DHCP Secure ARP、SSG Port-Bundle Host Key、SSG TCP Redirect、SESM、および SSG/DHCP Awareness が設定された SSG インターネット ゲートウェイのコール フロー デバッグ
内容
概要
このドキュメントでは、SSG と DHCP が稼働していて、ポータル サービスに SESM を使用する IOS インターネット ゲートウェイに焦点を当てています。
前提条件
要件
このドキュメントに特有の要件はありません。
使用するコンポーネント
このドキュメントの内容は、特定のソフトウェアやハードウェアのバージョンに限定されるものではありません。
表記法
ドキュメント表記の詳細は、『シスコ テクニカル ティップスの表記法』を参照してください。
背景説明
テクノロジーと機能の概要
Service Selection Gateway(SSG)
Service Selection Gateway(SSG)は、ネットワーク サービスへの同時並行アクセスを可能にする Digital Subscriber Line(DSL; デジタル加入者線)、ケーブル モデム、あるいはワイヤレスなどのブロードバンド アクセス テクノロジーにより、加入者にイントラネット、エクストラネット、およびインターネット接続を提供するサービス プロバイダーのためのスイッチング ソリューションです。
SSG は Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager(SESM)と組み合されて機能します。 SESM と組み合されることにより、SSG では、加入者の認証、サービス セレクション、およびサービス コネクションの機能がインターネット サービスの加入者に提供されます。加入者は標準のインターネット ブラウザを使用して、SESM Web アプリケーションと対話します。
SESM は次の 2 つのモードで動作します。
-
RADIUSモード:このモードは、RADIUSサーバから加入者およびサービス情報を取得します。RADIUS モードの SESM は SSD に似ています。
-
LDAPモード:Lightweight Directory Access Protocol(LDAP)モードでは、加入者およびサービスプロファイル情報に関するLDAP準拠のディレクトリへのアクセスが提供されます。このモードには SESM Web アプリケーション用の拡張機能も備わっており、ロールベース アクセス コントロール(RBAC)モデルを使用して加入者アクセスが管理されます。
SSG Port Bundle Host Key
SSG Port-Bundle Host Key 機能では、ホストの送信元 IP アドレスと送信元ポートを使用して加入者の識別と監視を行うメカニズムにより、SSG と SESM 間の通信と機能が拡張されます。
SSG Port-Bundle Host Key 機能により、SSG では、加入者と SESM サーバ間の HTTP トラフィックにポート アドレス変換(PAT)とネットワーク アドレス変換(NAT)が実行されます。加入者が SESM サーバに HTTP パケットを送信する際に、送信元 IP アドレスを設定済み SSG 送信元 IP アドレスに変更し、さらに、送信元 TCP ポートを SSG によって割り当てられたポートに変更するマップが SSG により作成されます。ある加入者が Web ページにアクセスする際には、複数の TCP セッションが並行して確立される場合があるため、各加入者には SSG によりポート群が割り当てられます。割り当てられたホスト鍵、あるいは、ポート群と SSG 送信元 IP アドレスの組み合せにより、各加入者は一意に識別されます。ホスト鍵は SESM サーバと SSG 間で送信される RADIUS パケットでは、加入者の IP VSA(vendor-specific attribute; ベンダー固有属性)内で搬送されます。 SESM サーバから加入者に応答が送信される際に、SSG により、宛先 IP アドレスと宛先 TCP ポートがポート マップに従って変換されます。
SSG TCP Redirection(非認証ユーザが対象)
非認証ユーザのリダイレクションでは、ユーザがサービス プロバイダーで認可されていない場合に、ユーザからのパケットがリダイレクトされます。非認可加入者が TCP ポートでサービスに(たとえば、www.cisco.com に対して)接続しようとした場合、SSG TCP Redirection により、パケットがキャプティブ ポータル(SESM あるいは SESM デバイスのグループ)にリダイレクトされます。SESM ではブラウザにリダイレクトして、ログイン ページを表示します。加入者は SESM にログインして、認証と認可が行われます。次に、SESM により、カスタマイズされたホーム ページ、サービス プロバイダーのホーム ページ、あるいは、オリジナルの URL が表示されます。
DHCP Secured IP Address Assignment
DHCP Secure IP Address Assignment 機能では、DHCP データベースで Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol(DHCP)リースに対する ARP テーブル エントリをセキュア保護する機能が導入されています。この機能により DHCP バインディングに対するクライアントの MAC アドレスのセキュア保護と同期が行われ、これにより、非認可クライアントやハッカーが DHCP サーバをスプーフィングして認可クライアントの DHCP リースを乗っ取ることが阻止されます。この機能がイネーブルになっていて、DHCP サーバが DHCP クライアントに IP アドレスを割り当てると、DHCP サーバでは、その割り当てられた IP アドレスとそのクライアントの MAC アドレスで ARP テーブルにセキュア ARP エントリを追加します。この ARP エントリがこれ以外の ARP パケットでアップデートされることはなく、この ARP エントリは、設定されたリース期間中あるいはそのリースがアクティブである間は ARP テーブルに存在します。セキュア保護された ARP エントリを削除できるのは、DHCP バインディングが期限切れになった際の DHCP クライアントか DHCP サーバからの明示的な終了メッセージだけです。この機能は新しい DHCP ネットワークに設定できますが、現行のネットワークのセキュリティのアップグレードにも使用できます。この機能の設定によりサービスが中断されることはなく、DHCP クライアントから認識されることもありません。
テストベッド ダイアグラム
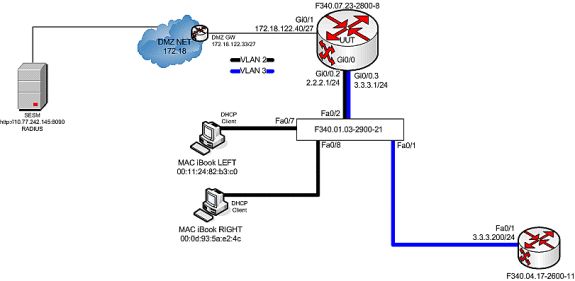
コール フロー デバッグ
次のステップを実行します。
-
MAC iBook LEFTが最初にこのネットワークにイーサネットケーブルを接続すると、「F340.07.23-2800-8」で稼働するIOS DHCPサーバからIPアドレス2.2.2.5/29がリースされます。
debug ip dhcp server packet debug ssg dhcp events *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: DHCP-DISCOVER event received. SSG-dhcp awareness feature enabled *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2. *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool name called for 0011.2482.b3c0. No hostobject *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool class called, class name = Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPOFFER to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: IP address notification received. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: HostObject not present *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Can't find any hostname to update *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPACK to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). F340.07.23-2800-8#show ip dhcp binding Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF: IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type Hardware address/ User name 2.2.2.5 0100.1124.82b3.c0 Oct 13 2008 08:37 PM Automatic -
