Introduzione
In questa configurazione di esempio vengono fornite informazioni su come configurare Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) per l'accesso a un server di posta situato nella rete esterna.
Fare riferimento alla versione ASA 8.3 e successive: Accesso al server di posta (SMTP) sull'esempio di configurazione della DMZ per ulteriori informazioni su come configurare l'appliance di sicurezza ASA per l'accesso a un server di posta/SMTP situato sulla rete DMZ.
Fare riferimento alla versione ASA 8.3 e successive: Esempio di configurazione dell'accesso al server di posta (SMTP) sulla rete interna per configurare l'appliance di sicurezza ASA in modo che possa accedere a un server di posta/SMTP sulla rete interna.
Fare riferimento a PIX/ASA 7.x e versioni successive: Esempio di configurazione dell'accesso al server di posta (SMTP) sulla rete esterna per la stessa configurazione su Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) con versione 8.2 e precedenti.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Nessun requisito specifico previsto per questo documento.
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Convenzioni
Fare riferimento a Cisco Technical Tips Conventions per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni dei documenti.
Configurazione
In questa sezione vengono presentate le informazioni necessarie per configurare le funzionalità descritte più avanti nel documento.
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi menzionati in questa sezione, usare Cisco CLI Analyzer.
Esempio di rete
Nel documento viene usata questa impostazione di rete:
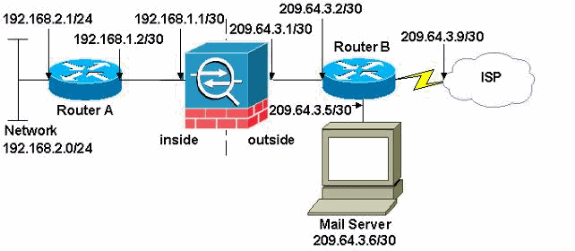
Nota: gli schemi di indirizzamento IP utilizzati in questa configurazione non sono legalmente instradabili su Internet. Si tratta degli indirizzi RFC 1918 utilizzati in un ambiente lab.
La configurazione della rete usata in questo esempio ha l'ASA con la rete interna (192.168.1.0/30) e la rete esterna (209.64.3.0/30). Il server di posta con indirizzo IP 209.64.3.6 si trova nella rete esterna. Configurare l'istruzione NAT in modo che tutto il traffico proveniente dalla rete 192.168.2.x che passa dall'interfaccia interna (Ethernet0) all'interfaccia esterna (Ethernet 1) venga convertito in un indirizzo compreso nell'intervallo da 209.64.3.129 a 209.64.3.253. L'ultimo indirizzo disponibile (209.64.3.254) è riservato a Port Address Translation (PAT).
Configurazioni
Nel documento vengono usate queste configurazioni:
| ASA |
ASA#show run
: Saved
:
ASA Version 8.3(1)
!
hostname ASA
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
names
!
interface Ethernet0
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface Ethernet1
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface Ethernet2
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
!--- Configure the inside interface.
?
interface Ethernet3
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252
!
!--- Configure the outside interface.
interface Ethernet4
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 209.64.3.1 255.255.255.252
!
interface Ethernet5
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
boot system disk0:/asa831-k8.bin
ftp mode passive
pager lines 24
mtu inside 1500
mtu outside 1500
no failover
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
!--- This command states that any traffic !--- from the 192.168.2.x network that passes from the inside interface (Ethernet0) !--- to the outside interface (Ethernet 1) translates into an address !--- in the range of 209.64.3.129 through 209.64.3.253 and contains a subnet !--- mask of 255.255.255.128.
object network obj-209.64.3.129_209.64.3.253
range 209.64.3.129-209.64.3.253
!--- This command reserves the last available address (209.64.3.254) for !--- for Port Address Translation (PAT). In the previous statement, !--- each address inside that requests a connection uses one !--- of the addresses specified. If all of these addresses are in use, !--- this statement provides a failsafe to allow additional inside stations !--- to establish connections.
object network obj-209.64.3.254
host 209.64.3.254
!--- This command indicates that all addresses in the 192.168.2.x range !--- that pass from the inside (Ethernet0) to a corresponding global !--- designation are done with NAT. !--- As outbound traffic is permitted by default on the ASA, no !--- static commands are needed.
object-group network nat-pat-group
network-object object obj-209.64.3.129_209.64.3.253
network-object object obj-209.64.3.254
object network obj-192.168.2.0
subnet 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic nat-pat-group
!--- Creates a static route for the 192.168.2.x network with 192.168.1.2. !--- The ASA forwards packets with these addresses to the router !--- at 192.168.1.2.
route inside 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2 1
!--- Sets the default route for the ASA Firewall at 209.64.3.2.
