Configurazione e verifica di DHCP in un fabric VxLAN per Nexus 9000 con NX-OS e Windows Server 2022
Opzioni per il download
Linguaggio senza pregiudizi
La documentazione per questo prodotto è stata redatta cercando di utilizzare un linguaggio senza pregiudizi. Ai fini di questa documentazione, per linguaggio senza di pregiudizi si intende un linguaggio che non implica discriminazioni basate su età, disabilità, genere, identità razziale, identità etnica, orientamento sessuale, status socioeconomico e intersezionalità. Le eventuali eccezioni possono dipendere dal linguaggio codificato nelle interfacce utente del software del prodotto, dal linguaggio utilizzato nella documentazione RFP o dal linguaggio utilizzato in prodotti di terze parti a cui si fa riferimento. Scopri di più sul modo in cui Cisco utilizza il linguaggio inclusivo.
Informazioni su questa traduzione
Cisco ha tradotto questo documento utilizzando una combinazione di tecnologie automatiche e umane per offrire ai nostri utenti in tutto il mondo contenuti di supporto nella propria lingua. Si noti che anche la migliore traduzione automatica non sarà mai accurata come quella fornita da un traduttore professionista. Cisco Systems, Inc. non si assume alcuna responsabilità per l’accuratezza di queste traduzioni e consiglia di consultare sempre il documento originale in inglese (disponibile al link fornito).
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento viene descritto come configurare e risolvere i problemi relativi a DHCP in un fabric VxLAN con switch Nexus 9000.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Cisco raccomanda la conoscenza dei seguenti argomenti:
- Software Nexus NX-OS.
- Virtual Port Channel (vPC).
- VxLAN BGP L2VPN VPN
- IPv4 famiglia di indirizzi BGP
- OSPF
- PIM multicast (modalità sparse)
- DHCP
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
- Cisco Nexus 9000 con Cisco NX-OS.
- N9K-C93180YC-EX
- N9K-C93180YC-FX
- NX-OS 10.3(4a)
- Windows Server 2022 Data Center
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.

Nota: per qualsiasi domanda sulla configurazione e sull'integrabilità di software o hardware di terze parti, non è previsto il supporto Cisco. L'uso di strumenti di terze parti è il modo migliore per dimostrare al cliente la configurazione e il funzionamento dell'apparecchiatura Cisco.
Premesse
Configurazione della sovrapposizione e della sovrapposizione per VxLAN in laboratorio
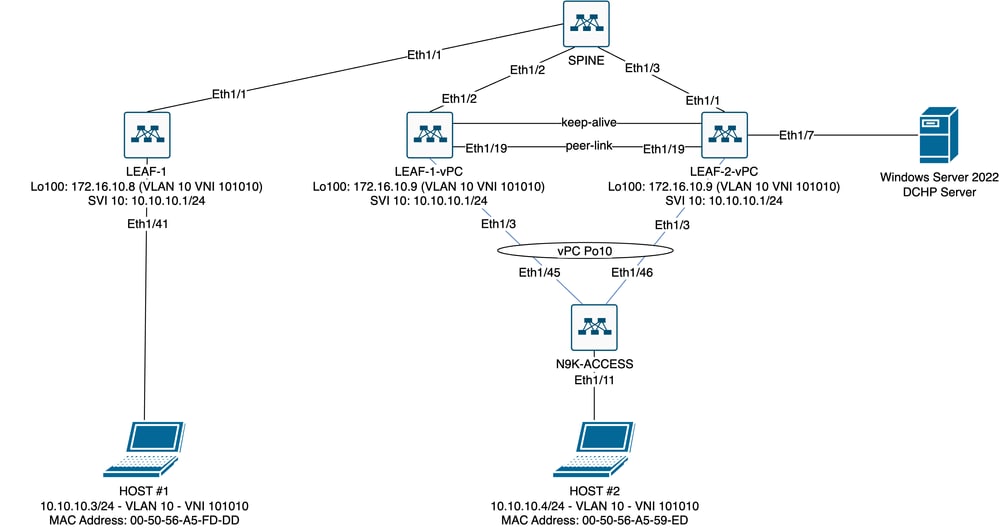 Diagramma fabric VxLAN in laboratorio
Diagramma fabric VxLAN in laboratorio
- DORSO:
- Questo switch Nexus invia pacchetti DHCP (Discover, Offre, Request, Ack) senza essere decapsulato in questo scenario. Viene utilizzata solo l'intestazione esterna.
- Funge da punto di routing centrale nel fabric di rete.
- Responsabile dell'interconnessione di tutti gli interruttori LEAF e della semplificazione del flusso di dati tra di essi.
- Partecipa a BGP per distribuire le route EVPN agli switch LEAF.
- Esegue il routing IP e può instradare il traffico tra subnet diverse o segmenti VxLAN guardando le intestazioni IP esterne.
- Separa la rete sovrapposta (VxLAN) dalla rete fisica sottostante.
- Gestisce la sovrapposizione con i protocolli di routing IP tradizionali, mentre la sovrapposizione è gestita da VxLAN con BGP EVPN, fornendo un'architettura di rete scalabile e flessibile.
- FOGLIA-1:
- Gli switch LEAF offrono connettività fisica per endpoint quali server, dispositivi di storage e altri accessori di rete.
- Gli switch LEAF svolgono la funzione di VTEP, ossia incapsulano e decapsulano i pacchetti VxLAN.
- In questo scenario, HOST#1 effettua la richiesta dell'indirizzo IP.
- LEAF-1 è responsabile dell'incapsulamento dei pacchetti DCHP nell'intestazione VxLAN.
- L'HOST 1 riceve i pacchetti DCHP in modo trasparente come Ethernet classico.
- LEAF-1-vPC e LEAF-2-vPC:
- Gli switch LEAF partecipano al control plane EVPN eseguendo BGP e scambiando informazioni sulla route. Ciò consente la distribuzione delle informazioni sugli indirizzi MAC e IP, garantendo che il traffico possa essere indirizzato in modo efficiente attraverso il fabric VxLAN.
- In questo scenario, il server DHCP viene associato alla VLAN 10 con il VNI 10101 e all'HOST 1. Questo significa che è solo un bridging VxLAN.
- Se il server DHCP è stato associato a un VNI diverso da HOST#1, un L3VNI sarebbe strettamente necessario per il routing. È necessario creare il VNI di origine e di destinazione.
- Il server DHCP riceve i pacchetti DCHP in modo trasparente come Ethernet classico.
- Il traffico BUM viene ricevuto da entrambi gli switch Nexus in vPC, ma solo lo switch Nexus primario operativo in vPC invia il traffico. Lo switch Nexus secondario scarta il traffico. In questo scenario, LEAF-1-vPC è operativo primario.
- L'uso delle infra-vlan è obbligatorio perché se l'interfaccia su LEAF-2-vPC su SPINE si interrompe, i pacchetti DCHP non possono essere inviati. Per inviare il traffico incapsulato VxLAN a LEAF-1-vPC, è necessaria questa VLAN di backup. In questo modo LEAF-1-vPC potrebbe inviare pacchetti DCHP a SPINE.
- ACCESSO N9K:
- Questo switch Nexus fornisce connettività solo a entrambi i sistemi Leafs utilizzando un canale della porta vPC a scopo di ridondanza verso HOST#2
DORSO
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature pim
feature netconf
feature nv overlay
ip pim rp-address 192.168.11.11 group-list 224.10.10.0/24
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
ip pim anycast-rp 192.168.11.11 192.168.0.11
ip prefix-list direct_routes seq 5 permit 10.104.11.0/30 le 32
route-map redistribution permit 10
match ip address prefix-list direct_routes
interface Ethernet1/1
speed 1000
ip address 10.104.11.1/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2
ip address 10.102.11.1/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3
speed 1000
ip address 10.103.11.1/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface loopback0
description ANYCAST-RP
ip address 192.168.0.11/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback1
description ANYCAST-RP-CANDIDATE
ip address 192.168.11.11/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
router ospf 1
router bgp 65000
neighbor 192.168.3.3
remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
route-reflector-client
neighbor 192.168.4.4
remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
route-reflector-client
neighbor 192.168.5.5
remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
route-reflector-clientFOGLIA-1
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature pim
feature interface-vlan
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature dhcp
feature nv overlay
fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 0000.0a0a.0a0a
ip pim rp-address 192.168.11.11 group-list 224.10.10.0/24
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
vlan 1,10,20,300
vlan 10
vn-segment 101010
vlan 20
vn-segment 202020
vlan 300
vn-segment 303030
spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 4096
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 5 permit 10.10.10.0/24 le 32
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 10 permit 192.168.20.0/24 le 32
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 15 permit 172.16.10.8/32
route-map direct_routes_tenant-a permit 10
match ip address prefix-list host_subnets
vrf context tenant-a
vni 303030
rd auto
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-target both auto
route-target both auto evpn
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100
interface Vlan20
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip address 192.168.20.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
interface Vlan300
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip forward
no ipv6 redirects
interface nve1
no shutdown
host-reachability protocol bgp
source-interface loopback0
member vni 101010
suppress-arp
mcast-group 224.10.10.10
member vni 202020
suppress-arp
mcast-group 224.10.10.10
member vni 303030 associate-vrf
interface Ethernet1/1
ip address 10.104.11.2/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface loopback0
description UNDERLAY-VERIFICATION
ip address 192.168.5.5/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback100
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.8/32
router ospf 1
router bgp 65000
address-family ipv4 unicast
neighbor 192.168.0.11
remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
vrf tenant-a
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute direct route-map direct_routes_tenant-a
evpn
vni 101010 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
vni 202020 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export autoLEAF-1-vPC
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature pim
feature interface-vlan
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature lacp
feature dhcp
feature vpc
feature nv overlay
fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 0000.0a0a.0a0a
ip pim rp-address 192.168.11.11 group-list 224.10.10.0/24
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
vlan 1,10,300,777
vlan 10
vn-segment 101010
vlan 300
vn-segment 303030
vlan 777
name BACKUP_VLAN_ROUTING_NVE_INFRA
spanning-tree vlan 1,10,300 hello-time 4
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 5 permit 10.10.10.0/24 le 32
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 15 permit 172.16.10.9/32
route-map direct_routes_tenant-a permit 10
match ip address prefix-list host_subnets
vrf context tenant-a
vni 303030
rd auto
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-target both auto
route-target both auto evpn
system nve infra-vlans 777
vpc domain 1
peer-switch
peer-keepalive destination 10.88.238.195
peer-gateway
layer3 peer-router
ip arp synchronize
interface Ethernet1/3
switchport
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,10,20
channel-group 10 mode active
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/19
switchport
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
no shutdown
interface port-channel1
switchport
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree port type network
vpc peer-link
interface port-channel10
switchport
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,10
vpc 10
interface mgmt0
vrf member management
ip address 10.88.238.194/29
interface loopback0
description UNDERLAY-VERIFICATION
ip address 192.168.3.3/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback1
description OVERLAY-NVE
ip address 192.168.13.1/32
ip address 192.168.13.254/32 secondary
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback10
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.1/32
interface loopback100
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.9/32
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100
interface Vlan300
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip forward
no ipv6 redirects
interface Vlan777
description BACKUP_UNDERLAY_INFRA-VLAN
no shutdown
no ip redirects
ip address 10.255.77.1/30
no ipv6 redirects
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface Ethernet1/2
ip address 10.102.11.2/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface nve1
no shutdown
host-reachability protocol bgp
advertise virtual-rmac
source-interface loopback1
member vni 101010
suppress-arp
mcast-group 224.10.10.10
member vni 303030 associate-vrf
router ospf 1
router bgp 65000
address-family ipv4 unicast
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise-pip
neighbor 192.168.0.11
remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
neighbor 192.168.88.2
remote-as 65000
description OVERLAY_BACKUP
update-source Vlan888
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
vrf tenant-a
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute direct route-map direct_routes_tenant-a
evpn
vni 101010 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
vni 202020 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export autoLEAF-2-vPC
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature pim
feature interface-vlan
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature lacp
feature dhcp
feature vpc
feature nv overlay
fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 0000.0a0a.0a0a
ip pim rp-address 192.168.11.11 group-list 224.10.10.0/24
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
vlan 1,10,20,300,777
vlan 10
vn-segment 101010
vlan 20
vn-segment 202020
vlan 300
vn-segment 303030
vlan 777
name BACKUP_VLAN_ROUTING_NVE_INFRA
spanning-tree vlan 1,10,20,300 hello-time 4
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 5 permit 10.10.10.0/24 le 32
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 10 permit 192.168.20.0/24 le 32
ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 15 permit 172.16.10.10/32
route-map direct_routes_tenant-a permit 10
match ip address prefix-list host_subnets
vrf context tenant-a
vni 303030
rd auto
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-target both auto
route-target both auto evpn
system nve infra-vlans 777
vpc domain 1
peer-switch
peer-keepalive destination 10.88.238.194
peer-gateway
layer3 peer-router
ip arp synchronize
interface Ethernet1/1
ip address 10.103.11.2/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/19
switchport
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
no shutdown
interface port-channel1
switchport
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree port type network
vpc peer-link
interface port-channel10
switchport
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,10,20
vpc 10
interface mgmt0
vrf member management
ip address 10.88.238.195/29
interface loopback0
description UNDERLAY-VERIFICATION
ip address 192.168.4.4/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback1
description OVERLAY-NVE
ip address 192.168.13.2/32
ip address 192.168.13.254/32 secondary
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback10
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.2/32
interface loopback100
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.10/32
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100
interface Vlan20
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip address 192.168.20.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
interface Vlan300
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip forward
no ipv6 redirects
interface Vlan777
description BACKUP_UNDERLAY_INFRA-VLAN
no shutdown
no ip redirects
ip address 10.255.77.2/30
no ipv6 redirects
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface nve1
no shutdown
host-reachability protocol bgp
advertise virtual-rmac
source-interface loopback1
member vni 101010
suppress-arp
mcast-group 224.10.10.10
member vni 202020
suppress-arp
mcast-group 224.10.10.10
member vni 303030 associate-vrf
router ospf 1
router bgp 65000
address-family ipv4 unicast
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise-pip
neighbor 192.168.0.11
remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
neighbor 192.168.88.1
remote-as 65000
description OVERLAY_BACKUP
update-source Vlan888
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
vrf tenant-a
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute direct route-map direct_routes_tenant-a
evpn
vni 101010 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
vni 202020 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export autoN9K-ACCESS
feature lacp
vlan 1,10
interface port-channel10
switchport
switchport mode trunk
interface Ethernet1/11
switchport
switchport access vlan 10
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/45
switchport
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 10 mode active
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/46
switchport
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 10 mode active
no shutdownConfigurazione DHCP sugli switch Nexus
FOGLIA-1
Passaggio 1. Attivare la funzionalità DCHP.
LEAF-1(config)# feature dhcp
Nota: il server DHCP e il servizio di comando dell'agente di inoltro dhcp, ip dhcp relay e ipv6 dhcp relay sono abilitati per impostazione predefinita da NX-OS 7.x.
Passaggio 2. Applicare il comando ip dhcp relay information option.
LEAF-1(config)# ip dhcp relay information option
Nota: questo comando consente all'agente di inoltro DHCP di inserire e rimuovere le informazioni dell'opzione 82 sui pacchetti inoltrati.
Passaggio 3. Applicare il comando ip dhcp relay information option vpn.
LEAF-1(config)# ip dhcp relay information option vpn
Nota: questo comando abilita le richieste di inoltro DHCP che arrivano su VRF diversi a cui appartiene il server DHCP.
Passaggio 4. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay address [ip address of DCHP server]".

