Esempi di configurazioni e debug di IPSec Over Cable
Sommario
Introduzione
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) è una struttura di standard aperti che assicura comunicazioni private protette su reti IP. Basato sugli standard sviluppati dalla Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), IPsec garantisce la riservatezza, l'integrità e l'autenticità delle comunicazioni dei dati su una rete IP pubblica. IPsec è un componente necessario per una soluzione flessibile e basata su standard per l'implementazione di criteri di sicurezza a livello di rete.
In questo documento viene illustrato un esempio di configurazione di IPsec tra due modem cablati Cisco. Questa configurazione crea un tunnel di crittografia su una rete cablata tra due router modem cablati Cisco serie uBR9xx. Tutto il traffico tra le due reti è crittografato. Tuttavia, il traffico destinato ad altre reti può passare non crittografato. Per gli utenti di uffici di piccole dimensioni o privati (SOHO), questa soluzione consente di creare reti VPN (Virtual Private Network) su una rete cablata.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Nessun requisito specifico previsto per questo documento.
Componenti usati
Per configurare IPsec su due modem via cavo, i modem devono essere conformi ai seguenti requisiti:
-
Cisco uBR904, uBR905 o uBR924 in modalità di routing
-
Set funzionalità IPsec 56
-
Software Cisco IOS® versione 12.0(5)T o successive
Inoltre, è necessario disporre di un CMTS (Cable Modem Termination System), ovvero un router di cavi headend conforme alle specifiche dell'interfaccia di servizio Data-Over-Cable (DOCSIS), ad esempio Cisco uBR7246, Cisco uBR7223 o Cisco uBR7246VXR.
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Convenzioni
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni usate, consultare il documento Cisco sulle convenzioni nei suggerimenti tecnici.
Nozioni di base
Nell'esempio riportato in questo documento viene usato un modem via cavo uBR904, un modem cablato uBR924 e un CMTS uBR7246VXR. I modem via cavo eseguono il software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(6), mentre il CMTS esegue il software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(4)EC.
Nota: questo esempio viene eseguito con la configurazione manuale sui modem via cavo tramite la porta console. Se si esegue un processo automatico tramite il file di configurazione DOCSIS (lo script ios.cfg viene creato con la configurazione IPsec), gli elenchi degli accessi 100 e 101 non possono essere utilizzati. Infatti, l'implementazione Cisco della tabella docsDevNmAccess del protocollo SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) utilizza gli elenchi degli accessi Cisco IOS. Viene creato un elenco degli accessi per interfaccia. Sugli uBR904, 924 e 905 vengono in genere utilizzati i primi due elenchi degli accessi (100 e 101). Su un modem via cavo che supporta USB (Universal Serial Bus), come il CVA120, vengono utilizzati tre elenchi degli accessi (100, 101 e 102).
Configurazione
In questa sezione vengono presentate le informazioni necessarie per configurare le funzionalità descritte più avanti nel documento.
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi menzionati in questo documento, usare lo strumento di ricerca dei comandi (solo utenti registrati).
Esempio di rete
Nel documento viene usata questa impostazione di rete:
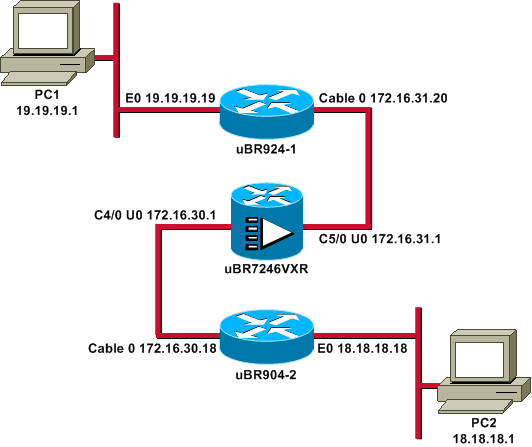
Nota: tutti gli indirizzi IP riportati nel diagramma hanno una maschera a 24 bit.
Configurazioni
Nel documento vengono usate queste configurazioni:
| uBR924-1 |
|---|
service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname ubr924-1 ! enable password ww ! ! ! ! clock timezone - -8 ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ! ! crypto isakmp policy 10 !--- Creates an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) policy with the specified priority !--- number of 10. The range for the priority is 1 to 10000, where 1 is the !--- highest priority. This command also enters Internet Security Association !--- and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) policy configuration command mode. hash md5 !--- Specifies the MD5 (HMAC variant) hash algorithm for packet authentication. authentication pre-share !--- Specifies that the authentication keys are pre-shared, as opposed to !--- dynamically negotiated using Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman (RSA) public !--- key signatures. group 2 !--- Diffie-Hellman group for key negotiation. lifetime 3600 !--- Defines how long, in seconds, each security association should exist before !--- it expires. Its range is 60 to 86400, and in this case, it is 1 hour. crypto isakmp key mykey address 18.18.18.18 !--- Specifies the pre-shared key that should be used with the peer at the !--- specific IP address. The key can be any arbitrary alphanumeric key up to !--- 128 characters. The key is case-sensitive and must be entered identically !--- on both routers. In this case, the key is mykey and the peer is the !--- Ethernet address of uBR904-2 . ! crypto IPSec transform-set TUNNELSET ah-md5-hmac esp-des !--- Establishes the transform set to use for IPsec encryption. As many as !--- three transformations can be specified for a set. Authentication Header !--- and ESP are in use. Another common transform set used in industry is !--- esp-des esp-md5-hmac. ! crypto map MYMAP local-address Ethernet0 !--- Creates the MYMAP crypto map and applies it to the Ethernet0 interface. crypto map MYMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp !--- Creates a crypto map numbered 10 and enters crypto map configuration mode. set peer 18.18.18.18 !--- Identifies the IP address for the destination peer router. In this case, !--- the Ethernet interface of the remote cable modem (ubr904-2) is used. set transform-set TUNNELSET !--- Sets the crypto map to use the transform set previously created. match address 101 !--- Sets the crypto map to use the access list that specifies the type of !--- traffic to be encrypted. !--- Do not use access lists 100, 101, and 102 if the IPsec config is !--- downloaded through the ios.cfg in the DOCSIS configuration file. ! ! ! ! voice-port 0 input gain -2 output attenuation 0 ! voice-port 1 input gain -2 output attenuation 0 ! ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 19.19.19.19 255.255.255.0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface cable-modem0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache cable-modem downstream saved channel 525000000 39 1 cable-modem mac-timer t2 40000 no cable-modem compliant bridge crypto map MYMAP !--- Applies the previously created crypto map to the cable interface. ! router rip version 2 network 19.0.0.0 network 172.16.0.0 ! ip default-gateway 172.16.31.1 ip classless ip http server ! access-list 101 permit ip 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 !--- Access list that identifies the traffic to be encrypted. In this case, !--- it is setting traffic from the local Ethernet network to the remote !--- Ethernet network. snmp-server manager ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 password ww login ! end |
La configurazione dell'altro modem via cavo è molto simile, quindi la maggior parte dei commenti della configurazione precedente vengono omessi.
| uBR904-2 |
|---|
version 12.1 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname ubr904-2 ! enable password ww ! ! ! ! ! clock timezone - -8 ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! ! ! crypto isakmp policy 10 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 lifetime 3600 crypto isakmp key mykey address 19.19.19.19 ! ! crypto IPSec transform-set TUNNELSET ah-md5-hmac ESP-Des ! crypto map MYMAP local-address Ethernet0 crypto map MYMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 19.19.19.19 !--- Identifies the IP address for the destination peer router. In this case, !--- the Ethernet interface of the remote cable modem (uBR924-1) is used. set transform-set TUNNELSET match address 101 ! ! ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 18.18.18.18 255.255.255.0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 ! interface cable-modem0 ip rip send version 2 ip rip receive version 2 no keepalive cable-modem downstream saved channel 555000000 42 1 cable-modem Mac-timer t2 40000 no cable-modem compliant bridge crypto map MYMAP ! router rip version 2 network 18.0.0.0 network 172.16.0.0 ! ip default-gateway 172.16.30.1 ip classless no ip http server ! access-list 101 permit ip 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 snmp-server manager ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 password ww login ! end |
Il CMTS uBR7246VXR esegue anche il Routing Information Protocol (RIP) versione 2, in modo che il routing funzioni. Questa è la configurazione RIP utilizzata nel CMTS:
| uBR7246VXR |
|---|
router rip version 2 network 172.16.0.0 no auto-summary |
Verifica
Per verificare che la configurazione funzioni correttamente, consultare questa sezione.
Per verificare che IPsec funzioni:
-
Verificare quanto segue:
-
Il software Cisco IOS supporta IPsec.
-
La configurazione corrente è corretta.
-
Interfacce attive.
-
Il routing funziona.
-
L'elenco degli accessi definito per crittografare il traffico è corretto.
-
-
Creare il traffico e verificare i parametri Encrypt e Decrypt per verificare la quantità in aumento.
-
Attivare i debug per la crittografia.
Lo strumento Output Interpreter (solo utenti registrati) (OIT) supporta alcuni comandi show. Usare l'OIT per visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show.
Eseguire il comando show version su entrambi i modem via cavo.
ubr924-1#show version Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) 920 Software (UBR920-K1O3SV4Y556I-M), Version 12.1(6), RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Copyright (c) 1986-2000 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Wed 27-Dec-00 16:36 by kellythw Image text-base: 0x800100A0, data-base: 0x806C1C20 ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 12.0(6r)T3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) ubr924-1 uptime is 1 hour, 47 minutes System returned to ROM by reload at 10:39:05 - Fri Feb 9 2001 System restarted at 10:40:05 - Fri Feb 9 2001 System image file is "flash:ubr920-k1o3sv4y556i-mz.121-6" cisco uBR920 CM (MPC850) processor (revision 3.e) with 15872K/1024K bytes of memory. Processor board ID FAA0422Q04F Bridging software. 1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 1 Cable Modem network interface(s) 3968K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write) 1536K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write) Configuration register is 0x2102
L'uBR924-1 esegue il software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(6) con il set di funzionalità VALUE SMALL OFFICE/VOICE/FW IPSec 56.
ubr904-2#show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (TM) 900 Software (UBR900-K1OY556I-M), Version 12.1(6),
RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Copyright (c) 1986-2000 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 27-DEC-00 11:06 by kellythw
Image text-base: 0x08004000, database: 0x085714DC
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.2(19980518:195057), RELEASED SOFTWARE
ROM: 900 Software (UBR900-RBOOT-M), Version 11.3(11)NA,
EARLY DEPLOYMENT RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
ubr904-2 uptime is 1 hour, 48 minutes
System returned to ROM by reload at 10:38:44 - Fri Feb 9 2001
System restarted at 10:40:37 - Fri Feb 9 2001
System image file is "flash:ubr900-k1oy556i-mz.121-6"
cisco uBR900 CM (68360) processor (revision D)
with 8192K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FAA0235Q0ZS
Bridging software.
1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
1 Cable Modem network interface(s)
4096K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)
2048K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write)
Configuration register is 0x2102
L'uBR904-2 esegue il software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(6) con una serie di funzioni SMALL OFFICE/FW IPSec 56.
ubr924-1#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet0 19.19.19.19 YES NVRAM up up cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 YES unset up up ubr904-2#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet0 18.18.18.18 YES NVRAM up up cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 YES unset up up
Dall'ultimo comando, è possibile vedere che le interfacce Ethernet sono attive. Gli indirizzi IP delle interfacce Ethernet sono stati immessi manualmente. Anche le interfacce dei cavi sono attive e hanno imparato i loro indirizzi IP tramite DHCP. Poiché gli indirizzi dei cavi sono assegnati in modo dinamico, non possono essere utilizzati come peer nella configurazione IPSec.
ubr924-1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - ISIS level-1, L2 - ISIS level-2, ia - ISIS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.31.1 to network 0.0.0.0
19.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 19.19.19.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0
R 18.0.0.0/8 [120/2] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 3 masks
R 172.16.135.0/25 [120/1] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
R 172.16.29.0/27 [120/1] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
R 172.16.30.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:23, cable-modem0
C 172.16.31.0/24 is directly connected, cable-modem0
R 192.168.99.0/24 [120/3] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:24, cable-modem0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 10.10.10.0 [120/2] via 172.16.31.1, 00:00:24, cable-modem0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.31.1
Da questo output si può vedere che l'uBR924-1 sta apprendendo la route 18.18.18.0, l'interfaccia Ethernet dell'uBR904-2.
ubr904-2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - ISIS, L1 - ISIS level-1, L2 - ISIS level-2, IA - ISIS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.30.1 to network 0.0.0.0
R 19.0.0.0/8 [120/2] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
18.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 18.18.18.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 3 masks
R 172.16.135.0/25 [120/1] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
R 172.16.29.224/27 [120/1] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
C 172.16.30.0/24 is directly connected, cable-modem0
R 172.16.31.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:17, cable-modem0
R 192.168.99.0/24 [120/3] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:18, cable-modem0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 10.10.10.0 [120/2] via 172.16.30.1, 00:00:18, cable-modem0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.30.1
Dalla tabella di routing dell'uBR904-2, si può notare che la rete per l'Ethernet dell'uBR924-1 è nella tabella di routing.
Nota: in alcuni casi, non è possibile eseguire un protocollo di routing tra i due modem via cavo. In questi casi, è necessario aggiungere percorsi statici sul CMTS per indirizzare il traffico sulle interfacce Ethernet dei modem via cavo.
La prossima cosa da verificare è la certificazione dell'elenco degli accessi; usare il comando show access-lists su entrambi i router.
ubr924-1#show access-lists
Extended IP access list 101
permit ip 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 (2045 matches)
ubr904-2#show access-lists
Extended IP access list 101
permit ip 18.18.18.0 0.0.0.255 19.19.19.0 0.0.0.255 (2059 matches)
L'elenco degli accessi imposta la sessione IPsec quando la LAN dietro a uBR924-1 (19.19.19.0) invia il traffico IP alla LAN dietro a uBR904-2 (18.18.18.0) e viceversa. Non utilizzare "any" (qualsiasi) negli elenchi degli accessi perché potrebbe causare problemi. Per ulteriori informazioni, fare riferimento a Configurazione della sicurezza di rete IPsec.
Nessun traffico IPsec. Eseguire il comando show crypto engine connection active.
ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0
Nessuna connessione IPSec. Nessun traffico corrispondente agli elenchi degli accessi.
Nota: consultare le informazioni importanti sui comandi di debug prima di usare i comandi di debug.
Il prossimo passaggio consiste nell'attivare alcuni debug crittografici per generare traffico interessante.
Nell'esempio, questi debug sono attivati:
-
debug crypto engine
-
debug crypto IPsec
-
debug crypto key-exchange
-
debug crypto isakmp
Per visualizzare l'output dei debug, è necessario prima generare del traffico interessante. Eseguire un ping esteso dalla porta Ethernet dell'uBR904-2 al PC su uBR924-1 (indirizzo IP 19.19.19.1).
