Seleção do caminho externo do OSPF: Tipo 2 externo (E2) VS NSSA Tipo 2 (N2)
Opções de download
Linguagem imparcial
O conjunto de documentação deste produto faz o possível para usar uma linguagem imparcial. Para os fins deste conjunto de documentação, a imparcialidade é definida como uma linguagem que não implica em discriminação baseada em idade, deficiência, gênero, identidade racial, identidade étnica, orientação sexual, status socioeconômico e interseccionalidade. Pode haver exceções na documentação devido à linguagem codificada nas interfaces de usuário do software do produto, linguagem usada com base na documentação de RFP ou linguagem usada por um produto de terceiros referenciado. Saiba mais sobre como a Cisco está usando a linguagem inclusiva.
Sobre esta tradução
A Cisco traduziu este documento com a ajuda de tecnologias de tradução automática e humana para oferecer conteúdo de suporte aos seus usuários no seu próprio idioma, independentemente da localização. Observe que mesmo a melhor tradução automática não será tão precisa quanto as realizadas por um tradutor profissional. A Cisco Systems, Inc. não se responsabiliza pela precisão destas traduções e recomenda que o documento original em inglês (link fornecido) seja sempre consultado.
Contents
Introduction
A finalidade deste documento é demonstrar o comportamento de seleção de caminho do OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) quando um roteador recebe um LSA (Link-State Advertisement, anúncio de estado de link) tipo 5 e um LSA tipo 7 para uma determinada rede externa. Quando a redistribuição é executada em uma área não NSSA, o OSPF injetará um LSA tipo 5 no domínio OSPF. A redistribuição em uma área NSSA cria um tipo especial de LSA, conhecido como Tipo 7, que só pode existir em uma área NSSA.
Prerequisites
Consulte o diagrama de rede na Figura 1 à medida que você usa este documento:
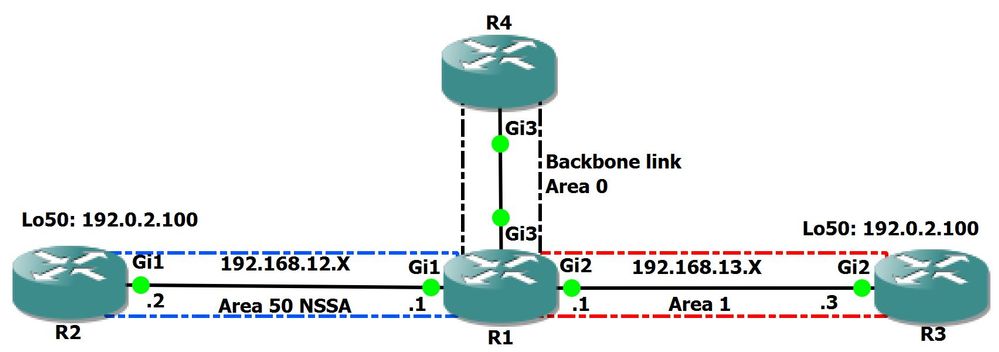
Figure 1
No diagrama de rede, há uma área de não backbone 1 e uma área NSSA 50 conectadas a R1. R1 é um roteador de borda de área (ABR) conectado à área de backbone 0. R2 e R3 são responsáveis por redistribuir o mesmo prefixo 192.0.2.100/32 no domínio OSPF.
Requirements
A Cisco recomenda que você tenha conhecimento do protocolo OSPF.
Componentes Utilizados
As informações neste documento são baseadas nestas versões de software:
- Cisco CSR1000V versão 16.4.1
Informações de Apoio
Os dispositivos Cisco IOS-XE suportam RFC 3101 para cálculo de caminho externo. O RFC 1587 é obsoleto pelo RFC 3101, mas o comportamento específico do RFC 1587 ainda pode ser ativado através da configuração. No Cisco IOS versão 15.1(2)S e versões posteriores, a saída do comando show ip ospf mostra se o dispositivo está usando RFC 3101 ou RFC 1587.
Resumo do RFC 3101 Seção 2.5
(e) If the current LSA is functionally the same as an installed LSA (i.e., same destination, cost and non-zero forwarding address) then apply the following priorities in deciding which LSA is preferred: 1. A Type-7 LSA with the P-bit set. 2. A Type-5 LSA. 3. The LSA with the higher router ID.
Resumo do RFC 1587 Seção 3.5
5. Otherwise, compare the cost of this new AS external path
to the ones present in the table. Note that type-5 and
type-7 routes are directly comparable. Type-1 external
paths are always shorter than Type-2 external paths.
Type-1 external paths are compared by looking at the sum
of the distance to the forwarding address/ASBR and the
advertised Type-1 paths (X+Y). Type-2 external paths are
compared by looking at the advertised Type-2 metrics,
and then if necessary, the distance to the forwarding
address/ASBR.
When a type-5 LSA and a type-7 LSA are found to have the
same type and an equal distance, the following priorities
apply (listed from highest to lowest) for breaking the tie.
a. Any type 5 LSA.
b. A type-7 LSA with the P-bit set and the forwarding
address non-zero.
c. Any other type-7 LSA.
If the new path is shorter, it replaces the present paths
in the routing table entry. If the new path is the same
cost, it is added to the routing table entry's list of
paths
Cenário 1
Diagrama de Rede

Figure 2
Neste cenário, veremos qual comportamento é observado ao usar o RFC 3101 para cálculo de caminho externo. Estaremos interessados no prefixo 192.0.2.100/32 que é redistribuído em R3 e R2.
O LSA tipo 1 de R1 está na saída abaixo:
R1#show ip ospf database router 1.1.1.1
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 51
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 1.1.1.1
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000007
Checksum: 0x3BD6
Length: 48
Area Border Router
AS Boundary Router
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 4.4.4.4
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.14.1
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 192.168.14.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Router Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 562
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 1.1.1.1
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 8000000C
Checksum: 0xEC26
Length: 48
Area Border Router
AS Boundary Router
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 3.3.3.3
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.13.1
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 192.168.13.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Router Link States (Area 50)
LS age: 562
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 1.1.1.1
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000012
Checksum: 0x42CA
Length: 48
Area Border Router
AS Boundary Router
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 2.2.2.2
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.12.1
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 192.168.12.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Em R1, temos os seguintes LSAs externos em nosso banco de dados:
R1#show ip ospf database external
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Type-5 AS External Link States
LS age: 706
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC, Upward)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0xE617
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.12.2
External Route Tag: 0
LS age: 600
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC, Upward)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 3.3.3.3
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0xBFAC
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 0
R1#show ip ospf database nssa-external
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 50)
LS age: 865
Options: (No TOS-capability, Type 7/5 translation, DC, Upward)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x32BC
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.12.2
External Route Tag: 0
Agora, vamos verificar qual LSA é preferencial em R1:
R1#show ip ospf rib 192.0.2.100
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
OSPF local RIB
Codes: * - Best, > - Installed in global RIB
LSA: type/LSID/originator
*> 192.0.2.100/32, NSSA2, cost 20, fwd cost 1, tag 0, area 50
SPF Instance 38, age 00:04:51
contributing LSA: 7/192.0.2.100/2.2.2.2 (area 50)
contributing LSA: 5/192.0.2.100/3.3.3.3
Flags: RIB, HiPrio, ViaFwAddr, IntraNonBB, NSSA P-bit
via 192.168.12.2, GigabitEthernet1 label 1048578
Flags: RIB
LSA: 7/192.0.2.100/2.2.2.2
Como podemos ver na saída acima, R1 prefere LSAs tipo 7 de R2. Isso ocorre porque estamos seguindo o RFC 3101, que tem a seguinte preferência de cálculo de caminho
1. Um LSA tipo 7 com o bit P definido.
2. Um LSA tipo 5.
3. O LSA com o maior ID de roteador.
Note: Esteja ciente de que a seguinte preferência de cálculo de caminho é aplicável se o LSA atual for funcionalmente o mesmo que um LSA instalado. Podemos verificar se a métrica de encaminhamento para ambos os LSAs é a mesma olhando para o LSA tipo 1 de R1.
Agora, se limparmos o bit P no LSA tipo 7 do NSSA de R2, veremos que preferiremos o LSA tipo 5 de R3:
Resumo do RFC 3101 Seção 2.4
An NSSA internal AS boundary router must set the P-bit in the LSA header's option field of any Type-7 LSA whose network it wants advertised into the OSPF domain's full transit topology. The LSAs of these networks must have a valid non-zero forwarding address. If the P-bit is clear the LSA is not translated into a Type-5 LSA by NSSA border routers. When an NSSA border router originates both a Type-5 LSA and a Type-7 LSA for the same network, then the P-bit must be clear in the Type-7 LSA so that it isn't translated into a Type-5 LSA by another NSSA border router.
Antes de prosseguirmos com a limpeza do bit P em R2, aqui está a saída do LSA tipo 7 de R2
R2#show ip ospf database nssa-external
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 1)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 50)
LS age: 1215
Options: (No TOS-capability, Type 7/5 translation, DC, Upward)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x32BC
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.12.2
External Route Tag: 0
O bit P pode ser limpo quando um roteador de borda NSSA origina um LSA tipo 5 e um LSA tipo 7 para a mesma rede.
