Configurando VPN MPLS sobre POS, SRP e ATM em GSRs Cisco
Contents
Introduction
Este documento fornece uma configuração de exemplo para Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS - Multiprotocol Label Switching) Virtual Private Network (VPN - Rede Virtual Privada) sobre ATM, pacote sobre SONET/SDH (POS - Packet over SDH) e SDH (Space Reuse Protocol) em Cisco 12000 Gigabit Switch Routers (GSRs).
Esses acrônimos são usados neste documento.
-
CE —roteador de borda do cliente
-
PE—Roteador de borda do provedor
-
P—Roteador do núcleo do provedor
-
VRF — Roteamento e encaminhamento virtual
Prerequisites
Requirements
Antes de tentar esta configuração, verifique se estes requisitos são atendidos:
-
Conhecimento básico do MPLS e do recurso VPN MPLS.
Componentes Utilizados
As informações neste documento são baseadas nestas versões de software e hardware:
-
Roteadores P e PE
-
Software Cisco IOS® versão 12.0(28)S em todos os roteadores
-
Roteadores Cisco GSR série 12000
-
-
Roteadores CE
-
Software Cisco IOS versão 12.0(28)S em todos os roteadores
-
Roteadores Cisco 7200VXR
-
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Produtos Relacionados
Essa configuração também pode ser usada com essas plataformas de roteador suportadas no núcleo do provedor (P):
-
Cisco 7200
-
Cisco 7500
-
Cisco 7600
-
Cisco 8500
-
Cisco 10000
-
Cisco 10700
-
Cisco 12000
Essa configuração também pode ser usada com essas plataformas de roteador suportadas na borda do provedor (PE):
-
Cisco 3600
-
Cisco 3700
-
Cisco 7200
-
Cisco 7500
-
Cisco 7600
-
Cisco 8500
-
Cisco 10000
-
Cisco 10700
-
Cisco 12000
Observação: os roteadores Cisco 3700/3600 não têm suporte para módulos POS e SRP. Qualquer plataforma abaixo do 3600 não oferece suporte à configuração de MPLS.
Conventions
Para obter mais informações sobre convenções de documento, consulte as Convenções de dicas técnicas Cisco.
Informações de Apoio
O MPLS é disponibilizado para suportar várias interfaces físicas. Essas interfaces incluem ATM, POS e SRP. Essas interfaces são tipicamente usadas para conexões de backbone devido ao seu suporte de alta largura de banda. O recurso VPN MPLS permite que os provedores de serviços interconectem vários locais sem a necessidade de ATM, POS ou SRP no lado do cliente.
Há duas implementações de MPLS sobre ATM. Um deles é o uso de VPI (Virtual Path Identifier, identificador de caminho virtual) e VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier, canal virtual identificado) como o rótulo que também é conhecido como MPLS sobre ATM "baseado em célula". Esta implementação está documentada em RFC 3035 ![]() . A segunda implementação ATM é o uso do "cabeçalho de calço" MPLS, também conhecido como MPLS sobre ATM baseado em pacotes. Esse cabeçalho de calço é inserido entre os cabeçalhos das Camadas 2 e 3. O formato do cabeçalho do shim é documentado em RFC 3032
. A segunda implementação ATM é o uso do "cabeçalho de calço" MPLS, também conhecido como MPLS sobre ATM baseado em pacotes. Esse cabeçalho de calço é inserido entre os cabeçalhos das Camadas 2 e 3. O formato do cabeçalho do shim é documentado em RFC 3032 ![]() . Esta configuração de exemplo é baseada na implementação do "cabeçalho de shim" para a interface ATM.
. Esta configuração de exemplo é baseada na implementação do "cabeçalho de shim" para a interface ATM.
Packet over Synchronous Optical Network/Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET/SDH) é uma tecnologia que coloca a camada IP diretamente acima da camada SONET. Elimina a sobrecarga necessária para executar IP sobre ATM sobre SONET. O POS suporta vários formatos de encapsulamento. Esses são PPP, HDLC e Frame Relay. O cabeçalho shim é usado para fornecer suporte a MPLS. Esta configuração de exemplo usa o encapsulamento HDLC padrão em interfaces Cisco POS.
O protocolo de reutilização espacial (SRP - Spatial Reuse Protocol) é uma tecnologia da camada 2 que fornece resiliência no nível da camada 2. Ele também é executado sobre SONET/SDH. O suporte a MPLS é fornecido pela implementação do cabeçalho do shim.
Configurar
Nesta seção, você encontrará informações para configurar os recursos descritos neste documento.
Observação: para encontrar informações adicionais sobre os comandos usados neste documento, use a ferramenta Command Lookup Tool (somente clientes registrados).
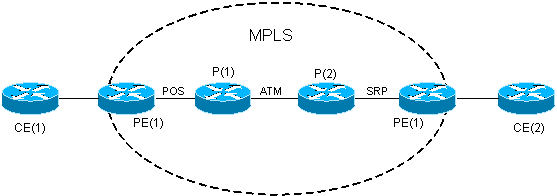
Diagrama de Rede
Este documento utiliza a seguinte configuração de rede:
Configurações
Isso lista algumas considerações feitas na configuração de exemplo:
-
O exemplo de serviço de configuração de VPN MPLS roteia o EIGRP dos CEs. O bug da Cisco ID CSCds09932 (somente clientes registrados) introduziu o suporte EIGRP para VPN MPLS com o Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(22)S. Ele foi portado para o Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2T através do bug da Cisco ID CSCdx26186 (somente clientes registrados) iniciando no Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(15)T. A aplicação do mesmo VRF em várias instâncias do EIGRP não é suportada e pode travar o roteador. Uma verificação deste problema foi posteriormente integrada com a ID de bug da Cisco CSCdz40426 (somente clientes registrados) . Consulte Suporte de VPN MPLS para EIGRP Entre a Borda do Provedor e a Borda do Cliente para saber mais sobre o suporte de VPN MPLS para EIGRP.
-
O sistema autônomo EIGRP é o mesmo em ambos os roteadores CE. O sistema autônomo BGP é o mesmo em ambos os roteadores PE.
-
O backbone MPLS é baseado em interfaces POS, ATM e SRP e configurado com OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) e MP-BGP. A conexão entre PE e CE é Fast Ethernet.
Este documento utiliza as seguintes configurações:
| CE(1) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ip cef !--- CEF is not required on the CE because there is no MPLS configuration. !--- CEF is the fastest switching algorithm on Cisco routers !--- and it is best to leave it enabled. ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 11.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 11.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.252 ! router eigrp 100 network 11.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 no auto-summary ! ip classless |
| PE(1) |
|---|
!
version 12.0
!
!--- CEF is enabled by default on GSR.
.
!
ip vrf Customer_A
rd 100:1
route-target export 100:1
route-target import 100:1
!--- Enables the VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) routing table.
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip vrf forwarding Customer_A
!--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface.
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.252
!
interface POS4/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!--- Enables dynamic Label Switching of IPv4 packets on an interface. !--- At minimum, this is all you need to configure MPLS over POS. !--- Note the default encapsulation of POS interfaces is HDLC. !--- An mpls ip command can also be used instead of tag-switching ip.
crc 32
clock source internal
!
!
router eigrp 1
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A
redistribute bgp 100 metric 10000 1 255 1 1500
network 192.168.2.0
no auto-summary
autonomous-system 100
!--- The autonomous-system 100 must match the AS used on the CE. !--- The bgp must be redistributed with metric. The default-metric !--- command can also be used.
exit-address-family
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 send-community both
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A
redistribute eigrp 100
!--- The EIGRP AS 100 must be redistributed to the BGP vrf instance.
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
ip classless |
| P(1) |
|---|
!
version 12.0
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface POS2/0
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!--- This enables MPLS over POS.
crc 32
!
!
interface ATM6/0
no ip address
!
interface ATM6/0.100 point-to-point
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
pvc 0/100
!
!--- This enables "packet-based" MPLS over ATM.
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
ip classless |
| P(2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 ! interface ATM4/0 no ip address ! interface ATM4/0.100 point-to-point ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 tag-switching ip pvc 0/100 !--- This enables "packet-based" MPLS over ATM. ! ! interface SRP5/0 ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast tag-switching ip !--- This enables MPLS over SRP. ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.1.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.2.2.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! ip classless |
| PE(2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ! ip vrf Customer_A rd 100:1 route-target export 100:1 route-target import 100:1 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 ! interface SRP4/0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.252 tag-switching ip !--- This enables MPLS over SRP. ! interface FastEthernet6/0 ip vrf forwarding Customer_A !--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface. ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252 ! ! router eigrp 1 ! address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A redistribute bgp 100 metric 10000 1 255 1 1500 network 192.168.1.0 no auto-summary autonomous-system 100 exit-address-family !--- The autonomous-system 100 must match the AS used on the CE. !--- The bgp must be redistributed with metric. The default-metric !--- command can also be used. ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router bgp 100 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A redistribute eigrp 100 !--- The EIGRP AS 100 must be redistributed to the BGP vrf instance. no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family ! ip classless |
| CE(2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ip cef !--- CEF is not required on the CE because there is no MPLS configuration. !--- CEF is the fastest switching algorithm on Cisco routers so it is !--- best to leave it enabled. ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 22.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 22.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 22.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252 ! ! router eigrp 100 network 22.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 no auto-summary ! |
Verificar
Esta seção fornece informações que você pode usar para confirmar se sua configuração está funcionando adequadamente.
A Output Interpreter Tool (somente clientes registrados) oferece suporte a determinados comandos show, o que permite exibir uma análise da saída do comando show.
-
show ip vrf — Verifica se o VRF correto existe.
-
show ip route vrf Customer_A — Verifica as informações de roteamento nos roteadores PE.
-
ping vrf Customer_A <ip address> — Verifica a conectividade enviando pacotes ICMP.
-
traceroute vrf Customer_A <endereço ip> — Verifica as informações de roteamento nos roteadores PE.
-
show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A neighbors — Verifica o vizinho EIGRP dentro da instância do VRF.
-
show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A topology —Verifica a topologia EIGRP dentro da instância do VRF.
-
show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf Customer_A — Verifica a tabela BGP dentro da instância do VRF.
-
show ip cef vrf Customer_A <ip address> detail — Verifica a tabela CEF dentro da instância do VRF.
-
show tag-switching forwarding-table —Verifica se há uma rota/tag para o prefixo de destino.
-
show ip route —Verifica se CEs trocam rotas.
PE(1)
PE(1)#show ip vrf
Name Default RD Interfaces
Customer_A 100:1 FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#show ip route vrf Customer_A
Routing Table: Customer_A
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
B 22.3.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
B 22.2.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
B 22.1.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 11.2.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
D 11.3.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
D 11.1.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 192.168.1.0 [200/0] via 4.4.4.4, 01:16:14
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#ping vrf Customer_A 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
D-GSR-12012-2A#ping vrf Customer_A ip ?
WORD Ping destination address or hostname
<cr>
PE(1)#ping vrf Customer_A ip
Target IP address: 192.168.1.2
Repeat count [5]: 100
Datagram size [100]: 1500
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]:
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 100, 1500-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (100/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
PE(1)#traceroute vrf Customer_A 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 192.168.1.2
1 10.0.0.2 [MPLS: Labels 18/28 Exp 0] 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec
2 10.1.1.2 [MPLS: Labels 19/28 Exp 0] 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec
3 192.168.1.1 4 msec 0 msec 0 msec
4 192.168.1.2 4 msec 0 msec *
PE(1)#show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 100
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq Type
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 192.168.2.2 Fa0/0 11 10:51:41 10 200 0 8
PE(1)#show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(100)/ID(192.168.2.1) Routing Table: Customer_A
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - Reply status
P 11.2.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 11.3.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 11.1.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 22.3.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 22.2.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 22.1.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 192.168.1.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via VPNv4 Sourced (28160/0)
P 192.168.2.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Connected, FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf Customer_A
BGP table version is 17, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 100:1 (default for vrf Customer_A)
*> 11.1.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*> 11.2.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*> 11.3.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*>i22.1.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i22.2.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i22.3.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i192.168.1.0/30 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 ?
*> 192.168.2.0/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
PE(1)#show ip cef vrf Customer_A
Prefix Next Hop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 drop Null0 (default route handler entry)
0.0.0.0/32 receive
11.1.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
11.2.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
11.3.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
22.1.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
22.2.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
22.3.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
192.168.1.0/30 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
192.168.2.0/30 attached FastEthernet0/0
192.168.2.0/32 receive
192.168.2.1/32 receive
192.168.2.2/32 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
192.168.2.3/32 receive
224.0.0.0/4 drop
224.0.0.0/24 receive
255.255.255.255/32 receive
PE(1)#show ip cef vrf Customer_A 11.1.1.0 detail
11.1.1.0/24, version 16, epoch 0, cached adjacency 192.168.2.2
0 packets, 0 bytes
tag information set, all rewrites owned
local tag: 27
via 192.168.2.2, FastEthernet0/0, 0 dependencies
next hop 192.168.2.2, FastEthernet0/0
valid cached adjacency
tag rewrite with Fa0/0, 192.168.2.2, tags imposed {}
PE(1)#show tag-switching forwarding-table
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
16 Pop tag 2.2.2.2/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
17 17 3.3.3.3/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
18 18 4.4.4.4/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
19 19 10.2.2.0/30 0 PO4/0 point2point
20 Pop tag 10.1.1.0/30 0 PO4/0 point2point
22 Untagged 11.2.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
26 Untagged 11.3.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
27 Untagged 11.1.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
28 Aggregate 192.168.2.0/30[V] 255132
PE(1)#show tag-switching forwarding-table vrf Customer_A
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
22 Untagged 11.2.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
26 Untagged 11.3.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
27 Untagged 11.1.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
28 Aggregate 192.168.2.0/30[V] 255132
P(1)
P(1)A#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 Pop tag 1.1.1.1/32 260843 PO2/0 point2point 17 Pop tag 3.3.3.3/32 0 AT6/0.100 point2point 18 19 4.4.4.4/32 269131 AT6/0.100 point2point 19 Pop tag 10.2.2.0/30 0 AT6/0.100 point2point
P(2)
P(2)#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 Pop tag 10.0.0.0/30 0 AT4/0.100 point2point 17 Pop tag 2.2.2.2/32 0 AT4/0.100 point2point 18 16 1.1.1.1/32 269930 AT4/0.100 point2point 19 Pop tag 4.4.4.4/32 276490 SR5/0 10.2.2.2
PE(2)
PE(2)#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 18 1.1.1.1/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 17 17 2.2.2.2/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 18 Pop tag 3.3.3.3/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 19 16 10.0.0.0/30 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 20 Pop tag 10.1.1.0/30 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 25 Untagged 22.1.1.0/24[V] 2280 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 26 Untagged 22.2.1.0/24[V] 570 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 27 Untagged 22.3.1.0/24[V] 570 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 28 Aggregate 192.168.1.0/30[V] 251808
CE(1)
CE(1)#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 22.3.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
D 22.2.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
D 22.1.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 11.2.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback1
C 11.3.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 11.1.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.1.0 [90/30720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:46, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
CE(1)#ping 22.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 22.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
CE(2)
D-R7206-5A#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 22.3.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 22.2.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback1
C 22.1.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 11.2.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
D 11.3.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
D 11.1.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.2.0 [90/30720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:33, FastEthernet2/0
CE(2)#ping 11.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 11.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Troubleshoot
Atualmente, não existem informações disponíveis específicas sobre Troubleshooting para esta configuração.
Informações Relacionadas
Histórico de revisões
| Revisão | Data de publicação | Comentários |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
05-Jun-2005 |
Versão inicial |
Contate a Cisco
- Abrir um caso de suporte

- (É necessário um Contrato de Serviço da Cisco)
 Feedback
Feedback