Nota: nell'esempio, l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP è 10.10.150.
LEAF-1(config)# interface vlan 10
LEAF-1(config-if)# ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150Passaggio 5. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay source-interface [unique loopback]".

Nota: questo comando configura l'indirizzo IP di origine per l'agente di inoltro DHCP per gestire Discover, Offre, Request e ACK, per la comunicazione unicast che l'agente di inoltro DHCP utilizza come indirizzo IP di origine dell'agente di inoltro DHCP. Questa operazione non è desiderata perché l'indirizzo IP è condiviso da più VTEP ed è possibile che i pacchetti DHCP rimangano bloccati. Per evitare ciò, è necessario un indirizzo IP univoco (che utilizzi un'interfaccia di loopback) per distinguere ciascun VTEP.
LEAF-1(config)# interface vlan 10
LEAF-1(config-if)# ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100Passaggio 6. Nel tenant corrispondente VRF all'interno di BGP, ridistribuzione diretta della route con un prefisso-elenco e una route-map che include l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback.

Nota: questa interfaccia di loopback appartiene al tenant di SVI.
LEAF-1(config)# show running-config interface loopback 100
interface loopback100
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.8/32
LEAF-1(config)# ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 15 permit 172.16.10.8/32
LEAF-1(config)# route-map direct_routes_tenant-a permit 10
LEAF-1(config-route-map)# match ip address prefix-list host_subnets
LEAF-1(config-route-map)# router bgp 65000
LEAF-1(config-router)# vrf tenant-a
LEAF-1(config-router-vrf)# address-family ipv4 unicast
LEAF-1(config-router-vrf-af)# redistribute direct route-map direct_routes_tenant-aPassaggio 7. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback venga annunciato in BGP L2VPN VPN agli Spine con il comando show bgp l2vpn evpn [loopback IP] vrf [tenant vrf].
LEAF-1(config)# show bgp l2vpn evpn 172.16.10.8 vrf tenant-a
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
Route Distinguisher: 192.168.5.5:4 (L3VNI 303030)
BGP routing table entry for [5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.8]/224, version 421
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn
Advertised path-id 1
Path type: local, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop
Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated
192.168.5.5 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.5.5)
Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 32768
Received label 303030
Extcommunity: RT:65000:303030 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:707d.b9b8.4daf
Path-id 1 advertised to peers:
192.168.0.11 <<<< SpinePassaggio 8. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback venga inserito nell'EVPN BGP L2VPN in cui si trova il server DHCP.

Nota: se vi sono switch Nexus in vPC, verificare che entrambi conoscano l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback in BGP L2VPN EVPN.
LEAF-1# show bgp l2vpn evpn 172.16.10.8
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
Route Distinguisher: 192.168.5.5:4
BGP routing table entry for [5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.8]/224, version 754
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn, is not in HW
Advertised path-id 1
Path type: internal, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop
Imported to 2 destination(s)
Imported paths list: tenant-a L3-303030
Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
AS-Path: NONE, path sourced internal to AS
192.168.5.5 (metric 45) from 192.168.0.11 (192.168.0.11)
Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 0
Received label 303030
Extcommunity: RT:65000:303030 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:707d.b9b8.4daf
Originator: 192.168.5.5 Cluster list: 192.168.0.11
Path-id 1 not advertised to any peer
Route Distinguisher: 192.168.3.3:4 (L3VNI 303030)
BGP routing table entry for [5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.8]/224, version 761
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn, is not in HW
Advertised path-id 1
Path type: internal, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop
Imported from 192.168.5.5:4:[5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.8]/224
Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
AS-Path: NONE, path sourced internal to AS
192.168.5.5 (metric 45) from 192.168.0.11 (192.168.0.11)
Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 0
Received label 303030
Extcommunity: RT:65000:303030 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:707d.b9b8.4daf
Originator: 192.168.5.5 Cluster list: 192.168.0.11
Path-id 1 not advertised to any peerPassaggio 9. Verificare che esista una route per il server DHCP nel tenant di origine con il comando show ip route [DHCP server IP] vrf [tenant vrf].

Nota: la voce della route da utilizzare deve essere da VxLAN a VRF predefinita. Se non è disponibile alcuna route, verificare che il VTEP conosca localmente l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP.
LEAF-1# show running-config interface vlan 10
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a <<<< source tenant
no ip redirects
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150 <<<< DHCP server
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100
LEAF-1# show ip route 10.10.10.150 vrf tenant-a
10.10.10.150/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via 192.168.13.254%default, [200/0], 2w0d, bgp-65000, internal, tag 65000, segid: 303030 tunnelid: 0xd0d0dfe encap: VXLANPassaggio 10. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP sia raggiungibile utilizzando l'interfaccia di loopback e il VRF corrispondente come origine VRF con il comando ping [DHCP server IP] source-interface loopback [x] vrf [tenant vrf].
LEAF-1# ping 10.10.10.150 source-interface loopback 100 vrf tenant-a
PING 10.10.10.150 (10.10.10.150): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=0 ttl=126 time=1.262 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=1 ttl=126 time=0.833 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=2 ttl=126 time=0.808 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=3 ttl=126 time=0.795 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=4 ttl=126 time=0.78 ms
--- 10.10.10.150 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0.00% packet lossPassaggio 11. Verificare lo stato dell'agente di inoltro DHCP.
LEAF-1# show ip dhcp status
Current CLI Operation: show ip dhcp status
Last CLI Operation: DME: ip dhcp relay information option enable
Last CLI Operation Status: SUCCESSPassaggio 12. Verificare l'opzione 82, ad esempio vpn option e l'indirizzo IP corretto del relay nell'agente di inoltro.
LEAF-1# show ip dhcp relay
DHCP relay service is enabled <<<<<<
Insertion of option 82 is enabled <<<<<<
Insertion of option 82 customize circuitid is disabled
TLV format in CircuitId and RemoteId suboptions is enabled
Insertion of VPN suboptions is enabled <<<<<<<
Insertion of cisco suboptions is disabled
Global smart-relay is disabled
Relay Trusted functionality is disabled
Relay Trusted Port is Globally disabled
V4 Relay Source Address HSRP is Globally disabled
Server-ID-override-disable is disabled
Smart-relay is enabled on the following interfaces:
------------------------------------------------------
Subnet-broadcast is enabled on the following interfaces:
------------------------------------------------------
Relay Trusted Port is enabled on the following interfaces:
----------------------------------------------------------
Relay Source Address HSRP is enabled on the following interfaces:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Helper addresses are configured on the following interfaces:
Interface Relay Address VRF Name
------------- ------------- --------
Vlan10 10.10.10.150 <<<<<<<<<Passaggio 13. Verificare le statistiche dei pacchetti elaborati e inoltrati.
LEAF-1# show ip dhcp global statistics
Packets processed 1297177
Packets received through cfsoe 0
Packets forwarded 1297175
Packets forwarded on cfsoe 0
Total packets dropped 0
Packets dropped from untrusted ports 0
Packets dropped due to MAC address check failure 0
Packets dropped due to Option 82 insertion failure 0
Packets dropped due to o/p intf unknown 0
Packets dropped which were unknown 0
Packets dropped due to no trusted ports 0
Packets dropped due to dhcp relay not enabled 0
Packets dropped due to no binding entry 0
Packets dropped due to interface error/no interface 0
Packets dropped due to max hops exceeded 0
Packets dropped due to Queue full 0Passaggio 14. Verificare le statistiche dei pacchetti relay.
LEAF-1# show ip dhcp relay statistics
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Message Type Rx Tx Drops
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Discover 260521 260520 0
Offer 289330 289330 0
Request(*) 267162 267161 0
Ack 8322 8322 0
Release(*) 181121 181121 0
Decline 1 1 0
Inform(*) 0 0 0
Nack 289280 289280 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 1295737 1295735 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
DHCP L3 FWD:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
Non DHCP:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
DROP:
DHCP Relay not enabled : 0
Invalid DHCP message type : 0
Interface error : 0
Tx failure towards server : 0
Tx failure towards client : 0
Unknown output interface : 0
Unknown vrf or interface for server : 0
Max hops exceeded : 0
Option 82 validation failed : 0
Packet Malformed : 0
DHCP Request dropped on MCT : 0
Relay Trusted port not configured : 0
* - These counters will show correct value when switch
receives DHCP request packet with destination ip as broadcast
address. If request is unicast it will be HW switchedDHCP LEAF-1-vPC
Passaggio 1. Attivare la funzionalità DCHP.
LEAF-1-VPC(config)#feature dhcp
Nota: il server DHCP e il servizio di comando dell'agente di inoltro dhcp, ip dhcp relay e ipv6 dhcp relay sono abilitati per impostazione predefinita da NX-OS 7.x.
Passaggio 2. Applicare il comando ip dhcp relay information option.
LEAF-1-VPC(config)#ip dhcp relay information option
Nota: questo comando consente all'agente di inoltro DHCP di inserire e rimuovere le informazioni dell'opzione 82 sui pacchetti inoltrati.
Passaggio 3. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay information option vpn".
LEAF-1-VPC(config)# ip dhcp relay information option vpn
Nota: questo comando abilita le richieste di inoltro DHCP che arrivano su VRF diversi a cui appartiene il server DHCP.
Passaggio 4. Applicare il comando ip dhcp relay address [ip address of DCHP server].

Nota: nell'esempio, l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP è 10.10.150.
LEAF-1-VPC(config)#interface vlan 10
LEAF-1-VPC(config-if)#ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150Passaggio 5. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay source-interface [unique loopback]".

Nota: questo comando configura l'indirizzo IP di origine per l'agente di inoltro DHCP per gestire Discover, Offre, Request e ACK, per la comunicazione unicast che l'agente di inoltro DHCP utilizza come indirizzo IP di origine dell'agente di inoltro DHCP. Questa operazione non è desiderata perché l'indirizzo IP è condiviso da più VTEP ed è possibile che i pacchetti DHCP rimangano bloccati. Per evitare ciò, è necessario un indirizzo IP univoco (che utilizzi un'interfaccia di loopback) per distinguere ciascun VTEP.
LEAF-1-VPC(config)#interface vlan 10
LEAF-1-VPC(config-if)# ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100Passaggio 6. Nel tenant corrispondente VRF all'interno di BGP, ridistribuzione diretta della route con un prefisso-elenco e una route-map che include l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback.

Nota: questa interfaccia di loopback appartiene al tenant di SVI.
LEAF-1-VPC(config)# show running-config interface loopback 100
interface loopback100
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.9/32
LEAF-1-VPC(config)# ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 15 permit 172.16.10.9/32
LEAF-1-VPC(config)# route-map direct_routes_tenant-a permit 10
LEAF-1-VPC(config-route-map)# match ip address prefix-list host_subnets
LEAF-1-VPC(config-route-map)# router bgp 65000
LEAF-1-VPC(config-router)# vrf tenant-a
LEAF-1-VPC(config-router-vrf)# address-family ipv4 unicast
LEAF-1-VPC(config-router-vrf-af)# redistribute direct route-map direct_routes_tenant-aPassaggio 7. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback venga annunciato in BGP L2VPN VPN agli Spine con il comando show bgp l2vpn evpn [loopback IP] vrf [tenant vrf].
LEAF-1-VPC# show bgp l2vpn evpn 172.16.10.9 vrf tenant-a
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
Route Distinguisher: 192.168.3.3:4 (L3VNI 303030)
BGP routing table entry for [5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.9]/224, version 637
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn
Advertised path-id 1
Path type: local, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop
Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated
192.168.13.1 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.3.3)
Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 32768
Received label 303030
Extcommunity: RT:65000:303030 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:6026.aa85.9887
Path-id 1 advertised to peers:
192.168.0.11 Passaggio 8. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback venga inserito nell'EVPN BGP L2VPN in cui si trova il server DHCP.

Nota: se vi sono switch Nexus in vPC, verificare che entrambi conoscano l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback in BGP L2VPN EVPN.
LEAF-1-VPC# show bgp l2vpn evpn 172.16.10.9
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
Route Distinguisher: 192.168.3.3:4 (L3VNI 303030)
BGP routing table entry for [5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.9]/224, version 637
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn
Advertised path-id 1
Path type: local, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop
Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated
192.168.13.1 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.3.3)
Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 32768
Received label 303030
Extcommunity: RT:65000:303030 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:6026.aa85.9887
Path-id 1 advertised to peers:
192.168.0.11 Passaggio 9. Verificare che nel tenant di origine sia presente una route per il server DHCP con il comando show ip route [DHCP server IP] vrf[tenant vrf].

