SNS Appliance Reference
Create a Bootable USB Device to Install Cisco ISE
Before you begin
-
Use the Fedora Media Writer tool to create a bootable USB device from the Cisco ISE installation ISO file.
Download Fedora Media Writerhttps://github.com/lmacken/liveusb-creator/releases/tag/3.12.0 to the local system.

Note
Other USB tools might work, but we recommend that you use Fedora Media Writer 3.12.0 as it has been tested with Cisco ISE.
-
Download the Cisco ISE installation ISO file to the local system.
-
Use a 8-GB (or higher) USB device.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Reformat the USB device using FAT16 or FAT32 to free up all the space. |
|
Step 2 |
Plug in the USB device to the local system and launch Fedora Media Writer. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Browse from the Use existing Live CD area and choose the Cisco ISE ISO file. |
|
Step 4 |
Choose the USB device from the Target Device drop-down list. If there is only one USB device connected to the local system, it is selected automatically. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Create Live USB. |
|
Step 6 |
From the USB drive, open the following text files in a text editor:
|
|
Step 7 |
Replace the term "cdrom" in both the files.
Specifically, replace all instances of the "cdrom" string. For example, replace ks=cdrom/ks.cfg with ks=hd:sdb1:/ks.cfg |
|
Step 8 |
Save the files and exit. |
|
Step 9 |
If you are using ise-2.4.0.357.SPA.x86_64_SNS-36x5_APPLIANCE_ONLY.iso to create Live USB, replace the BOOTX64.EFI and grub.efi files in the EFI/BOOT folder with the files available on the Cisco Software Download site and exit. |
|
Step 10 |
Safely remove the USB device from the local system. |
|
Step 11 |
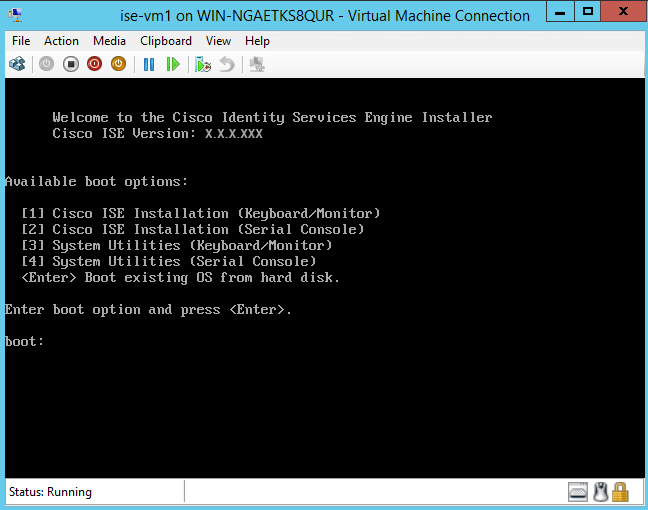
Plug in the bootable USB device to the Cisco ISE appliance, restart the appliance, and boot from the USB drive to install Cisco ISE. |
Reimage the Cisco SNS Hardware Appliance
The Cisco SNS hardware appliances do not have built-in DVD drives. Therefore, to reimage a Cisco ISE hardware appliance with Cisco ISE software, you can do one of the following:
 Note |
Cisco SNS hardware appliances support the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) secure boot feature. This feature ensures that only a Cisco-signed ISE image can be installed on the SNS hardware appliances, and prevents installation of any unsigned operating system even with physical access to the device. For example, generic operating systems, such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux or Microsoft Windows cannot boot on this appliance. |
The SNS 3515 and SNS 3595 appliances support only Cisco ISE 2.0.1 or later releases. You cannot install a release earlier than 2.0.1 on the SNS 3515 or SNS 3595 appliance.
-
Use the Cisco Integrated Management Controller (Cisco IMC) interface to map the installation .iso file to the virtual DVD device.
-
Create an install DVD with the installation .iso file and plug in an USB external DVD drive and boot the appliance from the DVD drive.
-
Create a bootable USB device using the installation .iso file and boot the appliance from the USB drive.

 Feedback
Feedback