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.64.3.2 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00
timeout mgcp-pat 0:05:00 sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart
telnet timeout 5
ssh timeout 5
console timeout 0
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
!--- SMTP/ESMTP is inspected since "inspect esmtp" is included in the map.
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns maximum-length 512
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect skinny
inspect sunrpc
inspect xdmcp
inspect sip
inspect netbios
inspect tftp
!
service-policy global_policy global
Cryptochecksum:8a63de5ae2643c541a397c2de7901041
: end |
| Router A |
Current configuration:
!
version 12.4
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname 2522-R4
!
enable secret 5 $1$N0F3$XE2aJhJlCbLWYloDwNvcV.
!
ip subnet-zero
!
!
!
!
!
interface Ethernet0
!--- Assigns an IP address to the inside Ethernet interface.
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
no ip directed-broadcast
!
interface Ethernet1
!--- Assigns an IP address to the ASA-facing interface.
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252
no ip directed-broadcast
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
shutdown
!
interface Serial1
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
shutdown
!
ip classless
!--- This route instructs the inside router to forward all !--- non-local packets to the ASA.
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1
!
!
line con 0
transport input none
line aux 0
autoselect during-login
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 5 0
password ww
login
!
end |
| Router B |
Current configuration:
!
version 12.4
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname 2522-R4
!
enable secret 5 $1$N0F3$XE2aJhJlCbLWYloDwNvcV.
!
ip subnet-zero
!
!
!
!
interface Ethernet0
!--- Assigns an IP address to the ASA-facing Ethernet interface.
ip address 209.64.3.2 255.255.255.252
no ip directed-broadcast
!
interface Ethernet1
!--- Assigns an IP address to the server-facing Ethernet interface.
ip address 209.64.3.5 255.255.255.252
no ip directed-broadcast
!
interface Serial0
!--- Assigns an IP address to the Internet-facing interface.
ip address 209.64.3.9 255.255.255.252
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mroute-cache
!
interface Serial1
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
!
ip classless
!--- All non-local packets are to be sent out serial 0. In this case, !--- the IP address on the other end of the serial interface is not known, !--- or you can specify it here.
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0
!
!--- This statement is required to direct traffic destined to the !--- 209.64.3.128 network (the ASA global pool) to the ASA to be translated !--- back to the inside addresses.
ip route 209.64.3.128 255.255.255.128 209.64.3.1
!
!
line con 0
transport input none
line aux 0
autoselect during-login
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 5 0
password ww
login
!
end |
Configurazione TLS ESMTP
Nota: se si usa la crittografia Transport Layer Security (TLS) per la comunicazione della posta elettronica, la funzione di ispezione ESMTP (abilitata per impostazione predefinita) nell'appliance ASA scarta i pacchetti. Per consentire i messaggi di posta elettronica con TLS abilitato, disabilitare la funzione di ispezione ESMTP come mostrato nell'output. per ulteriori informazioni, fare riferimento all'ID bug Cisco CSCtn08326.
ciscoasa(config)#
policy-map global_policy
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class inspection_default
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#no inspect esmtp
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#exit
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#exit
Verifica
Attualmente non è disponibile una procedura di verifica per questa configurazione.
Risoluzione dei problemi
Cisco CLI Analyzer supporta alcuni comandi show. Usare CLI Analyzer per visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show.
Il comando logging buffered 7 indirizza i messaggi alla console ASA. Se la connettività al server di posta rappresenta un problema, esaminare i messaggi di debug della console per individuare gli indirizzi IP delle stazioni di invio e di ricezione e determinare il problema.
Informazioni correlate

 Feedback
Feedback