Nota: la voce della route da utilizzare deve essere da VxLAN a VRF predefinita. Se non è disponibile alcuna route, verificare che il VTEP conosca localmente l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP.
LEAF-1-VPC# show running-config interface vlan 10
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a <<<< source tenant
no ip redirects
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100
LEAF-1-VPC# show ip route 10.10.10.150 vrf tenant-a
10.10.10.150/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 10.10.10.150, Vlan10, [190/0], 6d07h, hmmPassaggio 10. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP sia raggiungibile utilizzando l'interfaccia di loopback e il VRF corrispondente come origine VRF con il comando ping [DHCP server IP] source-interface loopback [x] vrf [tenvrf].
LEAF-1-VPC# ping 10.10.10.150 source-interface loopback 100 vrf tenant-a
PING 10.10.10.150 (10.10.10.150): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=0 ttl=126 time=0.965 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=1 ttl=126 time=0.57 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=2 ttl=126 time=0.488 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=3 ttl=126 time=0.524 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=4 ttl=126 time=0.502 ms
--- 10.10.10.150 ping statistics ---Passaggio 11. Verificare lo stato dell'agente di inoltro DHCP.
LEAF-1-VPC# show ip dhcp status
Current CLI Operation: show ip dhcp status
Last CLI Operation: DME: ip dhcp relay information option vpn enable
Last CLI Operation Status: SUCCESSPassaggio 12. Verificare l'opzione 82, ad esempio vpn option e l'indirizzo IP corretto del relay nell'agente di inoltro.
LEAF-1-VPC# show ip dhcp relay
DHCP relay service is enabled <<<<<<
Insertion of option 82 is enabled <<<<<<<
Insertion of option 82 customize circuitid is disabled
TLV format in CircuitId and RemoteId suboptions is enabled
Insertion of VPN suboptions is enabled <<<<<<<
Insertion of cisco suboptions is disabled
Global smart-relay is disabled
Relay Trusted functionality is disabled
Relay Trusted Port is Globally disabled
V4 Relay Source Address HSRP is Globally disabled
Server-ID-override-disable is disabled
Smart-relay is enabled on the following interfaces:
------------------------------------------------------
Subnet-broadcast is enabled on the following interfaces:
------------------------------------------------------
Relay Trusted Port is enabled on the following interfaces:
----------------------------------------------------------
Relay Source Address HSRP is enabled on the following interfaces:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Helper addresses are configured on the following interfaces:
Interface Relay Address VRF Name
------------- ------------- --------
Vlan10 10.10.10.150 <<<<<<<<<Passaggio 13. Verificare le statistiche dei pacchetti elaborati e inoltrati.
LEAF-1-VPC# show ip dhcp global statistics
Packets processed 263162
Packets received through cfsoe 0
Packets forwarded 263161
Packets forwarded on cfsoe 0
Total packets dropped 0
Packets dropped from untrusted ports 0
Packets dropped due to MAC address check failure 0
Packets dropped due to Option 82 insertion failure 0
Packets dropped due to o/p intf unknown 0
Packets dropped which were unknown 0
Packets dropped due to no trusted ports 0
Packets dropped due to dhcp relay not enabled 0
Packets dropped due to no binding entry 0
Packets dropped due to interface error/no interface 0
Packets dropped due to max hops exceeded 0
Packets dropped due to Queue full 0Passaggio 14. Verificare le statistiche dei pacchetti relay.
LEAF-1-VPC# show ip dhcp relay statistics
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Message Type Rx Tx Drops
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Discover 8 7 0
Offer 29304 29304 0
Request(*) 5029 5029 0
Ack 6535 6535 0
Release(*) 191482 191482 0
Decline 0 0 0
Inform(*) 3 3 0
Nack 29281 29281 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 261642 261641 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
DHCP L3 FWD:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
Non DHCP:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
DROP:
DHCP Relay not enabled : 0
Invalid DHCP message type : 0
Interface error : 0
Tx failure towards server : 0
Tx failure towards client : 0
Unknown output interface : 0
Unknown vrf or interface for server : 0
Max hops exceeded : 0
Option 82 validation failed : 0
Packet Malformed : 0
DHCP Request dropped on MCT : 0
Relay Trusted port not configured : 0
* - These counters will show correct value when switch
receives DHCP request packet with destination ip as broadcast
address. If request is unicast it will be HW switchedDHCP LEAF-2-vPC
Passaggio 1. Attivare la funzionalità DCHP.
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# feature dhcp
Nota: il server DHCP e il servizio di comando dell'agente di inoltro dhcp, ip dhcp relay e ipv6 dhcp relay sono abilitati per impostazione predefinita a partire da NX-OS 7.x.
Passaggio 2. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay information option".
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# ip dhcp relay information option
Nota: questo comando consente all'agente di inoltro DHCP di inserire e rimuovere le informazioni dell'opzione 82 sui pacchetti inoltrati.
Passaggio 3. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay information option vpn".
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# ip dhcp relay information option vpn
Nota: questo comando abilita le richieste di inoltro DHCP che arrivano su VRF diversi a cui appartiene il server DHCP.
Passaggio 4. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay address [ip address of DCHP server]".

Nota: nell'esempio, l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP è 10.10.150.
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# interface vlan 10
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150Passaggio 5. Applicare il comando "ip dhcp relay source-interface [unique loopback]".

Nota: questo comando configura l'indirizzo IP di origine per l'agente di inoltro DHCP per gestire Discover, Offre, Request e ACK, per la comunicazione unicast che l'agente di inoltro DHCP utilizza come indirizzo IP di origine dell'agente di inoltro DHCP. Questa operazione non è desiderata perché l'indirizzo IP è condiviso da più VTEP ed è possibile che i pacchetti DHCP rimangano bloccati. Per evitare ciò, è necessario un indirizzo IP univoco (che utilizzi un'interfaccia di loopback) per distinguere ciascun VTEP.
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# interface vlan 10
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback 100Passaggio 6. Nel tenant corrispondente VRF all'interno di BGP, ridistribuzione diretta della route con un prefisso-elenco e una route-map che include l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback.

Nota: questa interfaccia di loopback appartiene al tenant di SVI.
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# show running-config interface loopback 100
interface loopback100
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.10/32
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# ip prefix-list host_subnets seq 15 permit 172.16.10.10/32
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# route-map direct_routes_tenant-a permit 10
LEAF-2-VPC(config-route-map)# match ip address prefix-list host_subnets
LEAF-2-VPC(config-route-map)# router bgp 65000
LEAF-2-VPC(config-router)# vrf tenant-a
LEAF-2-VPC(config-router-vrf)# address-family ipv4 unicast
LEAF-2-VPC(config-router-vrf-af)# redistribute direct route-map direct_routes_tenant-a
Passaggio 7. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback venga annunciato in BGP L2VPN VPN agli Spine con il comando show bgp l2vpn evpn [loopback IP] vrf [tenant vrf].
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# show bgp l2vpn evpn 172.16.10.10 vrf tenant-a
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
Route Distinguisher: 192.168.4.4:4 (L3VNI 303030)
BGP routing table entry for [5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.10]/224, version 49
5
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn
Advertised path-id 1
Path type: local, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop
Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated
192.168.13.2 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.4.4)
Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 32768
Received label 303030
Extcommunity: RT:65000:303030 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:6026.aa85.9587
Path-id 1 advertised to peers:
192.168.0.11 <<<<< Spine Passaggio 8. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback venga inserito nell'EVPN BGP L2VPN in cui si trova il server DHCP.

Nota: se vi sono switch Nexus in vPC, verificare che entrambi conoscano l'indirizzo IP dell'interfaccia di loopback in BGP L2VPN EVPN.
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# show bgp l2vpn evpn 172.16.10.10
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
Route Distinguisher: 192.168.4.4:4 (L3VNI 303030)
BGP routing table entry for [5]:[0]:[0]:[32]:[172.16.10.10]/224, version 49
5
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn
Advertised path-id 1
Path type: local, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop
Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated
192.168.13.2 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.4.4)
Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 32768
Received label 303030
Extcommunity: RT:65000:303030 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:6026.aa85.9587
Path-id 1 advertised to peers:
192.168.0.11 Passaggio 9. Verificare che nel tenant di origine sia presente una route per il server DHCP con il comando show ip route [DHCP server IP] vrf[tenvrf].

Nota: la voce della route da utilizzare deve essere da VxLAN a VRF predefinita. Se non è disponibile alcuna route, verificare che il VTEP conosca localmente l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP.
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# show running-config interface vlan 10
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# show ip route 10.10.10.150 vrf tenant-a
10.10.10.150/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 10.10.10.150, Vlan10, [190/0], 01:01:28, hmmPassaggio 10. Verificare che l'indirizzo IP del server DHCP sia raggiungibile utilizzando l'interfaccia di loopback e il VRF corrispondente come origine VRF con il comando ping [DHCP server IP] source-interface loopback [x] vrf [tenant vrf].
LEAF-2-VPC(config-if)# ping 10.10.10.150 source-interface loopback 100 vrf tenant-a
PING 10.10.10.150 (10.10.10.150): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=0 ttl=127 time=0.928 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=0.475 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=2 ttl=127 time=0.455 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=3 ttl=127 time=0.409 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.150: icmp_seq=4 ttl=127 time=0.465 ms
--- 10.10.10.150 ping statistics ---Passaggio 11. Verificare lo stato dell'agente di inoltro DHCP.
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# show ip dhcp status
Current CLI Operation: show ip dhcp status
Last CLI Operation: DME: ip dhcp relay information option vpn enable
Last CLI Operation Status: SUCCESSPassaggio 12. Verificare l'opzione 82, ad esempio vpn option e l'indirizzo IP corretto del relay nell'agente di inoltro.
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# show ip dhcp relay
DHCP relay service is enabled <<<<<<<
Insertion of option 82 is enabled <<<<<<<<<
Insertion of option 82 customize circuitid is disabled
TLV format in CircuitId and RemoteId suboptions is enabled
Insertion of VPN suboptions is enabled <<<<<<<
Insertion of cisco suboptions is disabled
Global smart-relay is disabled
Relay Trusted functionality is disabled
Relay Trusted Port is Globally disabled
V4 Relay Source Address HSRP is Globally disabled
Server-ID-override-disable is disabled
Smart-relay is enabled on the following interfaces:
------------------------------------------------------
Subnet-broadcast is enabled on the following interfaces:
------------------------------------------------------
Relay Trusted Port is enabled on the following interfaces:
----------------------------------------------------------
Relay Source Address HSRP is enabled on the following interfaces:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Helper addresses are configured on the following interfaces:
Interface Relay Address VRF Name
------------- ------------- --------
Vlan10 10.10.10.150 <<<<Passaggio 13. Verificare le statistiche dei pacchetti elaborati e inoltrati.
LEAF-2-VPC(config)# show ip dhcp global statistics
Packets processed 103030
Packets received through cfsoe 0
Packets forwarded 103030
Packets forwarded on cfsoe 0
Total packets dropped 0
Packets dropped from untrusted ports 0
Packets dropped due to MAC address check failure 0
Packets dropped due to Option 82 insertion failure 0
Packets dropped due to o/p intf unknown 0
Packets dropped which were unknown 0
Packets dropped due to no trusted ports 0
Packets dropped due to dhcp relay not enabled 0
Packets dropped due to no binding entry 0
Packets dropped due to interface error/no interface 0
Packets dropped due to max hops exceeded 0
Packets dropped due to Queue full 0Passaggio 14. Verificare le statistiche dei pacchetti relay.
LEAF-2-VPC# show ip dhcp relay statistics
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Message Type Rx Tx Drops
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Discover 29312 29311 0
Offer 300001 300001 0
Request(*) 29324 29324 0
Ack 1574 1574 0
Release(*) 191493 191493 0
Decline 0 0 0
Inform(*) 1540 1540 0
Nack 472890 472890 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 1026134 1026133 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
DHCP L3 FWD:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
Non DHCP:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
DROP:
DHCP Relay not enabled : 0
Invalid DHCP message type : 0
Interface error : 0
Tx failure towards server : 0
Tx failure towards client : 0
Unknown output interface : 0
Unknown vrf or interface for server : 0
Max hops exceeded : 0
Option 82 validation failed : 0
Packet Malformed : 0
DHCP Request dropped on MCT : 0
Relay Trusted port not configured : 0
* - These counters will show correct value when switch
receives DHCP request packet with destination ip as broadcast
address. If request is unicast it will be HW switchedConfigurazione del server DHCP in Windows Server 2022
Configurazione dell'ambito di indirizzamento IP per gli host.
Passaggio 1. Aprire Server Manager e verificare che non vi siano allarmi sul server DHCP nel dashboard.
 Dashboard da Server Manager in Windows Server 2022
Dashboard da Server Manager in Windows Server 2022

Suggerimento: quando si fa doppio clic, l'immagine si ingrandisce.
Passaggio 2. Aprire l'applicazione server DHCP.
 Server DHCP su Windows Server 2022
Server DHCP su Windows Server 2022
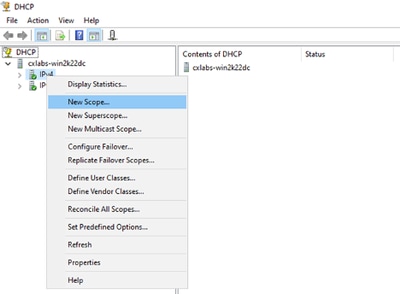
Passaggio 3. Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su IPv4 e selezionare New Scope (Nuovo ambito).
 Nuovo ambito in DCHP
Nuovo ambito in DCHP
Passaggio 4. Fare clic su Next (Avanti).
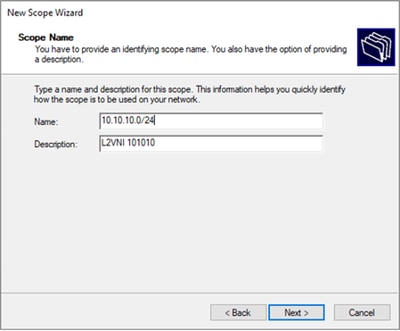
Passaggio 5. Scrivere un nome e una descrizione. Nell'esempio, il nome è la subnet che appartiene alla VLAN 10 e la descrizione è l'L2VNI come L2VNI elencato nella VLAN 10.
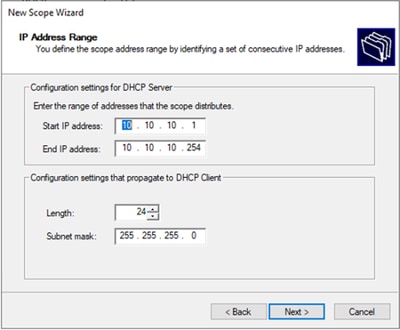
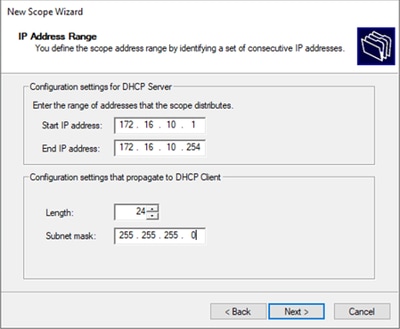
Passaggio 6. Configurare l'intervallo di indirizzi IP. Pool per gli host.
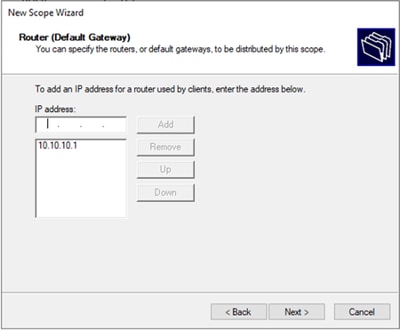
Passaggio 6. Escludere l'indirizzo IP condiviso dalla configurazione SVI nei VTEP. In questo esempio, l'interfaccia VLAN 10 ha l'indirizzo IP.10.10.1/24.

