Configurazione del routing tra VLAN con un router interno (scheda layer 3) sugli switch Catalyst 5500/5000 e 6500/6000 con software CatOS
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento viene illustrato come configurare il routing tra VLAN su uno switch Catalyst (con software Catalyst OS [CatOS]) con un router interno (scheda/modulo di layer 3 [L3]). Il termine router interno si riferisce alle schede/moduli L3 sugli switch Catalyst 5500/5000 e 6500/6000:
-
Multilayer Switch Feature Card (MSFC) sugli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000
-
MSFC2 sugli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000
-
Route Switch Feature Card (RSFC) sugli switch Catalyst serie 5500/5000
-
Route Switch Module (RSM) sugli switch Catalyst serie 5500/5000
Per ottenere gli stessi risultati, nel presente documento si sarebbe potuto usare uno switch Catalyst serie 5500/5000 o Catalyst serie 6500/6000 con CatOS e una scheda L3 supportata.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Questo documento è utile per conoscere i seguenti argomenti:
Nota: in questo documento non viene descritto come configurare il routing tra VLAN sugli switch Catalyst 4500/4000 con il modulo dei servizi L3 (WS-X4232-L3). Per ulteriori informazioni, fare riferimento ai seguenti documenti:
-
Nota sulla configurazione del modulo per il routing tra VLAN in Installazione e configurazione del modulo dei servizi Catalyst 4000 Layer 3
-
Configurazione e panoramica del modulo router per la famiglia Catalyst 4000 (WS-X4232-L3)
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
-
Switch Catalyst 5500 con RSM
-
Modulo Supervisor Engine (WS-X5530) con software CatOS 6.1(1)
-
Modulo RSM (WS-X5302) con software Cisco IOS® versione 12.0(5)W5(12)
Le configurazioni su tutti i dispositivi sono state cancellate con i comandi clear config all e write erase per assicurarsi che disponessero di una configurazione predefinita.
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Convenzioni
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni usate, consultare il documento Cisco sulle convenzioni nei suggerimenti tecnici.
Esempio di rete
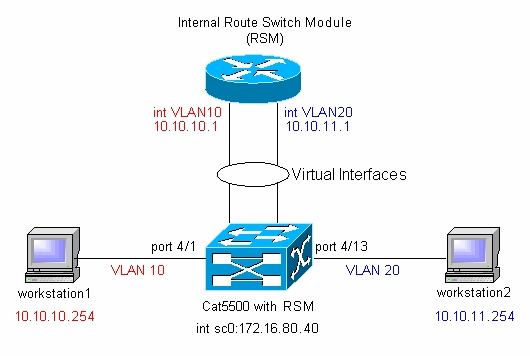
Nota: non connettere workstation1 e workstation2 se non richiesto in questo documento. In questo documento viene illustrato un problema comune segnalato dai clienti quando configurano il routing tra VLAN o più interfacce VLAN sul modulo del router. Vedere il problema comune: Interfaccia VLAN: per ulteriori informazioni, vedere la sezione inattiva/inattiva.
Task di configurazione generali
In questa sezione viene fornito un riepilogo delle principali attività di configurazione eseguite in questo documento:
-
Configurazione dello switch per la gestione
-
Creazione di VLAN sullo switch
-
Aggiunta di porte alle VLAN configurate
-
Configurare il router interno per la gestione
-
Configurazione del routing tra VLAN
-
Verificare la configurazione
Configurazione del routing tra VLAN
Per configurare il routing tra VLAN sullo switch Catalyst, attenersi alla seguente procedura:
-
Accedere alla porta della console sul Supervisor Engine.
In caso di problemi di accesso alla console, fare riferimento ai seguenti documenti:
-
Per gli switch Catalyst serie 5500/5000: collegamento di un terminale alla porta console sugli switch Catalyst.
-
Per gli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000: collegamento di una sezione Terminal del collegamento di un terminale alla porta console sugli switch Catalyst e connessione di un modem della sezione Collegamento di un modem alla porta console sugli switch Catalyst
-
-
Configurare lo switch per la gestione di base.
Utilizzare questo gruppo di comandi per configurare lo switch Catalyst per la gestione:
Console> enable) set system name Cat5500 !--- Configure the system name. System name set. Cat5500> (enable) set interface sc0 172.16.80.40 255.255.255.0 !--- Configure the IP address. Interface sc0 IP address and netmask set. Cat5500> (enable) set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.80.1 !--- Configure the default gateway.
Nota: se si desidera gestire uno switch che si trova sull'altro lato di un router, è necessario configurare un gateway predefinito sullo switch, in quanto lo switch non partecipa al routing IP e non ha quindi alcuna conoscenza della topologia L3 della rete. è possibile usare anche il comando set ip route default 172.16.80.1 per configurare il gateway predefinito anziché usare il comando set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.80.1.
-
Configurare il numero di VLAN richiesto sullo switch.
In base al diagramma di rete, è necessario configurare due nuove VLAN (VLAN 10 e VLAN 20) sullo switch.
Prima di poter creare una nuova VLAN, lo switch deve essere in modalità server VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) o in modalità VTP trasparente. Se lo switch è un server VTP, è necessario definire un nome di dominio VTP prima di poter aggiungere le VLAN. Questa impostazione deve essere definita indipendentemente dal numero di switch presenti nella rete (uno o molti) e indipendentemente dal fatto che si stia utilizzando il VTP per propagare le VLAN ad altri switch nella rete. Per ulteriori informazioni sul VTP, fare riferimento a questo documento:
La configurazione VTP predefinita dello switch è:
Cat5500> (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password -------------------------------- ------------ ----------- ----------- ---------- 1 2 server - Vlan-count Max-vlan-storage Config Revision Notifications ---------- ---------------- --------------- ------------- 5 1023 0 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans --------------- -------- -------- ------------------------- 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 2-1000Utilizzare il comando set vtp per impostare il nome di dominio e la modalità:
Cat5500> (enable) set vtp domain mode transparent VTP domain modified !--- Set the VTP mode. Cat5500> (enable) set vtp domain cisco VTP domain cisco modified !--- Set the VTP domain name.
Nota: Nell'esempio, la modalità VTP è impostata su trasparente. A seconda della rete in uso, impostare la modalità VTP di conseguenza. La modalità trasparente è stata scelta per evitare gli effetti negativi sugli altri switch e per evitare gli effetti negativi sugli altri switch in laboratorio.
-
Verificare la configurazione VTP usando il comando show vtp domain:
Cat5500> (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password -------------------------------- ------------ ----------- ----------- ---------- cisco 1 2 Transparent - Vlan-count Max-vlan-storage Config Revision Notifications ---------- ---------------- --------------- ------------- 5 1023 0 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans --------------- -------- -------- ------------------------- 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 2-1000
-
Creare le VLAN sullo switch.
Per impostazione predefinita, sullo switch è presente una sola VLAN, denominata VLAN 1. La VLAN 1 è chiamata anche VLAN predefinita. Per impostazione predefinita, tutte le porte appartengono alla VLAN. Non è possibile rinominare o eliminare questa VLAN.
Per creare le VLAN, usare il comando set vlan:
Cat5500> (enable) set vlan Usage: set vlan <mod/port> (An example of mod/port is 1/1,2/1-12,3/1-2,4/1-12) set vlan [name ] [type ] [state ] [said ] [mtu ] [ring ] [decring ] [bridge ] [parent ] [mode ] [stp ] [translation ] [backupcrf <off/on> [aremaxhop ] [stemaxhop ] (name = 1..32 characters, state = (active, suspend) type = (ethernet, fddi, fddinet, trcrf, trbrf) said = 1..4294967294, mtu = 576..18190 hex_ring_number = 0x1..0xfff, decimal_ring_number = 1..4095 bridge_number = 0x1..0xf, parent = 2..1005, mode = (srt, srb) stp = (ieee, ibm, auto), translation = 1..1005 hopcount = 1..13) Set vlan commands: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- set vlan Set vlan information set vlan mapping Map an 802.1Q vlan to an Ethernet vlan set vlan Vlan number(s)Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 10 !--- Create VLAN 10. VTP advertisements transmitting temporarily stopped and will resume after the command finishes. Vlan 10 configuration successful Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 20 !--- Create VLAN 20. VTP advertisements transmitting temporarily stopped and will resume after the command finishes. Vlan 20 configuration successful Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 10 4/1-12 !--- Add ports to VLAN 10. VLAN 10 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 10 4/1-12 Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 20 4/13-20 !--- Add ports to VLAN 20. VLAN 20 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 20 4/13-20 Cat5500> (enable) show vlan VLAN Name Status IfIndex Mod/Ports, Vlans ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------- ------------------------ 1 default active 443 1/1-2 3/1-3 4/21-24 11/1-48 12/1-2 10 VLAN0010 active 448 4/1-12 20 VLAN0020 active 449 4/13-20 1002 fddi-default active 444 1003 token-ring-default active 447 1004 fddinet-default active 445 1005 trnet-default active 446 VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2 ---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------ 1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0 10 enet 100010 1500 - - - - - 0 0 20 enet 100020 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1003 trcrf 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1005 trbrf 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0 !--- Output suppressed. -
Configurare Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) PortFast sulle porte che si connettono alle workstation o ai server.
