Configuring a Management IP Address on Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, 6500/6000, and Catalyst Fixed Configuration Switches
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure a management IP address on Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, and 6500/6000 series switches that run Catalyst OS (CatOS) and Cisco IOS® Software. This document also includes Catalyst fixed configuration switches, which run Cisco IOS Software only and include the 2900/3500XL, 2940, 2950, 2955, 2970, 3550, and 3750 series switches. An IP address is necessary if you want to manage the switch from a remote TCP/IP capable management station. A switch that is to be managed by a VT100 terminal on its console port does not require an IP address.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of the information in this section.
Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, 6500/6000 switches that run only CatOS are Layer 2 (L2) switches. The Catalyst fixed configuration switches 2900/3500XLs, 2940, 2950, 2955, and 2970 are also L2 switches. The TCP/IP protocol on an L2 switch is for management purposes only. Data that flows through the switch can have Layer 3 (L3) addresses, such as IP, Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX), AppleTalk, and so on. However, the switch uses only the data MAC address in order to determine from where traffic has come and which ports should receive the data. L2 switches ignore L3 addresses when the switches forward data.
The Catalyst 6500/6000, 4500/4000, and 3550/3750 series switches that run Cisco IOS Software are switch routers or L3 switches, and can use any interface for management. You can configure the management interface in any of these ways:
-
As a logical interface, like a loopback interface
-
As an L2 access port in a management VLAN
-
As an L3 interface with an IP address
Note: This is the same way in which you configure the interface on any Cisco router.
The Catalyst switches that this document discusses have these management interfaces:
-
Catalyst 5500/5000 and 6500/6000 series switches with Supervisor Engines that run CatOS have two configurable IP management interfaces:
-
The in-band (sc0) interface
-
The Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) (sl0) interface
-
-
Catalyst 4500/4000 switches with Supervisor Engines that run CatOS have three configurable IP management interfaces. The additional interface is called the management Ethernet (me1) interface.
-
Catalyst L2 fixed configuration switches that run Cisco IOS Software have only one configurable IP management interface, which by default is interface VLAN 1.
-
Pure layer 2 switches can have only one interface VLAN up at the time. This is called the management VLAN (in IOS) or the sc0 interface (in CatOS). The main purpose of this interface is management (telnet, SNMP, etc). If the switch is a Layer 3 switch, you can configure multiple VLANs and route between them. An L3 switch can handle multiple IPs, so there is no specific management VLAN on the switch.
-
Catalyst 3550/3750 series switches that run Cisco IOS Software can use any interface for management.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, and 6500/6000 Management Interfaces
The sc0 interface is an internal management interface connected to the switching fabric. The sc0 interface participates in all the functions of a normal switch port, which include:
-
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
-
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
-
Virtual LAN (VLAN) membership
The me1 and sl0 interfaces are out-of-band management interfaces that are not connected to the switching fabric and do not participate in any of these functions.
When you configure the IP address, subnet mask, and broadcast address (and, on the sc0 interface, VLAN membership) of the sc0 or me1 interface, you can access the switch through Telnet or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). When you configure the SLIP (sl0) interface, you can open a point-to-point connection to the switch through the console port from a workstation.
If you have the output of a show interface command from your Cisco device, you can use the Output Interpreter ![]() (registered customers only) tool to display potential issues and fixes.
(registered customers only) tool to display potential issues and fixes.
The sc0 does not have an external port for direct connection. This interface exists as a logical interface inside the switch and is accessible through any of the physical ports on the switch. This figure provides an illustration:
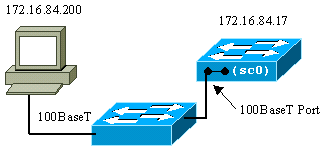
The me1 is actually a physical Ethernet port on the Supervisor Engine module on the Catalyst 4500/4000 series switches. This interface is used for network management only and does not support network switching.
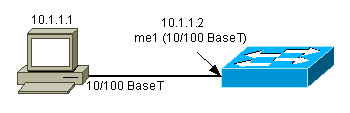
The sl0 uses the RS232 console port as its physical interface. The sl0 cannot be used as a VT100 console when it is in SLIP mode. This figure illustrates a SLIP connection to sl0:
Configure the sc0 Interface on Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, and 6500/6000 Switches That Run CatOS
This section describes how to configure an IP address on the in-band sc0 interface.