IPアドレス2.2.2.5が正常にリースされた後、MAC iBook LEFTはWebブラウザを開き、http://3.3.3.200を指します。これは、SSGサービス「distlearn」に関連付けられた保護されたリソースをシミュレートするために使用されます。 SSGサービス「distlearn」は、SSGルータ「F340.07.23-2800-8」でローカルに定義されます。
local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255"
実際には、http://3.3.3.200は「ip http server」用に設定されたCisco IOSルータで、TCP 80でリッスンするため、基本的にはWebサーバです。
MAC iBook LEFTがhttp://3.3.3.200を参照しようとすると、この接続は「ssg direction downlink」で設定されたインターフェイスに入力されるため、SSGルータは最初に、HTTP要求の送信元IPアドレスに対するアクティブなSSGホストオブジェクトの有無をチェックします。これは IP アドレス 2.2.2.5 からの最初のそのような要求なので、SSG Host Object は存在せず、次の設定により、ホスト 2.2.2.5 に対して SESM への TCP リダイレクトがインスタンス化されます。
ssg tcp-redirect port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 All hosts with destination requests on these TCP Ports are candidates for redirection. server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 10.77.242.145 is the SESM server and it’s listening for HTTP on TCP 8090. “server” MUST be in default network or open-garden. redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If an SSG router receives a packets on an interface with “ssg direction downlink” configured, it first compares the Source IP address of the packet with the SSG Host Object Table. If an Active SSG Host Object matching the Source IP address of this packet is not found, AND the destination TCP Port of the packet matches “port-list ports”, and the destination IP address is NOT included as a part of “ssg default-network” OR SSG Open Garden, then the user will be redirected because his is unauthenticated [no Host Object] and his packet is destined for a TCP port in the “port-list ports”. The user will then be captivated until an SSG Host Object is created, or until a timeout which is configurable via “redirect captivate initial default group”. debug ssg tcp redirect debug ssg ctrl-event *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: SSG-TCP-REDIR:-Up: created new remap entry for unauthorised user at 2.2.2.5 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Redirect server set to 10.77.242.145,8090 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Initial src/dest port mapping 49273<->80 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg tcp-redirect mappings Authenticated hosts: No TCP redirect mappings for authenticated users Unauthenticated hosts: Downlink Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 TCP remapping Host:2.2.2.5 to server:10.77.242.145 on port:8090 The initial HTTP request from 2.2.2.5 had a source TCP Port of 49273 and a destination IP address of 3.3.3.200 and TCP port of 80. Because of the SSG TCP Redirect, the destination IP header is overwritten with the socket of the SESM server 10.77.242.145:8090. If Port Bundle Host Key were NOT configured, the Source socket of 2.2.2.5:49273 would remain unchanged. However, in this case, Port Bundle Host Key is configured therefore the source address of this packet is ALSO changed based on this configuration: ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Any packets destined to SESM on TCP ports 80-8100 are subject to PBHK source NAT to IP socket 172.18.122.40, starting with a port of 64. *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: group:ssg_tr_unauth, web-proxy:0 *Oct 13 20:24:37.417: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Down: TCP-FIN Rxd for user at 2.2.2.5, port 49273 *Oct 13 20:24:37.421: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Up: TCP-FIN Rxd from user at 2.2.2.5, src port 49273 As a part of this SSG TCP Redirect, the original URL is preserved http://3.3.3.200 but the destination IP socket is rewritten to 10.77.242.145:8090. So, when the SESM receives this URL of http://3.3.3.200 on TCP port 8090, it sends an HTTP redirect back toward the client’s browser directing the client to the SESM login page, which is http://10.77.242.145:8080/home?CPURL=http%3A%2F%2F3.3.3. 200%2F&t=fma4443t. Notice the Browser Redirect points the Client Browser to TCP 8080 for captive portal. As such, the TCP session for the initial IOS SSG Redirect to 10.77.242.145:8090 is terminated. Also, notice SESM has captured the original URL of http://3.3.3.200 in the Redirect. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (4,&) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=4 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account status query for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, Ack the query with Complete ID. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 4 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext With Port Bundle Host Key configured, all HTTP communications between Client and SESM are subject to Port Bundling, which is effectively Source NAT for the TCP socket. Above, the “SSG-CTL-EVN” messages debug the communication between the SESM and the IOS SSG Router using a proprietary RADIUS-based protocol. When using Port Bundle Host Key, SESM always uses the Port Bundle to identify the host, which in this case is 172.18.122.40:64. You’ll see when SESM sends the HTTP redirect resulting in the Web browser connecting to 10.77.242.145:8090, SESM also queries SSG on the Control Channel for existence of Host Object for 172.18.122.40:64, which the SSG Router knows is actually 2.2.2.5. Since no Host Object is present, the SSG Router sends the SESM “No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64” This can be confirmed at this point like this: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host ### Total HostObject Count: 0この段階で、http://3.3.3.200 と入力された MAC iBook Left のブラウザを次に示します。
IOS SSG TCP と SESM HTTP でリダイレクトが行われると、画面は次のようになります。
-
SESM への SSG TCP リダイレクトと SESM により MAC iBook Left のブラウザに返された後続の HTTP リダイレクトの後、MAC iBook Left ではユーザ名に user1、パスワードに cisco と入力します。
-
OK ボタンを押すと、独自の RADIUS ベースのプロトコルで SESM から SSG ルータに次のクレデンシャルが送られます。
*Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (1,user1) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=1 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account logon for host 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: No auto-domain selected for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Authenticating user user1. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: ssg_aaa_nasport_fixup function *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: slot=0, adapter=0, port=0, vlan-id=2, dot1q-tunnel-id=0, vpi=0, vci=0, type=10 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext
-
次に、SSG ルータで RADIUS アクセス要求パケットが組み立てられ、これが RADIUS に送られて user1 が認証されます。
*Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS(00000008): Send Access-Request to 10.77.242.145:1812 id 1645/11, len 88 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: authenticator F0 56 DD E6 7E 28 3D EF - BC B1 97 6A A9 4F F2 A6 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Password [2] 18 * *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40
-
RADIUSはuser1のAccess-Acceptで応答し、SSGホストオブジェクトが「F340.07.23-2800-8」で作成されます。
*Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Received from id 1645/11 10.77.242.145:1812, Access-Accept, len 273 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: authenticator 52 7B 50 D7 F2 43 E6 FC - 7E 3B 22 A4 22 A7 8F A6 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 23 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 17 "NInternet-Basic" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 13 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 7 "Niptv" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 14 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 8 "Ngames" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ndistlearn" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ncorporate" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 22 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 16 "Nhome_shopping" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nbanking" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nvidconf" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS(00000008): eceived from id 1645/11 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 4 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating radius packet *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Response is good *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-EVN: HostObject::HostObject: size = 616 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::Reset *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList NInternet-Basic *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Niptv *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ngames *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ndistlearn *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ncorporate *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nhome_shopping *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nbanking *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nvidconf *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: DoAccountLogon: ProfileCache is Enabled *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Account logon is accepted [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, user1] *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 1 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for host 2.2.2.5 Finally, our SSG Host Object is created for 2.2.2.5. Notice that “user1” RADIUS profile is configured with many ssg-account-info VSA with “N” Attribute, which is an SSG code for Service to which the user is subscribed. Please note, this doesn’t mean “user1” has any Active services at this point, which can be confirmed with: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 1: 2.2.2.5 [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64] ### Active HostObject Count: 1 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content --- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:37:09.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: NONE AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE
-
この時点で、user1 は SSG Host Object として定義されていますが、まだどの SSG サービスへもアクセスしていません。MAC iBook Left が Service Selection 画面に表示されており、次のように Distance Learning をクリックします。
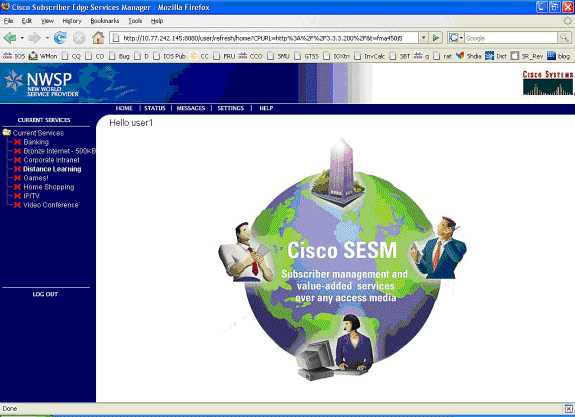
-
Distance Learning をクリックすると、次のように、SESM ボックスがコントロール チャネルで SSG ルータへのコミュニケーションを行います。
debug ssg ctrl-events *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (11,distlearn) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 SSG Router is receiving control channel command that SSG User 172.18.122.40:64 [maps to 2.2.2.5] wants to activate SSG Service ‘distlearn’. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=11 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling service logon for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating pseudo ServiceInfo for service: distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-EVN: ServiceInfo::ServiceInfo: size = 416 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: ServiceInfo: Init servQ and start new process for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Got profile for distlearn locally Since “distlearn” is available from local configuration: local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" ...we don’t need to make a AAA call to download SSG Service Information. However, please note that in most real-world SSG implementations, SSG Services are defined on the RADIUS AAA Server. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Create a new service table for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service bound on this interface are : distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service distlearn bound to interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 firsthop 0.0.0.0 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: Service Address List : *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: Addr:3.3.3.200 mask:255.255.255.255 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add a new service distlearn to an existing table Here the SSG creates a Service Table for distlearn and binds it to an “ssg direction uplink” interface complete with the R attribute for the Service. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking connection activation for 172.18.122.40:64 to distlearn. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating ConnectionObject (172.18.122.40:64, distlearn) *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: ConnectionObject::ConnectionObject: size = 304 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 2 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking maximum service count. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Opening connection for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Connection opened *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service logon is accepted. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating the ConnectionObject. Once the Service is verified locally, SSG needs to build a “Connection” where a “Connection” is a tuple with: A. SSG Host Object B. SSG Service Name and Attributes C. SSG Downlink interface D. SSG Upstream interface A-D are used to create a pseudo hidden VRF service table for which traffic from this host can transit. See here: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg connection 2.2.2.5 distlearn ------------------------ConnectionObject Content ---- User Name: user1 Owner Host: 2.2.2.5 Associated Service: distlearn Calling station id: 0011.2482.b3c0 Connection State: 0 (UP) Connection Started since: *20:40:21.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:41:04.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 Connection Traffic Statistics: Input Bytes = 420, Input packets = 5 Output Bytes = 420, Output packets = 5 Session policing disabled F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content ----------- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:40:23.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: distlearn; AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE -
SSG 接続はアップしており、コールフローが完全に実行されます。MAC iBook Left では、http://3.3.3.200: のブラウズが正常に実行できます。
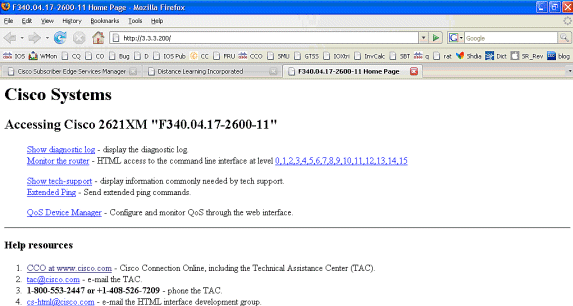
フィーチャ ドキュメントをともなう SSG ルータ設定の説明
version 12.4 service nagle no service pad service tcp-keepalives-in service tcp-keepalives-out service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname F340.07.23-2800-8 ! boot-start-marker boot system flash flash: c2800nm-adventerprisek9-mz.124-21.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1024000 debugging ! aaa new-model ! aaa authorization network default group radius ! aaa session-id common no ip source-route ! ip cef ip dhcp relay information trust-all ip dhcp use vrf connected ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.1 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.2 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.3 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.4 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.6 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.7 We are excluding 2.2.2.1-4 and 2.2.2.6-7 to ensure the only DHCP address that will be leased is 2.2.2.5/29. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server ip dhcp pool dhcp_guest_v3501 network 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.248 default-router 2.2.2.1 dns-server 172.18.108.34 lease 0 4 update arp If an interface on this router is configured with an address in the 2.2.2.0/29 range, it will field DHCP request from host on that network and assign IP address 2.2.2.5, GW 2.2.2.1, and DNS Server 172.18.108.24. The lease time on the IP address will be 4 hours. Also, “update arp” will ensure ARP entries for IP addresses leased via DHCP will match the MAC entry in the DHCP Binding table. This will prevent SSG session hijacking in the event a static user re-uses a DHCP [or is given] leased address. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuring DHCP Services for Accounting and Security ! no ip domain lookup ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3 ip admission max-nodata-conns 3 ! voice-card 0 no dspfarm ! ssg enable Enables SSG subsystem. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg intercept dhcp Enables SSG/DHCP Awareness. In our example, this will result in an SSG Host object being destroyed when either of these occur: A. A DHCPRELEASE message is received for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. B. A DHCP Lease expires for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. Configuring SSG for On-Demand IP Address Renewal ssg default-network 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 All packets ingress to “ssg direction downlink” interfaces can access the “ssg default-network” regardless as to whether a Host or Connection Object exists. SSG allows all users, even unauthenticated users, to access the default network. Typically, SESM belongs to the default network. However, other types of servers, such as DNS/DHCP servers or TCP-Redirect servers, can also be part of the default network. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg service-password cisco If an SSG Service is not defined locally and we therefore need to make a RADIUS call when a user subscribes to an SSG Service, the password “cisco” is used in the RADIUS Access-Request for the Service. ssg radius-helper auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 ssg radius-helper key cisco Used to communicate with SESM on SSG Control Channel. SESM must also maintain a similar static configuration for each SSG Router it serves. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg auto-logoff arp match-mac-address interval 30 In the absence of user traffic, SSG will send an ARP Ping for all Active Host Objects and will invoke an AutoLogoff if either the host fails to reply or the MAC address of the host has changed. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg bind service distlearn GigabitEthernet0/0.3 SSG traffic is not routed using the Global routing table. Instead it’s routed from “ssg direction downstream” interface using the information in the mini-VRF seen in “show ssg connection”, which includes a manual binding of Service<-->”ssg direction uplink” interface. Hence, it is a requirement of SSG to manually bind services to interfaces or next-hop IP addresses. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services ssg timeouts session 64800 Absolute timeout for SSG Host Object is 64800 seconds. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Port Bundle Host Key configuration. All traffic destined to 10.77.242.145 in the range of TCP 80 to 8100 will be Source NATed to 172.18.122.40. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg tcp-redirect Enters SSG redirect sub-config. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 Defines a list of destination TCP ports which are candidates for TCP redirection. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 Defines a redirect server list and defines the TCP port on which they’re listening for redirects. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If a Host Object does NOT exist and the traffic is ingress to an “ssg direction downlink” interface AND its destination port is in port-list ports, THEN redirect this traffic to “server-group ssg_tr_unauth”. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers ssg service-search-order local remote Look for SSG Service defined in a local-profile in IOS configuration before making a AAA call to download Service information. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" Local definition of SSG Service “distlearn” 26 9 251 is Vendor Specific, Cisco, SSG Service Info Attributes defined herein: R: Destination Network, Specifies IP routes belonging to this Service Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services RADIUS Profiles and Attributes for SSG interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 description Guest Wireless Vlan encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.248 no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip mroute-cache ssg direction downlink All SSG Host Objects should be located on downlink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 description Routed connection back to Blue encapsulation dot1Q 3 ip address 3.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 ssg direction uplink All SSG Services should be located on uplink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.122.40 255.255.255.224 duplex auto speed auto ! ip forward-protocol nd ip route 10.77.242.144 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 157.157.157.0 255.255.255.0 3.3.3.5 ip route 172.18.108.34 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 172.18.124.101 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip radius source-interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ! radius-server host 10.77.242.145 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 timeout 5 retransmit 3 key 7 070C285F4D06 ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
