Contents
- Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Information About Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Benefits of Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Feature Design of Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Supported Websense Server Features on a Cisco IOS Firewall
- How to Configure Websense URL Filtering
- Configuring Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Verifying Cisco IOS Firewall and Websense URL Filtering
- Maintaining the Cache Table
- Monitoring the URL Filter Subsystems
- Configuration Examples for the Firewall and Webserver
- Example URL Filter Client (Firewall) Configuration
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Glossary
Firewall Websense URL Filtering
The Firewall Websense URL Filtering feature enables your Cisco IOS firewall (also known as Cisco Secure Integrated Software [CSIS]) to interact with the Websense URL filtering software, thereby allowing you to prevent users from accessing specified websites on the basis of some policy. The Cisco IOS firewall works with the Websense server to know whether a particular URL should be allowed or denied (blocked).
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Information About Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- How to Configure Websense URL Filtering
- Configuration Examples for the Firewall and Webserver
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Glossary
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Firewall Websense URL Filtering
Websense Server Requirement
To enable this feature, you must have at least one Websense server; however, two or more Websense servers are preferred. Although there is no limit to the number of Websense servers you may have, and you can configure as many servers as you wish, only one server will be active at any given time--the primary server. URL look-up requests will be sent only to the primary server.
URL Filtering Support Restriction
This feature supports only one active URL filtering scheme at a time. (Before enabling Websense URL filtering, you should always ensure that there is not another URL filtering scheme configured, such as N2H2.)
Username Restriction
This feature does not pass the username and group information to the Websense server. However, the Websense server can work for user-based policies because it has another mechanism for getting the username to correspond to an IP address.
Exclusive Domain List Restriction
This feature does not resolve the domains before it searches an exclusive domain list. When a questionable URL is presented to the filtering server, this feature searches only for the value that was specified in the command-line interface (CLI). That is, if an exclusive domain list was configured via the ip urlfilter exclusive-domain deny 198.168.1.1command, a user entering http://198.168.1.1. into a browser will be denied access. However, a user who is trying to access this same domain and who enters http://www.cisco.com, will be allowed access because 198.168.1.1 was specified via the CLI, not www.cisco.com.
PISA URL Filtering Restrictions -- Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)ZYA
- Only one inspection rule is supported.
- Only HTTP filtering is supported. (HTTPS and FTP filtering are not supported.)
- HTTP over ports used by static Network Based Application Recognition (NBAR) protocols are not supported.
- Context-based Access Control (CBAC) is not supported.
- Only Layer 3 SVIs, Layer 3 routed ports, and Layer 3 subinterfaces are supported.
- The clear ip urlfilter cache and show ip urlfilter cache commands are not supported.
- Only the Websense URL filtering server is supported. (N2H2/SmartFilter/Trend Micro filtering servers are not supported.)
- Usernames are not passed on from PISA to Websense.
Information About Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Benefits of Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Feature Design of Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Supported Websense Server Features on a Cisco IOS Firewall
Benefits of Firewall Websense URL Filtering
The Cisco IOS Firewall Websense URL Filtering feature provides an Internet management application that allows you to control web traffic for a given host or user on the basis of a specified security policy. In addition, the following functions are available in this feature:
Primary and Secondary Servers
When users configure multiple Websense servers, the firewall will use only one server at a time--the primary server; all other servers are called secondary servers. When the primary server becomes unavailable for any reason, it becomes a secondary server and one of the secondary servers becomes the primary server.
A firewall marks a primary server as down when sending a request to or receiving a response from the server fails. When a primary server goes down, the system will go to the beginning of the configured servers list and try to activate the first server on the list. If the first server on the list is unavailable, it will try the second server on the list; the system will keep trying to activate a server until it is successful or until it reaches the end of the server list. If the system reaches the end of the server list, it will set a flag indicating that all of the servers are down, and it will enter allow mode.
When all the servers are down and the system is in allow mode, a periodic event that occurs for each minute will trace through the server list, trying to bring up a server by opening a TCP connection. If the TCP connection is successfully opened, the server is considered to be up, and the system will return to operational mode.
IP Cache Table
This function provides an IP cache table that contains the IP addresses of web servers whose underlying URLs can be accessed by all users and hosts.
The caching algorithm involves three parameters--the maximum number of IP addresses that can be cached, an idle time, and an absolute time. The algorithm also involves two timers--idle timer and absolute timer. The idle timer is a small periodic timer (1 minute) that checks to see whether the number of cached IP addresses in the cache table exceeds 80 percent of the maximum limit. If the cached IP addresses have exceeded 80 percent, it will start removing idle entries; if it has not exceeded 80 percent, it will quit and wait for the next cycle. The absolute timer is a large periodic timer (1 hour) that is used to remove all of the elapsed entries. (The age of an elapsed entry is greater than the absolute time.) An elapsed entry will also be removed during cache lookup.
The idle time value is fixed at 10 minutes. The absolute time value is taken from the Websense look-up response, which is often greater than 15 hours. The absolute value for cache entry made out of exclusive-domains is 12 hours. The maximum number of cache entries is configurable.
To configure cache table parameters, use the ip urlfilter cache command.
Packet Buffering
This function allows you to increase the maximum number of HTTP responses that a Cisco IOS firewall can hold. If the HTTP responses arrive prior to a Websense server reply, this buffering scheme allows your firewall to store a maximum of 200 HTTP responses. (After 200 responses have been reached, the firewall will drop further responses.) The responses will remain in the buffer until an allow or deny message is received from Websense: if the status indicates that the URL is allowed, the firewall will release the HTTP responses in the buffer to the browser of the end user; if the status indicates that the URL is blocked, the firewall will discard the HTTP responses in the buffer and close the connection to both ends. This function prevents numerous HTTP responses from overwhelming your system.
To configure the maximum number of HTTP responses for your firewall, use the ip urlfilter max-resp-pak command.
Exclusive Domains
This function provides a configurable list of domain names so that the Cisco IOS firewall does not have to send a lookup request to the Websense server for the HTTP traffic that is destined for one of the domains in the exclusive list. Thus, the Websense server does not have to deal with look-up requests for HTTP traffic that is destined for a host that has already been marked as "allowed."
Flexibility when entering domain names is also provided; that is, the user can enter the complete domain name or a partial domain name. If the user adds a complete domain name, such as "www.cisco.com," to the exclusive domain list, all HTTP traffic whose URLs are destined for this domain (such as www.cisco.com/news and www.cisco.com/index) will be excluded from the Websense URL filtering policies, and based on the configuration, the URLs will be permitted or blocked (denied).
If the user adds only a partial domain name to the exclusive domain list, such as ".cisco.com," all URLs whose domain names end with this partial domain name (such as www.cisco.com/products and www.cisco.com/eng) will be excluded from the Websense URL filtering policies, and based on the configuration, the URLs will be permitted or blocked (denied).
To configure an exclusive domain list, use the ip urlfilter exclusive-domain command.
Allow Mode
The system will go into allow mode when connections to all the Websense servers are down. The system will return to normal mode when a connection to at least one web Websense server is up. Allow mode directs your system to forward or drop all packets on the basis of the configurable allow mode setting. By default, allow mode is off, so all HTTP requests are forbidden if all Websense servers are down.
To configure allow mode for your system, use the ip urlfilter allowmode command.
Feature Design of Firewall Websense URL Filtering
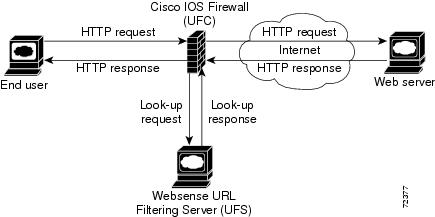
The figure below and the corresponding steps explain a sample URL filtering network topology.
- The end user browses a page on the web server, and the browser sends an HTTP request.
- After the Cisco IOS firewall receives this request, it forwards the request to the web server while simultaneously extracting the URL and sending a look-up request to the Websense server.
- After the Websense server receives the look-up request, it checks its database to see whether it should permit or deny the URL; it returns a permit or deny status via a look-up response to the Cisco IOS firewall.
- After the Cisco IOS firewall receives this look-up response, it performs one of the following functions:
- If the look-up response permits the URL, it sends the HTTP response to the end user.
- If the look-up response denies the URL, the Websense server redirects the user to its own internal web server, which displays a message that describes the category under which the URL is blocked; thereafter, the connection is reset to both ends.
Supported Websense Server Features on a Cisco IOS Firewall
The Cisco IOS firewall supports all of the filtering and user authentication methods that are supported by the Websense server.
The following filtering methods are supported:
- Global filtering, which is applied to all users, groups, and IP addresses
- User- or group-based filtering, which is applied to a specific user or group
- Keyword-based filtering, which is applied on the basis of specific keywords (for example, a user can configure a policy for which all URLs with the keyword "dog" will be denied)
- Category-based filtering, which is applied on the basis of specific categories
- Customized filtering, which allows the user to apply a policy for customized URLs
The NT LAN Manager (NTLM) and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) user authentication methods are supported in this feature. Websense uses these methods to authenticate the user when the firewall does not pass the authenticated username along with the look-up request.
When the username is not passed along with the look-up request, the Websense server retrieves the username through one of the following methods:
- Manual authentication--Websense redirects the user to its own internal web server, which displays a challenge or response for the username and password. (This process is similar to when a user is blocked, but in this process, an authentication message is displayed instead of a blocked message.) Thereafter, Websense checks the NTLM or LDAP directory service to see if the username and password are a match. If there is a match, Websense associates the username with the source IP address and policies can be created for that username.
- Transparent ID (XID)--Websense has an agent that automatically associates users, when they log onto a Windows network, to their IP addresses. Unlike manual authentication, this method does not require an additional logon by the user. However, this method can be used only for Windows.
 Note | Although Websense also supports user authentication via TACACS or RADIUS, this feature currently does not support these protocols for user authentication. |
How to Configure Websense URL Filtering
- Configuring Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Verifying Cisco IOS Firewall and Websense URL Filtering
- Maintaining the Cache Table
- Monitoring the URL Filter Subsystems
Configuring Firewall Websense URL Filtering
Websense is a third-party filtering software that can filter HTTP requests on the basis of the following policies: destination hostname, destination IP address, keywords, and username. The software maintains a URL database of more than 20 million sites organized into more than 60 categories and subcategories.
Before enabling Websense URL filtering, you should always ensure that there is not another URL filtering scheme configured, such as N2H2. If you try to enter a new filtering scheme when one already exists, the new scheme will be ignored, and the system will display an error message that says, "different URL filtering scheme cannot co-exist."
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
This feature introduces the following alert messages:
- "%URLF-3-SERVER_DOWN: Connection to the URL filter server 10.92.0.9 is down"
This level three LOG_ERR-type message is displayed when a configured UFS goes down. When this happens, the firewall will mark the configured server as secondary and try to bring up one of the other secondary servers and mark that server as the primary server. If there is no other server configured, the firewall will enter allow mode and display the "URLF-3-ALLOW_MODE" message.
- %URLF-3-ALLOW_MODE: Connection to all URL filter servers are down and ALLOW MODE is OFF
This LOG_ERR type message is displayed when all UFSs are down and the system enters allow mode.
 Note | Whenever the system goes into allow mode (all filter servers are down), a periodic keepalive timer will be triggered that will try to bring up a server by opening a TCP connection. |
- "%URLF-5-SERVER_UP: Connection to an URL filter server 10.92.0.9 is made; the system is returning from ALLOW MODE"
This LOG_NOTICE-type message is displayed when the UFSs are detected as being up and the system is returning from allow mode.
- "%URLF-4-URL_TOO_LONG:URL too long (more than 3072 bytes), possibly a fake packet?"
This LOG_WARNING-type message is displayed when the URL in a look-up request is too long; any URL longer than 3K will be dropped.
- "%URLF-4-MAX_REQ: The number of pending request exceeds the maximum limit <1000>"
This LOG_WARNING-type message is displayed when the number of pending requests in the system exceeds the maximum limit and all further requests are dropped.
To display these alert messages, use the ip urlfilter alert command.
This feature introduces the following syslog messages:
- "%URLF-6-SITE_ALLOWED: Client 10.0.0.2:12543 accessed server 10.76.82.21:8080"
This message is logged for each request whose destination IP address is found in the cache. It includes the source IP address, source port number, destination IP address, and destination port number. The URL is not logged because the IP address of the request is found in the cache, so parsing the request and extracting the URL is a waste of time.
- "%URLF-4-SITE-BLOCKED: Access denied for the site 'www.sports.com'; client 10.54.192.6:34557 server 172.24.50.12:80"
This message is logged when a request finds a match against one of the blocked domains in the exclusive-domain list or the corresponding entry in the IP cache.
- "%URLF-6-URL_ALLOWED: Access allowed for URL http://www.websense.com/; client 10.54.192.6:54123 server 192.168.0.1:80"
This message is logged for each URL request that is allowed by a UFS. It includes the allowed URL, source IP address, source port number, destination IP address, and destination port number. Longer URLs will be truncated to 300 bytes and then logged.
- "%URLF-6-URL_BLOCKED: Access denied URL http://www.google.com; client 12.54.192.6:54678 server 64.192.14.2:80"
This message is logged for each URL request that is blocked by a UFS. It includes the blocked URL, source IP address, source port number, destination IP address, and destination port number. Longer URLs will be truncated to 300 bytes and then logged.
To display these syslog messages, use the ip urlfilter audit-trail command.
Verifying Cisco IOS Firewall and Websense URL Filtering
To verify that the Firewall Websense URL Filtering feature is working, perform any of the following optional steps:
|
Command or Action |
Purpose |
||
|---|---|---|---|
enable
Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
show ip urlfilter cache
Router# show ip urlfilter cache |
Displays the destination IP addresses that are cached into the cache table.
|
||
show ip urlfilter config
Router# show ip urlfilter config |
Displays the size of the cache, the maximum number of outstanding requests, the allow mode state, and the list of configured Websense servers. |
||
show ip urlfilter statistics
Router# show ip urlfilter statistics |
Displays information such as the number of requests that are sent to the Websense server, the number of responses received from the Websense server, the number of pending requests in the system, the number of failed requests, the number of blocked URLs. |
Maintaining the Cache Table
To clear the cache table of a specified address or of all IP addresses, perform the following optional steps.
Monitoring the URL Filter Subsystems
To monitor the URL filter subsystems, perform the following optional steps:
|
Command or Action |
Purpose |
|---|---|
enable
Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
debug ip urlfilter
func-trace
detailed
events
Router# debug ip urlfilter detailed |
Enables debugging information of the URL filter subsystems.
|
Configuration Examples for the Firewall and Webserver
Example URL Filter Client (Firewall) Configuration
The following example shows how to configure the Cisco IOS firewall (also known as the URL filter client [UFC]) for Websense URL filtering:
hostname fw9-7200b ! logging buffered 64000 debugging enable secret 5 $1$qMOf$umPb75mb3sV27JpNbW//7. ! clock timezone PST -8 clock summer-time PDT recurring ip subnet-zero ip cef no ip domain lookup ! ip inspect name test http urlfilter ip urlfilter cache 5 ip urlfilter exclusive-domain permit .cat.com ip urlfilter exclusive-domain deny .dog.com ip urlfilter exclusive-domain permit www.store.com ip urlfilter audit-trail ip urlfilter alert ip urlfilter server vendor websense 192.168.3.1 ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ip port-map http port 8080 ! no voice hpi capture buffer no voice hpi capture destination ! mta receive maximum-recipients 0 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.3.254 255.255.255.0 ip access-group 101 out ip nat inside ip inspect test in no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface Ethernet1/0 ip address 10.6.9.7 255.255.0.0 ip nat outside no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! interface Ethernet1/1 no ip address no ip mroute-cache shutdown duplex half ! interface Ethernet1/2 no ip address no ip mroute-cache shutdown duplex half ! interface Ethernet1/3 no ip address no ip mroute-cache shutdown duplex half ! interface Serial2/0 no ip address no ip mroute-cache shutdown dsu bandwidth 44210 framing c-bit cablelength 10 serial restart_delay 0 fair-queue ! ip nat pool devtest 10.6.243.21 10.6.243.220 netmask 255.255.0.0 ip nat inside source list 1 pool devtest ip nat inside source static 192.168.3.1 10.6.243.1 ip nat inside source static 192.168.3.2 10.6.243.2 ip nat inside source static 192.168.3.3 10.6.243.3 ip classless ip route 192.168.0.30 255.255.255.255 10.6.0.1 no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip pim bidir-enable ! ! access-list 101 deny tcp any any access-list 101 deny udp any any access-list 101 permit ip any any access-list 102 deny tcp any any access-list 102 deny udp any any access-list 102 permit ip any any dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit dialer-list 1 protocol ipx permit ! ! call rsvp-sync ! ! mgcp profile default ! dial-peer cor custom !! ! gatekeeper shutdown ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password letmein login ! exception core-file sisu-devtest/coredump/fw9-7200b.core exception dump 192.168.0.1 no scheduler max-task-time ! end
Additional References
Related Documents
MIBs
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Firewall Websense URL Filtering
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for Firewall Websense URL Filtering |
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Firewall Websense URL Filtering |
12.2(11)YU 12.2(15)T 12.2(18)ZYA |
This feature enables your Cisco IOS firewall to interact with the Websense URL filtering software, thereby allowing you to prevent users from accessing specified websites on the basis of some policy. In 12.2(18)ZYA, support was added on the Catalyst 6500 series of switches equipped with the PISA. The following commands were introduced or modified: clear ip urlfilter cache, debug ip urlfilter, ip inspect name, ip urlfilter alert, ip urlfilter allowmode, ip urlfilter audit-trail, ip urlfilter cache, ip urlfilter exclusive-domain, ip urlfilter max-request, ip urlfilter max-resp-pak, ip urlfilter server vendor, ip urlfilter urlf-server-log, show ip urlfilter cache, show ip urlfilter config, show ip urlfilter statistics. In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)ZYA, the following command was introduced: ip urlfilter mode |
Glossary
CSIS--Cisco Secure Integrated Software. CSIS is a content-based firewall that currently inspects application data, checks for protocol conformance, extracts the relevant port information to create dynamic access list entries that successfully allow return traffic, and closes the ports at the end of the session.
UFC--URL filter client. UFC is a separate process that accepts URLs from CSIS, forwards the URL to the Websense server, and processes the replies from the vendor server (Websense or N2H2).
UFS--URL filter server. UFS is a generic name given to the vendor server (Websense or N2H2), which processes URLs and decides whether to allow or deny web traffic on the basis of a given policy.
 Note | Refer to the Internetworking Terms and Acronyms for terms not included in this glossary.. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.

 Feedback
Feedback