{2}
CHILD_SA vpn-to-asa{3} established with SPIs c9080c93_i 3f570a23_o and TS 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24
connection 'vpn-to-asa' established successfully
anurag@strongswan214:~$ sudo ipsec down vpn-to-asa
closing CHILD_SA vpn-to-asa{3} with SPIs c9080c93_i (0 bytes) 3f570a23_o (0 bytes) and TS 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24
sending DELETE for ESP CHILD_SA with SPI c9080c93
generating INFORMATIONAL_V1 request 3465984663 [ HASH D ]
sending packet: from 172.16.0.0[500] to 10.10.10.10[500] (76 bytes)
deleting IKE_SA vpn-to-asa[2] between 172.16.0.0[172.16.0.0]...10.10.10.10[10.10.10.10]
sending DELETE for IKE_SA vpn-to-asa[2]
generating INFORMATIONAL_V1 request 2614622058 [ HASH D ]
sending packet: from 172.16.0.0[500] to 10.10.10.10[500] (92 bytes)
IKE_SA [2] closed successfully
$ sudo ipsec restart
Stopping strongSwan IPsec...
Starting strongSwan 5.8.2 IPsec [starter]...
$ sudo ipsec status
Security Associations (1 up, 0 connecting):
vpn-to-asa[1]: ESTABLISHED 35 seconds ago, 172.16.0.0[172.16.0.0]...10.10.10.10[10.10.10.10]
vpn-to-asa{1}: REKEYED, TUNNEL, reqid 1, expires in 7 hours
vpn-to-asa{1}: 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24
vpn-to-asa{2}: INSTALLED, TUNNEL, reqid 1, ESP SPIs: c0d93265_i 599b4d60_o
vpn-to-asa{2}: 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24
$ sudo ipsec statusall
Status of IKE charon daemon (strongSwan 5.8.2, Linux 5.4.0-37-generic, x86_64):
uptime: 2 minutes, since Jun 27 07:15:14 2020
malloc: sbrk 2703360, mmap 0, used 694432, free 2008928
worker threads: 11 of 16 idle, 5/0/0/0 working, job queue: 0/0/0/0, scheduled: 3
loaded plugins: charon aesni aes rc2 sha2 sha1 md5 mgf1 random nonce x509 revocation constraints pubkey pkcs1 pkcs7 pkcs8 pkcs12 pgp dnskey sshkey pem openssl fips-prf gmp agent xcbc hmac gcm drbg attr kernel-netlink resolve socket-default connmark stroke updown eap-mschapv2 xauth-generic counters
Listening IP addresses:
172.16.0.0
192.168.2.122
Connections:
vpn-to-asa: %any...10.10.10.10 IKEv1, dpddelay=30s
vpn-to-asa: local: [172.16.0.0] uses pre-shared key authentication
vpn-to-asa: remote: [10.10.10.10] uses pre-shared key authentication
vpn-to-asa: child: 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24 TUNNEL, dpdaction=restart
Security Associations (1 up, 0 connecting):
vpn-to-asa[1]: ESTABLISHED 2 minutes ago, 172.16.0.0[172.16.0.0]...10.10.10.10[10.10.10.10]
vpn-to-asa[1]: IKEv1 SPIs: 57e24d839bf05f95_i* 6a4824492f289747_r, pre-shared key reauthentication in 40 minutes
vpn-to-asa[1]: IKE proposal: AES_CBC_256/HMAC_SHA1_96/PRF_HMAC_SHA1/MODP_1536
vpn-to-asa{2}: INSTALLED, TUNNEL, reqid 1, ESP SPIs: c0d93265_i 599b4d60_o
vpn-to-asa{2}: AES_CBC_256/HMAC_SHA1_96, 0 bytes_i, 0 bytes_o, rekeying in 7 hours
vpn-to-asa{2}: 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24
Ottenere i criteri e gli stati del tunnel IPsec:
$ sudo ip xfrm stato
src 172.16.0.0 dst 10.10.10.10
proto esp spi 0x599b4d60 reqid 1 mode tunnel
replay-window 0 flag af-unspec
auth-trunc hmac(sha1) 0x52c84359280868491a37e966384e4c6db05384c8 96
enc cbc(aes) 0x99e00f0989fec6baa7bd4ea1c7fbefdf37f04153e721a060568629e603e23e7a
anti-replay context: seq 0x0, oseq 0x0, bitmap 0x00000000
src 10.10.10.10 dst 172.16.0.0
proto esp spi 0xc0d93265 reqid 1 mode tunnel
replay-window 32 flag af-unspec
auth-trunc hmac(sha1) 0x374d9654436a4c4fe973a54da044d8814184861e 96
enc cbc(aes) 0xf51a4887281551a246a73c3518d938fd4918928088a54e2abc5253bd2de30fd6
anti-replay context: seq 0x0, oseq 0x0, bitmap 0x00000000
criteri $ sudo ip xfrm
src 192.168.2.0/24 dst 192.168.1.0/24
dir out priority 375423
tmpl src 172.16.0.0 dst 10.10.10.10
proto esp spi 0x599b4d60 reqid 1 mode tunnel
src 192.168.1.0/24 dst 192.168.2.0/24
dir fwd priority 375423
tmpl src 10.10.10.10 dst 172.16.0.0
proto esp reqid 1 mode tunnel
src 192.168.1.0/24 dst 192.168.2.0/24
dir in priority 375423
tmpl src 10.10.10.10 dst 172.16.0.0
proto esp reqid 1 mode tunnel
src 0.0.0.0/0 dst 0.0.0.0/0
socket in priority 0
src 0.0.0.0/0 dst 0.0.0.0/0
socket out priority 0
src 0.0.0.0/0 dst 0.0.0.0/0
socket in priority 0
src 0.0.0.0/0 dst 0.0.0.0/0
socket out priority 0
src ::/0 dst ::/0
socket in priority 0
src ::/0 dst ::/0
socket out priority 0
src ::/0 dst ::/0
socket in priority 0
src ::/0 dst ::/0
socket out priority 0
Ricaricare i segreti mentre il servizio è in esecuzione:
$ sudo ipsec readsecrets
Verificare se il traffico attraversa il tunnel:
$ sudo tcpdump esp
09:30:27.788533 IP 172.16.0.0 > 10.10.10.10: ESP(spi=0x599b4d60,seq=0x1e45), length 132
09:30:27.788779 IP 172.16.0.0 > 10.10.10.10: ESP(spi=0x599b4d60,seq=0x1e45), length 132
09:30:27.790348 IP 10.10.10.10 > 172.16.0.0: ESP(spi=0xc0d93265,seq=0x11), length 132
09:30:27.790512 IP 10.10.10.10 > 172.16.0.0: ESP(spi=0xc0d93265,seq=0x11), length 132
09:30:28.788946 IP 172.16.0.0 > 10.10.10.10: ESP(spi=0x599b4d60,seq=0x1e46), length 132
09:30:28.789201 IP 172.16.0.0 > 10.10.10.10: ESP(spi=0x599b4d60,seq=0x1e46), length 132
09:30:28.790116 IP 10.10.10.10 > 172.16.0.0: ESP(spi=0xc0d93265,seq=0x12), length 132
09:30:28.790328 IP 10.10.10.10 > 172.16.0.0: ESP(spi=0xc0d93265,seq=0x12), length 132
Verifica
Prima di verificare se il tunnel è attivo e se supera il traffico, accertarsi che il traffico di interesse sia inviato verso l'ASA o il server strongSwan.
Nota: sull'appliance ASA, è possibile usare lo strumento packet-tracer che corrisponde al traffico di interesse per avviare il tunnel IPSec (ad esempio, l'input packet-tracer all'interno di tcp 192.168.1.100 12345 192.168.2.200.80, dettagliato nell'esempio).
Sull'appliance ASA
Verifica fase 1
Per verificare se la fase 1 del protocollo IKEv1 è attiva sull'appliance ASA, immettere il comando show crypto ikev1 sa (o show crypto isakmp sa). L'output previsto è il seguente:
ASAv# show crypto ikev1 sa
IKEv1 SAs:
Active SA: 1
Rekey SA: 0 (A tunnel will report 1 Active and 1 Rekey SA during rekey)
Total IKE SA: 1
1 IKE Peer: 172.16.0.0
Type : L2L Role : responder
Rekey : no State : MM_ACTIVE
Verifica fase 2
Per verificare se IKEv1 fase 2 è attivo sull'appliance ASA, immettere il comando show crypto ipsec sa Nell'output previsto verrà visualizzato l'indice dei parametri di sicurezza (SPI, Security Parameter Index) in entrata e in uscita. Se il traffico attraversa il tunnel, è necessario verificare l'incremento dei contatori encaps/decaps.
Nota: per ciascuna voce dell'ACL viene creata una SA in entrata/in uscita distinta, che può generare un output del comando show crypto ipsec sa di lunga durata (a seconda del numero di voci ACE nell'ACL crittografico).
ASAv# show crypto ipsec sa peer 172.16.0.0
interface: outside
Crypto map tag: outside_map, seq num: 10, local addr: 10.10.10.10
access-list asa-strongswan-vpn extended permit ip 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0/0/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (192.168.2.0/255.255.255.0/0/0)
current_peer: 172.16.0.0
#pkts encaps: 37, #pkts encrypt: 37, #pkts digest: 37
#pkts decaps: 37, #pkts decrypt: 37, #pkts verify: 37
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 37, #pkts comp failed: 0, #pkts decomp failed: 0
#pre-frag successes: 0, #pre-frag failures: 0, #fragments created: 0
#PMTUs sent: 0, #PMTUs rcvd: 0, #decapsulated frgs needing reassembly: 0
#TFC rcvd: 0, #TFC sent: 0
#Valid ICMP Errors rcvd: 0, #Invalid ICMP Errors rcvd: 0
#send errors: 0, #recv errors: 0
local crypto endpt.: 10.10.10.10/0, remote crypto endpt.: 172.16.0.0/0
path mtu 1500, ipsec overhead 74(44), media mtu 1500
PMTU time remaining (sec): 0, DF policy: copy-df
ICMP error validation: disabled, TFC packets: disabled
current outbound spi: C8F1BFAB
current inbound spi : 3D64961A
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0x3D64961A (1030002202)
SA State: active
transform: esp-aes-256 esp-sha-hmac no compression
in use settings ={L2L, Tunnel, IKEv1, }
slot: 0, conn_id: 31, crypto-map: outside_map
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (kB/sec): (4373997/27316)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Anti replay bitmap:
0x000001FF 0xFFFFFFFF
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0xC8F1BFAB (3371286443)
SA State: active
transform: esp-aes-256 esp-sha-hmac no compression
in use settings ={L2L, Tunnel, IKEv1, }
slot: 0, conn_id: 31, crypto-map: outside_map
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (kB/sec): (4373997/27316)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Anti replay bitmap:
0x00000000 0x00000001
In alternativa, è possibile usare il comando show vpn-sessiondb per verificare i dettagli delle fasi 1 e 2 insieme.
ASAv# show vpn-sessiondb detail l2l filter ipaddress 172.16.0.0
Session Type: LAN-to-LAN Detailed
Connection :172.16.0.0
Index : 3 IP Addr : 172.16.0.0
Protocol : IKEv1 IPsec
Encryption : IKEv1: (1)AES256 IPsec: (1)AES256
Hashing : IKEv1: (1)SHA1 IPsec: (1)SHA1
Bytes Tx : 536548 Bytes Rx : 536592
Login Time : 12:45:14 IST Sat Jun 27 2020
Duration : 1h:51m:57s
IKEv1 Tunnels: 1
IPsec Tunnels: 1
IKEv1:
Tunnel ID : 3.1
UDP Src Port : 500 UDP Dst Port : 500
IKE Neg Mode : Main Auth Mode : preSharedKeys
Encryption : AES256 Hashing : SHA1
Rekey Int (T): 3600 Seconds Rekey Left(T): 2172 Seconds
D/H Group : 5
Filter Name :
IPsec:
Tunnel ID : 3.2
Local Addr : 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0/0/0
Remote Addr : 192.168.2.0/255.255.255.0/0/0
Encryption : AES256 Hashing : SHA1
Encapsulation: Tunnel
Rekey Int (T): 28800 Seconds Rekey Left(T): 22099 Seconds
Rekey Int (D): 4608000 K-Bytes Rekey Left(D): 4607476 K-Bytes
Idle Time Out: 30 Minutes Idle TO Left : 30 Minutes
Bytes Tx : 536638 Bytes Rx : 536676
Pkts Tx : 6356 Pkts Rx : 6389
Su strongSwan
# sudo ipsec statusall
Status of IKE charon daemon (strongSwan 5.8.2, Linux 5.4.0-37-generic, x86_64):
uptime: 2 minutes, since Jun 27 07:15:14 2020
malloc: sbrk 2703360, mmap 0, used 694432, free 2008928
worker threads: 11 of 16 idle, 5/0/0/0 working, job queue: 0/0/0/0, scheduled: 3
loaded plugins: charon aesni aes rc2 sha2 sha1 md5 mgf1 random nonce x509 revocation constraints pubkey pkcs1 pkcs7 pkcs8 pkcs12 pgp dnskey sshkey pem openssl fips-prf gmp agent xcbc hmac gcm drbg attr kernel-netlink resolve socket-default connmark stroke updown eap-mschapv2 xauth-generic counters
Listening IP addresses:
172.16.0.0
192.168.2.122
Connections:
vpn-to-asa: %any...10.10.10.10 IKEv1, dpddelay=30s
vpn-to-asa: local: [172.16.0.0] uses pre-shared key authentication
vpn-to-asa: remote: [10.10.10.10] uses pre-shared key authentication
vpn-to-asa: child: 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24 TUNNEL, dpdaction=restart
Security Associations (1 up, 0 connecting):
vpn-to-asa[1]: ESTABLISHED 2 minutes ago, 172.16.0.0[172.16.0.0]...10.10.10.10[10.10.10.10]
vpn-to-asa[1]: IKEv1 SPIs: 57e24d839bf05f95_i* 6a4824492f289747_r, pre-shared key reauthentication in 40 minutes
vpn-to-asa[1]: IKE proposal: AES_CBC_256/HMAC_SHA1_96/PRF_HMAC_SHA1/MODP_1536
vpn-to-asa{2}: INSTALLED, TUNNEL, reqid 1, ESP SPIs: c0d93265_i 599b4d60_o
vpn-to-asa{2}: AES_CBC_256/HMAC_SHA1_96, 0 bytes_i, 0 bytes_o, rekeying in 7 hours
vpn-to-asa{2}: 192.168.2.0/24 === 192.168.1.0/24
Risoluzione dei problemi
Debug dell'ASA
Per risolvere i problemi di negoziazione del tunnel IPSec IKEv1 su un firewall ASA, è possibile utilizzare i seguenti comandi edebug:
Attenzione: sull'appliance ASA, è possibile impostare vari livelli di debug; per impostazione predefinita, viene usato il livello 1. Se si modifica il livello di debug, il livello di dettaglio dei debug può aumentare. In questo caso, il livello 127 fornisce dettagli sufficienti per la risoluzione dei problemi. Procedere con cautela, soprattutto negli ambienti di produzione.
debug crypto ipsec 127
debug crypto isakmp 127
debug ike-common 10
Nota: se sull'appliance ASA sono presenti più tunnel VPN, si consiglia di utilizzare i debug condizionali (debug crypto condition peer A.B.C.D), in modo da limitare gli output di debug in modo da includere solo il peer specificato.
Debug strongSwan
Verificare che il debug charon sia abilitato nel file ipsec.conf:
charondebug = "all"
La posizione finale dei messaggi di log dipende dalla configurazione di syslog nel sistema. Le posizioni più comuni sono /var/log/daemon, /var/log/syslog o /var/log/messages.
Informazioni correlate
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
3.0 |
18-Jan-2024 |
SEO, Requisiti di personalizzazione e formattazione aggiornati. |
2.0 |
06-Oct-2022 |
Aggiornato per rimuovere PII, correzione del titolo, lunghezza dell'introduzione, traduzione automatica, requisiti di stile, gerundi e formattazione. |
1.0 |
04-Aug-2020 |
Versione iniziale |
Contributo dei tecnici Cisco
- Mario Enrique Solorio ZertucheResponsabile progetto
 Feedback
Feedback