Contents
- CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Prerequisites for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Restrictions for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Information About CUBE for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- TLS on the CUBE
- Supplementary Services Support on the Cisco UBE for RTP-SRTP Calls
- How to Configure CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Configuring CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Configuring the Certificate Authority
- Configuring a Trustpoint for the Secure Universal Transcoder
- Configuring DSP Farm Services
- Associating SCCP to the Secure DSP Farm Profile
- Registering the Secure Universal Transcoder to the CUBE
- Configuring SRTP-RTP Internetworking Support
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Enabling SRTP on the Cisco UBE
- Enabling SRTP Globally
- Enabling SRTP on a Dial Peer
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Verifying SRTP-RTP Supplementary Services Support on the Cisco UBE
- Configuration Examples for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- SRTP-RTP Internetworking Example
- Example: Enabling SRTP on the Cisco UBE
- Example: Enabling SRTP Globally
- Example: Enabling SRTP on a Dial Peer
- Feature Information for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
The Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature allows secure enterprise-to-enterprise calls and provides operational enhancements for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunks from Cisco Unified Call Manager and Cisco Unified Call Manager Express. Support for Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP)-Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) internetworking between one or multiple Cisco Unified Border Elements (Cisco UBEs) is enabled for SIP-SIP audio calls.
In Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1), the SRTP-RTP Interworking feature was extended to support supplementary services on Cisco UBEs.
- Prerequisites for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Restrictions for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Information About CUBE for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- How to Configure CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Configuration Examples for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Feature Information for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
Prerequisites for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- To enable SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature, you must have Cisco IOS Release 12.4(22)YB or a later release installed and running on your Cisco gateway. For detailed information on platform availability and subsequent releases.
- The Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature is supported in Cisco Unified CallManager 7.0 and later releases.
Restrictions for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
The following features are not supported by the Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature:
Information About CUBE for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
To configure support for SRTP-RTP internetworking, you should understand the following concepts:
- CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- TLS on the CUBE
- Supplementary Services Support on the Cisco UBE for RTP-SRTP Calls
CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
The Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature connects SRTP Cisco Unified CallManager domains with the following:
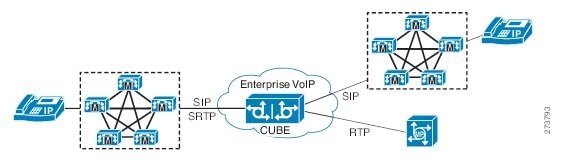
- RTP Cisco Unified CallManager domains. Domains that do not support SRTP or have not been configured for SRTP, as shown in the figure below.
- RTP Cisco applications or servers. For example, Cisco Unified MeetingPlace, Cisco WebEx, or Cisco Unity, which do not support SRTP, or have not been configured for SRTP, or are resident in a secure data center, as shown in the figure below.
- RTP to third-party equipment. For example, IP trunks to PBXs or virtual machines, which do not support SRTP.
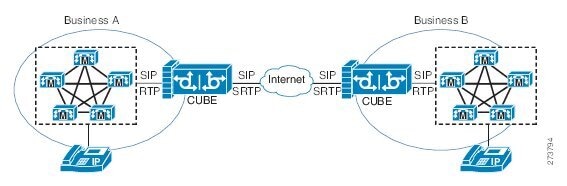
The Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature connects SRTP enterprise domains to RTP SIP provider SIP trunks. SRTP-RTP internetworking connects RTP enterprise networks with SRTP over an external network between businesses. This provides flexible secure business-to-business communications without the need for static IPsec tunnels or the need to deploy SRTP within the enterprise, as shown in the figure below.
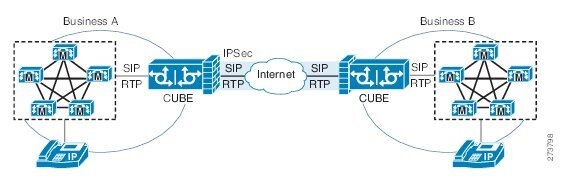
SRTP-RTP internetworking also connects SRTP enterprise networks with static IPsec over external networks, as shown inthe figure below.
SRTP-RTP internetworking on the Cisco UBE in a network topology uses single-pair key generation. Existing audio and dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) transcoding is used to support voice calls. SRTP-RTP internetworking support is provided in both flow-through and high-density mode. SRTP-SRTP pass-through is not impacted.
SRTP is configured on one dial peer and RTP is configured on the other dial peer using the srtp and srtp fallback commands. The dial-peer configuration takes precedence over the global configuration on the Cisco UBE.
