Configuração de exemplo: Uso de rotas estáticas flutuantes e do roteamento de discagem por demanda
Contents
Introduction
O objetivo deste original é configurar uma Interface de taxa básica (BRI, Basic Rate Interface) ISDN para discar e transportar tráfego para um local remoto em caso de uma falha lógica do circuito do Frame Relay.
O Protocolo de Roteamento IGRP Melhorado (Enhanced IGRP) não está em execução nas BRIs. Em vez disso, o exemplo neste documento usará rotas estáticas flutuantes para redirecionar o tráfego pela BRI apenas se as rotas normais aprendidas por meio do Protocolo de Roteamento IGRP Melhorado (Enhanced IGRP) pelo circuito Frame Relay forem perdidas.
Em todos os roteadores, assegure-se de que ip classless esteja habilitado.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Não existem requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento não se restringe a versões de software e hardware específicas.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Para obter mais informações sobre convenções de documento, consulte as Convenções de dicas técnicas Cisco.
Configurar
Essas configurações são trechos das configurações completas.
Nesta seção, você encontrará informações para configurar os recursos descritos neste documento.
Observação: para encontrar informações adicionais sobre os comandos usados neste documento, use a ferramenta Command Lookup Tool (somente clientes registrados).
Diagrama de Rede
Este documento utiliza a seguinte configuração de rede:
Figura 1 – Diagrama da Rede 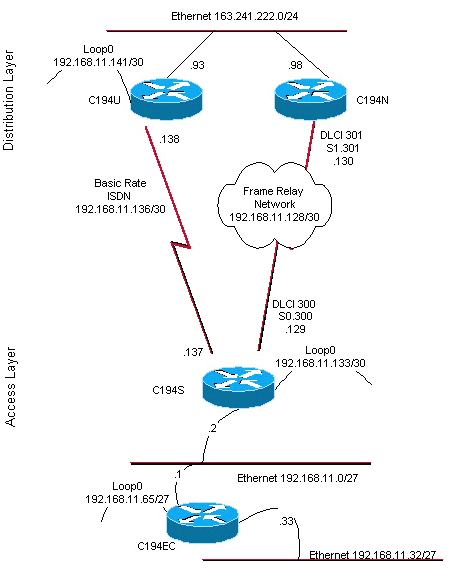
Configurações
Este documento utiliza as seguintes configurações:
-
Roteador de Camada de Distribuição nº 1
-
Roteador da camada de distribuição #2
-
Roteador da camada de acesso
-
Roteador de estação remota
O roteador C194u é um dos dois roteadores de camada de distribuição. Neste exemplo, o roteador C194u tem a BRI no local remoto. O outro roteador de camada de distribuição, C194n, tem a interface serial anexa no lado remoto.
| Roteador de Camada de Distribuição nº 1 |
|---|
hostname c194u ! !--- Create a username for the router at the remote site. username c194s password 7 XXXXXXXX ! ip subnet-zero isdn switch-type basic-dms100 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.11.141 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 163.241.222.93 255.255.255.0 media-type 10BaseT ! interface BRI0 description to Remote Site c194s, (this end 08358662 08358664) ip address 192.168.11.138 255.255.255.252 no ip mroute-cache encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache isdn spid1 0835866201 isdn spid2 0835866401 dialer idle-timeout 600 dialer wait-for-carrier-time 10 dialer map ip 192.168.11.137 name c194s broadcast 8358661 dialer map ip 192.168.11.137 name c194s broadcast 8358663 dialer hold-queue 5 dialer load-threshold 128 outbound dialer-group 1 no fair-queue ppp authentication chap ppp multilink ! router eigrp 65535 !--- We redistribute the static routes listed below, so if the Frame Relay !--- network fails, the other routers in this autonomous system (AS) will !--- begin to see the remote networks advertised from this router. !--- Normally these routes are learned through EIGRP across the Frame Relay link. !--- Make the BRI interfaces passive. An alternative is to use a dialer-list !--- to identify EIGRP packets as "uninteresting" packets. redistribute static passive-interface BRI0 network 192.168.11.0 network 163.241.0.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless !--- Both distribution layer routers have a default route to their Null !--- interfaces so that they advertise the 0/0 network to all other routers !--- in the AS. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null0 !--- There must be a static route for each network behind the C194s !--- router at the remote site. Use the IP address of the BRI interface !--- of router C194s, and ensure that the administrative distance is 240. !--- Note: Summarize these routes if your addressing scheme lends itself !--- to summarization. If the Frame Relay network fails, this will force !--- packets destined to the remote site out the BRI interface, and will cause !--- it to dial and restore connectivity. ip route 192.168.11.0 255.255.255.224 192.168.11.137 240 ip route 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 192.168.11.137 240 ip route 192.168.11.64 255.255.255.224 192.168.11.137 240 ip route 192.168.11.132 255.255.255.252 192.168.11.137 240 ! access-list 100 deny icmp any any access-list 100 permit ip any any dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 100 ! end |
Aqui está uma saída de comando show dialer para o roteador C194u:
| Roteador de Camada de Distribuição nº 1 |
|---|
c194u#show dialer
BRI0 - dialer type = ISDN
Dial String Successes Failures Last called Last status
8358663 4 1311 01:32:08 failed
8358661 1874 1315 00:02:07 successful
0 incoming call(s) have been screened.
BRI0:1 - dialer type = ISDN
Idle timer (600 secs), Fast idle timer (20 secs)
Wait for carrier (5 secs), Re-enable (15 secs)
Dialer state is physical layer up
Dial reason: ip (s=192.168.11.138, d=192.168.11.137)
|
O roteador seguinte, C194n, é o segundo roteador da camada de distribuição. Nesta ilustração, ele é o roteador de link do frame. Ele não tem nenhuma configuração especial. Ele tem apenas a rota padrão redistribuída no Protocolo de Roteamento IGRP Melhorado (Enhanced IGRP).
| Roteador da camada de distribuição #2 |
|---|
hostname c194n ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 163.241.222.98 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial1 no ip address bandwidth 1544 no ip mroute-cache encapsulation frame-relay no fair-queue ! interface Serial1.301 point-to-point ip address 192.168.11.130 255.255.255.252 bandwidth 32 frame-relay interface-dlci 301 ! router eigrp 65535 redistribute static network 192.168.11.0 network 163.241.0.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null0 ! |
O próximo roteador, C194s, é o roteador do site remoto, o roteador da camada de acesso. Ele conecta a rede remota ao backbone por meio do roteador da camada de distribuição.
| Roteador da camada de acesso |
|---|
! hostname c194s ! !--- Create a username for the distribution layer router. username c194u password 7 XXXXXXXXX ! isdn switch-type basic-dms100 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.11.133 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.11.2 255.255.255.224 ! interface Serial0 no ip address bandwidth 64 encapsulation frame-relay ! interface Serial0.300 point-to-point ip address 192.168.11.129 255.255.255.252 bandwidth 32 frame-relay interface-dlci 300 ! interface BRI0 description to Hub Site c194u, (this end 08358661 08358663) ip address 192.168.11.137 255.255.255.252 no ip mroute-cache encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache isdn spid1 0835866101 isdn spid2 0835866301 dialer idle-timeout 600 dialer wait-for-carrier-time 10 dialer map ip 192.168.11.138 name c194u broadcast 8358662 dialer map ip 192.168.11.138 name c194u broadcast 8358664 dialer hold-queue 5 dialer load-threshold 128 dialer-group 1 no fair-queue ppp multilink ppp authentication chap ! router eigrp 65535 !--- Redistribute the static route, so any routers which you could have attached !--- to the Ethernet network 192.168.11.0/27 will see this router as their way !--- out to the remainder of the network. However, do not allow this default !--- route back into your distribution layer routers. Use a distribute list !--- to block the advertisement. redistribute static passive-interface BRI0 network 192.168.11.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 distribute-list 2 out Serial0.300 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless !--- Use the IP address of the BRI interface of the distribution layer router to !--- Add a default route. When the frame network goes down, this will !--- push your traffic out the BRI interface, and cause it to dial and !--- restore connectivity. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.11.138 240 ! access-list 1 permit any ! access-list 2 deny 0.0.0.0 access-list 2 permit any ! dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 1 ! end ! |
O roteador seguinte representa a rede de local remoto. Nada de especial precisa ser feito aqui. Basta informar, no IGP Dynamic Routing Protocol, EIGRP, o roteador de camada de acesso.
| Roteador de estação remota |
|---|
hostname c194ec ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.11.65 255.255.255.224 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.224 ! interface Ethernet1 ip address 192.168.11.33 255.255.255.224 ! ! router eigrp 65535 network 192.168.11.0 default-metric 64 200 255 1 1500 no auto-summary eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless ! end |
Verificar
Esta seção fornece informações que você pode usar para confirmar se sua configuração está funcionando adequadamente.
A Output Interpreter Tool (somente clientes registrados) oferece suporte a determinados comandos show, o que permite exibir uma análise da saída do comando show.
Com a rede Frame Relay desativada, tente um traceroute a partir da rede no local remoto. Com base no diagrama de rede (consulte a figura 1), o endereço IP de destino é a interface de loopback do roteador de local de hub.
c194ec#trace
Target IP address: 192.168.11.141
Source address: 192.168.11.65
Tracing the route to 192.168.11.141
1 192.168.11.2 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec
2 * * *
3 * *
192.168.11.138 24 msec
Observe como ele exigiu diversos pacotes para ativar a interface BRI. Emita o comando traceroute novamente, antes da BRI ficar inativa e os pacotes serem perdidos:
c194ec#traceroute 192.168.11.141 Tracing the route to 192.168.11.141 1 192.168.11.2 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec 2 192.168.11.138 20 msec * 20 msec
Reative o switch de frame. Com a rede Frame Relay agora operacional, você não usa ISDN:
c194ec#traceroute 192.168.11.141 Tracing the route to 192.168.11.141 1 192.168.11.2 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec 2 192.168.11.130 36 msec 36 msec 32 msec 3 163.241.222.93 36 msec * 32 msec
As tabelas de roteamento da rede Frame Relay operacional são mostradas abaixo. Observe como as rotas individuais são aprendidas com o Protocolo de Roteamento IGRP Melhorado (Enhanced IGRP) para redes no local de hub. Também há uma rota padrão aprendida com o Protocolo de Roteamento IGRP Melhorado (Enhanced IGRP).
c194ec#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.11.2 to network 0.0.0.0
163.241.0.0 255.255.255.0 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 163.241.222.0 [90/2221056] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:09, Ethernet0
192.168.11.0 is variably subnetted, 7 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.11.64 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet1
C 192.168.11.0 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.128 255.255.255.252
[90/2195456] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:13, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.132 255.255.255.252
[90/409600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:23:14, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.136 255.255.255.252
[90/40537600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:23:14, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.140 255.255.255.252
[90/2349056] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:10, Ethernet0
D*EX 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [170/40614400] via 192.168.11.2, 00:02:10, Ethernet
As tabelas de roteamento para quando a rede Frame Relay estiver desativada são mostradas abaixo. Ainda há uma rota padrão, mas algumas rotas de redes individuais novamente no local de hub são perdidas. Mas como ip classless está habilitado e você tem uma rota padrão, ainda assim você chegará a qualquer lugar na rede.
c194ec#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.11.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.11.0 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.11.64 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet1
C 192.168.11.0 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.132 255.255.255.252
[90/409600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:25:27, Ethernet0
D 192.168.11.136 255.255.255.252
[90/40537600] via 192.168.11.2, 01:25:27, Ethernet0
D*EX 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [170/40076800] via 192.168.11.2, 00:00:15, Ethernet
Troubleshoot
Atualmente, não existem informações disponíveis específicas sobre Troubleshooting para esta configuração.
Informações Relacionadas
Histórico de revisões
| Revisão | Data de publicação | Comentários |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
15-Sep-2005 |
Versão inicial |
Contate a Cisco
- Abrir um caso de suporte

- (É necessário um Contrato de Serviço da Cisco)
 Feedback
Feedback