Call Flow Debugging van een SSG Internet Gateway geconfigureerd met DHCP Secure ARP, SSG Port-Bundle Host Key, SSG TCP Redirect, SESM en SSG/DHCP-bewustzijn
Inhoud
Inleiding
De focus van dit document is een IOS Internet Gateway die SSG en DHCP met SESM voor poortservices runt.
Voorwaarden
Vereisten
Er zijn geen specifieke vereisten van toepassing op dit document.
Gebruikte componenten
Dit document is niet beperkt tot specifieke software- en hardware-versies.
Conventies
Achtergrondinformatie
Overzicht van technologie en functies
Service Selection Gateway (SSG)
Service Selection Gateway (SSG) is een switching-oplossing voor serviceproviders die intranet, extranet en internetverbindingen aanbieden aan abonnees met technologie voor breedbandtoegang, zoals Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL), kabelmodems of draadloze verbindingen om gelijktijdige toegang tot netwerkservices mogelijk te maken.
SSG werkt in combinatie met Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager (SESM). Samen met het SESM biedt SSG abonnees van internetservices de verificatie van abonnees, servicesselectie en -aansluitingsmogelijkheden. Abonnees reageren met een SESM-webtoepassing op een standaard Internet-browser.
Het SESM werkt in twee modi:
-
RADIUS-modus: in deze modus vindt u abonnees en servicemateriaal op een RADIUS-server. SESM in RADIUS-modus is gelijk aan de SSD.
-
LDAP-modus: de lichtgewicht Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)-modus geeft toegang tot een folder die compatibel is met LDAP voor abonnees en dienstenprofiel. Deze modus heeft ook de functionaliteit voor SESM-webtoepassingen verbeterd en gebruikt een op rol gebaseerd toegangscontrolemodel (RBAC) om de toegang van abonnees te beheren.
SSG-poortbundel host-toets
De SSG Port-Bundle Host Key optie verbetert de communicatie en functionaliteit tussen SSG en SESM met een mechanisme dat het IP-adres en de bronpoort van de host-bron gebruikt om abonnees te identificeren en te controleren.
Met de SSG Port-Bundle Host Key optie, voert SSG port-adreevertaling (PAT) en Network-Address Translation (NAT) uit op het HTTP-verkeer tussen de abonnee en de SESM-server. Wanneer een abonnee een HTTP-pakket naar de SESM-server stuurt, maakt SSG een poortkaart die het bron-IP-adres wijzigt in een geconfigureerd SSG-bron-IP-adres en de bron-TCP-poort wijzigt in een poort die door SSG wordt toegewezen. SSG wijst een bundel poorten aan elke abonnee toe omdat één abonnee meerdere gelijktijdige TCP-sessies kan hebben wanneer hij toegang krijgt tot een webpagina. De toegewezen host-toets, of de combinatie van poortbundel en SSG IP-adres, identificeert elke abonnee uniek. De host-toets wordt in RADIUS-pakketten verzonden tussen de SESM-server en SSG in de Subscriber IP-leverancierspecifieke eigenschap (VSA). Wanneer de SESM-server een antwoord naar de abonnee stuurt, vertaalt SSG het IP-adres van de bestemming en de TCP-poort van de bestemming in overeenstemming met de poortkaart.
SSG TCP-omleiding voor niet-geauthentiseerde gebruikers
Omleiding voor niet-geauthentiseerde gebruikers richt pakketten van een gebruiker op als de gebruiker niet bij de serviceprovider heeft geautoriseerd. Wanneer een niet-geautoriseerde abonnee probeert verbinding te maken met een service op een TCP-poort (bijvoorbeeld naar www.cisco.com), stuurt SSG TCP-omleiding het pakket terug naar het poort (SESM of een groep SESM-apparaten). SESM geeft een herleiding naar de browser uit om de openings van een aanmelding pagina weer te geven. De abonnee logt in bij SESM en is gecertificeerd en geautoriseerd. SESM presenteert de abonnee vervolgens met een gepersonaliseerde startpagina, de startpagina van de serviceprovider of de oorspronkelijke URL.
DHCP-beveiligde IP-adrestoewijzing
Met de optie DHCP Secure IP-adrestoewijzing kunt u ARP-tabelitems beveiligen met DHCP-leaseovereenkomsten (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) in de DHCP-database. Deze optie waarborgt en synchroniseert het MAC-adres van de client naar de DHCP-band, waardoor niet-geautoriseerde klanten of hackers de DHCP-server niet kunnen spoofen en een DHCP-lease van een geautoriseerde client kunnen overnemen. Wanneer deze optie is ingeschakeld en de DHCP-server een IP-adres aan de DHCP-client wijst, voegt de DHCP-server een beveiligde ARP-ingang toe aan de ARP-tabel met het toegewezen IP-adres en het MAC-adres van de client. Deze ARP ingang kan niet door een andere dynamische ARP pakketten worden bijgewerkt, en deze ARP ingang bestaat in de ARP tabel voor de geconfigureerde leasetijd of zolang de lease actief is. De beveiligde ARP-ingang kan alleen worden verwijderd door een expliciet eindbericht van de DHCP-client of DHCP-server wanneer de DHCP-binding verloopt. Deze optie kan worden ingesteld voor een nieuw DHCP-netwerk of worden gebruikt om de beveiliging van een bestaand netwerk te verbeteren. De configuratie van deze optie onderbreekt de service niet en is niet zichtbaar voor de DHCP-client.
Testbed Diagram
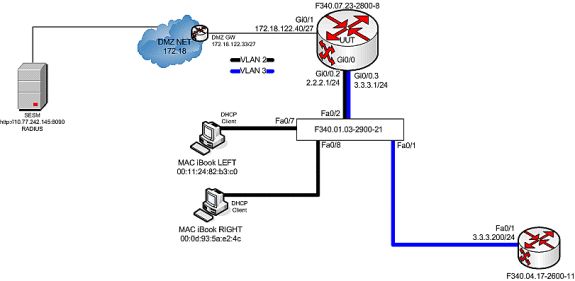
Call Flow Debug
Voer de volgende stappen uit:
-
Wanneer MAC LEFT de Ethernet-kabel voor het eerst met dit netwerk verbindt, leaset het IP-adres 2.2.2.5/29 van de IOS DHCP-server die op "F340.07.23-2800-8 loopt."
debug ip dhcp server packet debug ssg dhcp events *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: DHCP-DISCOVER event received. SSG-dhcp awareness feature enabled *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2. *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool name called for 0011.2482.b3c0. No hostobject *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool class called, class name = Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPOFFER to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: IP address notification received. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: HostObject not present *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Can't find any hostname to update *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPACK to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). F340.07.23-2800-8#show ip dhcp binding Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF: IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type Hardware address/ User name 2.2.2.5 0100.1124.82b3.c0 Oct 13 2008 08:37 PM Automatic -
Nadat het IP-adres 2.2.2.5 met succes heeft gehuurd, opent MAC iBook LEFT een webbrowser en wijst deze op http://3.3.3.200, dat wordt gebruikt om beschermde bronnen te simuleren die zijn gekoppeld aan SSG Service "distlearning" (distlearning van SSG-services). SSG-service "distlearning" is lokaal gedefinieerd in de SSG-router "F340.07.23-2800-8":
local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255"
In realiteit is http://3.3.3.200 een Cisco IOS router die voor "ip http server" is geconfigureerd en luistert op TCP 80, dus het is in principe een webserver.
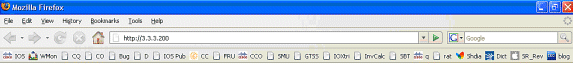
Nadat het MAC iBook LEFT probeert om naar http://3.3.3.200 te bladeren, aangezien deze verbinding op een interface is ingesteld die is geconfigureerd met "ssg Richting downlink", controleert de SSG router eerst op het bestaan van een actief SSG Host Object voor het bron IP-adres van het HTTP-verzoek. Omdat dit het eerste dergelijke verzoek van IP adres 2.2.2.5 is, bestaat een SSG Host Object niet en wordt een TCP-omleiding naar SESM geconcretiseerd voor host 2.2.2.5 door deze configuratie:
ssg tcp-redirect port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 All hosts with destination requests on these TCP Ports are candidates for redirection. server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 10.77.242.145 is the SESM server and it’s listening for HTTP on TCP 8090. “server” MUST be in default network or open-garden. redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If an SSG router receives a packets on an interface with “ssg direction downlink” configured, it first compares the Source IP address of the packet with the SSG Host Object Table. If an Active SSG Host Object matching the Source IP address of this packet is not found, AND the destination TCP Port of the packet matches “port-list ports”, and the destination IP address is NOT included as a part of “ssg default-network” OR SSG Open Garden, then the user will be redirected because his is unauthenticated [no Host Object] and his packet is destined for a TCP port in the “port-list ports”. The user will then be captivated until an SSG Host Object is created, or until a timeout which is configurable via “redirect captivate initial default group”. debug ssg tcp redirect debug ssg ctrl-event *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: SSG-TCP-REDIR:-Up: created new remap entry for unauthorised user at 2.2.2.5 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Redirect server set to 10.77.242.145,8090 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Initial src/dest port mapping 49273<->80 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg tcp-redirect mappings Authenticated hosts: No TCP redirect mappings for authenticated users Unauthenticated hosts: Downlink Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 TCP remapping Host:2.2.2.5 to server:10.77.242.145 on port:8090 The initial HTTP request from 2.2.2.5 had a source TCP Port of 49273 and a destination IP address of 3.3.3.200 and TCP port of 80. Because of the SSG TCP Redirect, the destination IP header is overwritten with the socket of the SESM server 10.77.242.145:8090. If Port Bundle Host Key were NOT configured, the Source socket of 2.2.2.5:49273 would remain unchanged. However, in this case, Port Bundle Host Key is configured therefore the source address of this packet is ALSO changed based on this configuration: ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Any packets destined to SESM on TCP ports 80-8100 are subject to PBHK source NAT to IP socket 172.18.122.40, starting with a port of 64. *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: group:ssg_tr_unauth, web-proxy:0 *Oct 13 20:24:37.417: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Down: TCP-FIN Rxd for user at 2.2.2.5, port 49273 *Oct 13 20:24:37.421: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Up: TCP-FIN Rxd from user at 2.2.2.5, src port 49273 As a part of this SSG TCP Redirect, the original URL is preserved http://3.3.3.200 but the destination IP socket is rewritten to 10.77.242.145:8090. So, when the SESM receives this URL of http://3.3.3.200 on TCP port 8090, it sends an HTTP redirect back toward the client’s browser directing the client to the SESM login page, which is http://10.77.242.145:8080/home?CPURL=http%3A%2F%2F3.3.3. 200%2F&t=fma4443t. Notice the Browser Redirect points the Client Browser to TCP 8080 for captive portal. As such, the TCP session for the initial IOS SSG Redirect to 10.77.242.145:8090 is terminated. Also, notice SESM has captured the original URL of http://3.3.3.200 in the Redirect. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (4,&) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=4 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account status query for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, Ack the query with Complete ID. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 4 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext With Port Bundle Host Key configured, all HTTP communications between Client and SESM are subject to Port Bundling, which is effectively Source NAT for the TCP socket. Above, the “SSG-CTL-EVN” messages debug the communication between the SESM and the IOS SSG Router using a proprietary RADIUS-based protocol. When using Port Bundle Host Key, SESM always uses the Port Bundle to identify the host, which in this case is 172.18.122.40:64. You’ll see when SESM sends the HTTP redirect resulting in the Web browser connecting to 10.77.242.145:8090, SESM also queries SSG on the Control Channel for existence of Host Object for 172.18.122.40:64, which the SSG Router knows is actually 2.2.2.5. Since no Host Object is present, the SSG Router sends the SESM “No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64” This can be confirmed at this point like this: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host ### Total HostObject Count: 0Op dit punt ziet de browser op MAC iBook Left er zo uit als wanneer http://3.3.3.200 is ingevoerd:
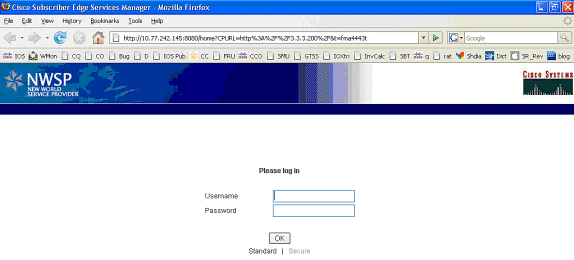
Na de IOS SSG TCP- en SESM HTTP-omleidingen ziet het scherm er zo uit:
-
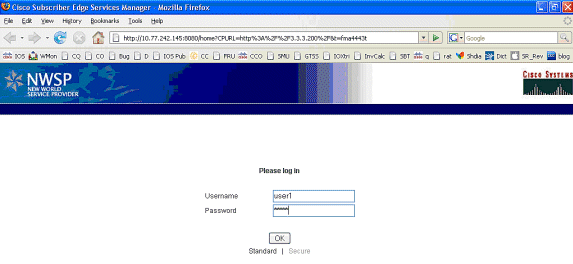
Nadat de SSG TCP opnieuw is gericht op SESM en de daaropvolgende HTTP-herleiding die door SESM is verzonden naar de browser van MAC iBook Left, geeft MAC iBook Left user1 in als de gebruikersnaam en cisco als het wachtwoord:
-
Nadat de knop OK is ingedrukt, stuurt het SESM de SSG-router deze aanmeldingsgegevens via een eigen RADIUS-gebaseerd protocol.
*Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (1,user1) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=1 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account logon for host 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: No auto-domain selected for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Authenticating user user1. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: ssg_aaa_nasport_fixup function *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: slot=0, adapter=0, port=0, vlan-id=2, dot1q-tunnel-id=0, vpi=0, vci=0, type=10 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext
-
Op zijn beurt bouwt de SSG router een Packet voor RADIUS-toegangsaanvraag en stuurt het naar RADIUS om gebruiker1 te authentiseren:
*Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS(00000008): Send Access-Request to 10.77.242.145:1812 id 1645/11, len 88 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: authenticator F0 56 DD E6 7E 28 3D EF - BC B1 97 6A A9 4F F2 A6 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Password [2] 18 * *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40
-
RADIUS reageert met een access-Accept voor gebruiker1 en een SSG Host Object wordt aangemaakt in "F340.07.23-2800-8":
*Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Received from id 1645/11 10.77.242.145:1812, Access-Accept, len 273 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: authenticator 52 7B 50 D7 F2 43 E6 FC - 7E 3B 22 A4 22 A7 8F A6 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 23 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 17 "NInternet-Basic" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 13 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 7 "Niptv" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 14 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 8 "Ngames" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ndistlearn" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ncorporate" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 22 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 16 "Nhome_shopping" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nbanking" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nvidconf" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS(00000008): eceived from id 1645/11 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 4 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating radius packet *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Response is good *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-EVN: HostObject::HostObject: size = 616 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::Reset *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList NInternet-Basic *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Niptv *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ngames *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ndistlearn *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ncorporate *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nhome_shopping *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nbanking *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nvidconf *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: DoAccountLogon: ProfileCache is Enabled *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Account logon is accepted [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, user1] *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 1 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for host 2.2.2.5 Finally, our SSG Host Object is created for 2.2.2.5. Notice that “user1” RADIUS profile is configured with many ssg-account-info VSA with “N” Attribute, which is an SSG code for Service to which the user is subscribed. Please note, this doesn’t mean “user1” has any Active services at this point, which can be confirmed with: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 1: 2.2.2.5 [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64] ### Active HostObject Count: 1 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content --- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:37:09.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: NONE AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE
-
Op dit punt is user1 gedefinieerd als een SSG Host Object maar heeft nog geen toegang tot SSG-services. MAC-iBook Links wordt weergegeven met het servicesselectiescherm en klikt op Afstand leren:
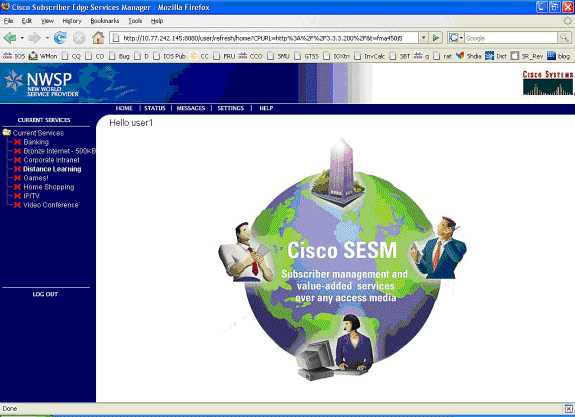
-
Nadat op afstandsbediening is gedrukt, communiceert het SESM-venster met het controlekanaal naar de SSG-router:
