Adaptive Security Appliance에서 QoS 구성
다운로드 옵션
편견 없는 언어
본 제품에 대한 문서 세트는 편견 없는 언어를 사용하기 위해 노력합니다. 본 설명서 세트의 목적상, 편견 없는 언어는 나이, 장애, 성별, 인종 정체성, 민족 정체성, 성적 지향성, 사회 경제적 지위 및 교차성에 기초한 차별을 의미하지 않는 언어로 정의됩니다. 제품 소프트웨어의 사용자 인터페이스에서 하드코딩된 언어, RFP 설명서에 기초한 언어 또는 참조된 서드파티 제품에서 사용하는 언어로 인해 설명서에 예외가 있을 수 있습니다. 시스코에서 어떤 방식으로 포용적인 언어를 사용하고 있는지 자세히 알아보세요.
이 번역에 관하여
Cisco는 전 세계 사용자에게 다양한 언어로 지원 콘텐츠를 제공하기 위해 기계 번역 기술과 수작업 번역을 병행하여 이 문서를 번역했습니다. 아무리 품질이 높은 기계 번역이라도 전문 번역가의 번역 결과물만큼 정확하지는 않습니다. Cisco Systems, Inc.는 이 같은 번역에 대해 어떠한 책임도 지지 않으며 항상 원본 영문 문서(링크 제공됨)를 참조할 것을 권장합니다.
목차
소개
이 문서에서는 QoS(Quality of Service)가 Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance에서 작동하는 방식을 설명하고 구현 방법에 대한 예제를 제공합니다.
사전 요구 사항
요구 사항
Cisco에서는 MPF(Modular Policy Framework)에 대한 지식을 보유한 것을 권장합니다.
사용되는 구성 요소
이 문서의 정보는 버전 9.2를 실행하는 ASA(Adaptive Security Appliance)를 기반으로 하지만 이전 버전도 사용할 수 있습니다.
이 문서의 정보는 특정 랩 환경의 디바이스를 토대로 작성되었습니다. 이 문서에 사용된 모든 디바이스는 초기화된(기본) 컨피그레이션으로 시작되었습니다. 현재 네트워크가 작동 중인 경우 모든 명령의 잠재적인 영향을 미리 숙지하시기 바랍니다.
배경 정보
보안 어플라이언스에서 QoS를 구성하여 개별 플로우 및 VPN 터널 플로우 모두에 대해 선택한 네트워크 트래픽에 대해 속도 제한을 제공하여 모든 트래픽이 제한된 대역폭에서 균등한 점유율을 갖도록 할 수 있습니다. 이 기능은 Cisco 버그 IDCSCsk06260에 통합되었습니다.
QoS는 특정 유형의 인터넷 트래픽에 우선 순위를 부여할 수 있는 네트워크 기능입니다. 인터넷 사용자가 모뎀에서 DSL(Digital Subscriber Line) 및 케이블과 같은 고속 광대역 연결로 액세스 포인트를 업그레이드할 경우, 특정 시점에 한 명의 사용자가 사용 가능한 대역폭의 대부분을 흡수할 수 있으므로 다른 사용자가 고갈될 가능성이 높아집니다. QoS는 한 명의 사용자 또는 사이트 대 사이트 연결이 공정한 대역폭 점유율을 초과하여 소비하는 것을 방지하기 위해 모든 사용자가 사용할 수 있는 최대 대역폭을 조절하는 폴리싱 기능을 제공합니다.
QoS는 기본 기술의 제한된 대역폭으로 최상의 전체 서비스를 위해 다양한 기술을 통해 선택된 네트워크 트래픽에 더 나은 서비스를 제공하는 네트워크의 기능을 의미합니다.
보안 어플라이언스에서 QoS의 기본 목표는 개별 플로우 또는 VPN 터널 플로우 모두에 대해 선택된 네트워크 트래픽에 대해 속도 제한을 제공하여 모든 트래픽이 제한된 대역폭을 공평하게 분담하도록 하는 것입니다. 흐름은 여러 가지 방법으로 정의할 수 있습니다. 보안 어플라이언스에서 QoS는 소스 및 목적지 IP 주소, 소스 및 목적지 포트 번호, IP 헤더의 ToS(Type of Service) 바이트의 조합에 적용할 수 있습니다.
ASA에서 구현할 수 있는 QoS에는 폴리싱, 셰이핑 및 우선순위 큐잉의 세 가지 종류가 있습니다.
트래픽 폴리싱
폴리싱을 사용하면 지정된 제한을 초과하는 트래픽이 삭제됩니다. 폴리싱은 어떤 트래픽도 사용자가 구성하는 최대 속도(비트/초)를 초과하지 않도록 하는 방법으로, 어떤 트래픽 흐름이나 클래스도 전체 리소스를 인수할 수 없도록 합니다. 트래픽이 최대 속도를 초과하면 ASA에서 초과 트래픽을 삭제합니다. 또한 폴리싱은 허용되는 최대 단일 트래픽 버스트를 설정합니다.
이 다이어그램은 트래픽 속도가 구성된 최대 속도에 도달하면 초과 트래픽이 삭제되는 트래픽 폴리싱이 수행하는 작업을 보여줍니다. 그 결과, 출력 속도는 톱니 모양으로 표시됩니다.
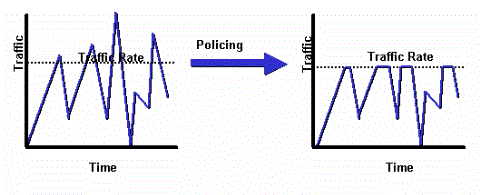
다음 예에서는 아웃바운드 방향으로 특정 사용자에 대해 대역폭을 1Mbps로 제한하는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
ciscoasa(config)# access-list WEB-LIMIT permit ip host 192.168.10.1 any
ciscoasa(config)# class-map Class-Policy
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# match access-list WEB-LIMIT
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#exit
ciscoasa(config)# policy-map POLICY-WEB
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# class Class-Policy
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# police output 1000000 conform-action transmit exceed-
action drop
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#exit
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#exit
ciscoasa(config)# service-policy POLICY-WEB interface outside
트래픽 셰이핑
트래픽 셰이핑은 디바이스 및 링크 속도를 일치시키기 위해 사용되는데, 이는 패킷 손실, 가변 지연, 링크 채도를 제어하여 지터 및 지연을 유발할 수 있습니다. 보안 어플라이언스의 트래픽 셰이핑을 통해 디바이스에서 트래픽 흐름을 제한할 수 있습니다. 이 메커니즘은 속도 제한을 초과하여 트래픽을 버퍼링하고 나중에 트래픽 전송을 시도합니다.
특정 유형의 트래픽에 대해서는 셰이핑을 구성할 수 없습니다. 셰이핑된 트래픽에는 디바이스를 통과하는 트래픽뿐만 아니라 디바이스에서 시작되는 트래픽도 포함됩니다.
이 다이어그램은 트래픽 셰이핑이 수행하는 기능을 보여줍니다. 초과 패킷을 대기열에 유지한 다음, 시간의 증분에 따라 이후의 전송을 위해 초과 패킷을 예약합니다. 트래픽 쉐이핑의 결과는 평활화된 패킷 출력 속도입니다.

참고: 트래픽 셰이핑은 ASA 버전 5505, 5510, 5520, 5540 및 5550에서만 지원됩니다. 멀티코어 모델(예: 5500-X)은 셰이핑을 지원하지 않습니다.
트래픽 셰이핑을 사용하면 특정 제한을 초과하는 트래픽은 다음 타임 슬라이스 동안 대기(버퍼링)되고 전송됩니다.
방화벽의 트래픽 셰이핑은 업스트림 디바이스가 네트워크 트래픽에 병목 현상을 일으키는 경우 가장 유용합니다. 예를 들어, 100Mbit 인터페이스가 있는 ASA가 있고 케이블 모뎀을 통해 인터넷에 업스트림 연결이 있거나 라우터에서 종료되는 T1이 있습니다. 트래픽 셰이핑을 통해 사용자는 인터페이스(예: 외부 인터페이스)에서 최대 아웃바운드 처리량을 구성할 수 있습니다. 방화벽은 해당 인터페이스에서 나가는 트래픽을 지정된 대역폭까지 전송한 다음 나중에 링크의 포화가 적을 때 전송을 위해 과도한 트래픽을 버퍼링하려고 시도합니다.
셰이핑은 지정된 인터페이스를 이그레스(egress)하는 모든 집계 트래픽에 적용됩니다. 특정 트래픽 흐름만 형성하도록 선택할 수 없습니다.
