EtherChannel entre Catalyst 3550/3560/3750 Series Switches e Catalyst Switches Executando o Exemplo de Configuração do Cisco IOS System Software
Contents
Introduction
Este documento fornece uma configuração de exemplo sobre como configurar um EtherChannel entre um Catalyst 3550 e um Catalyst 6500/6000 que executam o Cisco IOS® System Software. O EtherChannel pode ser chamado de Fast EtherChannel ou Gigabit EtherChannel, dependendo da velocidade das interfaces ou portas usadas para formar o EtherChannel.
Observação: os comandos EtherChannel aplicados ao switch Catalyst 3550 neste documento também podem ser aplicados aos switches da série Catalyst 3750.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Não existem requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
As informações neste documento são baseadas nestas versões de software e hardware:
-
Catalyst 3550 Switch running Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(14)EA
-
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switch running Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(13)E1
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Consulte as Convenções de Dicas Técnicas da Cisco para obter mais informações sobre convenções de documentos.
Material de Suporte
Neste documento, duas interfaces Gigabit Ethernet em um switch Catalyst 3550 — a interface GigabitEthernet no 3500 é uma interface Ethernet negociada 10/100/1000 — foram agrupadas em um Fast EtherChannel com duas interfaces Fast Ethernet de um switch Catalyst 6500/6000 executando o Cisco IOS System Software para formar um EtherChannel de Camada 2 (L2).
Observação: neste documento, Fast EtherChannel, Gigabit EtherChannel, canal de porta e grupo de canais se referem a EtherChannel.
A configuração do Switch Catalyst neste documento se aplica a qualquer Switch da série Catalyst 6500/6000 ou Catalyst 4500/4000 que esteja executando o Software Cisco IOS System.
Este documento mostra arquivos de configuração apenas para os Switches, bem como a saída dos comandos show de exemplo relacionados. Para obter detalhes sobre como configurar um EtherChannel, consulte estes documentos:
-
Seção Configurando EtherChannels de camada 2 de Configurando o EtherChannel (Switch Catalyst 3550)
-
Seção Configurando EtherChannels de camada 3 de Configurando o EtherChannel (Switch Catalyst 3560)
-
Seção Configurando EtherChannels de camada 2 de Configurando o EtherChannel (Switch Catalyst 3750)
-
Configurando EtherChannel de Camada 3 e Camada 2 (Catalyst 6500/6000 executando o Cisco IOS System Software)
-
Configurando a seção EtherChannel de Camada 2 de Entendendo e Configurando o EtherChannel (Catalyst 4500/4000 executando o Cisco IOS System Software)
Notas importantes
O EtherChannel pode ser configurado manualmente com os comandos apropriados. Você também pode configurar o EtherChannel automaticamente com Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) para que o switch negocie o canal com o outro lado. Para obter detalhes sobre PAgP, consulte estes documentos:
-
Entendendo a seção Port Aggregation Protocol de Configuração do EtherChannel (Catalyst 3550 Switch)
-
Entendendo a seção Port Aggregation Protocol de Configuração do EtherChannel (Catalyst 3560 switch)
-
Seção Protocolo de agregação de porta em Configurando EtherChannels (Switch Catalyst 3750)
-
Compreendendo a seção de protocolo de agregação de portas da configuração de EtherChannel (Catalyst 6500/6000 executando software Cisco IOS System)
-
Entendendo a seção Port Aggregation Protocol de Entendendo e Configurando o EtherChannel (Catalyst 4500/4000 executando o Cisco IOS System Software)
As configurações nesse documento são implementadas com o uso do modo desejado. Se você planeja configurar o EtherChannel manualmente, use as etapas fornecidas para criar um canal de porta. Evita problemas com o Protocolo de Abrangência de Árvore (STP) durante o processo de configuração. O STP pode desligar algumas portas, com um status de porta desabilitado por erro [errdisable], se um lado estiver configurado como um canal antes que o outro lado possa ser configurado como um canal.
Execute estas etapas para criar um canal de porta:
-
Deixe as interfaces a serem usadas na canalização de porta como desligamento administrativo.
-
Create the port channel (channel group) on the Catalyst 6500/6000 Switch.
Certifique-se de definir o modo de canal como on, por exemplo, channel-group 1 mode on.
-
Crie canais de porta no switch Catalyst 3550, 3560 ou 3750.
Certifique -se de ter definido o modo de canal para on.
-
Reative as interfaces que foram desabilitadas anteriormente no switch Catalyst 6500/6000 com o comando no shut.
Configurar
Nesta seção, você encontrará informações para configurar os recursos descritos neste documento.