Avviso: se non si esclude l'indirizzo IP dall'SVI (o gateway predefinito), è possibile che gli indirizzi IP vengano duplicati e il traffico recapitato venga compromesso.
LEAF-1# show running-config interface vlan 10
<snip>
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-a
no ip redirects
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.10.150
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback100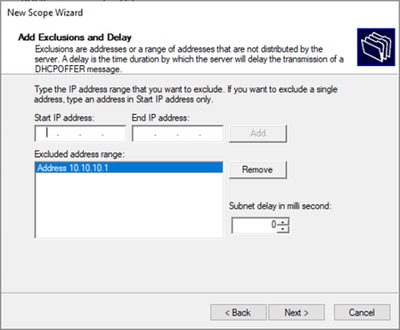
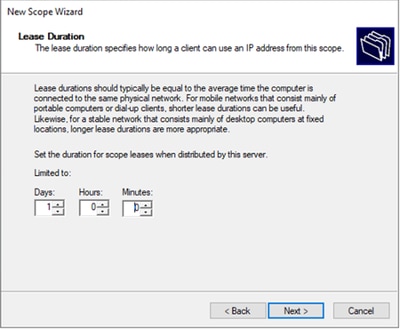
Passaggio 7. Configurare la durata del lease dell'indirizzo IP. Questo valore si riferisce alla quantità di tempo durante la quale un host può utilizzare l'indirizzo IP assegnato prima di rinnovarlo.
Passaggio 8. Selezionare Sì, configurare le opzioni ora.
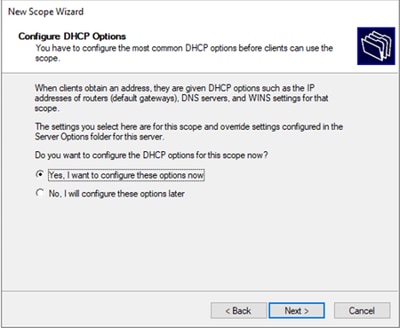
Passaggio 9. Configurare l'indirizzo IP del gateway predefinito.
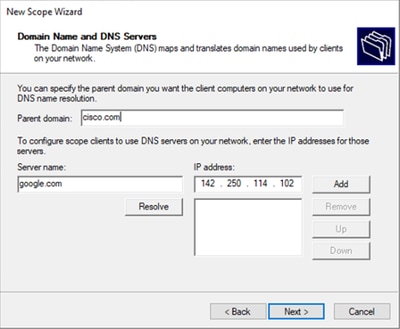
Passaggio 10. Configurare il nome di dominio e il server DNS.
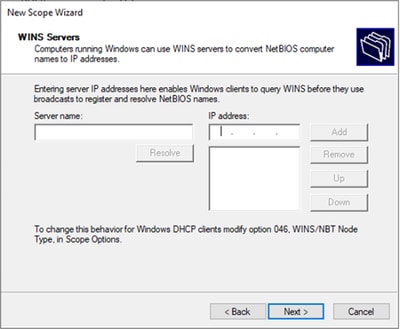
Passaggio 11. Configurare il server WINS, se applicabile. Questa operazione può essere ignorata se le informazioni non sono note.
Passaggio 12. Selezionare Sì, attiva l'ambito ora.
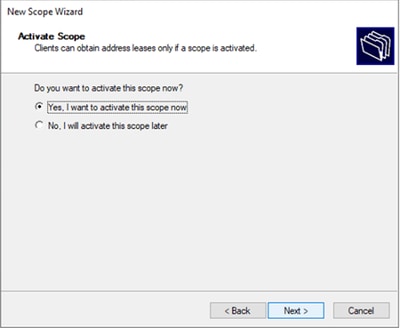
Configurazione dell'ambito per gli indirizzi IP univoci dai loopback in SVI come agente di inoltro DCHP.
Passaggio 1. Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su IPv4 e selezionare IPv4Scope.
 Nuovo ambito in DCHP
Nuovo ambito in DCHP
Passaggio 2. Scrivere un nome e una descrizione. In questo esempio, name è la subnet utilizzata per la subnet con indirizzo di loopback.

IPte: viene utilizzato un loopback per un indirizzo IP univoco loopback in tutta la struttura VxLAN per il tenant VxLAN. Questo deve essere annunciato nella ridistribuzione della route VPN BGP L2VPN in BGP all'interno del VRF del tenant corrispondente nell'indirizzo IPv4-famIPv4
LEAF-1# show running-config interface loopback 100
<snip>
interface loopback100
vrf member tenant-a
ip address 172.16.10.8/32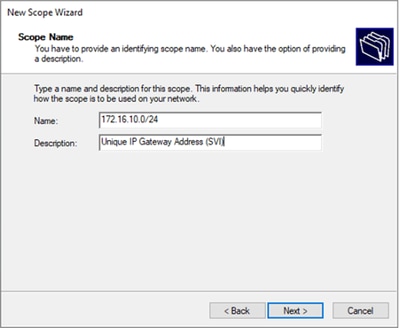
Passaggio 3. Configurare l'intervallo di indirizzi IPip. Pool di loopback.
Passaggio 4. Configurare le esclusioni (facoltativo perché il server DHCP non assegna in lease indirizzi IP appartenenti a questa subnet).
Passaggio 5. Ignorare la durata del lease e fare clic su Avanti.
Passaggio 6. Selezionare No. Queste opzioni verranno configurate in seguito.
Passaggio 7. Fare clic su Finish (Fine).
Passaggio 8. Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse sull'ambito creato e selezionare attiva.
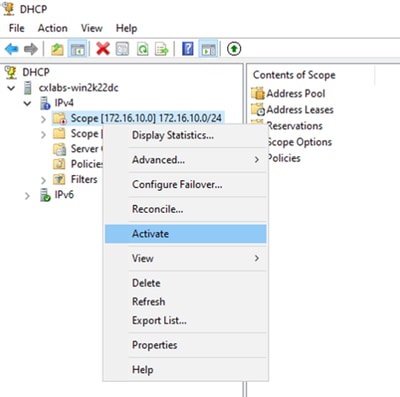
Configurazione dell'ambito esteso per l'infrastruttura VxLAN.
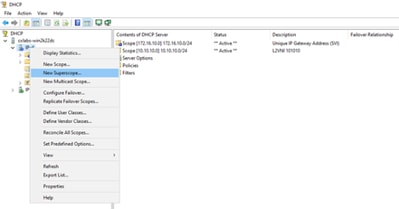
Passaggio 1. Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su IPv4 e selezionare Nuovo ambito esteso.
Passaggio 2. Fare clic su Next (Avanti).
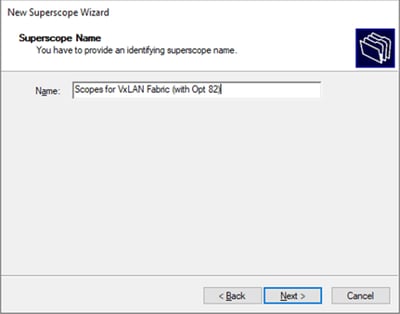
Passaggio 3. Scrivere il nome dell'ambito esteso.
Passaggio 4. Selezionare tutti gli ambiti che appartengono a VxLAN Fabric.
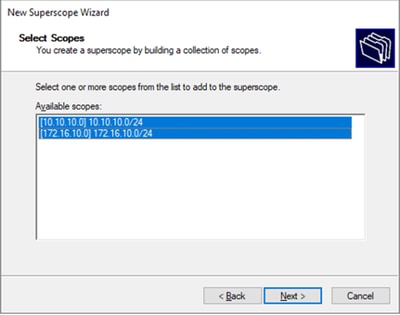
Passaggio 5. Selezionare tutti gli ambiti che appartengono a VxLAN Fabric.
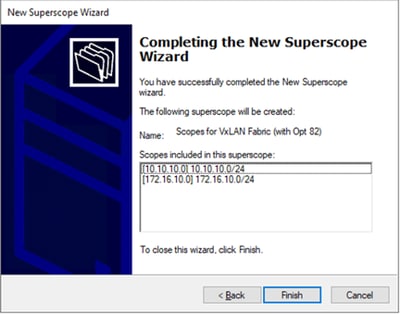
Passaggio 6. Verificare che tutto l'ambito esteso dell'infrastruttura VxLAN sia presente e fare clic su Fine.
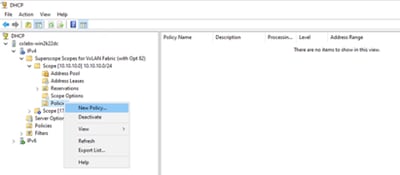
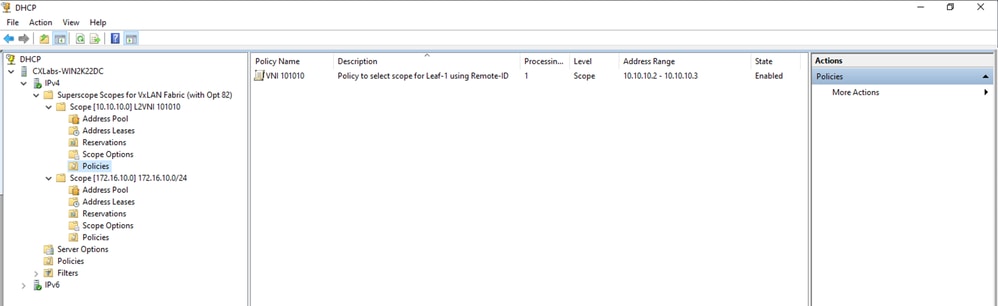
Configurare l'opzione 82 negli ambiti host.
Passaggio 1. Fare clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su Policy (ultima opzione) all'interno dell'ambito per l'host e fare clic su New Policy.
Passaggio 2. Scrivere un nome e una descrizione e fare clic su Avanti.

Nota: in questo esempio, il criterio viene creato per selezionare paIP di indirizzamento IP, in particolare per gli host in Leaf-1 per VNI 101010 basedVNI Remote-ID (parametro dell'opzione 82).
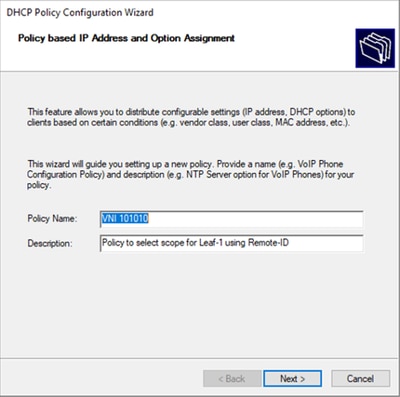
Passaggio 3. Fare clic su Add. In Criteri, selezionare Inoltra informazioni sull'agente. In Operatore, selezionare Uguale a. Quindi selezionare Agent Remote ID e digitare il valore. Fare clic su OK, quindi su Avanti.

Nota: l'ID remoto viene ottenuto dall'indirizzo MAC dell'SVI a cui è associata la SVI.

Suggerimento: è possibile applicare un criterio a più ID remoti (o VTEP) aggiungendo ulteriori condizioni e selezionando OR anziché AND.
LEAF-1# show interface vlan 10
Vlan10 is up, line protocol is up, autostate enabled
Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 707d.b9b8.4daf <<<<
Internet Address is 10.10.10.1/24
<snip>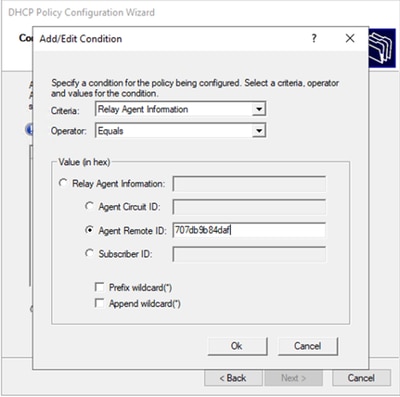
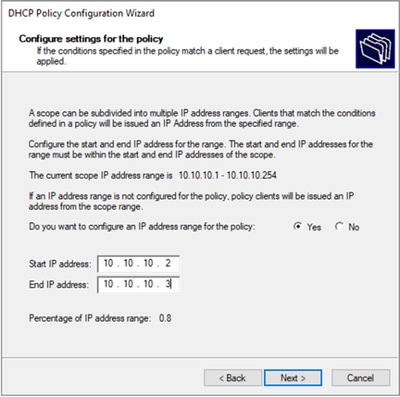
Passaggio 4. Configurare l'indirizzo IP che gli indirizzi IP esistenti possono utilizzare sui VTEP selezionati dall'ID, quindi fare clic su Avanti.

