EtherSwitch Network Module (ESW) Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for the EtherSwitch Network Module installed in the Integrated Service Router (ISR). This document does not discuss the configuration example for EtherSwitch Service Module.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco 2800 Series Router on Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.4 or later
-
NM-16ESW-PWR= 16 port 10/100 EtherSwitch Network Module (NM)
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with these hardware and software versions:
-
Cisco 2600/3600/3700/3800 Series Routers.
-
Refer to Table 4 in Cisco EtherSwitch Network Modules - Data Sheet.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
EtherSwitch Modules - Concepts
There are two types of EtherSwitch Modules available for Cisco ISRs. They are:
-
EtherSwitch Network Module (ESW)
-
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES)
ESW modules are configured by router IOS. These modules do not run separate software. The software is integrated into the host router IOS. You can create VLANs, configure VLANs, spanning tree, VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP), and so forth from the host router. The router also stores the VLAN database file (vlan.dat) in the Flash. This document shows the configuration example for the ESW module.
-
Refer to Cisco EtherSwitch Network Modules - Data Sheet for more information on ESW modules.
-
Refer to Cisco EtherSwitch Network Modules Feature Guide to understand how to configure ESW modules.
ES modules have their own processors, switching engines and Flash memory that run independent of the host router resources. After the ES module is installed in the router, you can console into the ES module from the host router. Then you can create VLANs, configure VLANs, spanning tree, VTP, and so forth from the ES module. ES modules are based on the Catalyst 3750 platform.
-
Refer to Cisco EtherSwitch Service Modules - Data Sheet for more information on ES modules.
-
Refer to Cisco EtherSwitch Service Modules Feature Guide to understand how to administrate ES modules.
-
Refer to Catalyst 3750 Series Switches - Configuration Guides to understand how to configure ES modules.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
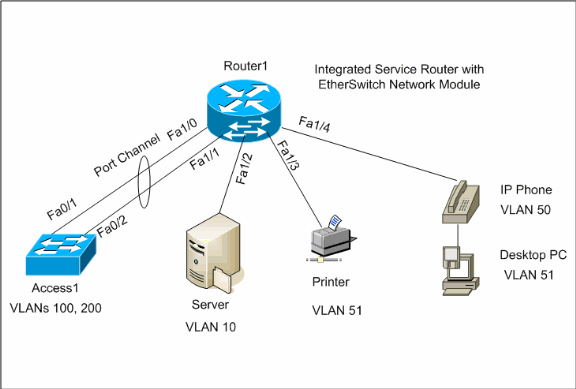
Configurations
This document uses these configurations:
Configure VLAN Interfaces
By default all the ports belong to VLAN1. You can create VLANs only from VLAN database mode. After the VLANs are created from VLAN database mode, the vlan.dat file is created and stored in the Flash file system of the router. You can view the VLANs using the show vlan-switch command. In this example, a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server (172.16.10.20) is located in VLAN 10. The ip helper-address command is configured on all the VLANs except VLAN 10 in order to obtain the IP address from the DHCP server to the devices located at these VLANs.
| Router1 |
|---|
Create VLANs
Router1#vlan database
Router1(vlan)#vlan 10
VLAN 10 added:
Name: VLAN0010
Router1(vlan)#vlan 51
VLAN 51 added:
Name: VLAN0051
Router1(vlan)#vlan 50
VLAN 50 added:
Name: VLAN0050
Router1(vlan)#vlan 100
VLAN 100 added:
Name: VLAN0100
Router1(vlan)#vlan 200
VLAN 200 added:
Name: VLAN0200
Router1(vlan)#exit
APPLY completed.
Exiting....
Router1#
Configure VLANs
Router1(config)#interface vlan 10
Router1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#interface vlan 50
Router1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.50.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#ip helper-address 172.16.10.20
Router1(config-if)#interface vlan 51
Router1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.51.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#ip helper-address 172.16.10.20
Router1(config-if)#interface vlan 100
Router1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.100.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#ip helper-address 172.16.10.20
Router1(config-if)#interface vlan 200
Router1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.200.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#ip helper-address 172.16.10.20
|
Router1#show vlan-switch
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa1/0, Fa1/2, Fa1/3, Fa1/4,
Fa1/5, Fa1/6, Fa1/7, Fa1/8,
Fa1/9, Fa1/10, Fa1/11, Fa1/12
Fa1/13, Fa1/14, Fa1/15
10 VLAN0010 active
50 VLAN0050 active
51 VLAN0051 active
100 VLAN0100 active
200 VLAN0200 active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 1002 1003
10 enet 100010 1500 - - - - - 0 0
50 enet 100050 1500 - - - - - 0 0
51 enet 100051 1500 - - - - - 0 0
100 enet 100100 1500 - - - - - 0 0
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
200 enet 100200 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 1 1003
1003 tr 101003 1500 1005 0 - - srb 1 1002
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 1 ibm - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - 1 ibm - 0 0
Configure VTP, Trunk, Port Channel, and Spanning Tree
By default, VTP mode is the server and the domain name is blank. VTP can be configured only from VLAN database mode. The only spanning tree mode supported is PVST+. Default trunk encapsulation is dot1q. When you configure the trunk port to allow only specified VLANs, you might get an error message that says Bad VLAN allowed list. In this case, you might need to allow the default VLANs 1-2, 1002-1005 along with your custom VLAN list. Because of this, you also need to allow the default VLANs and your custom VLANs on the neighbor switch connected to this trunk port to avoid trunk inconsistencies.
| Router1 |
|---|
VTP Configuration Router1#vlan database Router1(vlan)#vtp transparent Setting device to VTP TRANSPARENT mode. Router1(vlan)#vtp domain LAB Changing VTP domain name from NULL to LAB Router1(vlan)#exit APPLY completed. Exiting.... Spanning-Tree Configuration Router1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary Router1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10 root primary Router1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 50 root primary Router1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 51 root primary Router1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 100 root primary Router1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 200 root primary Trunk and Port Channel Configuration Router1(config)#interface port-channel 1 Router1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk !--- dot1q is the default encapsulation. Router1(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 100,200 Command rejected: Bad VLAN allowed list. You have to include all default vlans, e.g. 1-2,1002-1005. Command rejected: Bad VLAN allowed list. You have to include all default vlans, e.g. 1-2,1002-1005. Router1(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1002-1005,100,200 Router1(config-if)#exit Router1(config)#interface range fastEthernet 1/0 - 1 Router1(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk !--- dot1q is the default encapsulation. Router1(config-if-range)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1002-1005,100,200 Router1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on Router1(config-if-range)#exit |
| Access1 |
|---|
Access1 Switch Configuration Access1(config)#vlan 100,200 Access1(config-vlan)#exit Access1(config)#vtp mode transparent Setting device to VTP TRANSPARENT mode. Access1(config)#vtp domain LAB Changing VTP domain name from NULL to LAB Access1(config)#interface port-channel 1 Access1(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q Access1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk Access1(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1002-1005,100,200 Access1(config-if)#exit Access1(config)#interface range FastEthernet 0/1 - 2 Access1(config-if-range)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q Access1(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk Access1(config-if-range)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,1002-1005,100,200 Access1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on Access1(config-if-range)#exit |
Router1#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 52 Number of existing VLANs : 10 VTP Operating Mode : Transparent VTP Domain Name : LAB VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x8D 0x71 0x37 0x29 0x6C 0xB0 0xF2 0x0E Configuration last modified by 172.22.1.197 at 2-20-07 22:31:06 Router1#
Router1#show interface fastethernet 1/0 trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Fa1/0 on 802.1q trunk-inbndl 1
(Po1)
Port Vlans allowed on trunk
Fa1/0 1,100,200,1002-1005
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa1/0 1,100,200
Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
Fa1/0 1,100,200
Router1#show spanning-tree summary
Root bridge for: VLAN1, VLAN10, VLAN50, VLAN51, VLAN100, VLAN200.
PortFast BPDU Guard is disabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
-------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
VLAN1 0 0 0 1 1
VLAN10 0 0 0 1 1
VLAN50 0 0 0 1 1
VLAN51 0 0 0 1 1
VLAN100 0 0 0 1 1
VLAN200 0 0 0 1 1
-------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
6 VLANs 0 0 0 6 6
Configure Access Ports
The access port configuration is similar to the standard LAN switch configuration.
| Router1 |
|---|
Port for Server Configuration Router1(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/2 Router1(config-if)#switchport mode access Router1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 Router1(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast Router1(config-if)#speed 100 Router1(config-if)#duplex full Router1(config-if)#exit Port for Printer Configuration Router1(config)#interface fastethernet 1/3 Router1(config-if)#switchport mode access Router1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 51 Router1(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast Router1(config-if)#exit |
Configure the Voice Port
The voice port configuration is similar to the standard LAN switch configuration.
| Router1 |
|---|
Configure the port for Voice Router1(config)#interface fastethernet 1/4 Router1(config-if)#switchport mode access Router1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 51 Router1(config-if)#switchport voice vlan 50 Router1(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast Router1(config-if)#mls qos trust cos |
Configure Quality of Service (QoS)
This is the default QoS configuration on the ESW module:
Router1#show wrr-queue bandwidth
WRR Queue : 1 2 3 4
Bandwidth : 1 2 4 8
wrr-queue bandwidth is disabled
Router1#show wrr-queue cos-map
CoS Value : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Priority Queue : 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
wrr-queue cos map is disabled
Router1#show mls qos maps cos-dscp
Cos-dscp map:
cos: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
--------------------------------
dscp: 0 8 16 26 32 46 48 56
Router1#show mls qos maps dscp-cos
Dscp-cos map:
dscp: 0 8 10 16 18 24 26 32 34 40 46 48 56
-----------------------------------------------
cos: 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 7
These sections explain these configurations:
Configure wrr Queues
You cannot configure port-based QoS on the Layer 2 switch ports. Queues can be configured only from a global configuration. The configuration example maps the CoS values to the four different queues. When a packet enters the Layer 2 engine directly from a switch port, it is placed into one of four queues in the dynamic, 32 MB shared memory buffer. Any voice bearer packets that come in from the Cisco IP phones on the voice VLAN are automatically placed in the highest priority (Queue 4) based on the 802.1p value (CoS 5) generated by the IP phone. The queues are then serviced on a weighted round robin (WRR) basis. The control traffic, which uses a CoS or Type of Service (ToS) of 3, is placed in Queue 3.
| Router1 |
|---|
Router1(config)#wrr-queue cos-map 1 0 1 Router1(config)#wrr-queue cos-map 2 2 Router1(config)#wrr-queue cos-map 3 3 4 Router1(config)#wrr-queue cos-map 4 5 6 7 !--- wrr-queue cos-map <queue-number> <cos values separated by space> Router(config)#wrr-queue bandwidth 1 16 64 255 !--- wrr-queue bandwidth <Weight of Queue1> <Weight of Queue2> !--- <Weight of Queue3> <Weight of Queue4> |
Verify the Queue parameters:
Router1#show wrr-queue bandwidth WRR Queue : 1 2 3 4 Bandwidth : 1 2 4 8 !--- Default values WRR Queue : 1 2 3 4 Bandwidth : 1 16 64 255 !--- Configured values Router1#show wrr-queue cos-map CoS Value : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Priority Queue : 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 !--- Default values CoS Value : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Priority Queue : 1 1 2 3 3 4 4 4 !--- Configured values
This table shows the queue number, CoS value and the weight of each queue after the configuration.
| Queue Number | CoS Value | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 16 |
| 3 | 3 4 | 64 |
| 4 | 5 6 7 | 255 |
Configure the Port to Trust CoS
| Router1 |
|---|
Router1(config)#interface fastethernet1/4 Router1(config-if)#mls qos trust cos !--- Trust the CoS value of the frames from the IP phone. Router1(config-if)#mls qos cos override !--- Reset the CoS value of the frames from PC to 0. Router1(config-if)#exit Router1(config)#interface range fastEthernet 1/0 - 1 Router1(config-if-range)#mls qos trust cos !--- Trust the CoS value of the frames from this trunk link. Router1(config-if-range)#exit |
Configure Policer
This sections shows the policer configuration on the interface fa1/2 to limit the FTP traffic to 5 Mbps.
| Router1 |
|---|
Router1(config)#ip access-list extended ACTIVE-FTP Router1(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp any any eq ftp Router1(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp any any eq ftp-data Router1(config-ext-nacl)#exit Router1(config)#class-map ACTIVE-FTP-CLASS Router1(config-cmap)#match class ACTIVE-FTP Router1(config-cmap)#exit Router1(config)#policy-map ACTIVE-FTP-POLICY Router1(config-pmap)#class ACTIVE-FTP-CLASS Router1(config-pmap-c)#police 5000000 conform-action transmit exceed-action drop Router1(config-pmap-c)#exit Router1(config-pmap)#exit Router1(config)#interface fastethernet1/2 Router1(config-if)#service-policy input ACTIVE-FTP-POLICY Router1(config-if)#exit |
There are few restrictions in the policer configuration in the ESW modules. They are listed here:
-
Policy maps with ACL classification in the egress direction are not supported and cannot be attached to an interface by using the service-policy input policy-map-name interface configuration command.
-
In a policy map, the class named class-default is not supported. The switch does not filter traffic based on the policy map defined by the class class-default policy-map configuration command.
-
You can create policy-map and apply only to ingress of the ESW interfaces. And in the policy-map, only the policer is supported.
Router1#show policy-map Policy Map FINANCE-POLICY Class FINANCE-CLASS set cos 4 Router1(config)#interface fastethernet1/4 Router1(config-if)#service-policy input FINANCE-POLICY %Error: FastEthernet1/4 Service Policy Configuration Failed.Only Police Action S upported -
There is no support for policing at a VLAN or switched virtual interface (SVI) level.
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
19-Mar-2007 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback