Table Of Contents
Introducing Cisco IPICS
Cisco IP Interoperability and Collaboration System (Cisco IPICS) is an intelligent platform that controls media and information, enabling intra- and inter-organizational communication, interoperability, and operational efficiencies. By taking advantage of IP standards and protocols, Cisco IPICS bridges communications from existing and proprietary radio networks to IP networks and devices such as the Cisco IPICS Push-to-Talk Management Center (PMC), and supported models of the Cisco Unified IP Phone.
This chapter provides an overview of Cisco IPICS. It describes the advantages and benefits that Cisco IPICS offers to various organizations. It also introduces the primary components of a Cisco IPICS deployment.
This chapter includes these topics:
Cisco IPICS Benefits
Communications interoperability, data integration, and true event- and incident-based contextual collaboration between agencies and organizations are important requirements in many markets, including the following segments:
•
Enterprise (operations and safety and security)
•
Commercial
•
Financial Services
•
Retail
•
Education
•
Healthcare
•
Utilities
•
Oil and gas
•
Public safety
•
Transportation
•
Military/Defense
•
Government
•
Service provider
Organizations in these market segments typically deploy several wired networks and wireless networks to achieve their business and service goals. However, such disparate solutions often do not support interoperability and collaboration, which can affect operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Examples of such disparate networks include:
•
Legacy push-to-talk (PTT) radio networks (analog or digital at different frequencies) that are used for voice communications within groups. Communication is usually restricted within a specified group or network because of radio frequency (RF) limitations and proprietary protocols.
•
Traditional hoot bridges that are connected over time-division multiplexing (TDM) circuits. These deployments cannot provide audit trails and they do not seamlessly integrate with other PTT or Voice over IP (VoIP) networks. In addition, they do not offer the mobility and serviceability that an IP deployment provides.
•
VoIP networks that are used to carry packetized voice on wired or wireless IP phones or on other IP clients. These clients do not interact with the PTT services.
For organizations that use disparate networks, the Cisco IPICS solution provides the following benefits:
•
Incident management framework graphical user interface (GUI)—Facilitates tasks that are associated with operations and command and control
•
Easy-to-use installation, management, and operational features—Enables a migration path to more robust IP applications, devices, and IP-based solutions to achieve greater operational efficiencies
•
Effective solution—Streamlines operations, and command and control while protecting investments in deployed radio networks or legacy hoot bridges and applications
•
Efficient deployment—Leverages current IP infrastructure with minimal upgrades required, decreasing total cost of ownership
•
Resiliency—Eliminates communications silos and single points of failure
Cisco IPICS Components
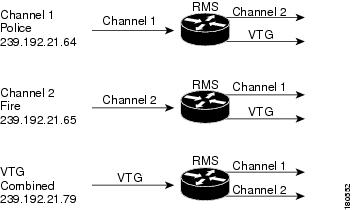
A Cisco IPICS deployment involves several hardware and software components to enable true interoperability and collaboration. Components include new products, such as the Cisco IPICS server and the PMC, and existing technologies, such as land mobile radio (LMR), Cisco gateways, and VoIP. A deployment also employs applications of existing technologies, such as the use of the router media services (RMS) functionality for channel mixing.
Figure 1-1 illustrates the major components of a Cisco IPICS deployment.
Figure 1-1 Cisco IPICS Components
Table 1-1 provides an overview of the Cisco IPICS components. Other chapters in this manual provide more detailed information about using and configuring several of these components. In addition, Cisco provides a wide variety of technical and user documentation that explains in detail Cisco components that are used in the deployment of Cisco IPICS. These documents include information about installing, configuring, operating, managing, maintaining, and troubleshooting components.
For version and compatibility information, refer to Cisco IPICS Compatibility Matrix.

 Feedback
Feedback