-
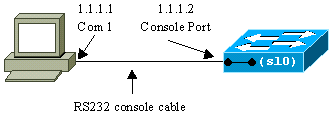
Connect a terminal to the console ports of the switches.
For details on how to connect to the console ports of the Catalyst switches, refer to Connecting a Terminal to the Console Port on Catalyst Switches.
-
Issue the show interface command at the switch prompt in order to view the default status of the management interfaces.
Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=51<DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=63<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 1 inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 me1: flags=62<DOWN,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 !--- Catalyst 5500/5000 and 6500/6000 series switches !--- do not display the me1 interface in the output. Switch-A> (enable) -
Issue the set interface sc0 172.16.84.17 255.255.255.0 172.16.84.255 command in order to configure an IP address for sc0.
The message that the switch returns tells you which parameters have been changed.
Note: When you issue the set interface sc0 command, you cannot enter the broadcast address without the subnet mask of the IP address.
Switch-A> (enable) set interface sc0 172.16.84.17 255.255.255.0 172.16.84.255 Interface sc0 IP address, netmask, and broadcast set. Switch-A> (enable)
Issue the show interface command in order to view the changes.
Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=51<DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=63<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 1 inet 172.16.84.17 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.84.255 me1: flags=62<DOWN,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 Switch-A> (enable)If you enter only an IP address after the set interface sc0 172.16.84.17 command, the default mask and the default broadcast address for the address class are automatically configured. Here is an example:
Switch-A> (enable) set interface sc0 172.16.84.17 !--- Notice that neither the mask nor the broadcast address is specified. Interface sc0 IP address and netmask set. Switch-A> (enable) Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=51<DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=63<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 1 inet 172.16.84.17 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.16.255.255 !--- Notice that the switch took the default mask !--- and the broadcast address of class B. me1: flags=62<DOWN,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 Switch-A> (enable)If you enter the IP address and subnet mask after the set interface sc0 command, the broadcast address for the specific subnet is automatically configured.
-
In order to change the VLAN on the sc0 interface, issue the set interface sc0 vlan# command, which specifies the VLAN number.
Note: By default, the sc0 interface belongs to VLAN 1.
If you want to change the membership of sc0 to VLAN 2, issue this command:
Switch-A> (enable) set interface sc0 2 Interface sc0 vlan set. Switch-A> (enable)
Note: Be sure that you have configured VLAN 2 on the switch before you issue this command. The configuration of VLANs on Catalyst switches is beyond the scope of this document. For more information, refer to Creating Ethernet VLANs on Catalyst Switches.
Issue the show interface command in order to view the changes.
Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=51<DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=63<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 2 inet 172.16.84.17 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.84.255 me1: flags=62<DOWN,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 Switch-A> (enable) -
Issue the show ip route command.
Note: If you want to be able to manage the switch through a router, you must configure a default gateway. The switch does not participate in IP routing. Therefore, the switch has no knowledge of the L3 topology of the network.
When you issue the show ip route command, notice that the gateway for the subnet sc0 is assigned to its own address.
Switch-A> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- enabled enabled enabled Destination Gateway RouteMask Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ---------- ----- -------- --------- 172.16.84.0 172.16.84.17 0xffffff00 U 395 sc0 default default 0xff000000 UH 0 sl0 Switch-A> (enable)
-
Issue the set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.84.1 command or the set ip route default 172.16.84.1 command in order to establish the default route.
The second IP address is the directly connected router that will be your path through the rest of the network. This IP address must be part of the same IP subnet as the switch. You can define up to three default IP gateways. Use the primary keyword with the set ip route command in order to make a gateway the primary gateway. If you do not specify a primary default gateway, the first gateway that is configured is the primary gateway. If more than one gateway is designated as primary, the last primary gateway that is configured is the primary default gateway.
-
Switch-A> (enable) set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.84.1 Route added. Switch-A> (enable)
or
-
Switch-A> (enable) set ip route default 172.16.84.1 Route added. Switch-A> (enable)
Issue the show ip route command in order to view the changes.
Switch-A> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- enabled enabled enabled The primary gateway: 172.16.84.1 Destination Gateway RouteMask Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ---------- ----- -------- --------- default 172.16.84.1 0x0 UG 0 sc0 172.16.84.0 172.16.84.17 0xffffff00 U 525 sc0 default default 0xff000000 UH 0 sl0 Switch-A> (enable)
-
-
If you need to clear the routes from the routing table, issue the clear ip route all command.
Note: If you are connected to the switch through Telnet from a different subnet, you lose connection when you clear the routes. You cannot reach the switch again until someone reenters the gateway address through an attached console or a PC/terminal that is on the same subnet as the switch.
Switch-A> (enable) clear ip route all All routes deleted. Switch-A> (enable)
You can clear a single route if you specify only that route. Issue the clear ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.84.1 command.
Configure the SLIP (sl0) Interface on Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, and 6500/6000 Switches That Run CatOS
You can use a SLIP connection over sl0 in order to monitor or manage the switch remotely with a TCP/IP-capable device where there is no other path to the switch except through the console port.
A network manager can use a remote PC to dial up switches anywhere in the world and manage the switches with the use of SNMP or Telnet over SLIP. You can also upload system software over the sl0 interface with the use of TFTP. Without SLIP, the console port can only be used for VT100 access (tty) or Kermit file transfers. Refer to Connecting a Modem to the Console Port on Catalyst Switches for more information on how to enable dialup connectivity to a Catalyst switch.
This figure shows an example of the management of a switch by a remote terminal with the use of sl0. This type of management is sometimes referred to as out-of-band management. Out-of-band means that a management terminal accesses the device through a path that does not include the network to which the switch is connected.
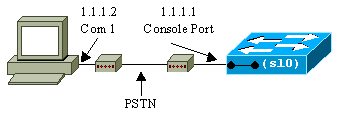
If you set up and activate the sl0 interface from a directly attached console terminal, you lose your console connection. If the terminal that you use supports SLIP, establish a SLIP session with the switch. Deactivate the SLIP connection when you finish in order to allow direct console connectivity. If you activate SLIP and your terminal does not support SLIP, you must establish a Telnet connection to the switch and deactivate sl0 or power cycle the switch in order to regain access to the console port.
Note: Unless you have a terminal that can run SLIP and you know how to use it, only perform these steps from a Telnet connection to the switch.
-
Establish a Telnet session to the switch.
-
Issue the set interface sl0 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.2 command at the command prompt in order to set the SLIP address of the switch and the destination IP address.
Here is an example:
Switch-A> (enable) set interface sl0 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.2 Interface sl0 slip and destination address set. Switch-A> (enable)
-
Issue the slip attach command at the command prompt in order to activate SLIP mode.
Here is an example:
Switch-A> (enable) slip attach Console Port now running SLIP. Switch-A> (enable)
-
Issue the slip detach command at the command prompt in order to deactivate SLIP mode.
Here is an example:
Switch-A> (enable) slip detach SLIP detached on Console port. Switch-A> (enable)
Configure the Management Ethernet Interface (me1) on a Catalyst 4500/4000 That Runs CatOS
This section explains how to configure an IP address on the me1 that is present on the Catalyst 4500/4000 series switches. Packets received on the me1 interface never reach the switching fabric, and there is no access to the me1 interface except through the Ethernet port on the Supervisor Engine.
Another characteristic of the me1 interface is that, when the switch is in ROM monitor (ROMmon), interface me1 is the only interface that is active. You can boot from the network through me1 or upgrade the Cisco IOS Software through me1 while in ROMmon. However, you must be directly on the console port. You can use this interface when you recover a Catalyst 4500/4000 series switch from a corrupted or missing software image or from an upgrade failure. For those details, refer to the Recovering the Catalyst 4000, Catalyst 2948G, Catalyst 2980G, and Catalyst 4912G section of Recovering Catalyst Switches Running CatOS from Booting Failures.
You configure the IP address on the me1 interface in a way that is similar to the configuration on the sc0 interface. The only difference is that you cannot attach the me1 interface to any VLAN because this interface does not reach the switching fabric as the sc0 interface does.
Complete these steps in order to configure an IP address on the me1 interface:
-
Connect a terminal to the console port of the switch.
-
Issue the show interface command at the switch prompt in order to view the default status of the me1 interface.
Here is an example:
Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=51<DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=63<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 1 inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 me1: flags=62<DOWN,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 Switch-A> (enable) -
Issue the set interface me1 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.255 command in order to configure an IP address for me1.
The message that the switch returns tells you which parameters have been changed.
Note: You must enter a netmask in order to configure a broadcast address.
Switch-A> (enable) set interface me1 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.255 Interface me1 IP address, netmask, and broadcast set. Switch-A> (enable)
Issue the show interface command in order to view the changes that you have made.
Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=50 <DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=63 <UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 1 inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 me1: flags=63 <UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 10.1.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.1.1.255 Switch-A> (enable)If you enter only an IP address after the set interface me1 10.1.1.2 command, the default mask and the default broadcast address for the address class that you used are configured. Here is an example:
Switch-A> (enable) set interface me1 10.1.1.2 !--- Notice that neither the mask nor the broadcast address is specified. Interface sc0 IP address and netmask set. Switch-A> (enable) Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=50 <DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=63 <UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 1 inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 me1: flags=63 <UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 10.1.1.2 netmask 255.0.0.0 broadcast 10.255.255.255 !--- Notice that the switch took the !--- default mask and the broadcast address of class A. Switch-A> (enable)Note: Normally, the me1 interface is configured to be in a different subnet than the sc0 interface, which allows both interfaces to remain up. Both interfaces can be configured in the same subnet or with the same IP address, but the sc0 interface is shut down in this case. Interface me1 always takes precedence in this instance. For example, if you have already configured the sc0 interface with an IP address of 172.16.84.17 255.255.255.0, and you try to configure the me1 interface in the same subnet (172.16.84.18 255.255.255.0), you see these messages:
Switch-A> (enable) set interface me1 172.16.84.18 255.255.255.0 172.16.80.255 This command places me1 and sc0 into the same ip subnet. The sc0 interface will be automatically configured down if necessary to resolve the conflict. Do you want to continue (y/n) [n]?y Interface me1 IP address, netmask, and broadcast set. Interface sc0 administratively down due to conflict. Console> (enable) !--- Check the configuration. Switch-A> (enable) show interface sl0: flags=50 <DOWN,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING> slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0 sc0: flags=62 <DOWN,BROADCAST,RUNNING> vlan 1 inet 172.16.84.17 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.84.255 me1: flags=63 <UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING> inet 172.16.84.18 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.84.255 Switch-A> (enable) -
If you noticed in Step 3 that the status of me1 is down instead of up, issue this command in order to bring the interface up manually:
Switch-A> (enable) set interface me1 up Interface me1 administratively up. Switch-A> (enable)
-
Issue the show ip route command.
Note: If you want to be able to manage the switch through a router, you must configure a default gateway because the switch does not participate in IP routing. Therefore, the switch has no knowledge of the L3 topology of the network.
When you issue the show ip route command, notice that the gateway for the subnet me1 is assigned to its own address.
Switch-A> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- enabled enabled enabled Destination Gateway RouteMask Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ---------- ----- -------- --------- 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.2 0xffffff00 U 0 me1 Switch-A> (enable)
-
Issue the set ip route 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.3 command or the set ip route default 10.1.1.3 command in order to establish the default route.
The second IP address is the directly connected router that will be your path through the rest of the network. This IP address must be part of the same IP subnet as the switch.
-
Switch-A> (enable)set ip route 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.3 Route added. Switch-A> (enable)
or
-
Switch-A> (enable) set ip route default 10.1.1.3 Route added. Switch-A> (enable)
Issue the show ip route command in order to view the changes.
Switch-A> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- enabled enabled enabled The primary gateway: 10.1.1.3 Destination Gateway RouteMask Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ---------- ----- -------- --------- default 10.1.1.3 0x0 UG 0 me1 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.2 0xffffff00 U 1 me1 Switch-A> (enable)
Note: If sc0 and me1 are in different subnets, you can configure multiple default gateways. However, the gateway that is defined first becomes the primary gateway. If this is the gateway that you intend, you must use the keyword primary at the end of the command in order to change the primary default gateway. For example, 172.16.84.1 is the primary gateway in a case in which both these item are true:
-
You have sc0 with IP address 172.16.84.17 255.255.255.0 configured first with the default gateway of 172.16.84.1.
-
You configure me1 with an IP address of 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 and with the default gateway of 10.1.1.3.
You can issue these commands in order to change the primary gateway to 10.1.1.3:
Switch-A> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- enabled enabled enabled The primary gateway: 172.16.80.1 Destination Gateway RouteMask Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ---------- ----- -------- --------- default 10.1.1.3 0x0 G 0 me1 default 172.16.84.1 0x0 UG 11 sc0 172.16.80.0 172.16.84.17 0xffffff00 U 38 sc0 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.2 0xffffff00 U 4 me1 !--- Notice that 172.16.84.1 is the primary default gateway. Switch-A> (enable) !--- Change the primary default gateway to 10.1.1.3. Switch-A> (enable) set ip route default 10.1.1.3 primary Primary route changed Switch-A> (enable) !--- This message displays when the primary gateway is changed: %SYS-5-RTE_DEFGATEFROM:Default Gateway switching from 172.16.80.1 %SYS-5-RTE_DEFGATETO:Default Gateway switching to 10.1.1.3 !--- Verify the change. Switch-A> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- enabled enabled enabled The primary gateway: 10.1.1.3 Destination Gateway RouteMask Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ---------- ----- -------- --------- default 10.1.1.3 0x0 UG 0 me1 default 172.16.84.1 0x0 G 11 sc0 172.16.80.0 172.16.84.17 0xffffff00 U 38 sc0 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.2 0xffffff00 U 4 me1 !--- Notice that now the primary default gateway is 10.1.1.3.
-
-
If you need to clear the routes from the routing table, issue the clear ip route all command.
Note: If you are connected to the switch through Telnet from a different subnet, your connection is lost when you clear the routes. You cannot reach the switch again until someone reenters the gateway address via an attached console or a PC/terminal on the same subnet as the switch.
Switch-A> (enable) clear ip route all All routes deleted. Switch-A> (enable)
You can clear a single route if you specify only that route. Issue the clear ip route 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.3 command.
Configure a Management Interface for Catalyst 4500/4000 Series Switches That Run Cisco IOS Software
On a Catalyst 4500/4000 Supervisor Engine III/IV that runs Cisco IOS Software, any routable interface can be used for management. There are three options to configure this interface.
Note: The Ethernet management port (labeled 10/100 MGT) on a Supervisor Engine III (WS-X4014) or Supervisor Engine IV (WS-X4515) is used in ROMmon mode only to recover a switch software image that is missing or corrupted. This port is not active during normal switch operation and cannot be used as a management interface.
Option 1—Configure a loopback interface for switch management. There are a few advantages to a loopback interface. A loopback is a virtual interface that is always up. Packets that are routed to the loopback interface are rerouted back to the L3 switch or router and processed locally. IP packets that are routed out the loopback interface but are not destined to the loopback interface are dropped. This means that the loopback interface serves as the null 0 interface also. The loopback interface serves as the router ID for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and so on. This example uses loopback 0:
Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#interface loopback 0 Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 !--- The loopback interface should have a 32-bit subnet mask, which means that !--- the 10.1.1.1 address is the only destination address in this subnet. Switch(config-if)#end Switch#
You must also configure a routing protocol to distribute the subnet that is assigned to the loopback address or create a static route.
Option 2—Configure the interface as an L3 routed interface with an IP address. All interfaces on a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch that runs Cisco IOS Software are L2 by default. Therefore, you need to make any interface that is connected to the rest of the network an L3 routed interface. Issue the no switchport command, and configure the desired IP address. The example provides an illustration. All interfaces are enabled by default, so you do not need to issue the no shutdown command. This example uses Fast Ethernet 5/30:
Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 5/30 Switch(config-if)#no switchport Switch(config-if)#ip address 11.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
If you issue the show running-config interface fastethernet 5/30 command, this output displays:
Building configuration... Current configuration : 80 bytes ! interface FastEthernet5/30 no switchport ip address 11.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 end
Option 3—Configure an L2 interface as a part of a specific VLAN. Issue the switchport mode access command and the switchport access vlan vlan-id command, and use a corresponding switched virtual interface (SVI) with an IP address.
Note: You must understand the difference between the management VLAN that is used to administer the switch and data VLANs that are used to pass L2 traffic. The management VLAN is an SVI the you create with use of the global interface vlan vlan-id command. Do not confuse this command with the commands that you use to create data VLANs to pass L2 traffic. On Catalyst 6500/6000 series switches that run Cisco IOS Software, you can configure data VLANs from the VLAN database or you can issue the global vlan vlan-id command.
Complete these steps:
-
Issue these commands:
Switch(config)#interface vlan 1 Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shut
Note: This example uses VLAN 1 as the management VLAN. VLAN 1 is in the VLAN database by default.
-
Issue the switchport mode access command under the desired physical interface if you want confirmation that the interface is an access switch port.
By default, all interfaces are L2 interfaces and are access switch ports in VLAN 1. If you plan to use VLAN 1 as the management VLAN, no configuration is necessary under the interface. But if you want confirmation in the configuration that the interface is indeed an access switch port, you need to use the switchport mode access command.
This example uses Fast Ethernet 5/32:
Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 5/32 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access
If you issue the show run interface fastethernet 5/32 command, this output now displays:
Switch#show run interface fastethernet 5/32 Building configuration... Current configuration : 84 bytes ! interface FastEthernet5/32 switchport mode access no snmp trap link-status end
-
If you want to change the management interface from the default VLAN 1 to another VLAN, issue the interface vlan vlan-id command in order to create a new SVI.
You must then issue the switchport access vlan vlan-id command in order to configure an L2 interface to be a part of the new VLAN. This example demonstrates this process:
Switch(config)#interface vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#ip address 20.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shut !--- Configure an interface to access the new management VLAN. Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 5/32 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switch access vlan 2
If you issue the show run interface fastethernet 5/32 command, this output now displays:
Building configuration... Current configuration : 110 bytes ! interface FastEthernet5/32 switchport access vlan 2 switchport mode access end
In order for the switch to access remote networks, you must have either:
-
A default gateway that is set for the next hop router that is directly connected to the switch
-
A dynamic routing protocol configured
If you are not routing IP, issue the ip default-gateway ip-address command in order to configure a gateway router IP address. In order to configure dynamic routing, use the router routing_protocol command. Issue the show ip route command in order to view the status of the routing table.
-
Configure a Management Interface for a Catalyst 6500/6000 Switch That Runs Cisco IOS Software
On a Catalyst 6500/6000 series switch that runs Cisco IOS Software, any routable interface can be used for management. There are three options to configure this interface.
Option 1—Configure a loopback interface for switch management. There are a few advantages to a loopback interface. A loopback is a virtual interface that is always up. Packets that are routed to the loopback interface are rerouted back to the L3 switch or router and processed locally. IP packets that are routed out the loopback interface but are not destined to the loopback interface are dropped. This means that the loopback interface serves as the null 0 interface also. The loopback interface serves as the router ID for OSPF and so on. This example uses loopback 0:
Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#interface loopback 0 Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 !--- The loopback interface should have a 32-bit subnet mask, which means that !--- the 10.1.1.1 address is the only destination address in this subnet. Switch(config-if)#end Switch#
You must also configure a routing protocol to distribute the subnet that is assigned to the loopback address or create a static route.
Option 2—Configure the interface as an L3 routed interface with an IP address. All interfaces on a Catalyst 6500/6000 switch that runs Cisco IOS Software are L3 by default. All interfaces are enabled by default, so you do not need to issue the no shutdown command. This example uses Fast Ethernet 5/30:
Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 5/30 Switch(config-if)#ip address 11.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
If you issue the show running-config interface fastethernet 5/30 command, this output displays:
Building configuration... Current configuration : 80 bytes ! interface FastEthernet5/30 no switchport ip address 11.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 end
Option 3—Configure an L2 interface as a part of a specific VLAN. Issue the switchport mode access command and the switchport access vlan vlan-id command, and use a corresponding SVI with an IP address.
Note: You must understand the difference between the management VLAN that is used to administer the switch and data VLANs that are used to pass L2 traffic. The management VLAN is an SVI that you create with use of the global interface vlan vlan-id command. Do not confuse this command with the commands that you use to create data VLANs to pass L2 traffic. On Catalyst 6500/6000 series switches that run Cisco IOS Software, you can configure data VLANs from the VLAN database or you can issue the global vlan vlan-id command.
Complete these steps:
-
Issue these commands:
Switch(config)#interface vlan 1 !--- Interface VLAN 1 is an SVI. Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shut
Note: This example uses VLAN 1 as the management VLAN. VLAN 1 is in the VLAN database by default.
-
Issue the switchport mode access command under the desired physical interface in order to make the interface an L2 interface in default VLAN 1.
Note: By default, all interfaces are L3 interfaces.
This example uses Fast Ethernet 5/32:
Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 5/32 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access
If you issue the show run interface fastethernet 5/32 command, this output now displays:
Switch#show run interface fastethernet 5/32 Building configuration... Current configuration : 84 bytes ! interface FastEthernet5/32 switchport mode access no snmp trap link-status end
-
If you want to change the management interface from the default VLAN 1 to another VLAN, issue the interface vlan vlan-id command in order to create a new SVI.
You must then issue the switchport access vlan vlan-id command in order to configure an L2 interface to be a part of the new VLAN. This example demonstrates this process:
Switch(config)#interface vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#ip address 20.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shut !--- Configure an interface to access the new management VLAN. Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 5/32 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switch access vlan 2
If you issue the show run interface fastethernet 5/32 command, this output now displays:
Building configuration... Current configuration : 110 bytes ! interface FastEthernet5/32 switchport access vlan 2 switchport mode access end
In order for the switch to access remote networks, you must have either:
-
A default gateway that is set for the next hop router that is directly connected to the switch
-
A dynamic routing protocol configured
If you are not routing IP, issue the ip default-gateway ip-address command in order to configure a gateway router IP address. In order to configure dynamic routing, use the router routing_protocol command. Issue the show ip route command in order to view the status of the routing table.
-
Configure a Management Interface for Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches
The Catalyst L2 fixed configuration switches run Cisco IOS Software, but are L2-capable switches only. These switches can have only one active management interface at a time. The default management interface is VLAN 1. You cannot delete VLAN 1 on these switches. However, you can create another VLAN interface for management, which the examples in this section demonstrate.
Note: You must understand the difference between the management VLAN that is used to administer the switch and VLANs that are used to pass L2 traffic. The management VLAN is an SVI that you create with use of the global interface vlan vlan-id command. Do not confuse this command with the commands that you use to create data VLANs to pass L2 traffic. On XL series switches, you can only create data VLANs with use of the vlan database command. In Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(9)EA1 and later for the 2950 (and in all software versions for the 2940, 2955, and 2970), there is an additional option for the configuration of data VLANs. This additional option is the global vlan vlan-id command.
These examples use Fast Ethernet 0/1 as an access switch port and as a member of the management VLAN. No configuration is necessary in order to make an interface a member of VLAN 1 because all interfaces are access switch ports in VLAN 1 by default.
This is the first example:
Switch(config)#interface vlan 1
Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
Switch(config-if)#end
Switch#
Switch#show run interface vlan 1
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
interface VLAN1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache
end
Switch#show run interface fastethernet 0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
!--- All interfaces are access switch ports in VLAN 1 by default.
end
Switch#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
VLAN1 10.1.1.1 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
Remember that you cannot delete the VLAN 1 management interface. If you want to change the management interface from the default VLAN 1 to another VLAN, issue the interface vlan vlan-id command in order to create a new SVI. You must then issue the switchport access vlan vlan-id command in order to configure an L2 interface to be a part of the new VLAN. This example demonstrates this process:
Note: The management interface can be in the shut down state after a reload if the management interface is not a member of VLAN 1 and if you have configured any of these commands on the switch:
-
ip ftp source-interface vlan vlan-id
-
ip tftp source-interface vlan vlan-id
-
ip telnet source-interface vlan vlan-id
Make the management interface a member of VLAN 1. Alternatively, remove these commands from the configuration or upgrade the switch software to the latest image in order to solve this issue.
Note: On XL series switches, you can use the optional management command under the new SVI in order to automatically shut down VLAN 1 and transfer the IP address to the new VLAN.
Switch(config)#interface vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#ip address 20.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shut !--- Configure an interface to access the new management VLAN. Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#end Switch#
If you issue the show run interface fastethernet 0/1 command, this output now displays:
Switch#show run interface fastethernet 0/1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 85 bytes ! interface FastEthernet 0/1 switchport access vlan 2 switchport mode access end Switch#
In order for the switch to access remote networks, you must have a default gateway that is configured for the next hop router that is directly connected to the switch. Issue the ip default-gateway ip-address command in order to configure a gateway router IP address.
Configure a Management Interface for 3550 and 3750 Series Switches
On Catalyst 3550 and 3750 series switches that run Cisco IOS Software, any routable interface can be used for management. There are three options to configure this interface.
Option 1—Configure a loopback interface for switch management. There are a few advantages to a loopback interface. A loopback is a virtual interface that is always up. Packets that are routed to the loopback interface are rerouted back to the L3 switch or router and processed locally. IP packets that are routed out the loopback interface but are not destined to the loopback interface are dropped. This means that the loopback interface serves as the null 0 interface also. The loopback interface serves as the router ID for OSPF and so on. This example uses loopback 0:
Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#interface loopback 0 Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 !--- The loopback interface should have a 32-bit subnet mask, which means that !--- the 10.1.1.1 address is the only destination address in this subnet. Switch(config-if)#end Switch#
You must also configure a routing protocol to distribute the subnet that is assigned to the loopback address or create a static route.
Option 2—Configure the interface as an L3 routed interface with an IP address. All interfaces on a Catalyst 3550 or 3750 switch that runs Cisco IOS Software are L2 by default. In order to make an L2 interface an L3 interface, issue the no switchport command and then configure an IP address. All interfaces are enabled by default, so you do not need to issue the no shutdown command. This example uses Fast Ethernet 2/0/1 on a Catalyst 3750:
Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 2/0/1 Switch(config-if)#no switchport Switch(config-if)#ip address 11.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#end Switch#
If you issue the show running-config interface fastethernet 2/0/1 command, this output displays:
Switch#show running-config interface fastethernet 2/0/1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 81 bytes ! interface FastEthernet2/0/1 no switchport ip address 11.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 end Switch#
Option 3—Configure an L2 interface as a part of a specific VLAN. Issue the switchport mode access command and the switchport access vlan vlan-id command, and use a corresponding SVI with an IP address.
Complete these steps:
-
Issue these commands:
Switch(config)#interface vlan 1 !--- Interface VLAN 1 is an SVI. Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shut
Note: This example uses VLAN 1 as the management VLAN. VLAN 1 is in the VLAN database by default.
-
Issue the switchport mode access command under the desired physical interface if you want confirmation that the interface is an access switch port.
By default, all interfaces are L2 interfaces and are access switch ports in VLAN 1. If you plan to use VLAN 1 as the management VLAN, no configuration is necessary under the interface. But if you want confirmation in the configuration that the interface is indeed an access switch port, you need to use the switchport mode access command.
This example uses Fast Ethernet 2/0/1:
Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 2/0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#end
If you issue the show run interface fastethernet 2/0/1 command, this output now displays:
Switch#show run interface fastethernet 2/0/1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 59 bytes ! interface FastEthernet2/0/1 switchport mode access end Switch#
-
If you want to change the management interface from the default VLAN 1 to another VLAN, issue the interface vlan vlan-id command in order to create a new SVI.
You must then issue the switchport access vlan vlan-id command in order to configure an L2 interface to be a part of the new VLAN. This example demonstrates this process:
Switch(config)#interface vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#ip address 20.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shut !--- Configure an interface to access the new management VLAN. Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 2/0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2 Switch(config-if)#end Switch#
If you issue the show run interface fastethernet 2/0/1 command, this output now displays:
Switch#show run interface fastethernet 2/0/1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 85 bytes ! interface FastEthernet2/0/1 switchport access vlan 2 switchport mode access end Switch#
In order for the switch to access remote networks, you must have either:
-
A default gateway that is set for the next hop router that is directly connected to the switch
-
A dynamic routing protocol configured
If you are not routing IP, issue the ip default-gateway ip-address command in order to configure a gateway router IP address.
If you plan to configure dynamic routing, keep in mind that IP routing is disabled by default. You must issue the global ip routing command in order to enable IP routing. Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is the only dynamic routing protocol that is supported when you use the Standard Multilayer Software Image (SMI). The Enhanced Multilayer Software Image (EMI) is required for Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP), Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP), OSPF, and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) support. In order to configure dynamic routing, use the router routing_protocol command. Issue the show ip route command in order to view the status of the routing table.
-
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
15-Mar-2006 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback