Configuração do Roteamento entre VLANs utilizando um Roteador Interno (Placa de Camada 3) em Switches Catalyst 5500/5000 e 6500/6000 que Executam o Software do Sistema do CatOS
Contents
Introduction
Este documento fornece informações básicas sobre como configurar o roteamento interVLAN em um switch Catalyst (que executa o software de sistema Catalyst OS [CatOS]) que usa um roteador interno (placa/módulo da camada 3 [L3]). O termo roteador interno refere-se a placas/módulos L3 nos switches das séries Catalyst 5500/5000 e 6500/6000:
-
Placa de recurso de switch multicamada (MSFC - Multilayer Switch Feature Card) nos switches da série Catalyst 6500/6000
-
MSFC2 nos Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches
-
RSFC (Route Switch Feature Card, placa de recursos do switch de rota) nos switches da série Catalyst 5500/5000
-
Route Switch Module (RSM) nos Catalyst 5500/5000 Series Switches
Qualquer Catalyst 5500/5000 ou Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switch executando CatOS com uma placa L3 suportada poderia ter sido usado neste documento para obter os mesmos resultados.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Os leitores deste documento devem estar cientes destes tópicos:
Observação: este documento não discute como configurar o roteamento entre VLANs em switches Catalyst 4500/4000 usando o módulo de serviços L3 (WS-X4232-L3). Para obter esses detalhes, consulte estes documentos:
-
Configurando o módulo para roteamento entre VLANs seção de Nota de instalação e configuração para o Módulo de Serviços da Camada 3 do Catalyst 4000
-
Configuração e Visão Geral do Router Module para o Catalyst Family 4000 (WS-X4232-L3)
Componentes Utilizados
As informações neste documento são baseadas nestas versões de software e hardware:
-
Switch Catalyst 5500 com RSM
-
Módulo de mecanismo supervisor (WS-X5530) que executa o software CatOS 6.1(1)
-
RSM (WS-X5302) que executa o software Cisco IOS® versão 12.0(5)W5(12)
As configurações em todos os dispositivos foram limpas com os comandos clear config all e write erase para garantir uma configuração padrão.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Diagrama de Rede
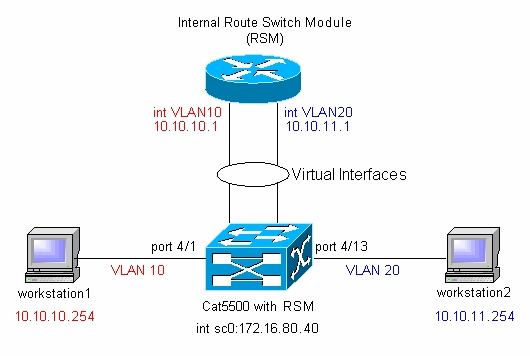
Observação: não conecte a estação de trabalho1 e a estação de trabalho2 a menos que você seja solicitado a fazer isso neste documento. Este documento aponta um problema comum que os clientes relatam quando configuram o roteamento entre VLANs ou várias interfaces VLAN no módulo do roteador. Veja o problema comum: Interface VLAN Mostra a seção down/down para obter detalhes.
Tarefas de configuração geral
Esta seção fornece um resumo das principais tarefas de configuração executadas neste documento:
-
Configurar o switch para gerenciamento
-
Criar VLANs no switch
-
Adicionar portas às VLANs configuradas
-
Configurar o roteador interno para gerenciamento
-
Configure o InterVLAN Routing
-
Verificar a configuração
Configure o InterVLAN Routing
Conclua estes passos para configurar o roteamento entre VLANs no switch Catalyst:
-
Acesse a porta do console no Supervisor Engine.
Se você tiver dificuldades para acessar o console, consulte estes documentos:
-
Para Catalyst 5500/5000 Series Switches—Conectando um Terminal à Porta de Console em Catalyst Switches.
-
Para os Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches — seção Conexão de um Terminal de Conexão de um Terminal à Porta de Console em Catalyst Switches e Conexão de um Modem da Conexão de um Modem à Porta de Console em Catalyst Switches
-
-
Configure o Switch para gerenciamento básico.