ubr904-2#ping ip Target IP address: 19.19.19.1 !--- IP address of PC1 behind the Ethernet of uBR924-1. Repeat count [5]: 100 !--- Sends 100 pings. Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 18.18.18.18 !--- IP address of the Ethernet behind uBR904-2. Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 100, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 19.19.19.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
L'uBR924-2 mostra questo output di debug:
ubr904-2#
01:50:37: IPSec(sa_request): ,
(key eng. msg.) src= 18.18.18.18, dest= 19.19.19.19,
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x19911A16(428939798), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4004
01:50:37: IPSec(sa_request): ,
(key Eng. msg.) src= 18.18.18.18, dest= 19.19.19.19,
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x7091981(118036865), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4004
01:50:37: ISAKMP: received ke message (1/2)
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): sitting IDLE. Starting QM immediately (QM_IDLE)
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): beginning Quick Mode exchange, M-ID of 1108017901
01:50:37: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP (1): sending packet to 19.19.19.19 (I) QM_IDLE
01:50:37: ISAKMP (1): received packet from 19.19.19.19 (I) QM_IDLE
01:50:37: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): processing SA payload. message ID = 1108017901
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: transform 1, AH_MD5
01:50:37: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:3.!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!7: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:37: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5
01:50:37: validate proposal 0
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DES
01:50:37: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:37: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:37: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:37: validate proposal 0
01:50:37: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:37: IPSec(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.1!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 99 percent (99/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 30/40/70 ms
ubr904-2#
Il primo ping ha avuto esito negativo. Questo perché deve stabilire la connessione.
L'uBR924-1 mostra questo output di debug:
ubr924-1#
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): received packet from 18.18.18.18 (R) QM_IDLE
01:50:24: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing SA payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: transform 1, AH_MD5
01:50:24: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:24: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:24: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5
01:50:24: validate proposal 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DES
01:50:24: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
01:50:24: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes
01:50:24: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0
01:50:24: validate proposal 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.
01:50:24: IPSec(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:24: IPSec(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #2,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:24: validate proposal request 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing NONCE payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing ID payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET src 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0
prot 0 Port 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): processing ID payload. Message ID = 1108017901
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET dst 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0
prot 0 Port 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): asking for 2 spis from IPSec
01:50:24: IPSec(key_engine): got a queue event...
01:50:24: IPSec(spi_response): getting spi 393021796 for SA
from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19 for prot 2
01:50:24: IPSec(spi_response): getting spi 45686884 for SA
from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19 for prot 3
01:50:24: ISAKMP: received ke message (2/2)
01:50:24: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): sending packet to 18.18.18.18 (R) QM_IDLE
01:50:24: ISAKMP (1): received packet from 18.18.18.18 (R) QM_IDLE
01:50:24: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1
01:50:24: IPSec allocate flow 0
01:50:24: IPSec allocate flow 0
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Creating IPSec SAs
01:50:24: inbound SA from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19
(proxy 18.18.18.0 to 19.19.19.0)
01:50:24: has spi 393021796 and conn_id 2000 and flags 4
01:50:24: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:24: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:24: outbound SA from 19.19.19.19 to 18.18.18.18
(proxy 19.19.19.0 to 18.18.18.0)
01:50:24: has spi 428939798 and conn_id 2001 and flags 4
01:50:24: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:24: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:24: ISAKMP (0:1): Creating IPSec SAs
01:50:24: inbound SA from 18.18.18.18 to 19.19.19.19
(proxy 18.18.18.0 to 19.19.19.0)
01:50:24: has spi 45686884 and conn_id 2002 and flags 4
01:50:24: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:24: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:24: outbound SA from 19.19.19.19 to 18.18.18.18
(proxy 19.19.19.0 to 18.18.18.0)
01:50:24: has spi 118036865 and conn_id 2003 and flags 4
01:50:25: lifetime of 3600 seconds
01:50:25: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes
01:50:25: ISAKMP (0:1): deleting node 1108017901 error FALSE reason
"quick mode done (await()"
01:50:25: IPSec(key_engine): got a queue event...
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x176D0964(393021796), conn_id= 2000, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) src= 19.19.19.19, dest= 18.18.18.18,
src_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x19911A16(428939798), conn_id= 2001, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) dest= 19.19.19.19, src= 18.18.18.18,
dest_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
src_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x2B92064(45686884), conn_id= 2002, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(initialize_sas): ,
(key Eng. msg.) src= 19.19.19.19, dest= 18.18.18.18,
src_proxy= 19.19.19.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
dest_proxy= 18.18.18.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
protocol= ESP, transform= ESP-Des ,
lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,
spi= 0x7091981(118036865), conn_id= 2003, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 19.19.19.19, sa_prot= 51,
sa_spi= 0x176D0964(393021796),
sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2000
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 18.18.18.18, sa_prot= 51,
sa_spi= 0x19911A16(428939798),
sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2001
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 19.19.19.19, sa_prot= 50,
sa_spi= 0x2B92064(45686884),
sa_trans= ESP-Des , sa_conn_id= 2002
01:50:25: IPSec(create_sa): sa created,
(sa) sa_dest= 18.18.18.18, sa_prot= 50,
sa_spi= 0x7091981(118036865),
sa_trans= ESP-Des , sa_conn_id= 2003
ubr924-1#
Dopo aver creato il tunnel IPsec, è possibile visualizzare la connessione e i pacchetti crittografati e decrittografati.
ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 0 99 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 99 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 0 99 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 99 0
La prima linea 200x mostra i 99 pacchetti ricevuti. I pacchetti devono essere decriptati per essere inviati a PC1. La seconda riga mostra 99 pacchetti inviati. I pacchetti devono essere crittografati prima di essere inviati all'uBR904-2. La terza e la quarta riga eseguono lo stesso processo, ma con la trasformazione ESP-DES invece di AH-MD5-HMAC.
Nota: se il set di trasformazioni configurato sul modem via cavo è ESP-DES ESP-MD5-HMAC, verranno visualizzati solo due sistemi autonomi (AS), a differenza dei quattro descritti nel precedente comando show.
ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 0 99 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 99 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 0 99 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 99 0
Eseguire un ping esteso su PC2 da uBR924-1 per verificare se i contatori aumentano per i pacchetti crittografati e decrittografati.
ubr924-1#ping ip Target IP address: 18.18.18.1 Repeat count [5]: 50 Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 19.19.19.19 Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 50, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 18.18.18.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (50/50), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/30/33 ms ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 0 149 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 149 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 0 149 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 149 0 ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 0 149 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 149 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 0 149 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 149 0
È possibile eseguire un altro ping esteso per verificare che i contatori aumentino di nuovo. Questa volta, inviare un ping di pacchetto 500 da uBR904-2 all'interfaccia Ethernet di uBR924-1 (19.19.19).
ubr904-2#ping ip Target IP address: 19.19.19.19 Repeat count [5]: 500 Datagram size [100]: 1000 Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 18.18.18.18 Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 500, 1000-byte ICMP Echos to 19.19.19.19, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 01:59:06: IPSec(encapsulate): encaps area too small, moving to new buffer: idbtype 0, encaps_size 26, header size 60, avail 84!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (500/500), round-trip min/avg/max = 98/135/352 ms ubr904-2#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 0 649 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set HMAC_MD5 649 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 0 649 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.30.18 set DES_56_CBC 649 0 ubr924-1#show crypto engine connection active ID Interface IP-Address State Algorithm Encrypt Decrypt 1 set HMAC_MD5+DES_56_CB 0 0 2000 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 0 649 2001 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set HMAC_MD5 649 0 2002 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 0 649 2003 cable-modem0 172.16.31.20 set DES_56_CBC 649 0
Per cancellare le connessioni, è possibile usare i comandi clear crypto isakmp e clear crypto sa. Inoltre, se durante il tempo di scadenza non c'è traffico attraverso il tunnel IPsec, IPsec ripristina automaticamente la connessione.
Risoluzione dei problemi
Non sono attualmente disponibili informazioni specifiche per risolvere i problemi relativi a questa configurazione.
Informazioni correlate
- Comandi per la sicurezza della rete IPsec
- Introduzione alla crittografia IPsec (IP Security) - Informazioni di debug
- Esempi di configurazione IPsec
- Configurazione della protezione di rete IPsec
- Configurazione dei Cisco serie uBR900 Cable Access Router
- Download per Cisco via cavo/banda larga (solo utenti registrati)
- Supporto della tecnologia via cavo a banda larga
- Documentazione e supporto tecnico – Cisco Systems
 Feedback
Feedback