R2#show ip ospf database nssa-external
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 1)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 50)
LS age: 44
Options: (No TOS-capability, No Type 7/5 translation, DC, Upward)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000003
Checksum: 0xBFAD
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 0
Aqui estão algumas características importantes sobre a saída acima mencionada abaixo:
- Bit P—Este bit é usado para informar ao ABR NSSA se deve traduzir o tipo 7 para o tipo 5.
- Nenhuma conversão de tipo 7/5 significa bit P = 0.
- Conversão tipo 7/5 significa bit P = 1.
- Se o bit P = 0, o ABR NSSA não deve converter esse LSA em Tipo 5. Isso acontece quando o NSSA ASBR também é um NSSA ABR.
- Se o bit P = 1, então o ABR NSSA deve converter esse LSA tipo 7 em um LSA tipo 5. Se houver vários ABRs NSSA, aquele com o maior ID de roteador fará isso.
Agora, quando verificamos o R1, vemos que preferimos o tipo 5 em vez do tipo 7 LSA.
R1#show ip ospf rib 192.0.2.100
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
OSPF local RIB
Codes: * - Best, > - Installed in global RIB
LSA: type/LSID/originator
*> 192.0.2.100/32, Ext2, cost 20, fwd cost 1, tag 0
SPF Instance 39, age 00:03:32
contributing LSA: 7/192.0.2.100/2.2.2.2 (area 50)
contributing LSA: 5/192.0.2.100/3.3.3.3
Flags: RIB, HiPrio, IntraNonBB
via 192.168.13.3, GigabitEthernet2 label 1048578
Flags: RIB
LSA: 5/192.0.2.100/3.3.3.3
Cenário 2
Diagrama de Rede

Figure 3
Neste cenário, veremos qual comportamento é observado ao usar o RFC 1587 para o cálculo do caminho externo. A conformidade com o RFC 3101 é automaticamente ativada em dispositivos IOS-XE. Para substituir a compatibilidade RFC 3101 com a compatibilidade RFC 1587 para seleção de rota em roteadores de borda de área (ABRs) não-tão-stubby area (NSSA), use o comando compatiblerfc1587 no modo de configuração de roteador ou no modo de configuração de família de endereços. Para restaurar a compatibilidade do RFC 3101, use a forma no desse comando.
Estaremos interessados no prefixo 192.0.2.100/32, que é redistribuído em R3 e R2. Primeiro, devemos habilitar a compatibilidade RFC 1587 em R1
R1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#compatible rfc1587 R1#show ip ospf | in RFC Supports NSSA (compatible with RFC 1587)
Depois de habilitar o Compatibility RFC 1587 em R1, podemos verificar quais caminhos estão em nosso banco de dados e qual LSA é preferencial:
R1#show ip ospf database external
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Type-5 AS External Link States
LS age: 115
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC, Upward)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 3.3.3.3
LS Seq Number: 80000003
Checksum: 0xBDAD
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 0
R1#show ip ospf database nssa-external
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 50)
LS age: 48
Options: (No TOS-capability, Type 7/5 translation, DC, Upward)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000005
Checksum: 0x2CBF
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.12.2
External Route Tag: 0
Agora, vamos verificar o que é LSA preferido em R1:
R1#show ip ospf rib 192.0.2.100
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
OSPF local RIB
Codes: * - Best, > - Installed in global RIB
LSA: type/LSID/originator
*> 192.0.2.100/32, Ext2, cost 20, fwd cost 1, tag 0
SPF Instance 44, age 00:01:56
contributing LSA: 7/192.0.2.100/2.2.2.2 (area 50)
contributing LSA: 5/192.0.2.100/3.3.3.3
Flags: RIB, HiPrio, IntraNonBB, PartialSPF
via 192.168.13.3, GigabitEthernet2 label 1048578
Flags: RIB
LSA: 5/192.0.2.100/3.3.3.3
O LSA tipo 5 é o preferido.
Na saída acima, você também pode ter notado que R1 não está convertendo o Tipo 7 em Tipo 5, isso ocorre porque somente as rotas Tipo 7 adicionadas à tabela de roteamento são candidatas para tradução.
Informações Relacionadas
Histórico de revisões
| Revisão | Data de publicação | Comentários |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
05-Jan-2018 |
Versão inicial |
Colaborado por engenheiros da Cisco
- Aleksandar Sofranic
Contate a Cisco
- Abrir um caso de suporte

- (É necessário um Contrato de Serviço da Cisco)
 Feedback
Feedback