Fallback handling occurs if one of the call endpoints does not support SRTP. The call can fall back to RTP-RTP, or the call can fail, depending on the configuration. Fallback takes place only if the srtp fallback command is configured on the respective dial peer. RTP-RTP fallback occurs when no transcoding resources are available for SRTP-RTP internetworking.
TLS on the CUBE
The Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature allows Transport Layer Security (TLS) to be enabled or disabled between the Skinny Call Control Protocol (SCCP) server and the SCCP client. By default, TLS is enabled, which provides added protection at the transport level and ensures that SRTP keys are not easily accessible. Once TLS is disabled, the SRTP keys are not protected.
SRTP-RTP internetworking is available with normal and universal transcoders. The transcoder on the Cisco Unified Border Element is invoked using SCCP messaging between the SCCP server and the SCCP client. SCCP messages carry the SRTP keys to the digital signal processor (DSP) farm at the SCCP client. The transcoder can be within the same router or can be located in a separate router. TLS should be disabled only when the transcoder is located in the same router. To disable TLS, configure the no form of the tls command in dsp farm profile configuration mode. Disabling TLS improves CPU performance.
Supplementary Services Support on the Cisco UBE for RTP-SRTP Calls
The Supplementary Services Support on Cisco UBE for RTP-SRTP Calls feature supports the following supplementary services on the Cisco UBE:
- Midcall codec change with voice class codec configuration for SRTP-RTP and SRTP pass-through calls.
- Reinvite-based call hold.
- Reinvite-based call resume.
-
Music on hold (MoH) invoked from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Cisco UCM), where the call leg changes between SRTP and RTP for an MoH source.
Reinvite-based call forward.
- Reinvite-based call transfer.
- Call transfer based on a REFER message, with local consumption or pass-through of the REFER message on the Cisco UBE.
- Call forward based on a 302 message, with local consumption or pass-through of the 302 message on the Cisco UBE.
- T.38 fax switchover.
- Fax pass-through switchover.
- DO-EO for SRTP-RTP calls.
- DO-EO for SRTP pass-through calls.
When the initial SRTP-RTP or SRTP pass-through call is established on the Cisco UBE, a call can switch between SRTP and RTP for various supplementary services that can be invoked on the end points. Transcoder resources are used to perform SRTP-RTP conversion on Cisco UBE. When the call switches between SRTP and RTP, the transcoder is dynamically inserted, deleted, or modified. Both normal transcoding and high-density (optimized) transcoding are supported.
For call transfers involving REFER and 302 messages (messages that are locally consumed on Cisco UBE), end-to-end media renegotiation is initiated from Cisco UBE only when you configure the supplementary-service media-renegotiate command in voice service voip configuration mode.
When supplementary services are invoked from the end points, the call can switch between SRTP and RTP during the call duration. Hence, Cisco recommends that you configure such SIP trunks for SRTP fallback.
How to Configure CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
Configuring CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Configuring the Certificate Authority
- Configuring a Trustpoint for the Secure Universal Transcoder
- Configuring DSP Farm Services
- Associating SCCP to the Secure DSP Farm Profile
- Registering the Secure Universal Transcoder to the CUBE
- Configuring SRTP-RTP Internetworking Support
- Enabling SRTP on the Cisco UBE
- Verifying SRTP-RTP Supplementary Services Support on the Cisco UBE
Configuring the Certificate Authority
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Trustpoint for the Secure Universal Transcoder
Perform the task in this section to configure, authenticate, and enroll a trustpoint for the secure universal transcoder.
Before you configure a trustpoint for the secure universal transcoder, you should configure the certificate authority, as described in the Configuring the Certificate Authority.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring DSP Farm Services
Before you configure DSP farm services, you should configure the trustpoint for the secure universal transcoder, as described in the Configuring a Trustpoint for the Secure Universal Transcoder.
DETAILED STEPS
Associating SCCP to the Secure DSP Farm Profile
Before you associate SCCP to the secure DSP farm profile, you should configure DSP farm services, as described in the Configuring DSP Farm Services.
DETAILED STEPS
Registering the Secure Universal Transcoder to the CUBE
Perform the task in this section to register the secure universal transcoder to the Cisco Unified Border Element. The Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature supports both secure transcoders and secure universal transcoders.
Before you register the secure universal transcoder to the Cisco Unified Border Element, you should associated SCCP to the secure DSP farm profile, as described in the Associating SCCP to the Secure DSP Farm Profile.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring SRTP-RTP Internetworking Support
Perform the task in this section to enable SRTP-RTP internetworking support between one or multiple Cisco Unified Border Elements for SIP-SIP audio calls. In this task, RTP is configured on the incoming call leg and SRTP is configured on the outgoing call leg.
Before you configure the Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature, you should register the secure universal transcoder to the Cisco Unified Border Element, as described in the Registering the Secure Universal Transcoder to the CUBE.
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling SRTP on the Cisco UBE
You can configure SRTP with the fallback option so that a call can fall back to RTP if SRTP is not supported by the other call end. Enabling SRTP is required for supporting nonsecure supplementary services such as MoH, call forward, and call transfer.
Enabling SRTP Globally
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling SRTP on a Dial Peer
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 1 | enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
Step 3 | dial-peer
voice
tag
voip
Example: Router(config)# dial-peer voice 10 voip |
Defines a particular dial peer to specify VoIP as the method of voice encapsulation and enters dial peer voice configuration mode. | ||
Step 4 | srtp
fallback
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# srtp fallback |
Enables specific dial-peer calls to fall back to nonsecure mode.
| ||
Step 5 | exit
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# exit |
Exits dial peer voice configuration mode. |
Verifying SRTP-RTP Supplementary Services Support on the Cisco UBE
Perform this task to verify the configuration for SRTP-RTP supplementary services support on the Cisco UBE. The show commands need not be entered in any specific order.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 |
enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode. Example:
Router> enable
|
| Step 2 |
show
call
active
voice
brief
Displays call information for voice calls in progress. Example:
Router# show call active voice brief
Telephony call-legs: 0
SIP call-legs: 2
H323 call-legs: 0
Call agent controlled call-legs: 0
SCCP call-legs: 2
ulticast call-legs: 0
Total call-legs: 4
0 : 1 12:49:45.256 IST Fri Jun 3 2011.1 +29060 pid:1 Answer 10008001 connected
dur 00:01:19 tx:1653/271092 rx:2831/464284 dscp:0 media:0
IP 10.45.40.40:7892 SRTP: on rtt:0ms pl:0/0ms lost:0/0/0 delay:0/0/0ms g711ulaw TextRelay: off
media inactive detected:n media contrl rcvd:n/a timestamp:n/a
long duration call detected:n long duration call duration:n/a timestamp:n/a
0 : 2 12:49:45.256 IST Fri Jun 3 2011.2 +29060 pid:22 Originate 20009001 connected
dur 00:01:19 tx:2831/452960 rx:1653/264480 dscp:0 media:0
IP 10.45.40.40:7893 SRTP: off rtt:0ms pl:0/0ms lost:0/0/0 delay:0/0/0ms g711ulaw TextRelay: off
media inactive detected:n media contrl rcvd:n/a timestamp:n/a
long duration call detected:n long duration call duration:n/a timestamp:n/a
0 : 3 12:50:14.326 IST Fri Jun 3 2011.1 +0 pid:0 Originate connecting
dur 00:01:19 tx:2831/452960 rx:1653/264480 dscp:0 media:0
IP 10.45.34.252:2000 SRTP: off rtt:0ms pl:0/0ms lost:0/0/0 delay:0/0/0ms g711ulaw TextRelay: off
media inactive detected:n media contrl rcvd:n/a timestamp:n/a
long duration call detected:n long duration call duration:n/a timestamp:n/a
0 : 5 12:50:14.326 IST Fri Jun 3 2011.2 +0 pid:0 Originate connecting
dur 00:01:19 tx:1653/271092 rx:2831/464284 dscp:0 media:0
IP 10.45.34.252:2000 SRTP: on rtt:0ms pl:0/0ms lost:0/0/0 delay:0/0/0ms g711ulaw TextRelay: off
media inactive detected:n media contrl rcvd:n/a timestamp:n/a
long duration call detected:n long duration call duration:n/a timestamp:n/a
|
| Step 3 |
show
sccp
connection
Displays SCCP connection details. Example:
Router# show sccp connection
sess_id conn_id stype mode codec sport rport ripaddr conn_id_tx
65537 4 s-xcode sendrecv g711u 17124 2000 10.45.34.252
65537 8 xcode sendrecv g711u 30052 2000 10.45.34.252
Total number of active session(s) 1, and connection(s) 2
|
| Step 4 |
show
dspfarm
dsp
active
Displays active DSP information about the DSP farm service. Example:
Router# show dspfarm dsp active
SLOT DSP VERSION STATUS CHNL USE TYPE RSC_ID BRIDGE_ID PKTS_TXED PKTS_RXED
0 1 30.0.209 UP 1 USED xcode 1 4 2876 1706
0 1 30.0.209 UP 1 USED xcode 1 5 1698 2876
Total number of DSPFARM DSP channel(s) 1
|
Configuration Examples for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
SRTP-RTP Internetworking Example
The following example shows how to configure Cisco Unified Border Element support for SRTP-RTP internetworking. In this example, the incoming call leg is RTP and the outgoing call leg is SRTP.
enable configure terminal ip http server crypto pki server 3845-cube database level complete grant auto no shutdown %PKI-6-CS_GRANT_AUTO: All enrollment requests will be automatically granted. % Some server settings cannot be changed after CA certificate generation. % Please enter a passphrase to protect the private key or type Return to exit Password: Re-enter password: % Generating 1024 bit RSA keys, keys will be non-exportable...[OK] % SSH-5-ENABLED: SSH 1.99 has been enabled % Exporting Certificate Server signing certificate and keys... % Certificate Server enabled. %PKI-6-CS_ENABLED: Certificate server now enabled. ! crypto pki trustpoint secdsp enrollment url http://10.13.2.52:80 serial-number revocation-check crl rsakeypair 3845-cube exit ! crypto pki authenticate secdsp Certificate has the following attributes: Fingerprint MD5: CCC82E9E 4382CCFE ADA0EB8C 524E2FC1 Fingerprint SHA1: 34B9C4BF 4841AB31 7B0810AD 80084475 3965F140 % Do you accept this certificate? [yes/no]: yes Trustpoint CA certificate accepted. crypto pki enroll secdsp % Start certificate enrollment .. % Create a challenge password. You will need to verbally provide this password to the CA Administrator in order to revoke your certificate. For security reasons your password will not be saved in the configuration. Please make a note of it. Password: Re-enter password: % The subject name in the certificate will include: 3845-CUBE % The serial number in the certificate will be: FHK1212F4MU % Include an IP address in the subject name? [no]: Request certificate from CA? [yes/no]: yes % Certificate request sent to Certificate Authority % The 'show crypto pki certificate secdsp verbose' command will show the fingerprint. CRYPTO_PKI: Certificate Request Fingerprint MD5: 56CE5FC3 B8411CF3 93A343DA 785C2360 CRYPTO_PKI: Certificate Request Fingerprint SHA1: EE029629 55F5CA10 21E50F08 F56440A2 DDC7469D %PKI-6-CERTRET: Certificate received from Certificate Authority ! voice-card 0 dspfarm dsp services dspfarm voice-card 1 dspfarm dsp services dspfarm exit ! sccp local GigabitEthernet 0/0 sccp ccm 10.13.2.52 identifier 1 version 5.0.1 sccp SCCP operational state bring up is successful.sccp ccm group 1 associate ccm 1 priority 1 associate profile 1 register sxcoder dspfarm profile 1 transcode universal security trustpoint secdsp codec g711ulaw codec g711alaw codec g729ar8 codec g729abr8 codec g729r8 codec ilbc codec g729br8 maximum sessions 84 associate application sccp no shutdown exit ! telephony-service %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface EDSP0, changed state to upsdspfarm units 1 sdspfarm transcode sessions 84 sdspfarm tag 1 sxcoder em logout 0:0 0:0 0:0 max-ephones 4 max-dn 4 ip source-address 10.13.2.52 Updating CNF files CNF-FILES: Clock is not set or synchronized, retaining old versionStamps CNF files updating complete secure-signaling trustpoint secdsp tftp-server-credentials trustpoint scme CNF-FILES: Clock is not set or synchronized, retaining old versionStamps CNF files update complete (post init) create cnf-files CNF-FILES: Clock is not set or synchronized, retaining old versionStamps no sccp ! sccp SCCP operational state bring up is successful. end %SDSPFARM-6-REGISTER: mtp-1:sxcoder IP:10.13.2.52 Socket:1 DeviceType:MTP has registered. %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console dial-peer voice 201 voip destination-pattern 5550111 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:10.13.25.102 incoming called-number 5550112 codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 200 voip destination-pattern 5550112 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:10.13.2.51 incoming called-number 5550111 srtp codec g711ulaw
Feature Information for CUBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
Feature History table for the ISR
| Table 1 | Feature Information for Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking |
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco Unified Border Element Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking |
12.4(22)YB |
This feature allows secure enterprise-to-enterprise calls. Support for SRTP-RTP internetworking between one or multiple Cisco Unified Border Elements is enabled for SIP-SIP audio calls. The following sections provide information about this feature: The following command was introduced: tls. |
|
Supplementary Services Support on Cisco UBE for RTP-SRTP Calls |
15.2(1)T |
The SRTP-RTP Internetworking feature was enhanced to support supplementary services for SRTP-RTP calls on Cisco UBE. |

 Feedback
Feedback