配置有DHCP安全的ARP, SSG端口套件主机密钥、SSG TCP重定向, SESM和SSG/DHCP感知的SSG互联网网关的呼叫流调试
简介
本文档重点介绍为门户服务运行SSG和DHCP及SESM的IOS Internet网关。
先决条件
要求
本文档没有任何特定的要求。
使用的组件
本文档不限于特定的软件和硬件版本。
规则
有关文档规则的详细信息,请参阅 Cisco 技术提示规则。
背景信息
技术和功能概述
服务选择网关 (SSG)
服务选择网关(SSG)是服务提供商的交换解决方案,通过宽带接入技术(如数字用户线路(DSL)、电缆调制解调器或无线)为用户提供内部网、外联网和互联网连接,从而允许同时访问网络服务。
SSG与思科用户边缘服务管理器(SESM)配合使用。 SSG与SESM一起为互联网服务的用户提供用户身份验证、服务选择和服务连接功能。用户使用标准Internet浏览器与SESM Web应用交互。
SESM在两种模式下运行:
-
RADIUS模式 — 此模式从RADIUS服务器获取用户和服务信息。RADIUS模式下的SESM与SSD类似。
-
LDAP模式 — 轻量级目录访问协议(LDAP)模式提供对符合LDAP的目录的访问,以获取订用程序和服务配置文件信息。此模式还增强了SESM Web应用的功能,并使用基于角色的访问控制(RBAC)模型来管理用户访问。
SSG端口套件主机密钥
SSG端口捆绑主机密钥功能通过使用主机源IP地址和源端口来识别和监控用户的机制增强了SSG和SESM之间的通信和功能。
借助SSG端口捆绑主机密钥功能,SSG对用户和SESM服务器之间的HTTP流量执行端口地址转换(PAT)和网络地址转换(NAT)。当用户向SESM服务器发送HTTP数据包时,SSG会创建端口映射,将源IP地址更改为已配置的SSG源IP地址,并将源TCP端口更改为SSG分配的端口。SSG为每个用户分配一个端口捆绑包,因为当一个用户访问网页时,它可以同时拥有多个TCP会话。分配的主机密钥或端口捆绑包和SSG源IP地址的组合,唯一标识每个用户。主机密钥在SESM服务器和用户IP供应商特定属性(VSA)中SSG之间发送的RADIUS数据包中携带。 当SESM服务器向用户发送应答时,SSG根据端口映射转换目的IP地址和目的TCP端口。
未经身份验证的用户的SSG TCP重定向
未经身份验证的用户的重定向会重定向来自用户的数据包(如果用户未经服务提供商授权)。当未授权用户尝试连接到TCP端口上的服务(例如,连接到www.cisco.com)时,SSG TCP重定向会将数据包重定向到强制网络门户(SESM或SESM设备组)。SESM发出重定向到浏览器以显示登录页面。用户登录到SESM并经过身份验证和授权。然后,SESM向用户显示个性化主页、服务提供商主页或原始URL。
DHCP 安全 IP 地址分配
DHCP安全IP地址分配功能引入了保护DHCP数据库中动态主机配置协议(DHCP)租用的ARP表条目的功能。此功能可保护客户端的MAC地址并将其同步到DHCP绑定,防止未授权客户端或黑客欺骗DHCP服务器并接管已授权客户端的DHCP租用。启用此功能后,DHCP服务器将IP地址分配给DHCP客户端,DHCP服务器会向ARP表中添加一个安全ARP条目,其中包含已分配的IP地址和客户端的MAC地址。此ARP条目无法由任何其他动态ARP数据包更新,并且此ARP条目在ARP表中存在于已配置的租用时间内或只要租用处于活动状态。仅当DHCP绑定到期时,DHCP客户端或DHCP服务器的显式终止消息才能删除安全ARP条目。此功能可配置为新的DHCP网络,也可用于升级当前网络的安全。此功能的配置不中断服务,对DHCP客户端不可见。
测试床图
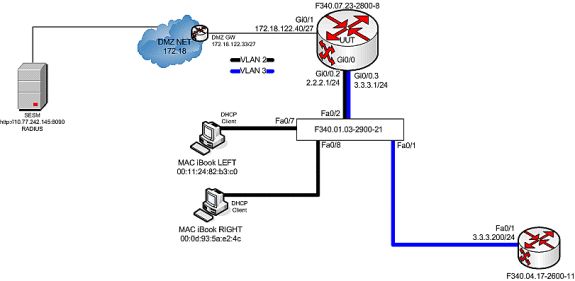
呼叫流调试
请完成以下步骤:
-
当MAC iBook LEFT首次将以太网电缆连接到此网络时,它会从运行于“F340.07.23-2800-8”上的IOS DHCP服务器租用IP地址2.2.2.5/29。
debug ip dhcp server packet debug ssg dhcp events *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: DHCP-DISCOVER event received. SSG-dhcp awareness feature enabled *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2. *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool name called for 0011.2482.b3c0. No hostobject *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool class called, class name = Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPOFFER to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: IP address notification received. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: HostObject not present *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Can't find any hostname to update *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPACK to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). F340.07.23-2800-8#show ip dhcp binding Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF: IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type Hardware address/ User name 2.2.2.5 0100.1124.82b3.c0 Oct 13 2008 08:37 PM Automatic -
在成功租用IP地址2.2.2.5后,MAC iBook LEFT打开Web浏览器并将其指向http://3.3.3.200,用于模拟与SSG服务“distlearn”关联的受保护资源。 SSG服务“distlearn”在SSG路由器“F340.07.23-2800-8”中本地定义:
local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255"
实际上, http://3.3.3.200是配置为“ip http server”并在TCP 80上侦听的Cisco IOS路由器,因此它基本上是Web服务器。
在MAC iBook LEFT尝试浏览到http://3.3.3.200后,由于此连接在配置了“ssg direction downlix”的接口上是入口,因此SSG路由器首先检查是否存在活动SSG主机对象,以查找HTTP请求的源IP地址。由于这是来自IP地址2.2.2.5的第一个此类请求,因此SSG主机对象不存在,通过以下配置为主机2.2.2.5实例化了指向SESM的TCP重定向:
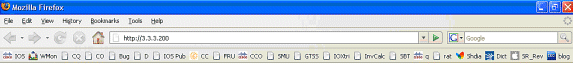
ssg tcp-redirect port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 All hosts with destination requests on these TCP Ports are candidates for redirection. server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 10.77.242.145 is the SESM server and it’s listening for HTTP on TCP 8090. “server” MUST be in default network or open-garden. redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If an SSG router receives a packets on an interface with “ssg direction downlink” configured, it first compares the Source IP address of the packet with the SSG Host Object Table. If an Active SSG Host Object matching the Source IP address of this packet is not found, AND the destination TCP Port of the packet matches “port-list ports”, and the destination IP address is NOT included as a part of “ssg default-network” OR SSG Open Garden, then the user will be redirected because his is unauthenticated [no Host Object] and his packet is destined for a TCP port in the “port-list ports”. The user will then be captivated until an SSG Host Object is created, or until a timeout which is configurable via “redirect captivate initial default group”. debug ssg tcp redirect debug ssg ctrl-event *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: SSG-TCP-REDIR:-Up: created new remap entry for unauthorised user at 2.2.2.5 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Redirect server set to 10.77.242.145,8090 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Initial src/dest port mapping 49273<->80 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg tcp-redirect mappings Authenticated hosts: No TCP redirect mappings for authenticated users Unauthenticated hosts: Downlink Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 TCP remapping Host:2.2.2.5 to server:10.77.242.145 on port:8090 The initial HTTP request from 2.2.2.5 had a source TCP Port of 49273 and a destination IP address of 3.3.3.200 and TCP port of 80. Because of the SSG TCP Redirect, the destination IP header is overwritten with the socket of the SESM server 10.77.242.145:8090. If Port Bundle Host Key were NOT configured, the Source socket of 2.2.2.5:49273 would remain unchanged. However, in this case, Port Bundle Host Key is configured therefore the source address of this packet is ALSO changed based on this configuration: ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Any packets destined to SESM on TCP ports 80-8100 are subject to PBHK source NAT to IP socket 172.18.122.40, starting with a port of 64. *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: group:ssg_tr_unauth, web-proxy:0 *Oct 13 20:24:37.417: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Down: TCP-FIN Rxd for user at 2.2.2.5, port 49273 *Oct 13 20:24:37.421: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Up: TCP-FIN Rxd from user at 2.2.2.5, src port 49273 As a part of this SSG TCP Redirect, the original URL is preserved http://3.3.3.200 but the destination IP socket is rewritten to 10.77.242.145:8090. So, when the SESM receives this URL of http://3.3.3.200 on TCP port 8090, it sends an HTTP redirect back toward the client’s browser directing the client to the SESM login page, which is http://10.77.242.145:8080/home?CPURL=http%3A%2F%2F3.3.3. 200%2F&t=fma4443t. Notice the Browser Redirect points the Client Browser to TCP 8080 for captive portal. As such, the TCP session for the initial IOS SSG Redirect to 10.77.242.145:8090 is terminated. Also, notice SESM has captured the original URL of http://3.3.3.200 in the Redirect. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (4,&) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=4 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account status query for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, Ack the query with Complete ID. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 4 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext With Port Bundle Host Key configured, all HTTP communications between Client and SESM are subject to Port Bundling, which is effectively Source NAT for the TCP socket. Above, the “SSG-CTL-EVN” messages debug the communication between the SESM and the IOS SSG Router using a proprietary RADIUS-based protocol. When using Port Bundle Host Key, SESM always uses the Port Bundle to identify the host, which in this case is 172.18.122.40:64. You’ll see when SESM sends the HTTP redirect resulting in the Web browser connecting to 10.77.242.145:8090, SESM also queries SSG on the Control Channel for existence of Host Object for 172.18.122.40:64, which the SSG Router knows is actually 2.2.2.5. Since no Host Object is present, the SSG Router sends the SESM “No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64” This can be confirmed at this point like this: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host ### Total HostObject Count: 0此时,输入http://3.3.3.200时,MAC iBook左侧的浏览器如下所示:
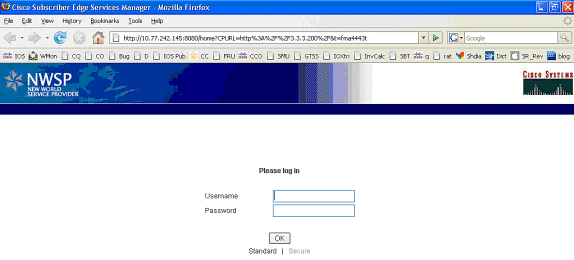
在IOS SSG TCP和SESM HTTP重定向后,屏幕如下所示:
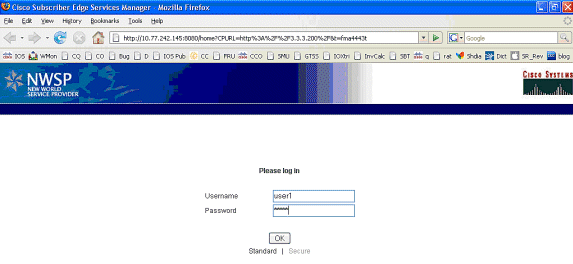
-
在SSG TCP重定向到SESM并且SESM随后发送的HTTP重定向返回MAC iBook Left的浏览器后,MAC iBook Left输入user1作为用户名,cisco作为密码:
-
按下OK按钮后,SESM通过基于RADIUS的专有协议向SSG路由器发送这些凭证。
*Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (1,user1) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=1 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account logon for host 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: No auto-domain selected for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Authenticating user user1. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: ssg_aaa_nasport_fixup function *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: slot=0, adapter=0, port=0, vlan-id=2, dot1q-tunnel-id=0, vpi=0, vci=0, type=10 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext
-
然后,SSG路由器会构建RADIUS访问请求数据包,并将其发送到RADIUS以对用户1进行身份验证:
*Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS(00000008): Send Access-Request to 10.77.242.145:1812 id 1645/11, len 88 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: authenticator F0 56 DD E6 7E 28 3D EF - BC B1 97 6A A9 4F F2 A6 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Password [2] 18 * *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40
-
RADIUS以Access-Accept for user1响应,并在“F340.07.23-2800-8”中创建SSG主机对象:
*Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Received from id 1645/11 10.77.242.145:1812, Access-Accept, len 273 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: authenticator 52 7B 50 D7 F2 43 E6 FC - 7E 3B 22 A4 22 A7 8F A6 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 23 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 17 "NInternet-Basic" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 13 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 7 "Niptv" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 14 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 8 "Ngames" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ndistlearn" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ncorporate" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 22 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 16 "Nhome_shopping" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nbanking" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nvidconf" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS(00000008): eceived from id 1645/11 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 4 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating radius packet *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Response is good *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-EVN: HostObject::HostObject: size = 616 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::Reset *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList NInternet-Basic *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Niptv *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ngames *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ndistlearn *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ncorporate *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nhome_shopping *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nbanking *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nvidconf *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: DoAccountLogon: ProfileCache is Enabled *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Account logon is accepted [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, user1] *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 1 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for host 2.2.2.5 Finally, our SSG Host Object is created for 2.2.2.5. Notice that “user1” RADIUS profile is configured with many ssg-account-info VSA with “N” Attribute, which is an SSG code for Service to which the user is subscribed. Please note, this doesn’t mean “user1” has any Active services at this point, which can be confirmed with: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 1: 2.2.2.5 [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64] ### Active HostObject Count: 1 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content --- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:37:09.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: NONE AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE
-
此时,用户1被定义为SSG主机对象,但尚未访问任何SSG服务。MAC iBook左侧显示“服务选择”屏幕,然后单击“远程学习”:
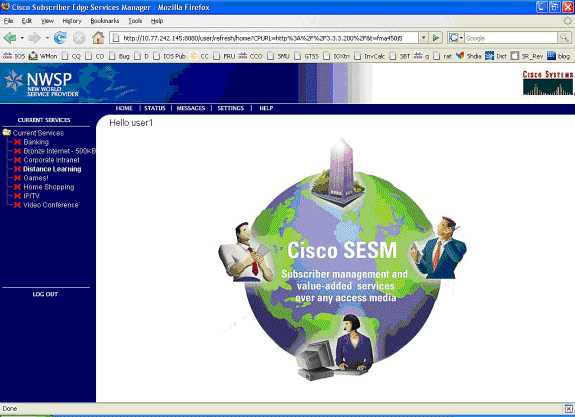
-
单击Distance Learning后,SESM框与SSG路由器通信,控制通道为:
debug ssg ctrl-events *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (11,distlearn) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 SSG Router is receiving control channel command that SSG User 172.18.122.40:64 [maps to 2.2.2.5] wants to activate SSG Service ‘distlearn’. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=11 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling service logon for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating pseudo ServiceInfo for service: distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-EVN: ServiceInfo::ServiceInfo: size = 416 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: ServiceInfo: Init servQ and start new process for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Got profile for distlearn locally Since “distlearn” is available from local configuration: local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" ...we don’t need to make a AAA call to download SSG Service Information. However, please note that in most real-world SSG implementations, SSG Services are defined on the RADIUS AAA Server. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Create a new service table for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service bound on this interface are : distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service distlearn bound to interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 firsthop 0.0.0.0 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: Service Address List : *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: Addr:3.3.3.200 mask:255.255.255.255 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add a new service distlearn to an existing table Here the SSG creates a Service Table for distlearn and binds it to an “ssg direction uplink” interface complete with the R attribute for the Service. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking connection activation for 172.18.122.40:64 to distlearn. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating ConnectionObject (172.18.122.40:64, distlearn) *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: ConnectionObject::ConnectionObject: size = 304 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 2 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking maximum service count. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Opening connection for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Connection opened *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service logon is accepted. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating the ConnectionObject. Once the Service is verified locally, SSG needs to build a “Connection” where a “Connection” is a tuple with: A. SSG Host Object B. SSG Service Name and Attributes C. SSG Downlink interface D. SSG Upstream interface A-D are used to create a pseudo hidden VRF service table for which traffic from this host can transit. See here: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg connection 2.2.2.5 distlearn ------------------------ConnectionObject Content ---- User Name: user1 Owner Host: 2.2.2.5 Associated Service: distlearn Calling station id: 0011.2482.b3c0 Connection State: 0 (UP) Connection Started since: *20:40:21.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:41:04.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 Connection Traffic Statistics: Input Bytes = 420, Input packets = 5 Output Bytes = 420, Output packets = 5 Session policing disabled F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content ----------- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:40:23.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: distlearn; AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE -
SSG连接已启用,呼叫流程已完成。MAC iBook左侧可以成功浏览到http://3.3.3.200:
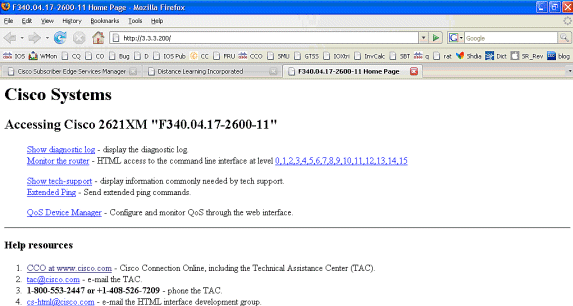
SSG路由器配置说明与功能文档
version 12.4 service nagle no service pad service tcp-keepalives-in service tcp-keepalives-out service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname F340.07.23-2800-8 ! boot-start-marker boot system flash flash: c2800nm-adventerprisek9-mz.124-21.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1024000 debugging ! aaa new-model ! aaa authorization network default group radius ! aaa session-id common no ip source-route ! ip cef ip dhcp relay information trust-all ip dhcp use vrf connected ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.1 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.2 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.3 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.4 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.6 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.7 We are excluding 2.2.2.1-4 and 2.2.2.6-7 to ensure the only DHCP address that will be leased is 2.2.2.5/29. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server ip dhcp pool dhcp_guest_v3501 network 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.248 default-router 2.2.2.1 dns-server 172.18.108.34 lease 0 4 update arp If an interface on this router is configured with an address in the 2.2.2.0/29 range, it will field DHCP request from host on that network and assign IP address 2.2.2.5, GW 2.2.2.1, and DNS Server 172.18.108.24. The lease time on the IP address will be 4 hours. Also, “update arp” will ensure ARP entries for IP addresses leased via DHCP will match the MAC entry in the DHCP Binding table. This will prevent SSG session hijacking in the event a static user re-uses a DHCP [or is given] leased address. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuring DHCP Services for Accounting and Security ! no ip domain lookup ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3 ip admission max-nodata-conns 3 ! voice-card 0 no dspfarm ! ssg enable Enables SSG subsystem. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg intercept dhcp Enables SSG/DHCP Awareness. In our example, this will result in an SSG Host object being destroyed when either of these occur: A. A DHCPRELEASE message is received for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. B. A DHCP Lease expires for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. Configuring SSG for On-Demand IP Address Renewal ssg default-network 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 All packets ingress to “ssg direction downlink” interfaces can access the “ssg default-network” regardless as to whether a Host or Connection Object exists. SSG allows all users, even unauthenticated users, to access the default network. Typically, SESM belongs to the default network. However, other types of servers, such as DNS/DHCP servers or TCP-Redirect servers, can also be part of the default network. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg service-password cisco If an SSG Service is not defined locally and we therefore need to make a RADIUS call when a user subscribes to an SSG Service, the password “cisco” is used in the RADIUS Access-Request for the Service. ssg radius-helper auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 ssg radius-helper key cisco Used to communicate with SESM on SSG Control Channel. SESM must also maintain a similar static configuration for each SSG Router it serves. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg auto-logoff arp match-mac-address interval 30 In the absence of user traffic, SSG will send an ARP Ping for all Active Host Objects and will invoke an AutoLogoff if either the host fails to reply or the MAC address of the host has changed. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg bind service distlearn GigabitEthernet0/0.3 SSG traffic is not routed using the Global routing table. Instead it’s routed from “ssg direction downstream” interface using the information in the mini-VRF seen in “show ssg connection”, which includes a manual binding of Service<-->”ssg direction uplink” interface. Hence, it is a requirement of SSG to manually bind services to interfaces or next-hop IP addresses. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services ssg timeouts session 64800 Absolute timeout for SSG Host Object is 64800 seconds. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Port Bundle Host Key configuration. All traffic destined to 10.77.242.145 in the range of TCP 80 to 8100 will be Source NATed to 172.18.122.40. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg tcp-redirect Enters SSG redirect sub-config. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 Defines a list of destination TCP ports which are candidates for TCP redirection. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 Defines a redirect server list and defines the TCP port on which they’re listening for redirects. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If a Host Object does NOT exist and the traffic is ingress to an “ssg direction downlink” interface AND its destination port is in port-list ports, THEN redirect this traffic to “server-group ssg_tr_unauth”. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers ssg service-search-order local remote Look for SSG Service defined in a local-profile in IOS configuration before making a AAA call to download Service information. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" Local definition of SSG Service “distlearn” 26 9 251 is Vendor Specific, Cisco, SSG Service Info Attributes defined herein: R: Destination Network, Specifies IP routes belonging to this Service Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services RADIUS Profiles and Attributes for SSG interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 description Guest Wireless Vlan encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.248 no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip mroute-cache ssg direction downlink All SSG Host Objects should be located on downlink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 description Routed connection back to Blue encapsulation dot1Q 3 ip address 3.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 ssg direction uplink All SSG Services should be located on uplink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.122.40 255.255.255.224 duplex auto speed auto ! ip forward-protocol nd ip route 10.77.242.144 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 157.157.157.0 255.255.255.0 3.3.3.5 ip route 172.18.108.34 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 172.18.124.101 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip radius source-interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ! radius-server host 10.77.242.145 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 timeout 5 retransmit 3 key 7 070C285F4D06 ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
安全和会话重用注意事项
当您同时使用SSG和DHCP时,这些方案可允许恶意用户重复使用允许未经身份验证访问安全资源的经过身份验证的SSG主机对象:
-
如果SSG/DHCP感知未配置“ssg intercept dhcp”,则新DHCP用户可以租用之前租用的IP地址,SSG主机对象仍然存在。由于来自此新用户的第一个TCP请求具有与源IP地址匹配的SSG主机对象(尽管已过时),因此该用户被授予对受保护资源的未经身份验证的使用。使用“ssg intercept dhcp”可以阻止此情况,这会导致在发生以下任一情况时删除SSG主机对象:
-
为与活动主机对象匹配的IP地址接收DHCPRELEASE。
-
DHCP租用对于与活动主机对象匹配的IP地址到期。
-
-
如果DHCP用户在非正常DHCP注销(即不发送DHCP注销)之前将租用的IP地址与恶意用户关联,则无论是否配置了“ssg intercept dhcp”,恶意用户都可以使用此IP地址静态配置计算机并重用SSG主机对象。在IOS DHCP池下配置“ssg intercept dhcp”和“update arp”,可以阻止此情况。“update arp”确保唯一能够添加或删除ARP条目的IOS子系统是DHCP服务器子系统。使用“update arp”时,IP到MAC DHCP绑定始终与ARP表中的IP到MAC绑定匹配。即使恶意用户具有与SSG主机对象匹配的静态配置IP地址,也不允许流量进入SSG路由器。由于MAC地址与当前DHCP绑定的MAC地址不匹配,IOS DHCP服务器会阻止创建ARP条目。
-
当SSG和DHCP一起配置时,“ssg intercept dhcp”和“update arp”会阻止会话重复使用。最后一个非安全相关的挑战是,当DHCP主机执行非平稳注销时释放DHCP租用和ARP条目。在“ssg direction downlik”接口上配置“authorized arp”会定期向所有主机发送ARP请求,以确保它们仍处于活动状态。如果没有从这些定期ARP消息收到响应,则释放DHCP绑定,IOS DHCP子系统清除ARP条目。
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 arp authorized arp probe interval 5 count 15
在本例中,会定期发送ARP请求,以每5秒刷新Fa0/0上的所有已知ARP条目。15次失败后,DHCP绑定被释放,IOS DHCP子系统清除ARP条目。
在没有“授权arp”的SSG环境中,如果DHCP主机执行非平稳注销,则DHCP租用及其关联的SSG主机对象将保持活动状态,直到此DHCP地址的租用到期,但只要全局配置了“ssg intercept dhcp”,则不会重用会话。
“authorized arp”会关闭配置该ARP的接口上的动态ARP学习。有关接口上的唯一ARP条目是IOS DHCP服务器在租用启动后添加的ARP条目。租约终止后,IOS DHCP服务器会清除这些ARP条目,原因有:收到DHCP RELEASE、租约到期或ARP探测失败,因为DHCP注销不正常。
实施说明:
-
“ssg auto-logoff arp”和“ssg auto-logoff icmp”是防止会话重复使用或导致安全问题的不必要方法。当在配置的“间隔”内SSG连接上未看到流量时,“ssg自动注销”的“arp”和“icmp”变体只发送ARP或IMCP PING,最低间隔为30秒。如果DHCP在30秒内租用之前使用的IP地址,或恶意用户在30秒内静态配置当前绑定的DHCP地址,则会重用会话,因为SSG会看到连接对象上的流量,并且“ssg auto-logoff”不会调用。
-
在所有使用案例中,如果恶意主机执行MAC地址欺骗,则不会阻止会话重用。
表1 - SSG/DHCP部署中的会话重用和安全注意事项
| 命令 | 功能 | 安全影响 |
|---|---|---|
| ssg auto-logoff arp [match-mac-address] [interval seconds] ssg auto-logoff icmp [timeout milliseconds] [packets number] [interval seconds] | 在ARP或ICMP PING失败后删除SSG主机对象,这些ARP或ICMP PING失败仅在“间隔”内SSG连接上未发现流量时才发送。 | 如果DHCP在30秒内租用之前使用的IP地址,或者恶意用户在30秒内静态配置当前绑定的DHCP地址,因为SSG看到连接对象上的流量,并且“ssg auto-logoff”不调用,则重新使用会话。 |
| ssg intercept dhcp | 创建SSG/DHCP感知,允许在以下事件中删除SSG主机对象:为与活动主机对象匹配的IP地址接收DHCPRELEASE。B.与活动主机对象匹配的IP地址的DHCP租用到期。 | 防止DHCP用户重用SSG会话,但不防止静态用户欺骗DHCP地址或重用SSG会话。 |
| ip dhcp pool TEST update arp | 确保唯一能够添加或删除ARP条目的IOS子系统是DHCP服务器子系统。 | 使用“ssg intercept dhcp”配置时,防止所有会话重复使用。 如果配置时没有“ssg intercept dhcp”,则如果DHCP租用以前使用的IP地址,则仍然可以重用会话。 |
| 接口FastEthernet0/0 ARP已授权 | 定期向所有主机发送ARP请求,以确保它们仍处于活动状态。关闭动态ARP学习。 | 当DHCP用户执行非平稳注销时,允许DHCP绑定和ARP条目删除。 |
相关信息
修订历史记录
| 版本 | 发布日期 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2008 |
初始版本 |
 反馈
反馈