Nota: in questo esempio esiste solo una macchina virtuale connessa a Foglia-1, quindi è richiesto un solo indirizzo IP. Qui viene aggiunto un secondo indirizzo IPn caso un altro host si connetta.
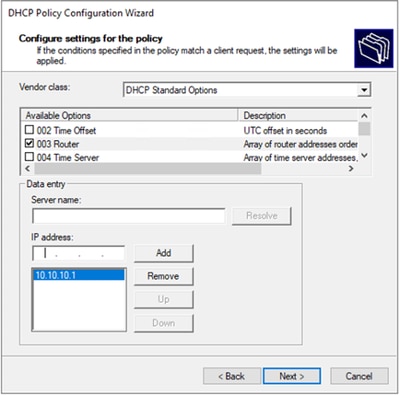
Passaggio 5. Selezionare la casella a sinistra di 003 Router in DCHP Standard Option. Scrivere quindi l'indirizzo IP del gateway predefinito per gli host che appartengono a questo criterio e premere Aggiungi. Fare clic su Next (Avanti).

Attenzione: è possibile selezionare più di un'opzione, ma in caso di dubbi sul valore da immettere, non selezionarla. Una configurazione incoerente o errata può causare un comportamento imprevisto.
Passaggio 6. Verificare le condizioni dei criteri e fare clic su Fine.
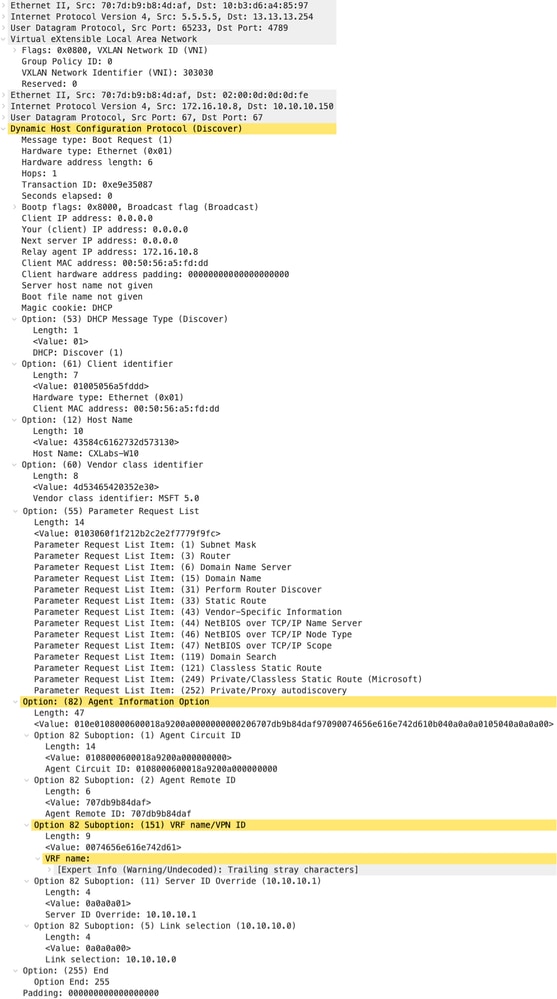
Packet-walk DCHP dall'inizio alla fine in VxLAN Fabric.
Discovery inviato dall'HOST-1
 |
Rilevamento su FOGLIA-1
| Rilevamento ricevuto su LEAF-1 | Individuazione invio da FOGLIA-1 |
 |
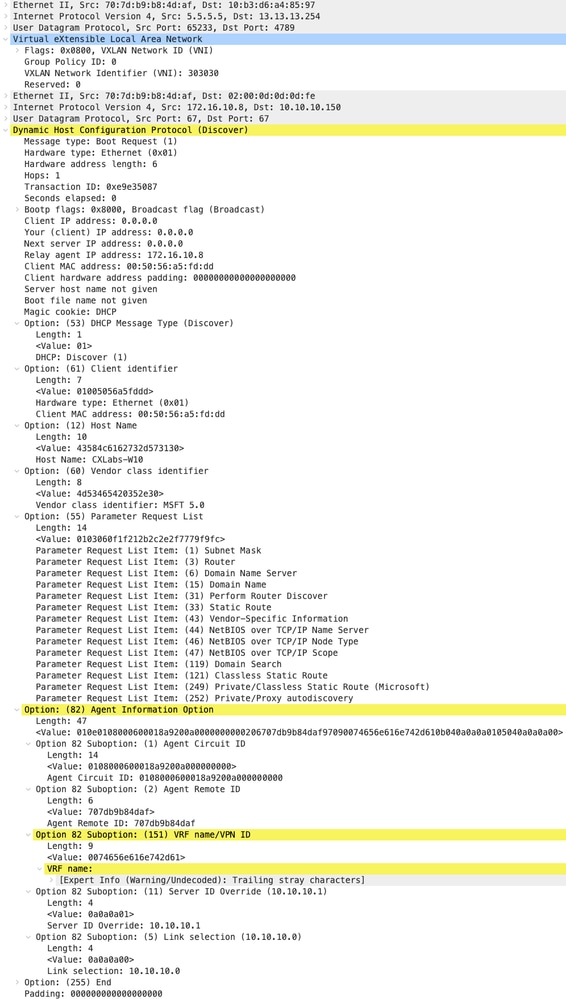 |

Suggerimento: quando si fa doppio clic, l'immagine si ingrandisce.
Rilevamento sul dorso
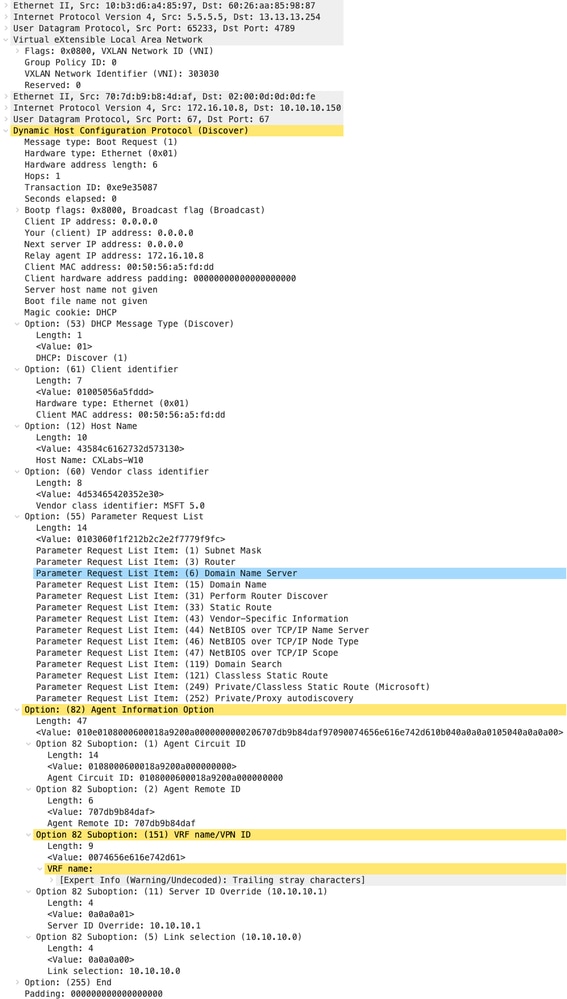
| Rilevamento ricevuto su SPINE | Individuazione invio per SPINE |
|
|
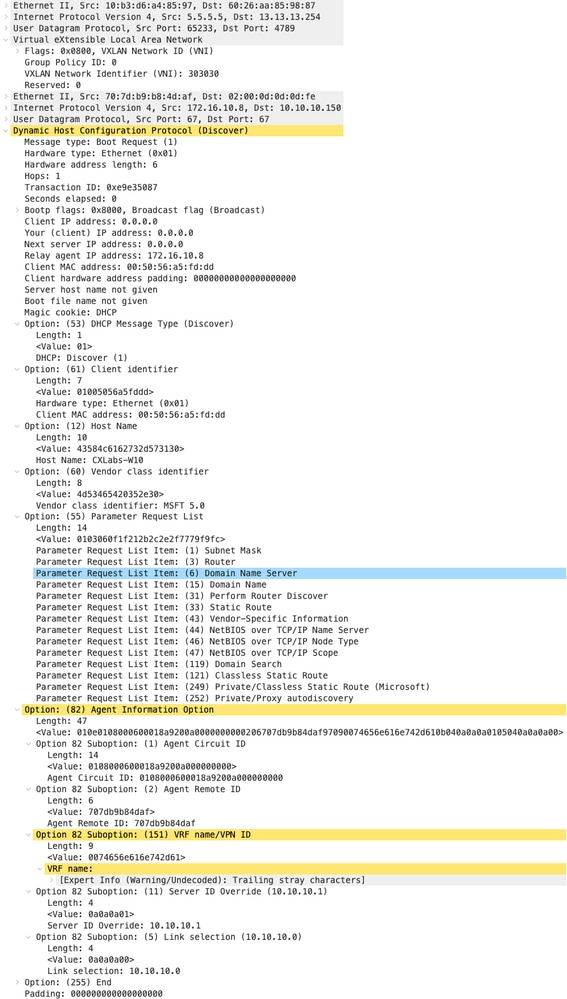 |
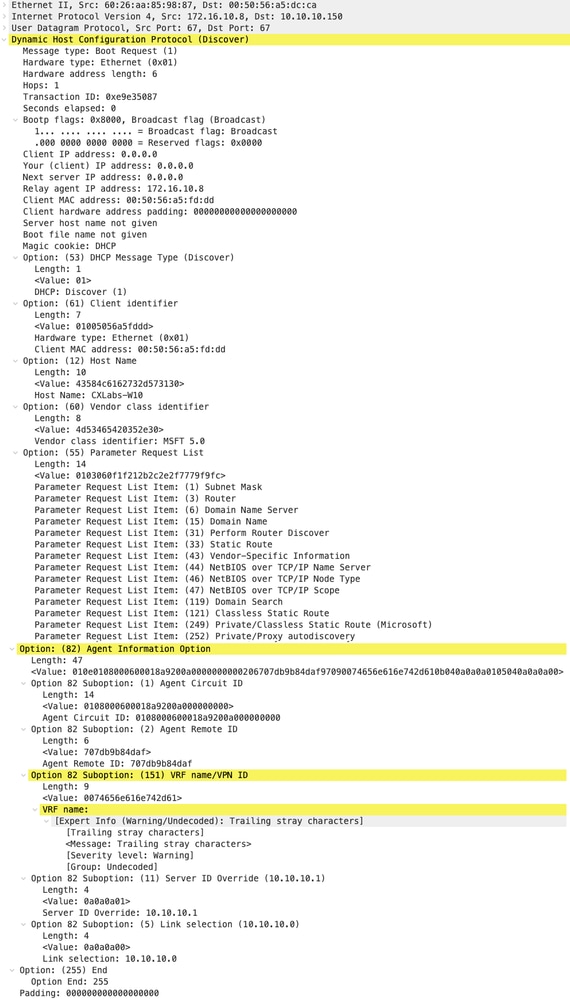
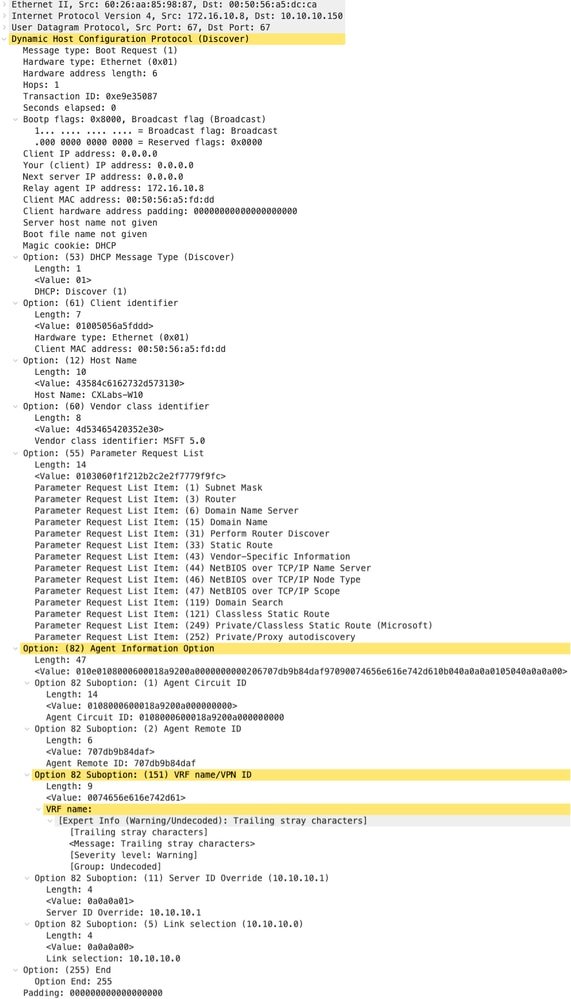
Discovery su LEAF-1-vPC
| Rilevamento ricevuto su LEAF-1-vPC | Discovery inviato da LEAF-1-vPC |
 |
 |

Nota: LEAF-2-vPC riceve il pacchetto Discovert, ma è solo commutato. L'indirizzo MAC di destinazione appartiene al server DHCP.
Rilevamento ricevuto sul server DHCP
 |
Offerta DHCP inviata dal server DHCP
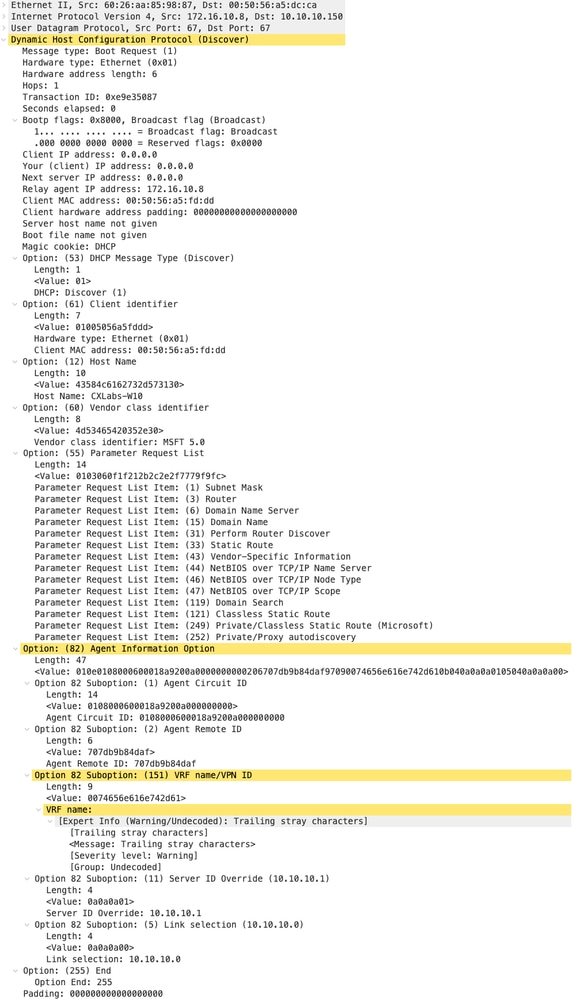 |
Offerta DHCP su LEAF-2-vPC
| Offerta ricevuta su LEAF-2-vPC | Offerta inviata da LEAF-2-vPC |
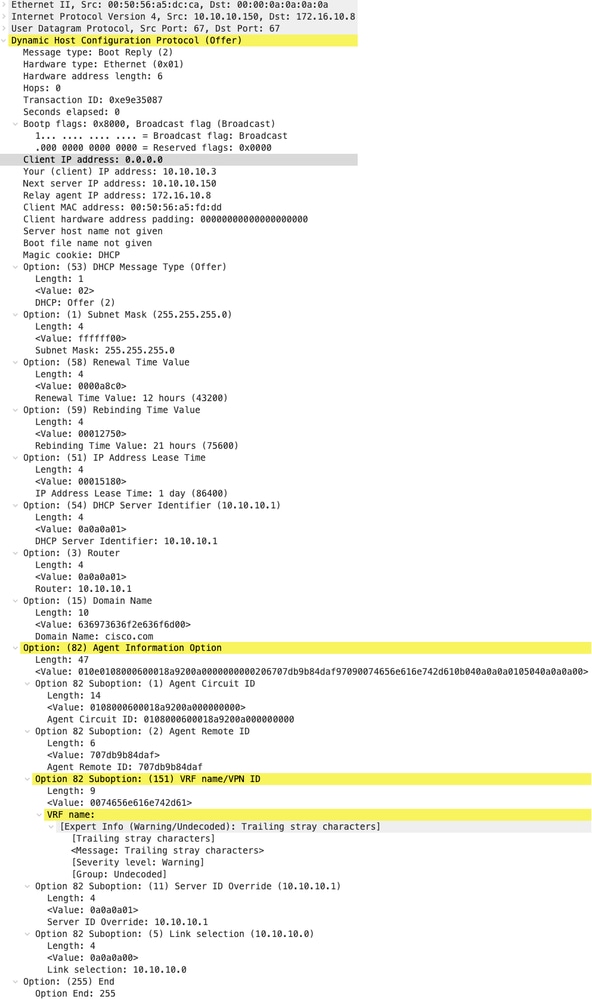 |
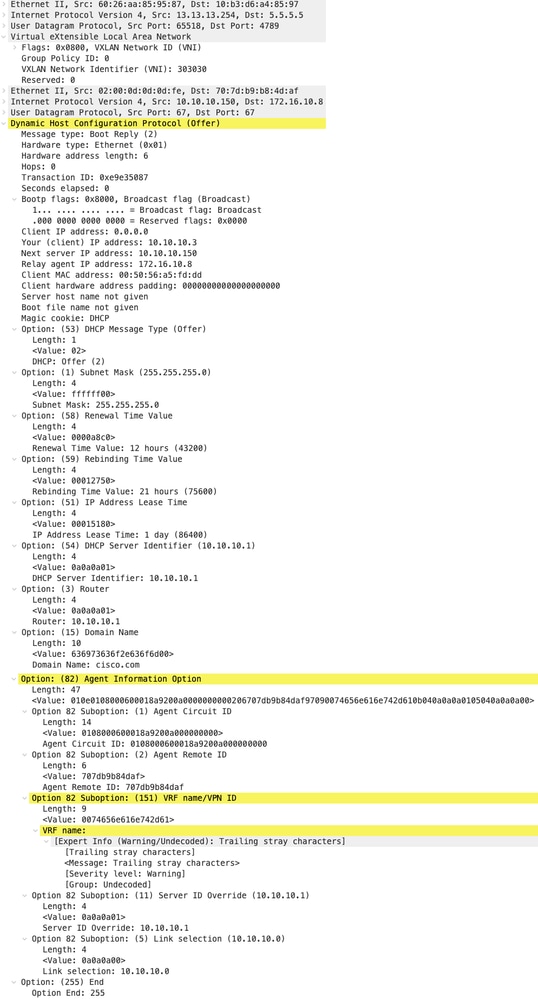 |
Offerta DHCP vPC SPINE
| Offerta ricevuta su SPINE | Invia offerta per SPINE |
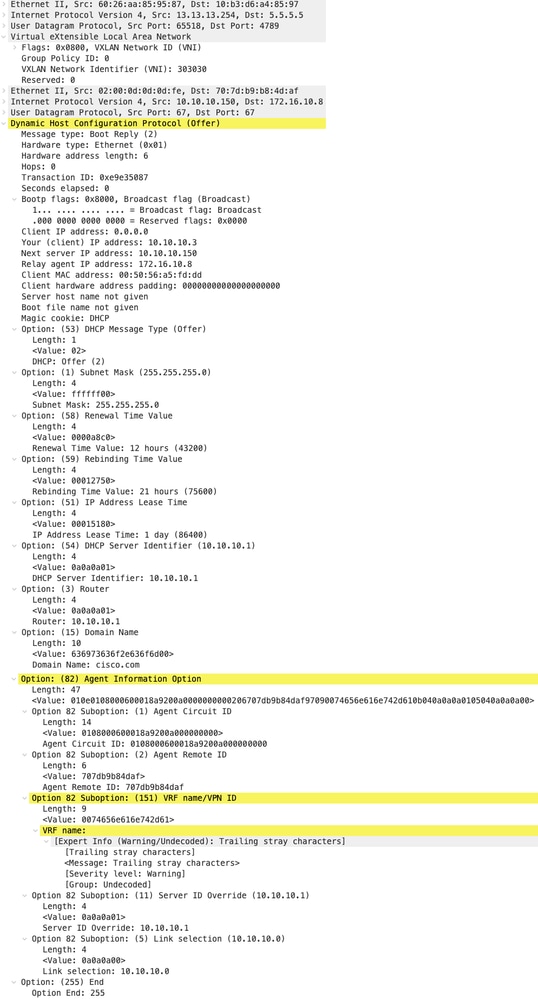 |
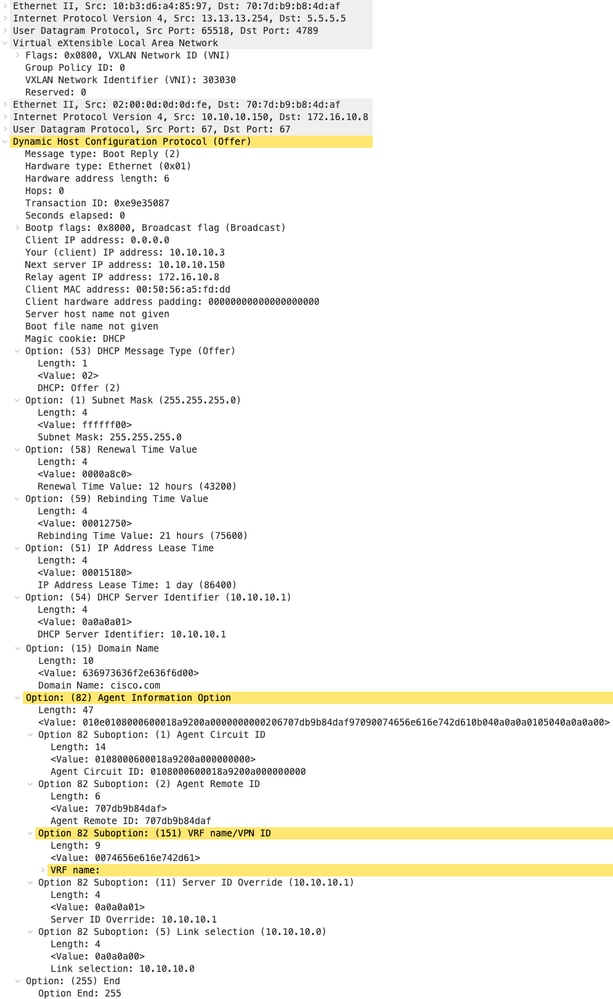 |
Offerta DHCP su LEAF-1
| Offerta ricevuta su LEAF-1 | Invio offerta su FOGLIA-1 |
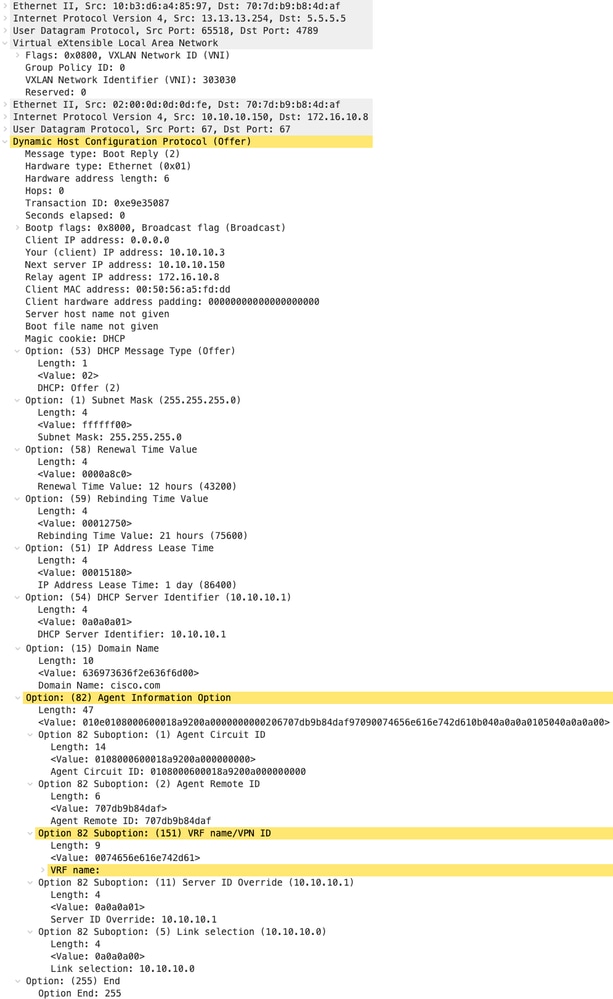 |
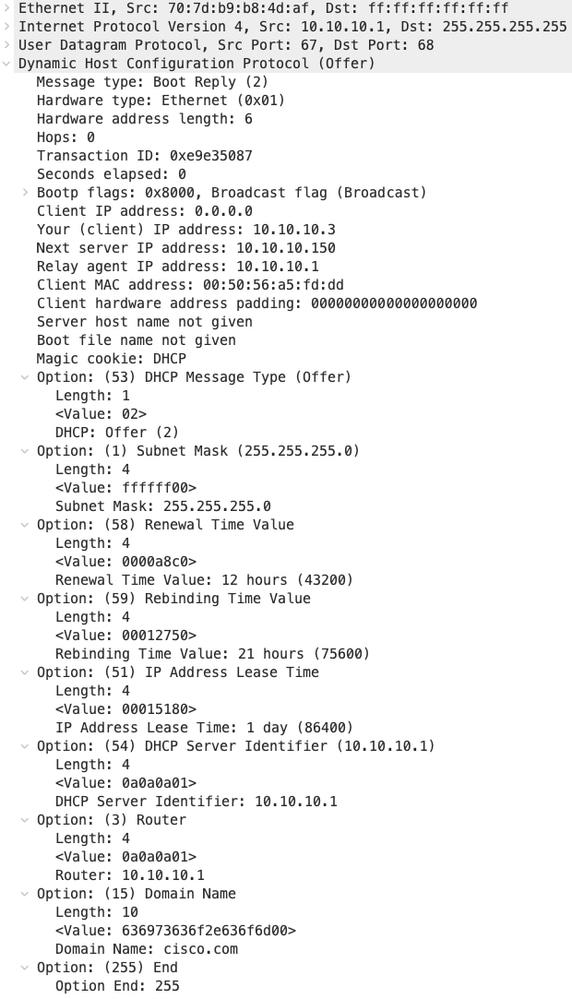 |
Offerta DHCP ricevuta su HOST-1
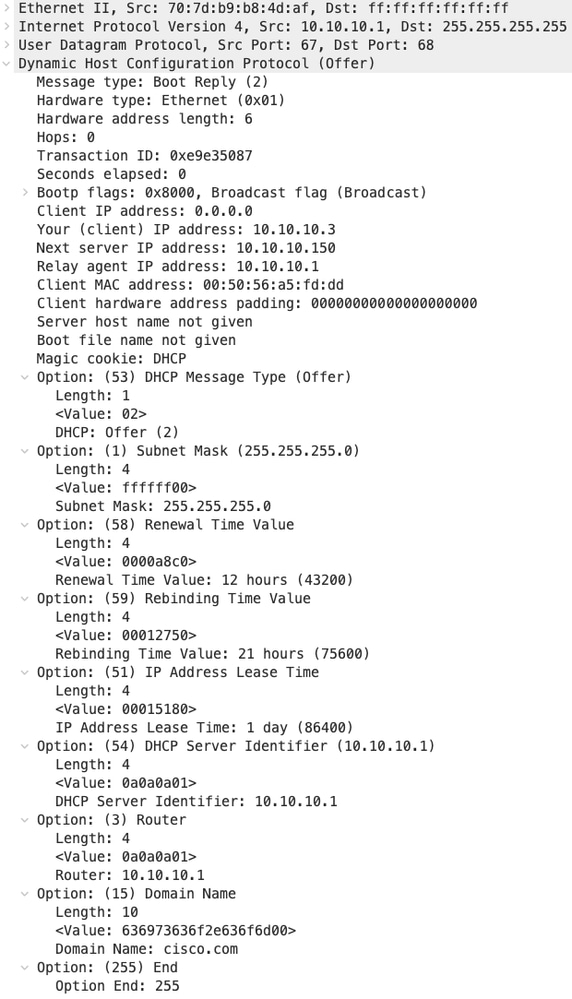 |