참고: 셰이핑은 암호화 후에 수행되며 VPN에 대해 내부 패킷 또는 터널 그룹을 기준으로 우선 순위를 지정할 수 없습니다.
우선순위 대기열 처리
우선 순위 큐잉을 사용하면 LLQ(Low Latency Queue)에 특정 트래픽 클래스를 배치할 수 있으며, 이 트래픽은 표준 대기열보다 먼저 처리됩니다.
참고: 셰이핑 정책에서 트래픽의 우선 순위를 지정하는 경우 내부 패킷 세부 정보를 사용할 수 없습니다. 방화벽은 보다 정교한 큐잉 및 QoS 메커니즘(WFQ(Weighted Fair Queueing), CBWFQ(Class-Based Weighted Fair Queueing) 등)을 제공할 수 있는 라우터와 달리 LLQ만 수행할 수 있습니다.
계층적 QoS 정책은 사용자가 계층적 방식으로 QoS 정책을 지정할 수 있는 메커니즘을 제공합니다. 예를 들어, 사용자가 인터페이스 및 셰이핑된 인터페이스 트래픽 내에서 트래픽을 셰이핑하려는 경우 VoIP 트래픽에 대한 우선순위 큐잉을 제공하면 사용자는 맨 위에 트래픽 셰이핑 정책을 지정하고 셰이핑 정책 아래에 우선순위 큐잉 정책을 지정할 수 있습니다. 계층적 QoS 정책 지원은 범위가 제한됩니다.
허용되는 옵션은 다음과 같습니다.
- 최상위 레벨에서 트래픽 셰이핑.
- 다음 수준에서 우선 순위 큐잉.
참고: 셰이핑 정책에서 트래픽의 우선 순위를 지정하는 경우 내부 패킷 세부 정보를 사용할 수 없습니다. 더 정교한 큐잉 및 QoS 메커니즘(WFQ, CBWFQ 등)을 제공할 수 있는 라우터와 달리 방화벽은 LLQ만 수행할 수 있습니다.
이 예에서는 셰이핑 예제와 같이 외부 인터페이스의 모든 아웃바운드 트래픽을 2Mbps로 셰이핑하기 위해 계층적 QoS 정책을 사용하지만, SSH(Secure Shell) 트래픽뿐만 아니라 DSCP(Differentiated Services Code Point) 값이 ef인 음성 패킷도 우선순위를 받도록 지정합니다.
기능을 활성화할 인터페이스에 우선순위 큐를 생성합니다.
ciscoasa(config)#priority-queue outsideciscoasa(config-priority-queue)#queue-limit
2048ciscoasa(config-priority-queue)#tx-ring-limit 256
DSCP ef와 일치하는 클래스:
ciscoasa(config)# class-map Voice
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# match dscp ef
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# exit
포트 TCP/22 SSH 트래픽과 일치시킬 클래스:
ciscoasa(config)# class-map SSH
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# match port tcp eq 22
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# exit
음성 및 SSH 트래픽의 우선 순위를 적용할 정책 맵:
ciscoasa(config)# policy-map p1_priority
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# class Voice
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# priority
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# class SSH
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# priority
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# exit
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# exit
모든 트래픽에 셰이핑을 적용하고 우선 순위가 지정된 음성 및 SSH 트래픽을 연결하는 정책 맵:
ciscoasa(config)# policy-map p1_shape
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# class class-default
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# shape average 2000000
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# service-policy p1_priority
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# exit
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# exit
마지막으로, 아웃바운드 트래픽을 형성하고 우선 순위를 지정할 인터페이스에 쉐이핑 정책을 첨부합니다.
ciscoasa(config)# service-policy p1_shape interface outside
VPN 터널을 통과하는 트래픽에 대한 QoS
IPsec VPN을 사용하는 QoS
RFC 2401에 따라 원래 IP 헤더의 ToS(Type of Service) 비트가 암호화된 패킷의 IP 헤더에 복사되므로 암호화 후 QoS 정책을 적용할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 DSCP/DiffServ 비트를 QoS 정책의 모든 위치에서 우선 순위에 사용할 수 있습니다.
IPsec 터널에서 폴리싱
특정 VPN 터널에 대해서도 폴리싱을 수행할 수 있습니다. 폴리싱할 터널 그룹을 선택하려면 클래스 맵에서 match tunnel-group <tunnel> 명령 및 match flow ip destination addresssses 명령을 사용합니다.
class-map tgroup_out
match tunnel-group ipsec-tun
match flow ip destination-address
policy-map qos
class tgroup_out
police output 1000000
match tunnel-groupcommand를 사용하면 입력 폴리싱이 현재 작동하지 않습니다. 자세한 내용은 Cisco 버그 ID CSCth48255를 참조하십시오. match flow ip destination-address로 입력 폴리싱을 수행하려고 하면 다음 오류가 발생합니다.
police input 10000000
ERROR: Input policing cannot be done on a flow destination basis
usematch tunnel-group(Cisco 버그 ID CSCth48255)을 사용할 때 현재 입력 폴리싱이 작동하지 않는 것으로 나타납니다. 입력 폴리싱이 작동하면 match flow ip destination-address 주소 없이 클래스 맵을 사용해야 합니다.
입력 폴리싱이 작동하면 match flow ip destination-address 주소 없이 클래스 맵을 사용해야 합니다.
class-map tgroup_in
match tunnel-group ipsec-tun
policy-map qos
class tgroup_in
police input 1000000
match ip 대상 주소가 없는 클래스 맵의 출력을 폴리싱하려고 하면 다음과 같은 메시지가 표시됩니다.
police output 10000000
ERROR: tunnel-group can only be policed on a flow basis
ACL(Access Control List), DSCP 등을 사용하여 내부 플로우 정보에 대한 QoS를 수행할 수도 있습니다. 앞서 언급한 버그로 인해 ACL은 현재 입력 폴리싱을 수행할 수 있는 방법입니다.
참고: 모든 플랫폼 유형에서 최대 64개의 정책 맵을 구성할 수 있습니다. 트래픽을 분할하려면 정책 맵 내에서 다른 클래스 맵을 사용합니다.
SSL(Secure Sockets Layer) VPN을 사용하는 QoS
ASA 버전 9.2까지는 ASA에서 ToS 비트를 보존하지 않았습니다.
이 기능에서는 SSL VPN 터널링이 지원되지 않습니다. 자세한 내용은 Cisco 버그 IDCSCsl73211을 참조하십시오.
ciscoasa(config)# tunnel-group a1 type webvpn
ciscoasa(config)# tunnel-group a1 webvpn-attributes
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-webvpn)# class-map c1
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# match tunnel-group a1
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# match flow ip destination-address
ciscoasa(config-cmap)# policy-map p1
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# class c1
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# police output 100000
ERROR: tunnel with WEBVPN attributes doesn't support police!
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# no tunnel-group a1 webvpn-attributes
ciscoasa(config)# policy-map p1
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# class c1
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# police output 100000
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#
참고: phone-vpn을 사용하는 사용자가 AnyConnect 클라이언트 및 DTLS(Datagram Transport Layer Security)를 사용하여 전화기를 암호화할 경우 AnyConnect가 DTLS 캡슐화에 DSCP 플래그를 유지하지 않으므로 우선 순위가 작동하지 않습니다.
자세한 내용은 개선 요청 Cisco 버그 IDCSCtq43909를 참조하십시오.
QoS 고려 사항
다음은 QoS에 대해 고려해야 할 몇 가지 사항입니다.
- MPF(Modular Policy Framework)를 통해 정책, 셰이핑, LLQ 등 엄격한 방식 또는 계층적 방식으로 적용됩니다.
- NIC(Network Interface Card)에서 DP(Data Path)로 이미 전달된 트래픽에만 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
- 인접 디바이스에 적용되지 않는 한 오버런(너무 일찍 발생함)에 대처할 수 없습니다.
- 폴리싱은 패킷이 허용된 이후의 입력 및 NIC 이전의 출력에 적용됩니다.
- 출력에서 레이어 2(L2) 주소를 다시 쓴 직후.
- 인터페이스의 모든 트래픽에 대해 아웃바운드 대역폭을 형성합니다.
- 제한된 업링크 대역폭(예: 10Mb 모뎀에 대한 1GE(기가비트 이더넷) 링크)에 유용합니다.
- 고성능 ASA558x 모델에서는 지원되지 않습니다.
- 우선 순위 큐잉은 최선형 트래픽을 굶주릴 수 있습니다.
- ASA5580 또는 VLAN 하위 인터페이스의 10GE 인터페이스에서는 지원되지 않습니다.
- 최적의 성능을 위해 인터페이스 링 크기를 추가로 조정할 수 있습니다.
컨피그레이션 예
VPN 터널의 VoIP 트래픽에 대한 QoS 컨피그레이션 예
네트워크 다이어그램
이 문서에서는 이 네트워크 설정을 사용합니다.

참고: IP 전화 및 호스트가 서로 다른 세그먼트(서브넷)에 배치되어야 합니다. 이는 올바른 네트워크 설계에 권장됩니다.
이 문서에서는 다음 설정을 사용합니다.
- DSCP 기반 QoS 컨피그레이션
- VPN 구성을 사용하는 DSCP 기반 QoS
- ACL 기반 QoS 컨피그레이션
- VPN 구성을 사용하는 ACL 기반 QoS
DSCP 기반 QoS 컨피그레이션
!--- Create a class map named Voice.
ciscoasa(config)#class-map Voice
!--- Specifies the packet that matches criteria that
!--- identifies voice packets that have a DSCP value of "ef".
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match dscp ef
!--- Create a class map named Data.
ciscoasa(config)#class-map Data
!--- Specifies the packet that matches data traffic to be passed through
!--- IPsec tunnel.
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match tunnel-group 10.1.2.1
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match flow ip destination-address
!--- Create a policy to be applied to a set
!--- of voice traffic.
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#policy-map Voicepolicy
!--- Specify the class name created in order to apply
!--- the action to it.
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class Voice
!--- Strict scheduling priority for the class Voice.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#priority
PIX(config-pmap-c)#class Data
!--- Apply policing to the data traffic.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#police output 200000 37500
!--- Apply the policy defined to the outside interface.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#service-policy Voicepolicy interface outside
ciscoasa(config)#priority-queue outside
ciscoasa(config-priority-queue)#queue-limit 2048
ciscoasa(config-priority-queue)#tx-ring-limit 256
참고: ef의 DSCP 값은 VoIP-RTP 트래픽과 일치하는 빠른 전달을 나타냅니다.
VPN 구성을 사용하는 DSCP 기반 QoS
ciscoasa#show running-config
: Saved
:
ASA Version 9.2(1)
!
hostname ciscoasa
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
names
!
interface GigabitEthernet0
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
ftp mode passive
!--- This crypto ACL-permit identifies the
!--- matching traffic flows to be protected via encryption.
access-list 110 extended permit ip 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
access-list 110 extended permit ip 10.1.5.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.6.0 255.255.255.0
pager lines 24
mtu inside 1500
mtu outside 1500
no failover
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.4.2 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart
!--- Configuration for IPsec policies.
crypto ipsec ikev1 transform-set myset esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
crypto map mymap 10 match address 110
!--- Sets the IP address of the remote end.
crypto map mymap 10 set peer 10.1.2.1
!--- Configures IPsec to use the transform-set
!--- "myset" defined earlier in this configuration.
crypto map mymap 10 set ikev1 transform-set myset
crypto map mymap interface outside
!--- Configuration for IKE policies
crypto ikev1 policy 10
!--- Enables the IKE policy configuration (config-isakmp)
!--- command mode, where you can specify the parameters that
!--- are used during an IKE negotiation.
authentication pre-share
encryption 3des
hash sha
group 2
lifetime 86400
!--- Use this command in order to create and manage the database of
!--- connection-specific records like group name
!--- as 10.1.2.1, IPsec type as L2L, and password as
!--- pre-shared key for IPsec tunnels.
tunnel-group 10.1.2.1 type ipsec-l2l
tunnel-group 10.1.2.1 ipsec-attributes
!--- Specifies the preshared key "cisco123" which should
!--- be identical at both peers.
ikev1 pre-shared-key *
telnet timeout 5
ssh timeout 5
console timeout 0
priority-queue outside
queue-limit 2048
tx-ring-limit 256
!
class-map Voice
match dscp ef
class-map Data
match tunnel-group 10.1.2.1
match flow ip destination-address
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns preset_dns_map
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect netbios
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect skinny
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect sunrpc
inspect tftp
inspect sip
inspect xdmcp
policy-map Voicepolicy
class Voice
priority
class Data
police output 200000 37500
!
service-policy global_policy global
service-policy Voicepolicy interface outside
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
: end
ACL 기반 QoS 컨피그레이션
!--- Permits inbound H.323 calls.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list 100 extended permit tcp 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
10.1.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq h323
!--- Permits inbound Session Internet Protocol (SIP) calls.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list 100 extended permit tcp 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
10.1.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq sip
!--- Permits inbound Skinny Call Control Protocol (SCCP) calls.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list 100 extended permit tcp 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
10.1.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq 2000
!--- Permits outbound H.323 calls.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list 105 extended permit tcp 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0
172.16.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq h323
!--- Permits outbound SIP calls.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list 105 extended permit tcp 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0
172.16.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq sip
!--- Permits outbound SCCP calls.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list 105 extended permit tcp 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0
172.16.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq 2000
!--- Apply the ACL 100 for the inbound traffic of the outside interface.
ciscoasa(config)#access-group 100 in interface outside
!--- Create a class map named Voice-IN.
ciscoasa(config)#class-map Voice-IN
!--- Specifies the packet matching criteria which
!--- matches the traffic flow as per ACL 100.
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match access-list 100
!--- Create a class map named Voice-OUT.
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#class-map Voice-OUT
!--- Specifies the packet matching criteria which
!--- matches the traffic flow as per ACL 105.
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match access-list 105
!--- Create a policy to be applied to a set
!--- of Voice traffic.
ciscoasa(config-cmap)#policy-map Voicepolicy
!--- Specify the class name created in order to apply
!--- the action to it.
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class Voice-IN
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class Voice-OUT
!--- Strict scheduling priority for the class Voice.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#priority
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#end
ciscoasa#configure terminal
ciscoasa(config)#priority-queue outside
!--- Apply the policy defined to the outside interface.
ciscoasa(config)#service-policy Voicepolicy interface outside
ciscoasa(config)#end
VPN 구성을 사용하는 ACL 기반 QoS
ciscoasa#show running-config
: Saved
:
ASA Version 9.2(1)
!
hostname ciscoasa
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
names
!
interface GigabitEthernet0
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet2
nameif DMZ1
security-level 95
ip address 10.1.5.1 255.255.255.0
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
ftp mode passive
!--- This crypto ACL-permit identifies the
!--- matching traffic flows to be protected via encryption.
access-list 110 extended permit ip 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
access-list 110 extended permit ip 10.1.5.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.6.0 255.255.255.0
!--- Permits inbound H.323, SIP and SCCP calls.
access-list 100 extended permit tcp 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq h323
access-list 100 extended permit tcp 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq sip
access-list 100 extended permit tcp 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq 2000
!--- Permit outbound H.323, SIP and SCCP calls.
access-list 105 extended permit tcp 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq h323
access-list 105 extended permit tcp 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq sip
access-list 105 extended permit tcp 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.0
255.255.255.0 eq 2000
pager lines 24
mtu inside 1500
mtu outside 1500
no failover
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
access-group 100 in interface outside
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.4.2 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart
crypto ipsec ikev1 transform-set myset esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
crypto map mymap 10 match address 110
crypto map mymap 10 set peer 10.1.2.1
crypto map mymap 10 set ikev1 transform-set myset
crypto map mymap interface outside
crypto ikev1 policy 10
authentication pre-share
encryption 3des
hash sha
group 2
lifetime 86400
tunnel-group 10.1.2.1 type ipsec-l2l
tunnel-group 10.1.2.1 ipsec-attributes
ikev1 pre-shared-key *
telnet timeout 5
ssh timeout 5
console timeout 0
priority-queue outside
!
class-map Voice-OUT
match access-list 105
class-map Voice-IN
match access-list 100
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns preset_dns_map
inspect ftp
!--- Inspection enabled for H.323, H.225 and H.323 RAS protocols.
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect netbios
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
!--- Inspection enabled for Skinny protocol.
inspect skinny
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect sunrpc
inspect tftp
!--- Inspection enabled for SIP.
inspect sip
inspect xdmcp
policy-map Voicepolicy
class Voice-IN
class Voice-OUT
priority
!
service-policy global_policy global
service-policy Voicepolicy interface outside
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
: end
참고: 이 섹션에서 사용되는 명령에 대한 자세한 내용을 보려면 Command Lookup Tool(registeredcustomers만 해당)을 사용합니다.
다음을 확인합니다.
구성이 올바르게 작동하는지 확인하려면 이 섹션을 활용하십시오.