Use este conjunto de comandos para configurar o switch Catalyst para gerenciamento:
Console> enable) set system name Cat5500 !--- Configure the system name. System name set. Cat5500> (enable) set interface sc0 172.16.80.40 255.255.255.0 !--- Configure the IP address. Interface sc0 IP address and netmask set. Cat5500> (enable) set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.80.1 !--- Configure the default gateway.
Observação: se quiser gerenciar um switch que esteja do outro lado de um roteador, você precisa configurar um gateway padrão no switch, já que o switch não participa do roteamento IP e, portanto, não tem conhecimento da topologia L3 da rede. Você pode também usar o comando set ip route default 172.16.80.1 para configurar o gateway padrão em vez de usar o comando set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.80.1.
-
Configure o número necessário de VLANs no switch.
De acordo com o Diagrama de Rede, você precisa configurar duas novas VLANs (VLAN 10 e VLAN 20) no switch.
Antes de criar uma nova VLAN, o switch deve estar no modo de servidor do VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) ou no modo transparente de VTP. Se o switch for um servidor de VTP, será necessário definir um nome de domínio de VTP para poder adicionar qualquer VLAN. Isso deve ser definido independentemente do número de switches na rede (um ou vários), e independentemente de você estar usando o VTP para propagar VLANs a outros switches na rede. Para obter mais informações sobre o VTP, consulte este documento:
A configuração padrão do VTP no switch é:
Cat5500> (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password -------------------------------- ------------ ----------- ----------- ---------- 1 2 server - Vlan-count Max-vlan-storage Config Revision Notifications ---------- ---------------- --------------- ------------- 5 1023 0 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans --------------- -------- -------- ------------------------- 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 2-1000Utilize o comando set vtp para definir o nome de domínio e o modo:
Cat5500> (enable) set vtp domain mode transparent VTP domain modified !--- Set the VTP mode. Cat5500> (enable) set vtp domain cisco VTP domain cisco modified !--- Set the VTP domain name.
Observação: no exemplo, o modo VTP está definido para ser transparente. Dependendo de sua rede, defina o modo VTP apropriadamente. O modo transparente foi escolhido para evitar ser afetado por outros switches e para evitar afetar os outros switches no laboratório.
-
Verifique a configuração do VTP emitindo o comando show vtp domain:
Cat5500> (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password -------------------------------- ------------ ----------- ----------- ---------- cisco 1 2 Transparent - Vlan-count Max-vlan-storage Config Revision Notifications ---------- ---------------- --------------- ------------- 5 1023 0 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans --------------- -------- -------- ------------------------- 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 2-1000
-
Crie VLANs no switch.
Por padrão, há apenas uma VLAN no switch, chamada VLAN 1. A VLAN 1 também é chamada de VLAN padrão. Todas as portas pertencem a esta VLAN por padrão. Essa VLAN não pode ser renomeada ou excluída.
Para criar VLANs, use o comando set vlan:
Cat5500> (enable) set vlan Usage: set vlan <mod/port> (An example of mod/port is 1/1,2/1-12,3/1-2,4/1-12) set vlan [name ] [type ] [state ] [said ] [mtu ] [ring ] [decring ] [bridge ] [parent ] [mode ] [stp ] [translation ] [backupcrf <off/on> [aremaxhop ] [stemaxhop ] (name = 1..32 characters, state = (active, suspend) type = (ethernet, fddi, fddinet, trcrf, trbrf) said = 1..4294967294, mtu = 576..18190 hex_ring_number = 0x1..0xfff, decimal_ring_number = 1..4095 bridge_number = 0x1..0xf, parent = 2..1005, mode = (srt, srb) stp = (ieee, ibm, auto), translation = 1..1005 hopcount = 1..13) Set vlan commands: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- set vlan Set vlan information set vlan mapping Map an 802.1Q vlan to an Ethernet vlan set vlan Vlan number(s)Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 10 !--- Create VLAN 10. VTP advertisements transmitting temporarily stopped and will resume after the command finishes. Vlan 10 configuration successful Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 20 !--- Create VLAN 20. VTP advertisements transmitting temporarily stopped and will resume after the command finishes. Vlan 20 configuration successful Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 10 4/1-12 !--- Add ports to VLAN 10. VLAN 10 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 10 4/1-12 Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 20 4/13-20 !--- Add ports to VLAN 20. VLAN 20 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 20 4/13-20 Cat5500> (enable) show vlan VLAN Name Status IfIndex Mod/Ports, Vlans ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------- ------------------------ 1 default active 443 1/1-2 3/1-3 4/21-24 11/1-48 12/1-2 10 VLAN0010 active 448 4/1-12 20 VLAN0020 active 449 4/13-20 1002 fddi-default active 444 1003 token-ring-default active 447 1004 fddinet-default active 445 1005 trnet-default active 446 VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2 ---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------ 1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0 10 enet 100010 1500 - - - - - 0 0 20 enet 100020 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1003 trcrf 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1005 trbrf 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0 !--- Output suppressed. -
Configure o protocolo STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) PortFast nas portas que se conectam às estações de trabalho ou aos servidores.
Emita o seguinte comando para habilitar o recurso STP PortFast:
Cat5500> (enable) set spantree portfast 4/1-20 enable Warning: Spantree port fast start should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to a fast start port can cause temporary spanning tree loops. Use with caution. Spantree ports 4/1-20 fast start enabled.
Observação: essa etapa é opcional, mas é uma boa prática ativar o STP PortFast nas portas que se conectam a estações de trabalho ou servidores regulares. Para obter detalhes sobre por que habilitar o PortFast, consulte este documento:
-
Configure uma interface VLAN no módulo do roteador para cada uma das VLANs entre as quais você deseja rotear o tráfego.
Acesse o módulo do roteador emitindo o comando session module#, onde module# é o slot no qual o módulo do roteador está localizado. No exemplo, o RSM está localizado no slot 7, como mostrado aqui:
Cat5500> (enable) show module 7 Mod Slot Ports Module-Type Model Sub Status --- ---- ----- ------------------------- ------------------- --- -------- 7 7 1 Route Switch WS-X5302 no ok Mod Module-Name Serial-Num --- ------------------- -------------------- 7 00006591991 Mod MAC-Address(es) Hw Fw Sw --- -------------------------------------- ------ ---------- ----------------- 7 00-e0-1e-91-b5-08 to 00-e0-1e-91-b5-09 4.5 20.20 12.0(5)W5(12) Cat5500> (enable) session 7 Trying Router-7... Connected to Router-7. Escape character is '^]'. Router>
-
Configure a senha habilitada e Telnet no módulo do roteador.
Novamente, essa etapa é opcional, mas a senha Telnet é necessária se você tentar acessar o módulo do roteador diretamente com Telnet e não através do Supervisor Engine. Use este conjunto de comandos para configurar as senhas no módulo do roteador:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal !--- Enter the global configuration mode. Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# enable password cisco !--- Set enable password. Router(config)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# login Router(config-line)# password cisco !--- Set Telnet password. Router(config-line)# end Router# 05:22:40: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (127.0.0.2) Router#
-
Crie duas interfaces VLAN, atribua endereços IP a essas interfaces VLAN e ative o roteamento no módulo.
Observação: esta etapa é a chave para configurar o roteamento entre VLANs.
Observação: no módulo do roteador, as interfaces VLAN são interfaces virtuais, mas são configuradas como interfaces físicas.
Emita este conjunto de comandos no modo exec privilegiado:
Router# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. !--- Configure interface VLAN 1 and assign it an IP address. !--- An interface VLAN 1 is configured for management purposes only !--- so that you can establish a Telnet session or ping the switch !--- from the workstation. Router(config)# interface vlan 1 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.80.79 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit !--- Configure interface VLAN 10 and assign it an IP address. Router(config)# interface vlan 10 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit !--- Configure interface VLAN 20 and assign it an IP address. Router(config)# interface vlan 20 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.11.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config)# ip routing !--- Enable routing protocol on the module. !--- The following two commands are optional; !--- they are only used if you have multiple routers in your network. !--- Depending on your network, you may want to use a different routing protocol. Router(config)# router rip Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 Router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 Router(config-router)# Ctrl-Z Router# 07:05:17: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (127.0.0.2) Router# write memory !--- Save the configuration. Building configuration... Router#
Neste ponto, de acordo com o Diagrama de Rede, a configuração entre VLANs está completa.
-
Retorne ao módulo Supervisor Engine emitindo o comando exit no prompt Router#:
Router# exit Cat5500> (enable
Problema comum: Interface de VLANs exibida/desativada
Esta seção explica um problema comum que os clientes encontram quando tentam configurar interfaces de VLAN nos módulos do roteador das séries Catalyst 5500/5000 ou Catalyst 6500/6000 (RSM, MSFC, RSFC).
Os clientes relatam que não podem fazer ping em algumas ou em todas as interfaces de VLAN configuradas no módulo do roteador. Além disso, seu status não é exibido como up/up quando eles executam o comando show interface vlan vlan#. Eles se certificaram de que configuraram no shutdown nessas interfaces. A única interface VLAN que aparece como up/up é a VLAN 1.
Nessa situação, se algumas ou todas as suas interfaces de VLAN não estiverem aparecendo/ativadas, a primeira coisa que você deve verificar é se há alguma porta ativa no switch para as VLANs em questão.
Nota importante: Uma interface VLAN no módulo do roteador só estará ativa/ativa se houver pelo menos uma porta atribuída a essa VLAN no switch (diferente da interface do roteador) e essa porta estiver conectada. Uma porta configurada como um tronco também satisfaz este requisito de up/up de VLAN. Se essa condição não for atendida, a interface do roteador não será ativada.
Na seção Diagrama de Rede, você é avisado para não conectar as estações de trabalho ao switch Catalyst 5500. Nesse ponto, se você emitir esse conjunto de comandos, você perceberá que apenas a interface VLAN 1 está aparecendo e os outros dois estão inativos:
Router# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 172.16.80.79 YES manual up up Vlan10 10.10.10.1 YES manual down down Vlan20 10.10.11.1 YES manual down down Router# show interface vlan 1 Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 172.16.80.79/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:02, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 10 Vlan10 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:25:48, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 20 Vlan20 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.11.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:01:04, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 2000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 1000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router#
A interface VLAN 1 está ativa/ativa, embora no switch você não tenha nenhuma porta conectada e ativa na VLAN 1. Você tem uma porta/interface ativa na VLAN 1, a interface sc0 no Módulo Supervisor. Por padrão, a interface sc0 é um membro da VLAN 1. Emita este comando no switch (Supervisor Engine) para verificar a configuração da interface sc0:
Cat5500> (enable) show interface
sl0: flags=51 <UP ,POINTOPOINT ,RUNNING>
slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0
sc0: flags=63 <UP ,BROADCAST ,RUNNING>
vlan 1 inet 172.16.80.40 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.80.255
Cat5500> (enable)
Neste ponto, conecte a estação de trabalho 1 na porta 4/1 e a estação de trabalho 2 na porta 4/13. Emita os comandos show port 4/1 e show port 4/13 no switch para ter certeza de que essas portas mostram o status como conectado:
Cat5500> (enable) show port 4/1 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 4/1 connected 10 normal a-half a-10 10/100BaseTX !--- Output suppressed. Cat5500> (enable) show port 4/13 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 4/13 connected 20 normal a-full a-100 10/100BaseTX !--- Output suppressed. Cat5500> (enable)
Agora, faça login no módulo do roteador e verifique o status das interfaces VLAN 10 e VLAN 20. Você deve vê-los como up/up. Emita este conjunto de comandos para verificar o status das interfaces VLAN no módulo do roteador:
Cat5500> (enable) session 7 Trying Router-7... Connected to Router-7. Escape character is '^]'. User Access Verification Password: !--- Enter the password; in this case, it is cisco. Router> enable Password: !--- Enter the password; in this case, it is cisco. Router# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 172.16.80.79 YES manual up up Vlan10 10.10.10.1 YES manual up up Vlan20 10.10.11.1 YES manual up up Router# show interface vlan 10 Vlan10 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:46:14, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 20 Vlan20 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.11.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:56, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 2000 bits/sec, 5 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 2000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# exit Cat5500> (enable)
Verificar a configuração
É possível realizar vários testes de ping para verificar a configuração explicada neste documento. Nesta seção, você usa a estação de trabalho2 para fazer ping na estação de trabalho1, na interface sc0 no switch e nas interfaces VLAN no módulo do roteador.
Observação: certifique-se de que você definiu os gateways padrão em suas estações de trabalho como as interfaces VLAN no módulo do roteador. De acordo com o Diagrama de Rede, o gateway padrão na estação de trabalho 1 é definido como 10.10.10.1 e 10.10.11.1 para a estação de trabalho 2.
Teste 1: Ping da estação 2 para a estação 1
C:\> ipconfig
!--- This command is used to check the IP configuration on the !--- Windows 2000 workstation. Use the appropriate commands on the workstations !--- that you use.
Windows 2000 IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.254
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.1
C:\> ping 10.10.10.254
Pinging 10.10.10.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Ping statistics for 10.10.10.254:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 10ms, Average = 2ms
Teste 2: Faça ping da Estação de Trabalho 2 para a Interface sc0 no Supervisor Engine
C:\> ping 172.16.80.40
Pinging 172.16.80.40 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Ping statistics for 172.16.80.40:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Teste 3: Faça ping da Estação de Trabalho 2 para a Interface VLAN 1 no Módulo do Roteador
C:\> ping 172.16.80.79
Pinging 172.16.80.79 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 172.16.80.79:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Teste 4: Faça ping da Estação de Trabalho 2 para a Interface VLAN 10 no Módulo do Roteador
C:\> ping 10.10.10.1
Pinging 10.10.10.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 10.10.10.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Teste 5: Faça ping da Estação de Trabalho 2 para a Interface VLAN 20 no Módulo do Roteador
C:\> ping 10.10.11.1
Pinging 10.10.11.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 10.10.11.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Appendix
Configuração do módulo do mecanismo supervisor
Cat5500> (enable) show config This command shows non-default configurations only. Use show config all to show both default and non-default configurations. ... begin ! # ***** NON-DEFAULT CONFIGURATION ***** ! ! #time: Tue Apr 10 2001, 09:09:54 ! #version 6.1(1) ! set option fddi-user-pri enabled set password $2$lx7B$WipkVnLnbYIfrBSqD2SN9. set enablepass $2$6/eK$I3lDb2nnP7Fc9JKF3XwRW/ set prompt Cat5500> ! #errordetection set errordetection portcounter enable ! #system set system name Cat5500 ! #frame distribution method set port channel all distribution mac both ! #vtp set vtp domain cisco set vtp mode transparent set vlan 1 name default type ethernet mtu 1500 said 100001 state active set vlan 1002 name fddi-default type fddi mtu 1500 said 101002 state active set vlan 1004 name fddinet-default type fddinet mtu 1500 said 101004 state active stp ieee set vlan 1005 name trnet-default type trbrf mtu 1500 said 101005 state active stp ibm set vlan 10,20 set vlan 1003 name token-ring-default type trcrf mtu 1500 said 101003 state active mode srb aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7 backupcrf off ! #ip set interface sc0 1 172.16.80.40/255.255.255.0 172.16.80.255 set ip route 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 172.16.80.79 ! #set boot command set boot config-register 0x2102 clear boot system all ! # default port status is enable ! ! #module 1 : 2-port 1000BaseSX Supervisor ! #module 2 : 4-port 10/100BaseTX Supervisor ! #module 3 : 3-port 1000BaseX Ethernet ! #module 4 : 24-port 10/100BaseTX Ethernet set vlan 10 4/1-12 set vlan 20 4/13-20 set spantree portfast 4/1-20 enable ! #module 5 : 2-port MM OC-3 Dual-Phy ATM ! #module 6 empty ! #module 7 : 1-port Route Switch ! #module 8 empty ! #module 9 empty ! #module 10 empty ! #module 11 : 48-port 10BaseT Ethernet ! #module 12 : 2-port MM MIC FDDI ! #module 13 empty end Cat5500> (enable)
Configuração de RSM
Router# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! enable password cisco ! ip subnet-zero ip cef ! ! process-max-time 200 ! interface Vlan1 ip address 172.16.80.79 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Vlan10 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Vlan20 ip address 10.10.11.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! ip classless ! ! line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login ! end Router#
Informações Relacionadas
- Configuração e Visão Geral do Router Module para o Catalyst Family 4000 (WS-X4232-L3)
- Utilização de Portfast e outros comandos para reparar retardos de conectividade da inicialização de estação de trabalho
- Páginas de Suporte de Produtos de LAN
- Página de suporte da switching de LAN
- Suporte Técnico - Cisco Systems
Histórico de revisões
| Revisão | Data de publicação | Comentários |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
30-Aug-2005 |
Versão inicial |
Contate a Cisco
- Abrir um caso de suporte

- (É necessário um Contrato de Serviço da Cisco)
 Feedback
Feedback