Utilizzare il seguente comando per abilitare la funzione PortFast STP:
Cat5500> (enable) set spantree portfast 4/1-20 enable Warning: Spantree port fast start should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to a fast start port can cause temporary spanning tree loops. Use with caution. Spantree ports 4/1-20 fast start enabled.
Nota: questo passaggio è facoltativo, ma è buona norma abilitare STP PortFast sulle porte che si connettono a normali workstation o server. Per i dettagli sui motivi per cui abilitare PortFast, fare riferimento a questo documento:
-
Configurare un'interfaccia VLAN sul modulo del router per ciascuna delle VLAN tra cui si desidera indirizzare il traffico.
Accedere al modulo del router usando il comando session module#, dove module# è lo slot in cui si trova il modulo del router. Nell'esempio, l'RSM si trova nello slot 7, come mostrato di seguito:
Cat5500> (enable) show module 7 Mod Slot Ports Module-Type Model Sub Status --- ---- ----- ------------------------- ------------------- --- -------- 7 7 1 Route Switch WS-X5302 no ok Mod Module-Name Serial-Num --- ------------------- -------------------- 7 00006591991 Mod MAC-Address(es) Hw Fw Sw --- -------------------------------------- ------ ---------- ----------------- 7 00-e0-1e-91-b5-08 to 00-e0-1e-91-b5-09 4.5 20.20 12.0(5)W5(12) Cat5500> (enable) session 7 Trying Router-7... Connected to Router-7. Escape character is '^]'. Router>
-
Configurare la password enable e Telnet sul modulo del router.
Anche in questo caso, questo passaggio è facoltativo, ma è necessaria la password Telnet se si tenta di accedere al modulo del router direttamente con Telnet e non tramite il Supervisor Engine. Utilizzare questo gruppo di comandi per configurare le password sul modulo del router:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal !--- Enter the global configuration mode. Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# enable password cisco !--- Set enable password. Router(config)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# login Router(config-line)# password cisco !--- Set Telnet password. Router(config-line)# end Router# 05:22:40: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (127.0.0.2) Router#
-
Creare due interfacce VLAN, assegnare gli indirizzi IP alle interfacce VLAN e abilitare il routing sul modulo.
Nota: questo passaggio è fondamentale per configurare il routing tra VLAN.
Nota: sul modulo del router, le interfacce VLAN sono interfacce virtuali, ma sono configurate come interfacce fisiche.
Utilizzare questo gruppo di comandi dalla modalità di esecuzione privilegiata:
Router# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. !--- Configure interface VLAN 1 and assign it an IP address. !--- An interface VLAN 1 is configured for management purposes only !--- so that you can establish a Telnet session or ping the switch !--- from the workstation. Router(config)# interface vlan 1 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.80.79 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit !--- Configure interface VLAN 10 and assign it an IP address. Router(config)# interface vlan 10 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit !--- Configure interface VLAN 20 and assign it an IP address. Router(config)# interface vlan 20 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.11.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config)# ip routing !--- Enable routing protocol on the module. !--- The following two commands are optional; !--- they are only used if you have multiple routers in your network. !--- Depending on your network, you may want to use a different routing protocol. Router(config)# router rip Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 Router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 Router(config-router)# Ctrl-Z Router# 07:05:17: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (127.0.0.2) Router# write memory !--- Save the configuration. Building configuration... Router#
A questo punto, in base al diagramma reticolare, la configurazione tra VLAN è stata completata.
-
Tornare al modulo Supervisor Engine usando il comando exit al prompt di Router#:
Router# exit Cat5500> (enable
Problema comune: Interfaccia VLAN inattiva/inattiva
In questa sezione viene illustrato un problema comune che i clienti incontrano quando provano a configurare le interfacce VLAN sui moduli router Catalyst serie 5500/5000 o Catalyst serie 6500/6000 (RSM, MSFC, RSFC).
I clienti segnalano di non essere in grado di eseguire il ping su alcune o tutte le interfacce VLAN configurate sul modulo del router. Inoltre, il loro stato non viene visualizzato come attivo/attivo quando usano il comando show interface vlan vlan#. e si sono assicurati di non aver configurato la funzione shutdown su queste interfacce. L'unica interfaccia VLAN attiva/attiva è la VLAN 1.
In questo caso, se alcune o tutte le interfacce VLAN non sono visualizzate/visualizzate, per prima cosa occorre verificare se sullo switch sono presenti porte attive per le VLAN in questione.
Nota importante: Un'interfaccia VLAN sul modulo del router è attiva/attiva solo se allo switch è assegnata almeno una porta (diversa dall'interfaccia del router) e se tale porta è connessa. Anche una porta configurata come trunk soddisfa questo requisito di operatività/operatività della VLAN. Se questa condizione non viene soddisfatta, l'interfaccia del router non viene visualizzata.
Nella sezione Diagramma reticolare, viene visualizzato un messaggio che avverte di non connettere le workstation allo switch Catalyst 5500. A questo punto, se si immette questa serie di comandi, solo l'interfaccia VLAN 1 viene visualizzata/visualizzata e le altre due sono inattive:
Router# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 172.16.80.79 YES manual up up Vlan10 10.10.10.1 YES manual down down Vlan20 10.10.11.1 YES manual down down Router# show interface vlan 1 Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 172.16.80.79/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:02, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 10 Vlan10 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:25:48, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 20 Vlan20 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.11.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:01:04, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 2000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 1000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router#
L'interfaccia VLAN 1 è attiva/attiva, anche se sullo switch non sono presenti porte connesse e attive nella VLAN 1. Una porta/interfaccia attiva è presente nella VLAN 1, l'interfaccia sc0 sul modulo Supervisor. Per impostazione predefinita, l'interfaccia sc0 è membro della VLAN 1. Utilizzare questo comando sullo switch (Supervisor Engine) per controllare la configurazione dell'interfaccia sc0:
Cat5500> (enable) show interface
sl0: flags=51 <UP ,POINTOPOINT ,RUNNING>
slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0
sc0: flags=63 <UP ,BROADCAST ,RUNNING>
vlan 1 inet 172.16.80.40 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.80.255
Cat5500> (enable)
A questo punto, collegare workstation1 sulla porta 4/1 e workstation2 sulla porta 4/13. Eseguire il comando show port 4/1 e show port 4/13 sullo switch per verificare che queste porte mostrino lo stato di connessione:
Cat5500> (enable) show port 4/1 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 4/1 connected 10 normal a-half a-10 10/100BaseTX !--- Output suppressed. Cat5500> (enable) show port 4/13 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 4/13 connected 20 normal a-full a-100 10/100BaseTX !--- Output suppressed. Cat5500> (enable)
A questo punto, accedere al modulo del router e controllare lo stato delle interfacce VLAN 10 e VLAN 20. Dovrebbero essere visualizzate come attive/attive. Utilizzare questo gruppo di comandi per controllare lo stato delle interfacce VLAN sul modulo del router:
Cat5500> (enable) session 7 Trying Router-7... Connected to Router-7. Escape character is '^]'. User Access Verification Password: !--- Enter the password; in this case, it is cisco. Router> enable Password: !--- Enter the password; in this case, it is cisco. Router# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 172.16.80.79 YES manual up up Vlan10 10.10.10.1 YES manual up up Vlan20 10.10.11.1 YES manual up up Router# show interface vlan 10 Vlan10 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:46:14, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 20 Vlan20 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.11.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:56, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 2000 bits/sec, 5 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 2000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# exit Cat5500> (enable)
Verifica della configurazione
È possibile eseguire diversi test ping per verificare la configurazione descritta in questo documento. In questa sezione, è possibile usare workstation2 per eseguire il ping tra workstation1, l'interfaccia sc0 sullo switch e le interfacce VLAN sul modulo del router.
Nota: accertarsi di aver impostato i gateway predefiniti sulle workstation come interfacce VLAN sul modulo del router. In base al diagramma reticolare, il gateway predefinito sulla workstation1 è impostato su 10.10.10.1 e su 10.10.11.1 per la workstation2.
Test 1: Ping da Workstation2 a Workstation1
C:\> ipconfig
!--- This command is used to check the IP configuration on the !--- Windows 2000 workstation. Use the appropriate commands on the workstations !--- that you use.
Windows 2000 IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.254
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.1
C:\> ping 10.10.10.254
Pinging 10.10.10.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Ping statistics for 10.10.10.254:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 10ms, Average = 2ms
Test 2: Eseguire il ping tra Workstation2 e l'interfaccia sc0 sul Supervisor Engine
C:\> ping 172.16.80.40
Pinging 172.16.80.40 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Ping statistics for 172.16.80.40:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Test 3: Eseguire il ping tra Workstation2 e l'interfaccia VLAN 1 sul modulo router
C:\> ping 172.16.80.79
Pinging 172.16.80.79 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 172.16.80.79:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Test 4: Eseguire il ping tra Workstation2 e l'interfaccia VLAN 10 sul modulo router
C:\> ping 10.10.10.1
Pinging 10.10.10.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 10.10.10.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Test 5: Eseguire il ping tra Workstation2 e l'interfaccia VLAN 20 sul modulo router
C:\> ping 10.10.11.1
Pinging 10.10.11.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 10.10.11.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Appendice
Configurazione del modulo Supervisor Engine
Cat5500> (enable) show config This command shows non-default configurations only. Use show config all to show both default and non-default configurations. ... begin ! # ***** NON-DEFAULT CONFIGURATION ***** ! ! #time: Tue Apr 10 2001, 09:09:54 ! #version 6.1(1) ! set option fddi-user-pri enabled set password $2$lx7B$WipkVnLnbYIfrBSqD2SN9. set enablepass $2$6/eK$I3lDb2nnP7Fc9JKF3XwRW/ set prompt Cat5500> ! #errordetection set errordetection portcounter enable ! #system set system name Cat5500 ! #frame distribution method set port channel all distribution mac both ! #vtp set vtp domain cisco set vtp mode transparent set vlan 1 name default type ethernet mtu 1500 said 100001 state active set vlan 1002 name fddi-default type fddi mtu 1500 said 101002 state active set vlan 1004 name fddinet-default type fddinet mtu 1500 said 101004 state active stp ieee set vlan 1005 name trnet-default type trbrf mtu 1500 said 101005 state active stp ibm set vlan 10,20 set vlan 1003 name token-ring-default type trcrf mtu 1500 said 101003 state active mode srb aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7 backupcrf off ! #ip set interface sc0 1 172.16.80.40/255.255.255.0 172.16.80.255 set ip route 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 172.16.80.79 ! #set boot command set boot config-register 0x2102 clear boot system all ! # default port status is enable ! ! #module 1 : 2-port 1000BaseSX Supervisor ! #module 2 : 4-port 10/100BaseTX Supervisor ! #module 3 : 3-port 1000BaseX Ethernet ! #module 4 : 24-port 10/100BaseTX Ethernet set vlan 10 4/1-12 set vlan 20 4/13-20 set spantree portfast 4/1-20 enable ! #module 5 : 2-port MM OC-3 Dual-Phy ATM ! #module 6 empty ! #module 7 : 1-port Route Switch ! #module 8 empty ! #module 9 empty ! #module 10 empty ! #module 11 : 48-port 10BaseT Ethernet ! #module 12 : 2-port MM MIC FDDI ! #module 13 empty end Cat5500> (enable)
Configurazione RSM
Router# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! enable password cisco ! ip subnet-zero ip cef ! ! process-max-time 200 ! interface Vlan1 ip address 172.16.80.79 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Vlan10 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Vlan20 ip address 10.10.11.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! ip classless ! ! line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login ! end Router#
Informazioni correlate
- Configurazione e panoramica del modulo router per la famiglia Catalyst 4000 (WS-X4232-L3)
- Utilizzo di PortFast e di altri comandi per correggere i ritardi di connettività all'avvio della postazione di lavoro
- Pagine di supporto dei prodotti LAN
- Pagina di supporto dello switching LAN
- Supporto tecnico – Cisco Systems
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
30-Aug-2005 |
Versione iniziale |
 Feedback
Feedback