Richiesta inviata da HOST-1
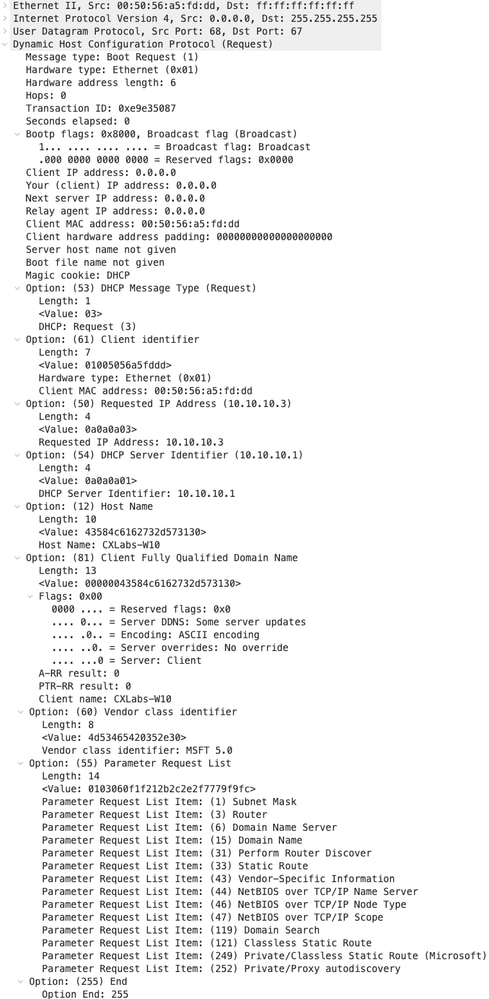 |
Richiesta su FOGLIA-1
| Richiesta ricevuta su LEAF-1 | Richiesta inviata da LEAF-1 |
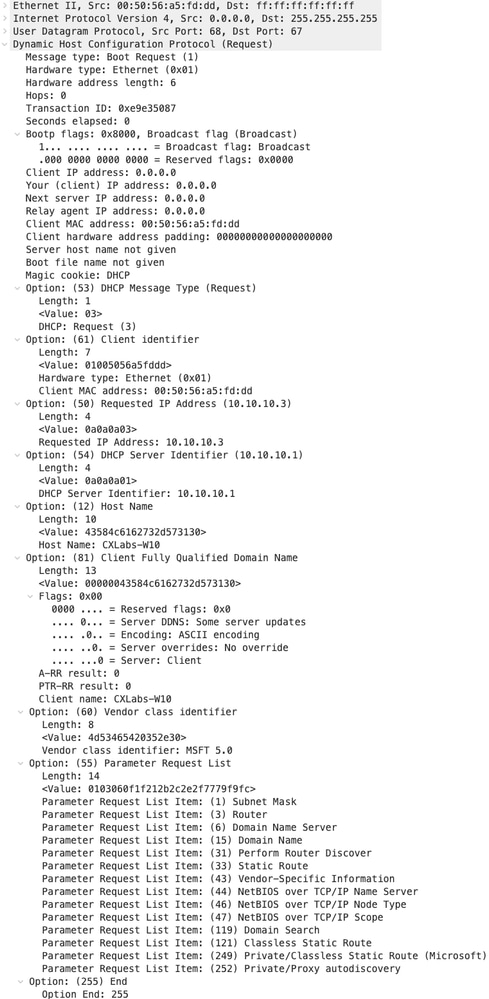 |
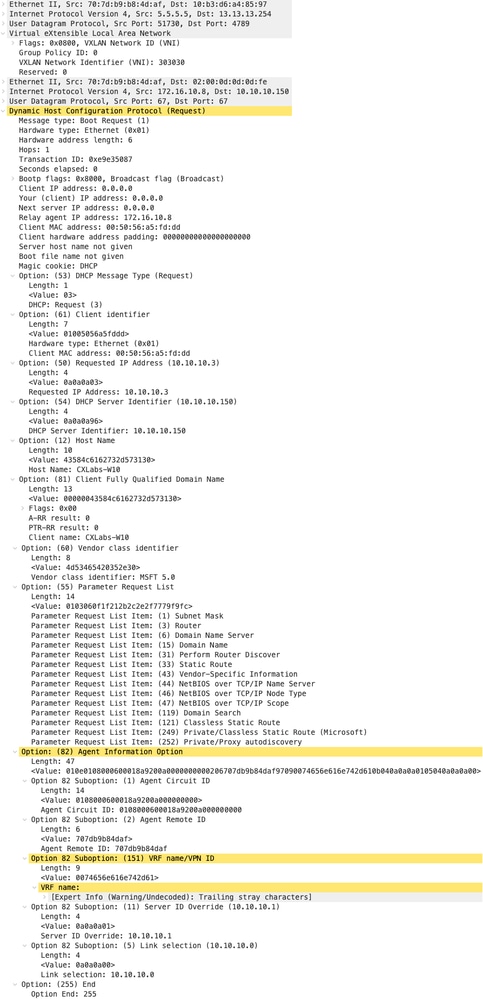 |
Richiesta sul dorso
| Richiesta ricevuta su SPINE | Richiesta inviata da SPINE |
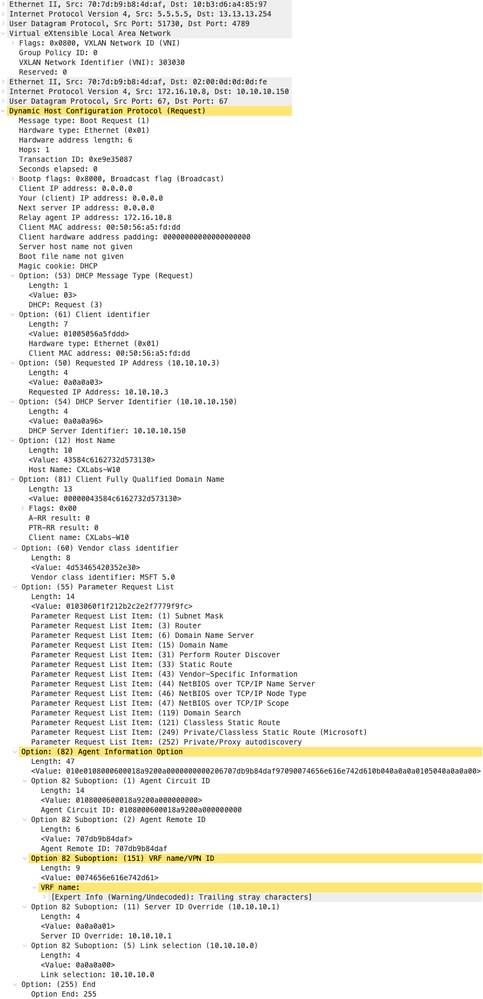 |
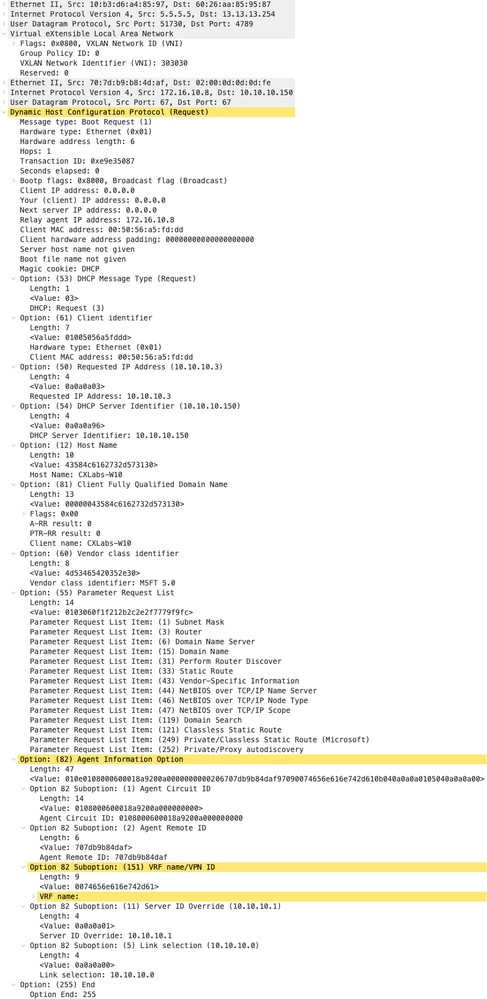 |
Richiesta su LEAF-2-vPC
| Richiesta receivePCd su LEAF-2-vPC | Richiesta di invio tramite vPCAF-2-vPC |
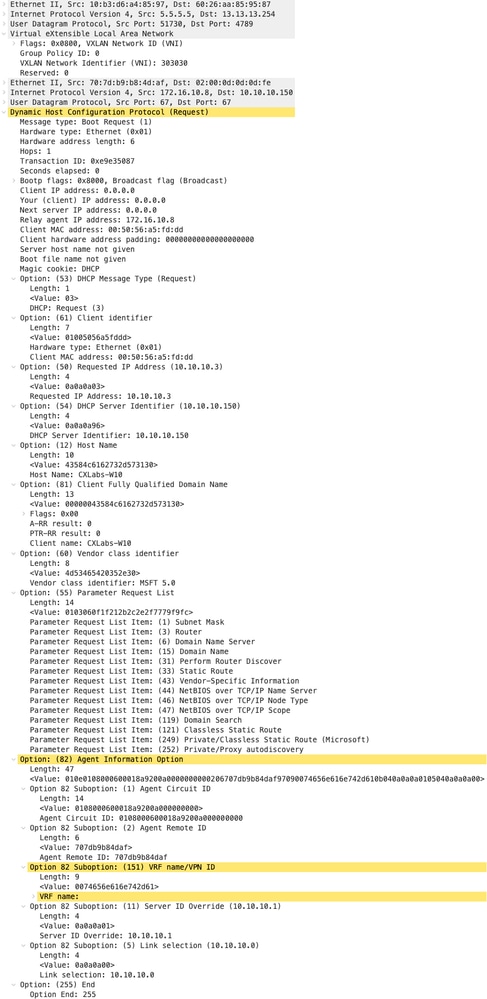 |
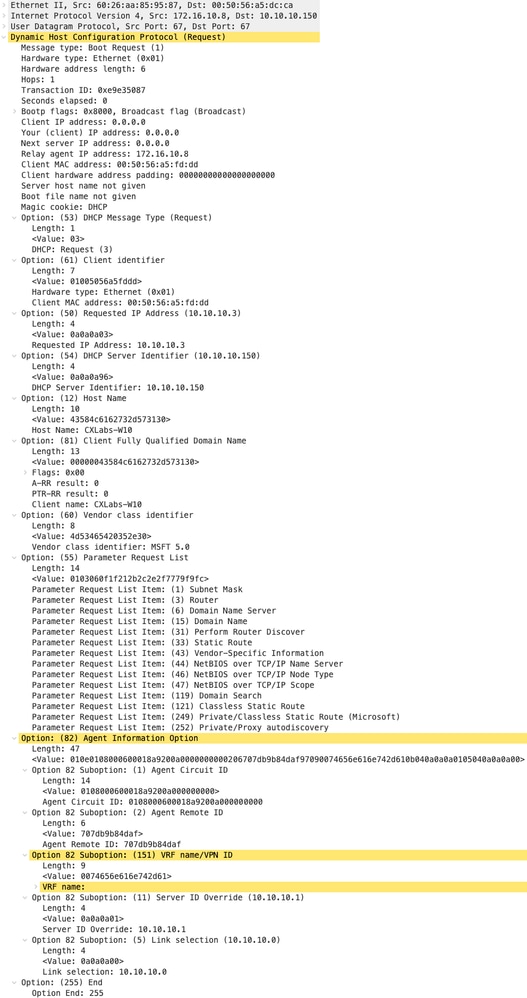 |
Richiesta ricevuta sul server DHCP
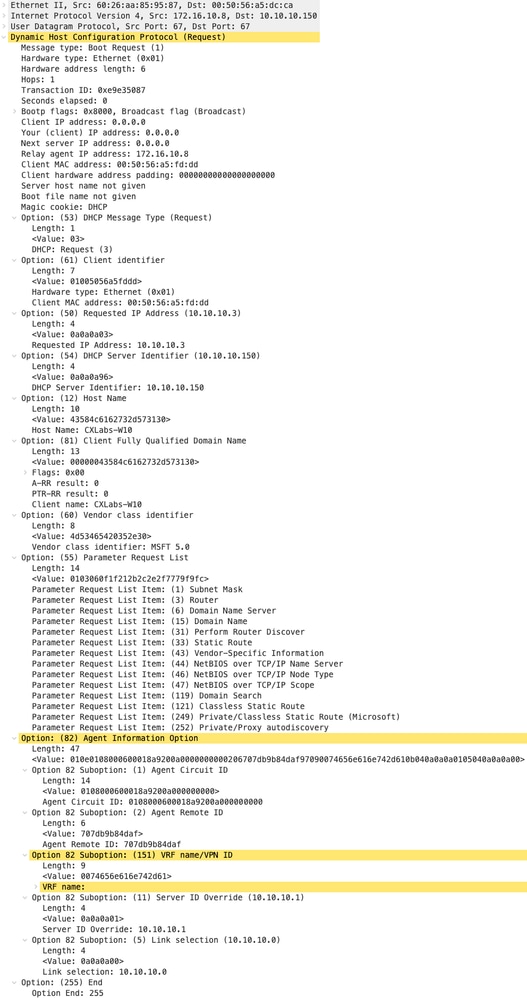 |
Invio ACK dal server DHCP
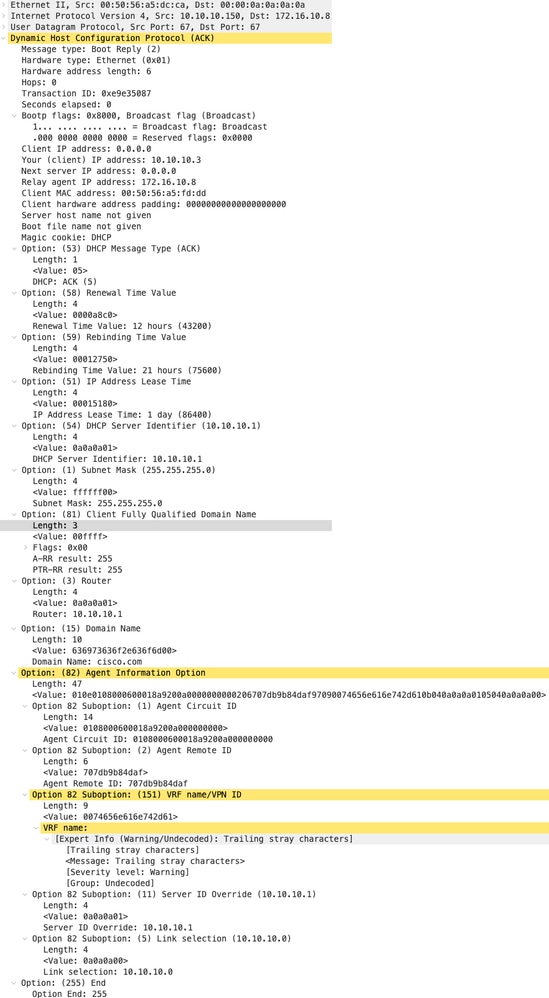 |
ACK su LEAF-2-vPC
| ACK ricevuti su LEAF-2-vPC | ACK inviati da LEAF-2-vPC |
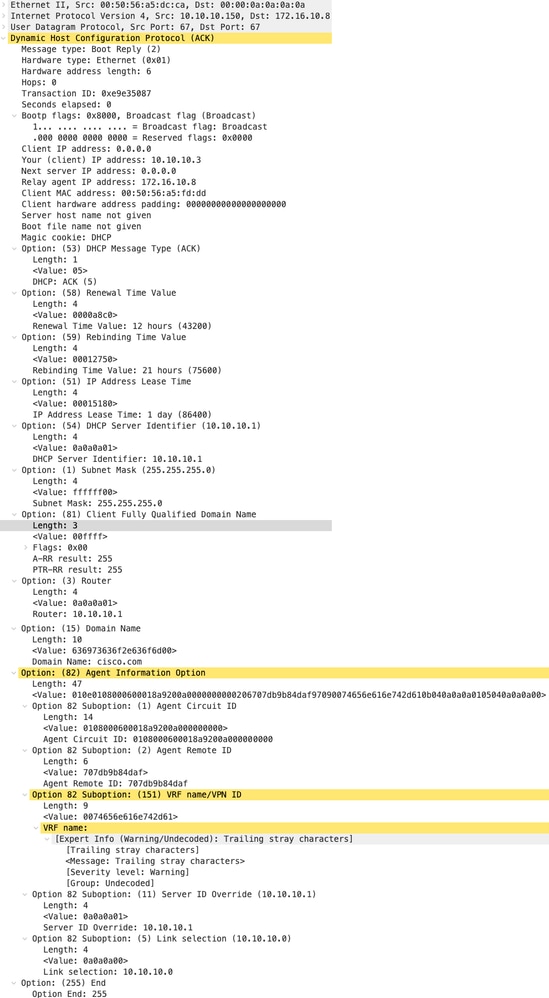 |