debug ssg ctrl-events *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (11,distlearn) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 SSG Router is receiving control channel command that SSG User 172.18.122.40:64 [maps to 2.2.2.5] wants to activate SSG Service ‘distlearn’. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=11 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling service logon for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating pseudo ServiceInfo for service: distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-EVN: ServiceInfo::ServiceInfo: size = 416 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: ServiceInfo: Init servQ and start new process for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Got profile for distlearn locally Since “distlearn” is available from local configuration: local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" ...we don’t need to make a AAA call to download SSG Service Information. However, please note that in most real-world SSG implementations, SSG Services are defined on the RADIUS AAA Server. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Create a new service table for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service bound on this interface are : distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service distlearn bound to interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 firsthop 0.0.0.0 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: Service Address List : *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: Addr:3.3.3.200 mask:255.255.255.255 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add a new service distlearn to an existing table Here the SSG creates a Service Table for distlearn and binds it to an “ssg direction uplink” interface complete with the R attribute for the Service. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking connection activation for 172.18.122.40:64 to distlearn. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating ConnectionObject (172.18.122.40:64, distlearn) *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: ConnectionObject::ConnectionObject: size = 304 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 2 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking maximum service count. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Opening connection for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Connection opened *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service logon is accepted. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating the ConnectionObject. Once the Service is verified locally, SSG needs to build a “Connection” where a “Connection” is a tuple with: A. SSG Host Object B. SSG Service Name and Attributes C. SSG Downlink interface D. SSG Upstream interface A-D are used to create a pseudo hidden VRF service table for which traffic from this host can transit. See here: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg connection 2.2.2.5 distlearn ------------------------ConnectionObject Content ---- User Name: user1 Owner Host: 2.2.2.5 Associated Service: distlearn Calling station id: 0011.2482.b3c0 Connection State: 0 (UP) Connection Started since: *20:40:21.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:41:04.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 Connection Traffic Statistics: Input Bytes = 420, Input packets = 5 Output Bytes = 420, Output packets = 5 Session policing disabled F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content ----------- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:40:23.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: distlearn; AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE -
De SSG Connection is omhoog, en de Call Flow wordt voltooid. MAC iBook Left kan met succes naar http://3.3.3.200 bladeren:
Configuratie-verklaring van SSG-router met functiedocumenten
version 12.4 service nagle no service pad service tcp-keepalives-in service tcp-keepalives-out service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname F340.07.23-2800-8 ! boot-start-marker boot system flash flash: c2800nm-adventerprisek9-mz.124-21.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1024000 debugging ! aaa new-model ! aaa authorization network default group radius ! aaa session-id common no ip source-route ! ip cef ip dhcp relay information trust-all ip dhcp use vrf connected ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.1 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.2 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.3 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.4 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.6 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.7 We are excluding 2.2.2.1-4 and 2.2.2.6-7 to ensure the only DHCP address that will be leased is 2.2.2.5/29. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server ip dhcp pool dhcp_guest_v3501 network 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.248 default-router 2.2.2.1 dns-server 172.18.108.34 lease 0 4 update arp If an interface on this router is configured with an address in the 2.2.2.0/29 range, it will field DHCP request from host on that network and assign IP address 2.2.2.5, GW 2.2.2.1, and DNS Server 172.18.108.24. The lease time on the IP address will be 4 hours. Also, “update arp” will ensure ARP entries for IP addresses leased via DHCP will match the MAC entry in the DHCP Binding table. This will prevent SSG session hijacking in the event a static user re-uses a DHCP [or is given] leased address. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuring DHCP Services for Accounting and Security ! no ip domain lookup ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3 ip admission max-nodata-conns 3 ! voice-card 0 no dspfarm ! ssg enable Enables SSG subsystem. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg intercept dhcp Enables SSG/DHCP Awareness. In our example, this will result in an SSG Host object being destroyed when either of these occur: A. A DHCPRELEASE message is received for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. B. A DHCP Lease expires for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. Configuring SSG for On-Demand IP Address Renewal ssg default-network 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 All packets ingress to “ssg direction downlink” interfaces can access the “ssg default-network” regardless as to whether a Host or Connection Object exists. SSG allows all users, even unauthenticated users, to access the default network. Typically, SESM belongs to the default network. However, other types of servers, such as DNS/DHCP servers or TCP-Redirect servers, can also be part of the default network. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg service-password cisco If an SSG Service is not defined locally and we therefore need to make a RADIUS call when a user subscribes to an SSG Service, the password “cisco” is used in the RADIUS Access-Request for the Service. ssg radius-helper auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 ssg radius-helper key cisco Used to communicate with SESM on SSG Control Channel. SESM must also maintain a similar static configuration for each SSG Router it serves. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg auto-logoff arp match-mac-address interval 30 In the absence of user traffic, SSG will send an ARP Ping for all Active Host Objects and will invoke an AutoLogoff if either the host fails to reply or the MAC address of the host has changed. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg bind service distlearn GigabitEthernet0/0.3 SSG traffic is not routed using the Global routing table. Instead it’s routed from “ssg direction downstream” interface using the information in the mini-VRF seen in “show ssg connection”, which includes a manual binding of Service<-->”ssg direction uplink” interface. Hence, it is a requirement of SSG to manually bind services to interfaces or next-hop IP addresses. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services ssg timeouts session 64800 Absolute timeout for SSG Host Object is 64800 seconds. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Port Bundle Host Key configuration. All traffic destined to 10.77.242.145 in the range of TCP 80 to 8100 will be Source NATed to 172.18.122.40. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg tcp-redirect Enters SSG redirect sub-config. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 Defines a list of destination TCP ports which are candidates for TCP redirection. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 Defines a redirect server list and defines the TCP port on which they’re listening for redirects. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If a Host Object does NOT exist and the traffic is ingress to an “ssg direction downlink” interface AND its destination port is in port-list ports, THEN redirect this traffic to “server-group ssg_tr_unauth”. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers ssg service-search-order local remote Look for SSG Service defined in a local-profile in IOS configuration before making a AAA call to download Service information. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" Local definition of SSG Service “distlearn” 26 9 251 is Vendor Specific, Cisco, SSG Service Info Attributes defined herein: R: Destination Network, Specifies IP routes belonging to this Service Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services RADIUS Profiles and Attributes for SSG interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 description Guest Wireless Vlan encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.248 no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip mroute-cache ssg direction downlink All SSG Host Objects should be located on downlink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 description Routed connection back to Blue encapsulation dot1Q 3 ip address 3.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 ssg direction uplink All SSG Services should be located on uplink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.122.40 255.255.255.224 duplex auto speed auto ! ip forward-protocol nd ip route 10.77.242.144 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 157.157.157.0 255.255.255.0 3.3.3.5 ip route 172.18.108.34 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 172.18.124.101 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip radius source-interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ! radius-server host 10.77.242.145 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 timeout 5 retransmit 3 key 7 070C285F4D06 ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
OVERWEGINGEN VOOR BEWERKING EN Sessiehergebruik
Wanneer u SSG en DHCP samen gebruikt, kunnen deze scenario's kwaadaardige gebruikers toestaan om een geauthentiek SSG Host Object te hergebruiken dat onecht toegang tot veilige bronnen toestaat:
-
Als de bestandsindeling voor SSG/DHCP niet is ingesteld met "ssg intercept dhcp", kan een nieuwe DHCP-gebruiker een eerder geleased IP-adres leasen waarvoor nog een SSG Host Object bestaat. Aangezien het eerste TCP-verzoek van deze nieuwe gebruiker een matching, maar ook groots, SSG Host Object dat overeenkomt met het bron IP-adres, wordt deze gebruiker onecht gebruik van beschermde resources verleend. Dit kan voorkomen worden met "ssg intercept dhcp," wat resulteert in het verwijderen van een SSG Host Object wanneer een van de volgende situaties zich voordoet:
-
DHCPRELEASE wordt ontvangen voor een IP adres dat een Actief Host Object aanpast.
-
De DHCP-lease verloopt voor een IP-adres dat overeenkomt met een actief hostobject.
-
-
Als een DHCP-gebruiker het geleasede IP-adres naar een kwaadaardige gebruiker socialiseert voordat er een DHCP-logout zonder scène wordt uitgevoerd, namelijk een DHCP-logout waarvoor geen DHCP-RELEASE wordt verzonden, kan de kwaadaardige gebruiker de machine statisch configureren met dit IP-adres en het SSG Host-object opnieuw gebruiken, ongeacht of "ssg intercept dhcp" is geconfigureerd. Dit kan voorkomen worden met een combinatie van "ssg intercept dhcp" en "update arp" ingesteld onder de IOS DHCP-pool. Het "update arp" garandeert dat het enige IOS subsysteem dat ARP-vermeldingen kan toevoegen of verwijderen het DHCP-serversubsysteem is. Met "update arp," past de IP-naar-MAC DHCP-binding altijd de IP-naar-MAC-binding in de ARP-tabel aan. Zelfs al heeft de kwaadaardige gebruiker een statistisch geconfigureerd IP-adres dat overeenkomt met het SSG Host-object, is het verkeer niet toegestaan om de SSG-router in te voeren. Omdat het MAC-adres niet overeenkomt met het MAC-adres van de huidige DHCP-binding voorkomt de IOS DHCP-server dat er een ARP-invoer wordt gemaakt.
-
Wanneer SSG en DHCP samen worden geconfigureerd, voorkomen "ssg intercept dhcp" en "update arp" dat de sessie wordt hergebruikt. De laatste niet met veiligheid verband houdende uitdaging is de DHCP-Lease en ARP-ingang te bevrijden wanneer een DHCP-host een niet-graceful logout uitvoert. De configuratie van "geautoriseerd arp" op de interface "ssg Richting downlink" resulteert in periodieke ARP verzoeken die naar alle hosts worden gestuurd om er zeker van te zijn dat ze nog steeds actief zijn. Als geen respons wordt ontvangen van deze periodieke ARP berichten, wordt de DHCP-binding vrijgegeven en wordt het IOS DHCP-subsysteem de ARP-ingang verwijderd.
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 arp authorized arp probe interval 5 count 15
In dit voorbeeld, wordt een ARP verzoek verzonden periodiek om alle bekende ARP ingangen op Fa0/0 elke 5s te verfrissen. Na 15 mislukkingen, wordt de DHCP-binding vrijgegeven en het IOS DHCP-subsysteem verwijdert de ARP-ingang.
In de context van SSG zonder "geautoriseerd arp," als een DHCP-host een niet-graceful logout uitvoert, blijven de DHCP-leaseoplossing en het bijbehorende SSG-hostobject actief totdat de lease voor dit DHCP-adres verloopt, maar er vindt geen sessie hergebruik plaats zolang "ssg intercept dhcp" mondiaal is geconfigureerd.
De "geautoriseerde arp" schakelt dynamisch ARP learning uit op de interface waarop deze is ingesteld. De enige ARP-vermeldingen op de interface in kwestie zijn die welke door de IOS DHCP-server worden toegevoegd nadat een lease is gestart. Deze ARP-vermeldingen worden vervolgens door IOS DHCP-server gewist nadat de lease is beëindigd, ofwel door ontvangst van een DHCP-RELEASE, een leasebeëindiging of een ARP-test wegens een niet-gracieus DHCP-logout.
Opmerkingen over implementatie:
-
De "ssg auto-logoff arp" en "ssg auto-logoff icmp" zijn onwenselijke methoden om te voorkomen dat sessie opnieuw wordt gebruikt of dat er beveiligingsproblemen ontstaan. De "arp"- en "icmp"-varianten van "ssg auto-logoff" sturen alleen een ARP- of IMCP PING als er geen verkeer wordt gezien op de SSG-verbinding binnen het geconfigureerde "interval", waarvan de laagste 30 seconden is. Als DHCP een eerder gebruikt IP-adres binnen 30 seconden leaset of een kwaadaardige gebruiker stort een momenteel-gebonden DHCP-adres binnen 30 seconden in, wordt de sessie opnieuw gebruikt omdat SSG verkeer op het verbindingsobject ziet en "ssg auto-logoff" niet aanvoert.
-
In alle use gevallen, wordt de sessie hergebruik niet voorkomen als een kwaadaardige host een MAC-adresplaats uitvoert.
Tabel 1 - Overwegingen bij hergebruik en beveiliging van sessie in SSG/DHCP-implementaties
| Opdracht | Functie | Security implicaties |
|---|---|---|
| ssg auto-logoff arp [overeenkomend-mac-adres] [interval seconden] ssg auto-logoff icmp [timeout milliseconden] [pakketnummer] [interval seconden] | Verwijdert SSG Host Object na het falen van ARP- of ICMP-PING, die alleen worden verzonden nadat er geen verkeer is gezien op de SSG-verbinding binnen het "interval." | Hergebruikt sessie als DHCP een eerder gebruikt IP-adres binnen 30 seconden leaset of als een kwaadaardige gebruiker een momenteel-gebonden DHCP-adres statistisch configureren binnen 30 seconden omdat SSG verkeer op het verbindingsobject ziet en "ssg auto-logoff" niet aanvoert. |
| SDG-onderschepping | Maakt SSG/DHCP-bewustzijn mogelijk waarmee het SSG Host Object binnen deze gebeurtenissen kan worden gewist: Een DHCPRELEASE wordt ontvangen voor een IP adres dat een Actief Host Object aanpast. B. De DHCP-leaseoplossing verloopt voor een IP-adres dat overeenkomt met een actief hostobject. | Hiermee voorkomt u dat DHCP-gebruikers opnieuw gebruik kunnen maken van SSG-sessies, maar het voorkomt niet dat statische gebruikers DHCP-adressen of het hergebruik van SSG-sessies spotten. |
| IP-pool - onderdeel TEST-update | Zorg ervoor dat het enige IOS-subsysteem dat geschikt is voor de toevoeging of verwijdering van ARP-items het subsysteem DHCP-server is. | Voorkomt dat alle sessie wordt hergebruikt als dit wordt geconfigureerd met "ssg intercept dhcp." Indien geconfigureerd zonder "ssg intercept dhcp", is wanneer DHCP een eerder gebruikt IP-adres leasen, sessiehergebruik nog mogelijk. |
| interface Fast Ethernet0/0 IP-pijp toegestaan | Zend periodieke ARP verzoeken aan alle gastheren toe om ervoor te zorgen dat zij nog actief zijn. Hiermee wordt dynamisch ARP-leren uitgeschakeld. | Hiermee kan DHCP-binding en ARP-entry gewist worden wanneer een DHCP-gebruiker een niet-graceful logout uitvoert. |
Gerelateerde informatie
Revisiegeschiedenis
| Revisie | Publicatiedatum | Opmerkingen |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2008 |
Eerste vrijgave |
Contact Cisco
- Een ondersteuningscase openen

- (Vereist een Cisco-servicecontract)
 Feedback
Feedback