Observação: para encontrar informações adicionais sobre os comandos usados neste documento, use a ferramenta Command Lookup Tool (somente clientes registrados). ![]()
Diagrama de Rede
Este documento utiliza a configuração de rede mostrada neste diagrama:
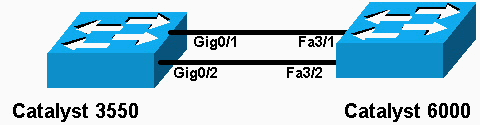
Observação: a interface Gigabit Ethernet no Catalyst 3550 é uma interface Ethernet negociada de 10/100/1000 Mbps. A porta Gigabit no Catalyst 3550 também pode ser conectada a uma porta FastEthernet (100 Mbps) em um Catalyst 6500/6000.
Observação: os switches da série Catalyst 3750 suportam EtherChannel de pilha cruzada, que permite que as interfaces de diferentes switches de pilha sejam membros do mesmo grupo EtherChannel. Para obter mais informações sobre o EtherChannel em um ambiente de switch empilhado, consulte a seção EtherChannel e Pilhas de Switch da documentação Configuração de EtherChannels para os switches da série Catalyst 3750.
Configurações
Este documento utiliza as seguintes configurações:
| Catalyst 3550 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 1610 bytes ! version 12.1 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Cat3550 ! enable password ww ! ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! ! ! ! !--- A logical port-channel interface is automatically created !--- when ports are grouped into a channel group. interface Port-channel 1 !--- In this example, the L2 EtherChannel is configured. !--- A Layer 3 (L3) EtherChannel can also be configured on the Catalyst 3550 switches. !--- For more information, refer to the document Configuring EtherChannel. switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status! !--- Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interface on the Catalyst 3550 is a !--- 10/100/1000 Mbps negotiated Ethernet interface. The Gigabit port on the Catalyst 3550 is !--- connected to a FastEthernet (100 Mbps) port on the Catalyst 6500/6000. !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status channel-group 1 mode desirable ! !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface GigabitEthernet0/3 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status ! !--- Output suppressed. interface GigabitEthernet0/12 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status !--- Interface VLAN1 is required for management purposes. interface Vlan1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! ip classless ip http server ! ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 5 15 ! end |
| Catalyst 6500/6000 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 5869 bytes ! version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname cat6500 ! boot buffersize 126968 boot bootldr bootflash:c6msfc-boot-mz.121-4.E1 enable password ww ! redundancy main-cpu auto-sync standard ip subnet-zero ! ! no ip finger ! ! ! ! !--- A logical port-channel interface is automatically created !--- when ports are grouped into a channel group. interface Port-channel 1 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/2 no ip address shutdown ! !--- Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interface on the Catalyst 3550 is a !--- 10/100/1000 Mbps negotiated Ethernet interface. The Gigabit port on the Catalyst 3550 is !--- connected to a FastEthernet (100 Mbps) port on the Catalyst 6500/6000. interface FastEthernet3/1 no ip address !--- In this example, the L2 EtherChannel is configured. !--- An L3 EtherChannel can also be configured on the Catalyst 6500/6000 running !--- Cisco IOS System Software. For more details, refer to the document !--- Configuring EtherChannel. !--- On a Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport !--- command once, without any keywords, in order to configure the interface as an L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default; !--- no additional command is required. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet3/2 no ip address !--- On a Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport !--- command once, without any keywords, in order to configure the interface as an L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default; !--- no additional command is required. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet3/3 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! !--- Output suppressed. ! interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! !--- Interface VLAN1 is required for management purposes. interface Vlan1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 ! end |
Observação: este exemplo de configuração mostra uma configuração EtherChannel com links de acesso. A mesma configuração se aplica aos links de troncos do EtherChannel. Emita o comando switchport mode trunk ou permita que os switches negociem o modo com o modo desejável dinâmico. Para obter mais informações sobre como configurar o entroncamento, consulte a seção Configurando troncos de VLAN do documento Configurando VLANs.
Configuração da subinterface do canal de porta
Outro exemplo da configuração do Port-Channel com subinterface no switch Catalyst 3560 executando o Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(25).
| Catalyst 3560 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 2480 bytes ! version 12.2 ! interface Port-channel5 no switchport no ip address ! interface Port-channel5.690 ! interface Port-channel10 no switchport no ip address ! interface Port-channel10.1 ! interface Port-channel10.690 ! interface Port-channel11 no switchport no ip address |
Verificar
Para verificar o canal de porta nos Catalyst 6500/6000 e Catalyst 3500 Switches que executam o Cisco IOS System Software, emita estes comandos:
Para verificar o status do STP nos Catalyst 6500/6000 e Catalyst 3500 Switches que executam o Cisco IOS System Software, emita este comando:
Catalyst 3550
Cat3550#show interface port-channel 1
Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 0002.4b28.db02 (bia 0002.4b28.db02)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 200000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is off
Members in this channel: Gi0/1 Gi0/2
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:03:27, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
26 packets input, 5344 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 17 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
59 packets output, 5050 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Cat3550#show spanning-tree vlan 1 detail
VLAN1 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
We are the root of the spanning tree
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 1 last change occurred 00:00:38 ago
from Port-channel1
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 0
Port 65 (Port-channel1) of VLAN1 is forwarding
Port path cost 12, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.65.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated port id is 128.65, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 34, received 0
Cat3550# show etherchannel 1 summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
U - port-channel in use
Group Port-channel Ports
-----+------------+-----------------------------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) Gi0/1(P) Gi0/2(P)
Cat3550# ping 10.1.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Catalyst 6500/6000
Cat6500# show interface port-channel 1
Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 0002.7ef1.36e1 (bia 0002.7ef1.36e1)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 200000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
Members in this channel: Fa3/1 Fa3/2
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/2000, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 1000 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
407 packets input, 34994 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 311 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
93 packets output, 16598 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Cat6500# show spanning-tree vlan 1 detail
VLAN1 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 00d0.024f.6001
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Current root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Root port is 833 (Port-channel1), cost of root path is 12
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:02:13 ago
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300
Port 833 (Port-channel1) of VLAN1 is forwarding
Port path cost 12, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 131.65.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated port id is 128.65, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 1, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 0, received 66
Cat6500# show etherchannel 1 summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
Group Port-channel Ports
-----+------------+-----------------------------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) Fa3/1(P) Fa3/2(P)
Cat6500# ping 10.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Troubleshoot
Estado Err-Disable
Um problema comum durante a configuração do EtherChannel é que as interfaces entram no modo err-disable. Isso pode ser visto quando o Etherchannel é comutado para o modo ON em um switch e o outro switch não é configurado imediatamente. Se permanecer nesse estado por um minuto ou mais, o STP no switch onde o EtherChannel está ativado acha que há um loop. Isso faz com que as portas de canalização sejam colocadas no estado err-disable. Consulte este exemplo para obter mais informações sobre como determinar se as interfaces EtherChannel estão no estado err-disable:
%SPANTREE-2-CHNL_MISCFG: Detected loop due to etherchannel misconfiguration of Gi0/9 %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: channel-misconfig error detected on Po10, putting Gi0/9 in err-disable state %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: channel-misconfig error detected on Po10, putting Gi0/10 in err-disable state
Switch1#show etherchannel summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
u - unsuitable for bundling
U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
d - default port
Number of channel-groups in use: 1
Number of aggregators: 1
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------
10 Po10(SD) - Gi0/9(D) Gi0/10(D)
Switch1#show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/9 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi0/9 err-disabled 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTX
Switch1#show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/10 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi0/10 err-disabled 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTX
A mensagem de erro indica que o EtherChannel encontrou um loop de spanning tree. Para resolver o problema, defina o modo do canal como desirable em ambos os lados da conexão e, em seguida, reative as interfaces:
Switch1#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch1(config)#interface gi0/9 Switch1(config-if)#channel-group 10 mode desirable
Isso faz com que cada lado forme um canal apenas se ambos concordarem em usar o canal. Se eles não concordarem com o canal, continuarão a funcionar como portas normais.
Depois que o modo de canal estiver definido como desirable em ambos os lados da conexão, emita os comandos shutdown e no shutdown na interface associada para reativar as portas manualmente:
Switch1(config-if)#shutdown Switch1(config-if)#no shutdown
O comando "speed nonegotiate" não é exibido na configuração atual
O comando speed nonegotiate configurado em um canal de porta nem sempre é exibido na configuração em execução. Isso acontece porque a não negociação na interface de canal de porta depende da interface de portas agrupadas. Ele é inserido quando o canal de porta está ativo e baseado na configuração de portas de canal individuais.
Informações Relacionadas
- Requisitos do sistema para implementar o EtherChannel nos Switches Catalyst
- Configuração de exemplo: EtherChannel entre Switches Catalyst Executando CatOS e Software do Sistema Cisco IOS
- Suporte ao Produto - Switches
- Suporte de tecnologia de switching de LAN
- Suporte Técnico e Documentação - Cisco Systems
 Feedback
Feedback