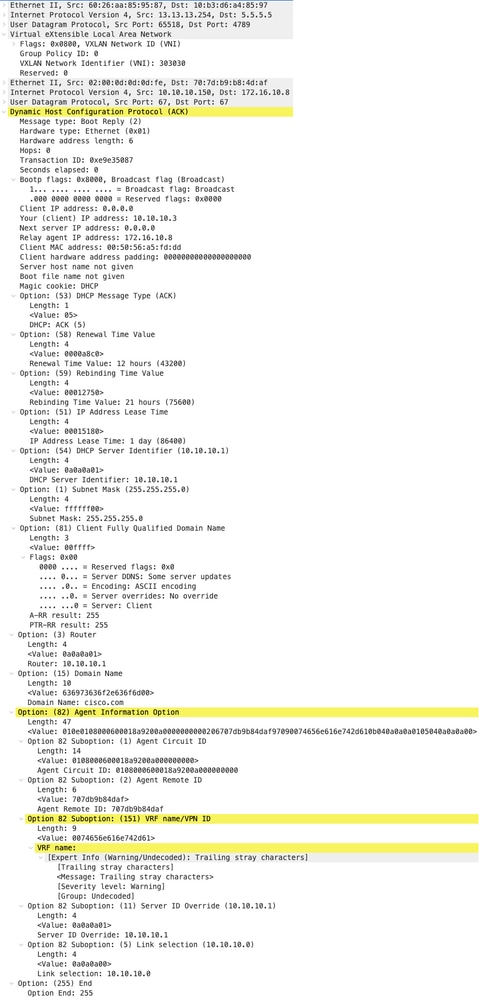 |
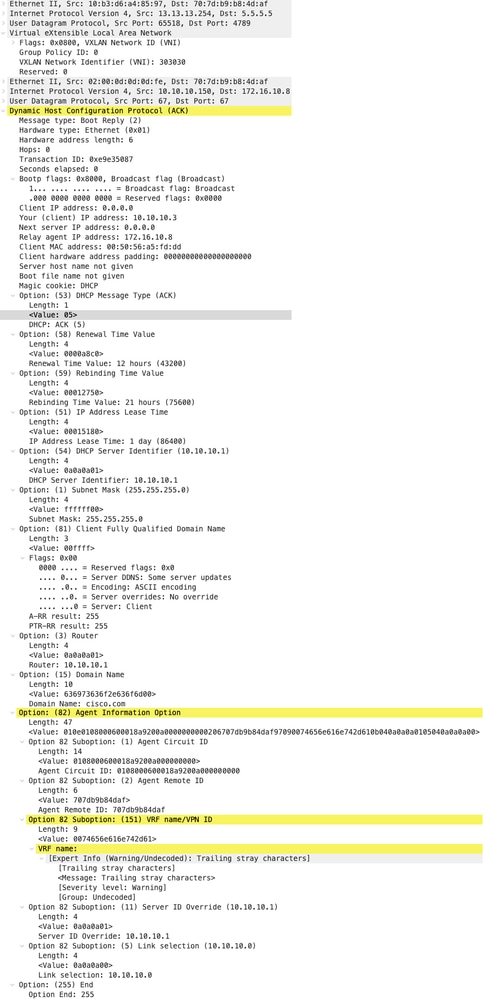
ACK sul DORSO
| ACK ricevuti su SPINE | ACK inviati da SPINE |
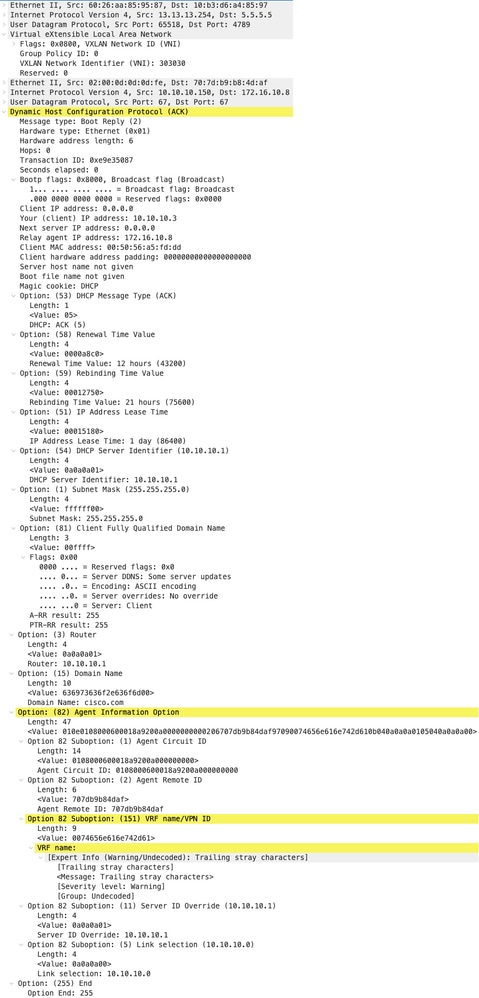 |
 |
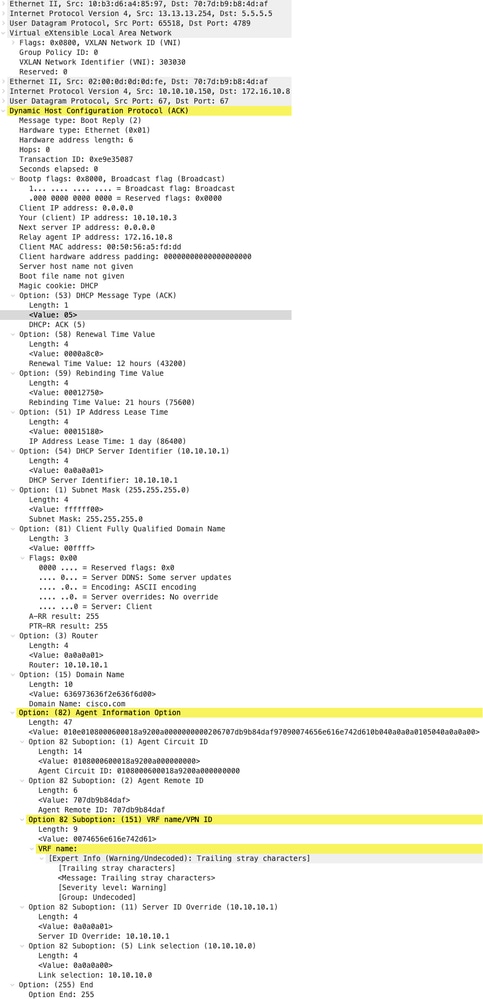
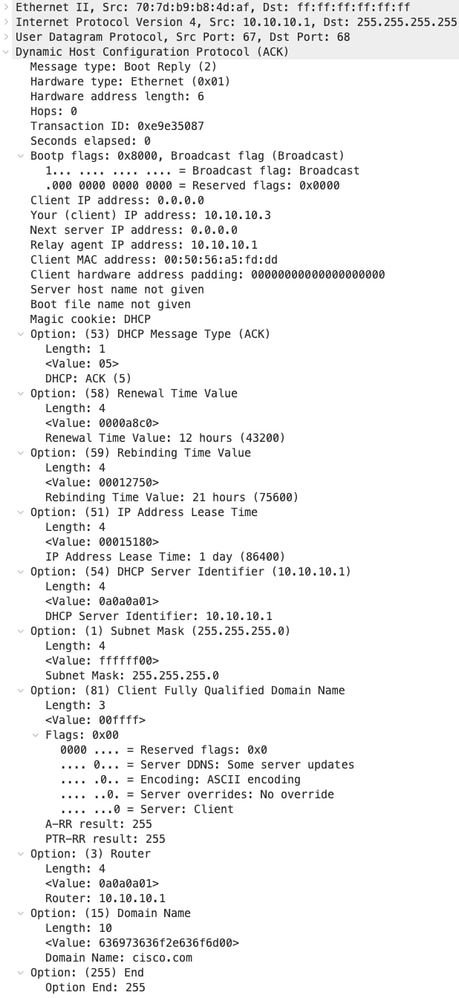
ACK su FOGLIA-1
| ACK ricevuti su FOGLIA-1 | ACK inviati da FOGLIA-1 |
 |
 |
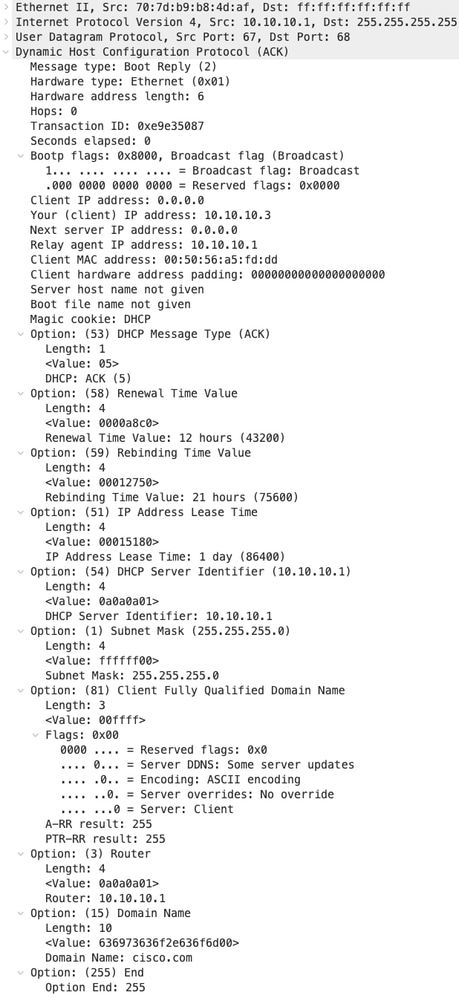
ACK su HOST-1
 |
Informazioni correlate
Configurazione di VXLAN BGP VPN
Risoluzione dei problemi relativi a DHCP su Nexus 9000
Guida alla configurazione di Cisco Nexus serie 9000 NX-OS VXLAN, versione 10.4(x)
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
29-Apr-2024 |
Versione iniziale |
Contributo dei tecnici Cisco
- David Martinez AguilarTecnico di consulenza
- Jose Antonio Vazquez GabianTecnico di consulenza
 Feedback
Feedback