쇼 서비스 정책 경찰
트래픽 폴리싱에 대한 QoS 통계를 보려면 police 키워드와 함께 show service-policy 명령을 사용합니다.
ciscoasa(config)# show ser
ciscoasa(config)# show service-policy police
Interface outside:
Service-policy: POLICY-WEB
Class-map: Class-Policy
Output police Interface outside:
cir 1000000 bps, bc 31250 bytes
conformed 0 packets, 0 bytes; actions: transmit
exceeded 0 packets, 0 bytes; actions: drop
conformed 0 bps, exceed 0 bps
show service-policy priority
priority 명령을 구현하는 서비스 정책에 대한 통계를 보려면 show service-policy 명령을 priority 키워드와 함께 사용합니다.
ciscoasa# show service-policy priority
Global policy:
Service-policy: qos_outside_policy
Interface outside:
Service-policy: qos_class_policy
Class-map: voice-traffic
Priority:
Interface outside: aggregate drop 0, aggregate transmit 9383
서비스 정책 셰이프 표시
ciscoasa(config)# show service-policy shape
Interface outside:
Service-policy: qos_outside_policy
Class-map: class-default
shape (average) cir 2000000, bc 16000, be 16000
Queueing
queue limit 64 packets
(queue depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
(pkts output/bytes output) 0/0
우선순위 큐 통계 표시
인터페이스에 대한 우선순위 대기열 통계를 표시하려면 특권 EXEC 모드에서 show priority-queue statistics 명령을 사용합니다. BE(best-effort) 큐 및 LLQ에 대한 통계가 결과로 표시됩니다. 이 예에서는 outside라는 인터페이스에 대해 show priority-queue statistics 명령을 사용하고 명령 출력을 보여 줍니다.
ciscoasa# show priority-queue statistics outside
Priority-Queue Statistics interface outside
Queue Type = BE
Packets Dropped = 0
Packets Transmit = 0
Packets Enqueued = 0
Current Q Length = 0
Max Q Length = 0
Queue Type = LLQ
Packets Dropped = 0
Packets Transmit = 0
Packets Enqueued = 0
Current Q Length = 0
Max Q Length = 0
ciscoasa#
이 통계 보고서에서 행 항목의 의미는 다음과 같습니다.
- Packets Dropped는 이 큐에서 삭제된 패킷의 전체 수를 나타냅니다.
- Packets Transmit은 이 큐에서 전송된 패킷의 전체 수를 나타냅니다.
- Packets Enqueued는 이 큐에 있는 패킷의 전체 수를 나타냅니다.
- Current Q Length(현재 큐 길이)는 이 큐의 현재 깊이를 나타냅니다.
- Max Q Length(최대 큐 길이)는 이 큐에서 발생한 최대 깊이를 나타냅니다.
출력 인터프리터 툴(등록된 고객만 해당)은 특정 showcommand를 지원합니다. show 명령 출력의 분석을 보려면 출력 인터프리터 툴을 사용합니다.
문제 해결
현재 이 설정에 사용할 수 있는 특정 문제 해결 정보가 없습니다.
추가 정보
다음은 트래픽 셰이핑 기능에 의해 소개된 몇 가지 버그입니다.
| Cisco 버그 IDCSCsq08550 | 우선 순위 큐잉을 사용하는 트래픽 셰이핑은 ASA에서 트래픽 실패를 일으킵니다. |
| Cisco 버그 IDCSCsx07862 | 우선 순위 큐잉을 사용하는 트래픽 셰이핑은 패킷 지연 및 삭제를 유발합니다. |
| Cisco 버그 IDCSCsq07395 | policy-map이 편집된 경우 쉐이핑 service-policy 추가는 실패합니다. |
FAQ
이 섹션에서는 이 문서에 설명된 정보와 관련하여 가장 자주 묻는 질문 중 하나에 대한 답변을 제공합니다.
VPN 터널을 통과할 때 QoS 마킹이 유지됩니까?
예. 공급자가 전송 중인 QoS 마킹을 제거하지 않는 경우 QoS 마킹이 사업자 네트워크를 통과할 때 터널에 보존됩니다.
팁: 자세한 내용은 CLI Book 2: Cisco ASA Series Firewall CLI 컨피그레이션 가이드, 9.2의 DSCP 및 DiffServ Preservationsection을 참조하십시오.
관련 정보
개정 이력
| 개정 | 게시 날짜 | 의견 |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
02-Mar-2007 |
최초 릴리스 |
 피드백
피드백