セキュリティとセッション再使用の考慮点
SSG と DHCP を一緒に使用すると、下記のシナリオで悪意を持つユーザに認証済みの SSG Host Object の再使用が許可される可能性があり、これにより、セキュアなリソースへの非認証アクセスが許可されます。
-
SSG/DHCP認識が「ssg intercept dhcp」で設定されていない場合、新しいDHCPユーザは、SSG Host Objectがまだ存在する以前にリースされたIPアドレスをリースできます。この新しいユーザからの最初の TCP 要求は、古いものであっても、送信元 IP アドレスが一致する SSG Host Object に一致するものがあるため、このユーザは保護されたリソースの非認証での使用が許可されます。これは、「ssg intercept dhcp」を使用して防止できます。この場合、次のいずれかが発生すると、SSG Host Objectが削除されます。
-
アクティブな Host Object に一致する IP アドレスに対する DHCPRELEASE を受け取る。
-
アクティブな Host Object に一致する IP アドレスに対する DHCP リースが期限切れになる。
-
-
DHCPRELEASEが送信されないDHCPログアウト前に、DHCPユーザがリースされたIPアドレスを悪意のあるユーザに関連付けると、悪意のあるユーザはこのIPアドレスでマシンを静的に設定し、「ssg intercept dhcp」が設定されているかどうかに関係関係なくSSG Hostオブジェクトを再利用できます。これは、IOS DHCPプールの下に「ssg intercept dhcp」と「update arp」を組み合わせて設定することで防止できます。「update arp」は、ARPエントリを追加または削除できる唯一のIOSサブシステムがDHCPサーバサブシステムであることを保証します。「update arp」を使用すると、IP-to-MAC DHCPバインディングは常にARPテーブルのIP-to-MACバインディングと一致します。悪意を持つユーザが、SSG Host Object に一致するスタティックに設定された IP アドレスを持ったとしても、そのトラフィックは SSG ルータに入ることを許可されません。MAC アドレスが、現行の DHCP バインディングの Mac アドレスに一致しないため、IOS DHCP サーバでは ARP エントリの作成が阻止されます。
-
SSGとDHCPを一緒に設定すると、「ssg intercept dhcp」と「update arp」によってセッションの再利用が防止されます。最終的な非セキュリティ関連チャレンジにより、DHCP Host で通常ではないログアウトが実行された際に、DHCP リースと ARP エントリが解放されます。「ssg direction downlink」インターフェイスで「authorized arp」を設定すると、すべてのホストに定期的なARP要求が送信され、それらがアクティブであることを確認します。これらの定期的な ARP メッセージに対して何の応答も受け取らなかった場合、DHCP バインディングが解放され、IOS DHCP サブシステムでは ARP エントリが排除されます。
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 arp authorized arp probe interval 5 count 15
この例では、ARP 要求が定期的に送られて、Fa0/0 の既知のすべての ARP エントリが 5 秒ごとにリフレッシュされます。15 回失敗すると、DHCP バインディングが解放され、IOS DHCP サブシステムでは ARP エントリが排除されます。
「authorized arp」を使用しないSSGのコンテキストでは、DHCPホストがグレースフルログアウトを実行すると、DHCPリースと関連するSSG Host Objectは、このDHCPアドレスのリースが期限切れになるまでアクティブなままですが、「ssg intercept dhcp」がグローバルに設定されている限は再利用されません。
「authorized arp」は、設定されているインターフェイスでダイナミックARPラーニングをオフにします。対象のインターフェイスで ARP エントリだけが、リースが開始された後で IOS DHCP サーバにより追加されたものです。これらのリースが終了すると、次に IOS DHCP サーバでこれらの ARP エントリが排除されますが、その理由は、DHCP RELEASE の受け取り、リースの期限切れ、あるいは、通常ではない DHCP ログアウトによる ARP プローブの失敗です。
実装上の注:
-
「ssg auto-logoff arp」と「ssg auto-logoff icmp」は、セッションの再利用や結果的なセキュリティ問題を防止するために望ましくない方法です。「ssg auto-logoff」の「arp」と「icmp」のバリアントは、設定された「間隔」内にトラフィックがSSG接続で見られない場合にのみ、ARPまたはIMCP PINGを送信します。PINGの最も低い値は30秒です。DHCPが以前に使用したIPアドレスを30秒以内にリースした場合、または悪意のあるユーザが30秒以内に現在バインドされたDHCPアドレスを静的に設定した場合、SSGは接続オブジェクトのトラフィックを参照するため、セッションは再利用されます。
-
すべての使用ケースで、悪意を持ったホストで MAC アドレスのスプーフィングが実行された場合、セッションの再使用は阻止されません。
表1:SSG/DHCP導入におけるセッションの再利用とセキュリティに関する考慮事項
| コマンド | 機能 | セキュリティ関連事項 |
|---|---|---|
| ssg auto-logoff arp [match-mac-address] [interval seconds] ssg auto-logoff icmp [timeout milliseconds] [packets number] [interval seconds] | ARPまたはICMP PINGの失敗後にSSG Host Objectを削除します。これは、「インターバル」の間にSSG接続でトラフィックが見つからない場合にのみ送信されます。 | DHCPが以前に使用したIPアドレスを30秒以内にリースした場合、または悪意のあるユーザが30秒以内に静的にバインドされたDHCPアドレスを設定した場合は、セッションを再利用します。これは、SSGが接続オブジェクトのトラフィックを検出しません。 |
| ssg intercept dhcp | 下記のイベントで SSG Host Object の削除を許可する SSG/DHCP Awareness を作成します。アクティブな Host Object に一致する IP アドレスに対する DHCPRELEASE を受け取る。B. アクティブな Host Object に一致する IP アドレスに対する DHCP リースが期限切れになる。 | DHCP ユーザが SSG セッションを再使用するのは阻止されますが、スタティック ユーザが DHCP アドレスのスプーフィングをしたり、SSG セッションの再使用をしたりすることは阻止されません。 |
| ip dhcp pool TEST update arp | ARP エントリの追加と削除を行える唯一の IOS サブシステムが DHCP サーバ サブシステムであることが保証されます。 | 「ssg intercept dhcp」を使用して設定した場合、すべてのセッションの再利用を防止します。 「ssg intercept dhcp」を使用せずに設定すると、DHCPが以前に使用したIPアドレスをリースする場合でも、セッションの再利用が可能になります。 |
| interface FastEthernet0/0 arp authorized | すべてのホストに ARP 要求を定期的に送って、相手がアクティブであることを確認します。ダイナミック ARP ラーニングをオフにします。 | DHCP ユーザが通常ではないログアウトを行った際に、DHCP バインディングと ARP エントリの削除を許可します。 |
関連情報
更新履歴
| 改定 | 発行日 | コメント |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2008 |
初版 |
 フィードバック
フィードバック