Wireless Multipoint Network Modules
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Connecting Cisco Wireless Multipoint Network Modules to the Network
Wireless Multipoint Network Modules
Hardware and Software Requirements
Connecting Wireless Ports to the Network
Wireless Multipoint Network Module LEDs
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Connecting Cisco Wireless Multipoint Network Modules to the Network
Revised: May 1, 2008, OL-12819-01
This guide describes how to connect Cisco wireless multipoint network modules to your network. It contains the following sections:
•
Wireless Multipoint Network Modules
•
Hardware and Software Requirements
•
Connecting Wireless Ports to the Network
•
Wireless Multipoint Network Module LEDs
•
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Wireless Multipoint Network Modules
The wireless multipoint network module, shown in Figure 1, also referred to as a subscriber unit (SU), provides a high-speed broadband fixed wireless radio-frequency (RF) link between each subscriber site and a single headend site. This link delivers full-duplex data in the licensed MMDS band (2.500 to 2.690 GHz) or unlicensed U-NII band (5.725 to 5.825 GHz).
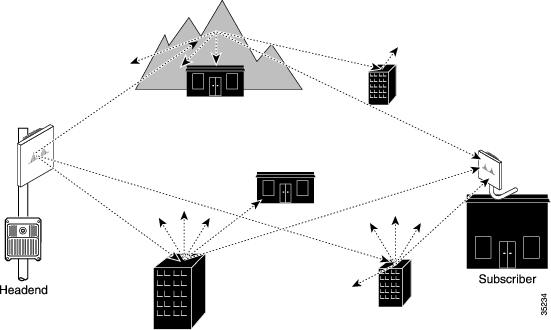
The headend of the system consists of a Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband router, one or more wireless modem cards, and the required subsystem for each modem card. The diversity option, which minimizes the effects of fading, uses two wireless transverters at each site, with each transverter connected to its own antenna. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 1 Wireless Multipoint Network Module with Diversity
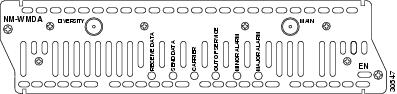
Figure 2 Multipoint Communications with Multipath and Diversity Reception
The network module provides the control and data interface to the radio frequency (RF) subsystem in the wireless transverter. It also provides the up-down conversion from baseband to intermediate frequency (IF). One network module supports one or two wireless transverters (main and diversity).
Subscriber-Unit System
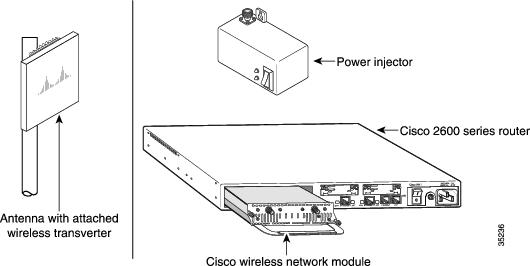
Each subscriber unit system (see Figure 3) consists of the necessary cables and these items:
•
A wireless multipoint network module in the router
•
One or two antennas to transmit and receive RF signals to and from the headend. (Diversity reception of headend transmissions requires two antennas.)
•
One wireless transverter for each antenna. The transverter can be attached to the back of the subscriber antenna, as shown in Figure 3, or mounted separately.
•
One power injector for each transverter. The power injector connects the network module to the wireless transverter, and provides the transverter with DC power, control signals, and IF signals.
Figure 3 Components of the Multipoint Subscriber-Unit System

Note
The antenna, wireless transverter, and power injector are third-party products. For further information about these components, see the manufacturer's documentation.
Hardware and Software Requirements
Wireless multipoint network modules require that the router have at least 16 MB of flash memory.
The wireless multipoint network modules require an external microcode bundle. You can download this microcode at http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/rsu.
Connecting Wireless Ports to the Network
Use an indoor IF coaxial cable to connect the wireless network module Main connector to a power injector. If you are using the diversity feature, connect the network module Diversity connector to a second power injector.
Wireless Multipoint Network Module LEDs
Wireless multipoint network modules have the LEDs shown in Table 1.
Related Documents
For additional information, see the following documents and resources.
Subscriber unit feature documentation
Multipoint Wireless Support for the Cisco 2600 and 3600 Series Routers
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1/12_1xm/feature/guide/ftwrlssu.htmlHeadend feature documentation
Multipoint Support for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1/12_1xm/feature/guide/ftwrlsmc.htmlRegulatory compliance and safety information
Cisco Network Modules and Interface Cards Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/interfaces/rcsi/IOHrcsi.htmlCisco IOS software website and reference documentation
Cisco IOS Software http://www.cisco.com/web/psa/products/index.html?c=268438303
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco StadiumVision, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn is a service mark; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0804R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback