Configuración de ejemplo: Cómo usar rutas estáticas flotantes y routing por marcado a pedido
Contenido
Introducción
El objetivo de este documento es configurar un ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI) para marcar y para llevar el tráfico a un sitio remoto en caso de error lógico del circuito de Frame Relay.
El protocolo de routing de gateway interior mejorado (EIGRP) no se está ejecutando en los BRI. En su lugar, el ejemplo de este documento utiliza rutas estáticas flotantes para redirigir el tráfico sobre el BRI solamente si se pierden las rutas normales aprendidas a través de EIGRP sobre el circuito de Frame Relay.
En todos los routers, asegúrese de que ip classless esté habilitado.
Prerequisites
Requirements
No hay requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento no tiene restricciones específicas en cuanto a versiones de software y de hardware.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Convenciones
Para obtener más información sobre las convenciones del documento, consulte Convenciones de Consejos Técnicos de Cisco.
Configurar
Estas configuraciones son fragmentos de la configuración completa.
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Para encontrar información adicional sobre los comandos usados en este documento, utilice la Command Lookup Tool (sólo clientes registrados) .
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
Figura 1: Diagrama de red 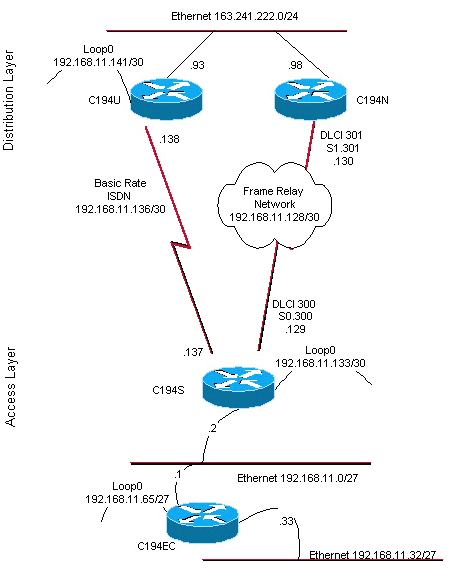
Configuraciones
En este documento, se utilizan estas configuraciones:
-
Router de distribución de capa nro. 1
-
Router de capa de distribución #2
-
Router de capa de acceso
-
Router del sitio remoto
En router C194u es uno de los dos routers de capa de distribución. En este ejemplo, el router C194u tiene el BRI en el sitio remoto. El otro router de capa de distribución, C194n, tiene la interfaz serial complementaria hacia el sitio remoto.
| Router de distribución de capa nro. 1 |
|---|
hostname c194u ! !--- Create a username for the router at the remote site. username c194s password 7 XXXXXXXX ! ip subnet-zero isdn switch-type basic-dms100 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.11.141 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 163.241.222.93 255.255.255.0 media-type 10BaseT ! interface BRI0 description to Remote Site c194s, (this end 08358662 08358664) ip address 192.168.11.138 255.255.255.252 no ip mroute-cache encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache isdn spid1 0835866201 isdn spid2 0835866401 dialer idle-timeout 600 dialer wait-for-carrier-time 10 dialer map ip 192.168.11.137 name c194s broadcast 8358661 dialer map ip 192.168.11.137 name c194s broadcast 8358663 dialer hold-queue 5 dialer load-threshold 128 outbound dialer-group 1 no fair-queue ppp authentication chap ppp multilink ! router eigrp 65535 !--- We redistribute the static routes listed below, so if the Frame Relay !--- network fails, the other routers in this autonomous system (AS) will !--- begin to see the remote networks advertised from this router. !--- Normally these routes are learned through EIGRP across the Frame Relay link. !--- Make the BRI interfaces passive. An alternative is to use a dialer-list !--- to identify EIGRP packets as "uninteresting" packets. redistribute static passive-interface BRI0 network 192.168.11.0 network 163.241.0.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless !--- Both distribution layer routers have a default route to their Null !--- interfaces so that they advertise the 0/0 network to all other routers !--- in the AS. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null0 !--- There must be a static route for each network behind the C194s !--- router at the remote site. Use the IP address of the BRI interface !--- of router C194s, and ensure that the administrative distance is 240. !--- Note: Summarize these routes if your addressing scheme lends itself !--- to summarization. If the Frame Relay network fails, this will force !--- packets destined to the remote site out the BRI interface, and will cause !--- it to dial and restore connectivity. ip route 192.168.11.0 255.255.255.224 192.168.11.137 240 ip route 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 192.168.11.137 240 ip route 192.168.11.64 255.255.255.224 192.168.11.137 240 ip route 192.168.11.132 255.255.255.252 192.168.11.137 240 ! access-list 100 deny icmp any any access-list 100 permit ip any any dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 100 ! end |
A continuación se muestra un ejemplo de resultado del comando show dialer para el router C194u:
| Router de distribución de capa nro. 1 |
|---|
c194u#show dialer
BRI0 - dialer type = ISDN
Dial String Successes Failures Last called Last status
8358663 4 1311 01:32:08 failed
8358661 1874 1315 00:02:07 successful
0 incoming call(s) have been screened.
BRI0:1 - dialer type = ISDN
Idle timer (600 secs), Fast idle timer (20 secs)
Wait for carrier (5 secs), Re-enable (15 secs)
Dialer state is physical layer up
Dial reason: ip (s=192.168.11.138, d=192.168.11.137)
|
El siguiente router, C194n, es el segundo router de capa de distribución porque En esta ilustración, es el router de link de trama. No tiene ninguna configuración especial. Sólo tiene la ruta predeterminada redistribuida en EIGRP.
| Router de capa de distribución #2 |
|---|
hostname c194n ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 163.241.222.98 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial1 no ip address bandwidth 1544 no ip mroute-cache encapsulation frame-relay no fair-queue ! interface Serial1.301 point-to-point ip address 192.168.11.130 255.255.255.252 bandwidth 32 frame-relay interface-dlci 301 ! router eigrp 65535 redistribute static network 192.168.11.0 network 163.241.0.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null0 ! |
El siguiente router, C194s, es el router del sitio remoto, el router de la capa de acceso. Conecta la red remota a la estructura básica a través del router de la capa de distribución.
| Router de capa de acceso |
|---|
! hostname c194s ! !--- Create a username for the distribution layer router. username c194u password 7 XXXXXXXXX ! isdn switch-type basic-dms100 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.11.133 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.11.2 255.255.255.224 ! interface Serial0 no ip address bandwidth 64 encapsulation frame-relay ! interface Serial0.300 point-to-point ip address 192.168.11.129 255.255.255.252 bandwidth 32 frame-relay interface-dlci 300 ! interface BRI0 description to Hub Site c194u, (this end 08358661 08358663) ip address 192.168.11.137 255.255.255.252 no ip mroute-cache encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache isdn spid1 0835866101 isdn spid2 0835866301 dialer idle-timeout 600 dialer wait-for-carrier-time 10 dialer map ip 192.168.11.138 name c194u broadcast 8358662 dialer map ip 192.168.11.138 name c194u broadcast 8358664 dialer hold-queue 5 dialer load-threshold 128 dialer-group 1 no fair-queue ppp multilink ppp authentication chap ! router eigrp 65535 !--- Redistribute the static route, so any routers which you could have attached !--- to the Ethernet network 192.168.11.0/27 will see this router as their way !--- out to the remainder of the network. However, do not allow this default !--- route back into your distribution layer routers. Use a distribute list !--- to block the advertisement. redistribute static passive-interface BRI0 network 192.168.11.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 distribute-list 2 out Serial0.300 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless !--- Use the IP address of the BRI interface of the distribution layer router to !--- Add a default route. When the frame network goes down, this will !--- push your traffic out the BRI interface, and cause it to dial and !--- restore connectivity. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.11.138 240 ! access-list 1 permit any ! access-list 2 deny 0.0.0.0 access-list 2 permit any ! dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 1 ! end ! |
El siguiente router representa la red del sitio remoto. Aquí no se necesita hacer nada especial, sólo participar en el protocolo de ruteo dinámico, IGP EIGRP, del router de capa de acceso.
| Router del sitio remoto |
|---|
hostname c194ec ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.11.65 255.255.255.224 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.224 ! interface Ethernet1 ip address 192.168.11.33 255.255.255.224 ! ! router eigrp 65535 network 192.168.11.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless ! end |
Verificación
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para confirmar que su configuración esté funcionando correctamente.
La herramienta Output Interpreter (sólo para clientes registrados) permite utilizar algunos comandos “show” y ver un análisis del resultado de estos comandos.
Con la red Frame Relay desactivada, intente un traceroute desde la red en el sitio remoto. Según el diagrama de red (consulte la figura 1), la dirección IP de destino es la interfaz de loopback del router del sitio del hub.
c194ec#trace
Target IP address: 192.168.11.141
Source address: 192.168.11.65
Tracing the route to 192.168.11.141
1 192.168.11.2 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec
2 * * *
3 * *
192.168.11.138 24 msec
Observe cómo se necesitaban varios paquetes para activar la interfaz BRI. Ejecute de nuevo el comando traceroute, antes de que el BRI se active y se pierdan los paquetes:
c194ec#traceroute 192.168.11.141 Tracing the route to 192.168.11.141 1 192.168.11.2 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec 2 192.168.11.138 20 msec * 20 msec
Vuelva a encender el switch de tramas. Con la red Frame Relay ahora en funcionamiento, no utiliza ISDN:
c194ec#traceroute 192.168.11.141 Tracing the route to 192.168.11.141 1 192.168.11.2 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec 2 192.168.11.130 36 msec 36 msec 32 msec 3 163.241.222.93 36 msec * 32 msec
A continuación se muestran las tablas de ruteo para la red de Frame Relay operativa. Observe cómo se aprenden las rutas individuales a través de EIGRP para las redes en el sitio del hub. También hay una ruta predeterminada aprendida a través de EIGRP.
c194ec#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.11.2 to network 0.0.0.0
163.241.0.0 255.255.255.0 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 163.241.222.0 [90/2221056] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:09, Ethernet0
192.168.11.0 is variably subnetted, 7 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.11.64 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet1
C 192.168.11.0 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.128 255.255.255.252
[90/2195456] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:13, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.132 255.255.255.252
[90/409600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:23:14, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.136 255.255.255.252
[90/40537600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:23:14, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.140 255.255.255.252
[90/2349056] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:10, Ethernet0
D*EX 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [170/40614400] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:10, Ethernet
A continuación se muestran las tablas de ruteo para cuando la red Frame Relay está inactiva. Todavía hay una ruta predeterminada, pero se pierden algunas rutas individuales de las redes en el sitio del hub. Pero debido a que ip classless está habilitado y usted tiene una ruta predeterminada, todavía puede llegar a todas partes en la red.
c194ec#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.11.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.11.0 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.11.64 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet1
C 192.168.11.0 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.132 255.255.255.252
[90/409600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:25:27, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.136 255.255.255.252
[90/40537600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:25:27, Ethernet0
D*EX 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [170/40076800] via 192.168.11.2, 00:00:15, Ethernet
Troubleshoot
Actualmente, no hay información específica de troubleshooting disponible para esta configuración.
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
15-Sep-2005 |
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios