Wireless Location Appliance FAQ
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document discusses some of the most frequently asked questions (FAQs) on the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance (WLA).
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Q. Why have a Wireless Location Appliance in a Cisco WLAN infrastructure?
A. The Cisco 2700 series Location Appliance is a device that operates within the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Solution infrastructure. The Cisco Wireless Location Appliance is the industry’s first location solution that simultaneously tracks thousands of devices. Location appliances compute, collect, and store historical location to track the physical location of up to 2500 wireless devices. This includes laptop clients, palmtop clients, VoIP telephone clients, active Radio Frequency Identifier (RFID) asset tags, and rogue access points and clients.
The collected location data can be viewed in GUI format in the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), the centralized WLAN management platform.
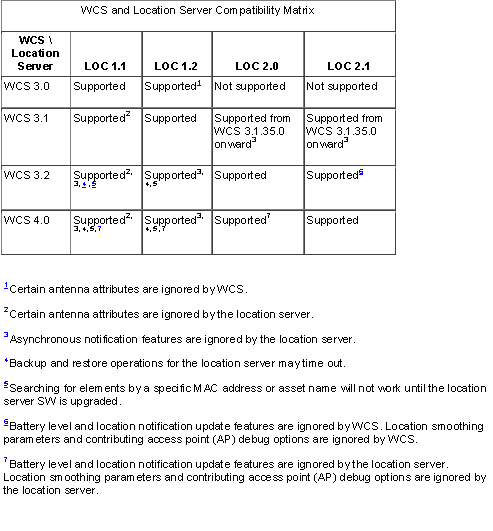
Q. Which version of the WCS is compatible with the location servers? Is there a compatibility matrix between the location servers and the WCS?
A. This table describes the compatibility between WCS and location server versions.
Q. What are the default username and password on the Cisco Location Appliance? What is the default port number used by the Location Appliance to communicate with the Cisco WCS?
A. The default username and password are both admin. The default port used by the location server is 8001.
Q. How does the Cisco Location Appliance calculate location information?
A. The Cisco Wireless Location Appliance uses the same Cisco lightweight access points that deliver traffic as location "readers" for 802.11 wireless clients and Wi-Fi tags. These access points collect received-signal-strength-indication (RSSI) information from all Wi-Fi devices, which include Wi-Fi enabled laptops, voice handsets, Wi-Fi tags, rogue (unauthorized) devices, and rogue access points. The collected RSSI information is then sent through the Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) to the Cisco Wireless LAN controllers or certain wireless integrated switches or routers. The Cisco Wireless LAN controllers then aggregate the RSSI information and send it to the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance through Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
The Cisco Wireless Location Appliance performs location computations based on the RSSI information received from the Cisco wireless LAN controllers. The Cisco wireless LAN controllers that gather the RSSI information must be associated with the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance.
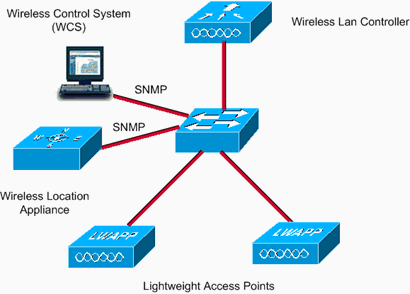
Once network maps and access points are added to the appliance, RF predictions and heatmaps can be generated to graphically display the location of thousands of devices on the site's floor plans. Cisco WCS Location displays its location information visually, which provides an immediate location application for customers who want to enhance their RF capacity management, utilize location based security, and have asset visibility for WLAN devices. This location information is also available to third-party applications through a Simple Object Access Protocol/Extensible Markup Language (SOAP/XML) API on the appliance, which creates an extensible foundation for a host of rich location based applications. The Location Appliance communicates with the WCS with help from the SNMP protocol. This diagram shows where the Location Appliance fits into the network:
Q. What is the location accuracy of the Wireless Location Appliance?
A. The Location Appliance uses patent pending RF Fingerprinting technology for increased location accuracy. 90% of the time, the device is within 10 meters. 50% of the time, the device is within 5 meters of the location displayed by the Location Appliance. In order to achieve this desired result, refer to the Access Point Placement guide. Accuracy varies depending on the placement of the access point.
Q. What are the tools that are available to deploy and manage the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance?
A. The Cisco Wireless Location Appliance includes a variety of pre- and post-deployment tools that simplify the deployment and management of location services.
Pre-Deployment Tools
Planning Mode Tool—This tool provides recommendations for access point placement and density to create a WLAN deployment that supports location accuracy within the specifications of the Location Appliance.
Location Readiness Assessment Tool—This tool helps customers determine if their current WLAN deployment is sufficient to support location accuracy within the specifications of the Location Appliance.
Post-Deployment Tools
Calibration Tool—Customers can choose to perform a post-deployment calibration of their network if the location of the network accuracy becomes out of specification. Within this calibration, an 802.11 wireless client device is used to take RSSI measurements in the environment. The measured RSSI is then used by the location appliance to fine tune the location accuracy of the location device. Improvements in location accuracy can be visualized with the Location Inspector Tool.
Location Inspector Tool—This tool is used post-deployment to determine the location accuracy throughout the WLAN. It provides a visual representation of the quality of location accuracy. It can also be used to tune future performance of the network.
Location Troubleshooting—When location accuracy does not conform to specifications, the location debug feature can be enabled on the WCS. This feature displays the access points that contributed to the location calculations, the signal strength of these devices, and a time stamp of when the signal strength measurement was last received. Screen shots of this display can be sent to the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) to help troubleshoot the location services.
Q. What are the basic parameters that need to be configured on the Wireless Location Appliance (WLA) before it can be configured and managed by the WCS?
A. For information on the basic configuration that needs to be done on the Cisco WLA, refer to Configuring the Location Appliance.
Q. I am not able to add the location server to my Cisco WCS. What can be the issue?
A. If you are not able to add the location server to the Cisco WCS, check if these parameters are correctly configured:
Check if the IP address of the location server configured is correct.
Use the ping command to check if there is connectivity between the WCS and Location Appliance.
Check if the SNMP parameters that are configured on the Location Appliance match those configured on the Cisco WCS. This is necessary because the WCS uses SNMP to communicate with the location server.
Check that the port number that is configured to communicate with the Location Appliance is correct. The default port number used by the Location Appliance to communicate with the Cisco WCS is 8001. Ensure that this port is not blocked in the pathway.
Check if the WCS and location servers are compatible with each other. The compatibility matrix should help.
Check if the username and password configured on the Location Appliance are correct. It is recommended to use the default username/password when you add the location server to the WCS. Change the password after you add the Location Appliance to the WCS.
Ensure that the time on the WCS and location server are in sync.
Refer to Adding and Deleting Location Servers for more information.
Q. I see a lot of Out-of-Sync alert messages on my WCS. Why does the WCS throw these messages?
A. The Out-of-Sync alarms are of Minor severity (yellow) and are raised in response to these conditions:
The elements have been modified in Cisco WCS. (The auto-sync policy pushes these elements.)
The elements have been modified in location servers. (The auto-sync policy pulls these elements.)
All the elements except controllers exist in the location server, but not in Cisco WCS. (The auto-sync policy pulls these elements.)
Elements have not been assigned to any location server. (The auto-sync policy does not apply.)
The Out-of-Sync alarms are cleared when these occur:
The location server is deleted.
The elements are synchronized manually or automatically.
The user manually clears the alarms. (The alarms can reappear in the future when the scheduled task is next performed.)
Note: When you delete a location server, the Out-of-Sync alarms for that server are also deleted. In addition, if you delete the last available location server, the alarms for "elements not assigned to any location server" can also be deleted.
Note: In order to avoid seeing Out-of-Sync alerts, the WCS and Location Appliance need to be in sync. Perform these steps to enable automatic synchronization:
Choose Administration > Scheduled Tasks.
Click Location Server Synchronization.
Check the Auto-Synchronization check box.
Click Submit.
Q. Is there a password recovery procedure for the Wireless Location Appliance?
A. Refer to Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2700 Series Location Appliance for step-by-step instructions.
Q. What is the procedure to upgrade the software on the location server?
A. Perform these steps in order to download software to a location server:
- Verify that you can ping the location server from the Cisco WCS Server or an external FTP server, whichever you use for the application code download.
- In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
- Click the name of the server to which you want to download the software.
- Click Maintenance (left).
- Click Download Software.
- In order to download software, do one of these:
In order to download software listed in the WCS directory, choose Select from uploaded images to transfer into the Location Server. Then, choose a binary image from the drop-down menu. Cisco WCS downloads the binary images listed in the drop-down menu into the FTP server directory that you have specified within the Cisco WCS installation.
In order to use downloaded software that is available locally or over the network, choose the Browse a new software image to transfer into the Location Server, and click Browse. Locate the file and click Open.
Note: If you upgrade a location server that has been installed with a pre-2.0 Version, you must first download and decompress the file (gzip -d imageFilename) before you install the image. After you decompress the file, run the *.bin installer file that results from this. Enter this command after the file download to make the file executable:
chmod + x. *.binNote: If you have a 2.0 or later Version of the location server image already installed, the software image automatically decompresses within its download from WCS.
- Enter the time in seconds (between 1 and 999) after which software download times out.
- Click Download to send the software to the /opt/locserver/installers directory on the location server. This figure shows the steps needed to upgrade the software on the WCS.
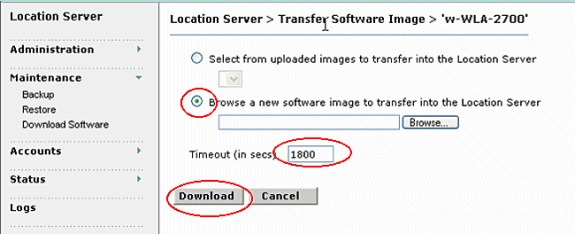
Note: After the image has been transferred to the location server, follow the instructions on the screen. Log on to the command-line interface (CLI) of the location server, stop the server, and run the installer image from the /opt/locserver/installers directory.
Q. Is there a procedure to upgrade the location server from the location server console?
A. Perform these steps in order to upgrade the software through a console session:
- Transfer the new Location Appliance code onto the hard drive of the Location Appliance. The image file is in .gz format, so you can decompress it first and run the .bin installer file that results.
- Log on as root and use the binary setting to send the application code (for example, AIR-LOC2700-L-K9-1-2-17-0.bin; 1-2-17-0 is the release number and changes with each release) from an external FTP server root directory. Your entries should look like this:
#cd /opt/locserver/installers #ftp <FTP Server IP address> Name: <login> !--- The default login name for the FTP server is ftp-user. Password: <password> binary get AIR-LOC2700-L-K9-1-2-17-0.bin <CTRL-Z> #- Verify that the application code (AIR-LOC2700-L-K9-x-x-x-x.bin) is in the Location Appliance /opt/locserver/installers directory.
- Make sure that the AIR-LOC2700-L-K9-x-x-x-x.bin file has execute permissions for the root user. If it does not, enter chmod 755 AIR-LOC2700-L-K9-x-x-x-x.bin.
- Manually stop the old Location Appliance application. In order to do this, log on as root and enter /etc/init.d/locserverd stop.
- Enter /opt/installers/AIR-LOC2700-L-K9-x-x-x-x.bin to install the new Location Appliance application files.
- Issue the /etc/init.d/locserverd start command in order to start the new Location Appliance application.
Note: You can use tail in order to monitor progress of the upgrade.
Note: Only uninstall the Location Appliance if the system instructs you to do so. The removal of the application files unnecessarily erases your historical data. See How do I uninstall a software image from the Cisco Wireless Location Server? to learn how to uninstall the Location Appliance software from the server.
Q. How do I uninstall a software image from the Cisco Wireless Location Server?
A. Complete these steps:
- Log on as a root.
- CD to the uninstall/ directory.
- Enter the ./uninstall command in order to run the uninstall routine.
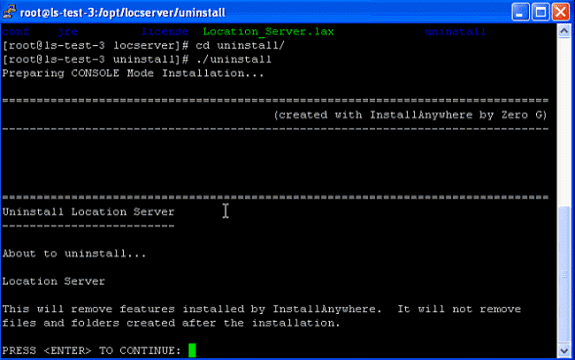
- Accept the prompt to uninstall the old software. The screen shot shows the procedure of these steps.
InstallAnywhere uninstalls the old software. This screen shot shows the prompt upon completion of uninstall.
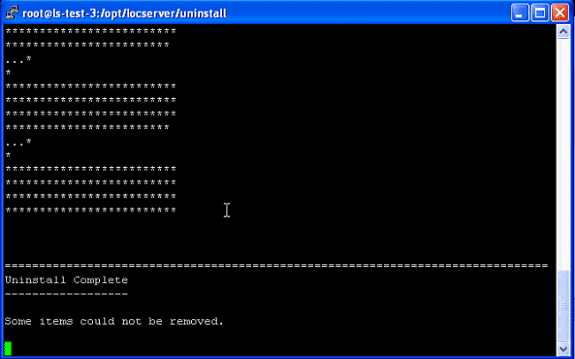
Q. How can I stop the Location Appliance?
A. The Location Appliance software automatically runs after the initial configuration and each reboot. In order to manually stop the software, enter /etc/init.d/locserverd stop in the Location Appliance CLI interface. This screen shot shows the messages from the server after it stops the Location Appliance.
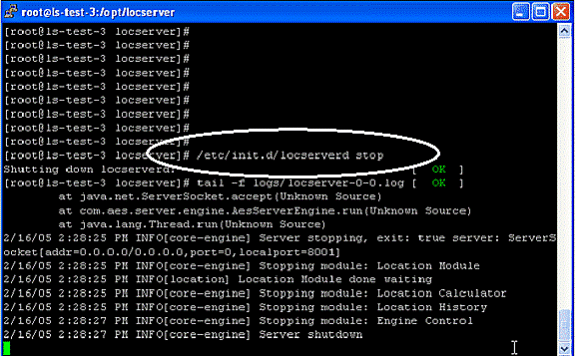
Q. How can I start the Location Appliance?
A. The Location Appliance software automatically runs after the initial configuration and each reboot. In order to manually stop the software, enter /etc/init.d/locserverd start in the Location Appliance CLI interface.
Q. How can I reset the location server to factory defaults with the WCS?
A. In order to clear the location server configuration and restore the factory defaults with Cisco WCS, complete these steps:
- In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
- Click the name of the server that you want to configure.
- Click Administration (left) to display the administrative configuration options.
- Click Advanced Parameters.
- In the Advanced Commands section, click Clear Configuration.
Note: This command also clears the database of the server.
- Click OK in order to clear the location server configurations.
Q. I want to check if my wireless location server works as expected. How do I do that?
A. If you can browse to the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance User interfaces in the Wireless Control System (WCS), there is connectivity.
You can verify the Location Appliance software state at any time from the console. In the Location appliance CLI interface, enter /opt/locserver/bin/getserverinfo. If the Location Appliance is on, the command output looks like this example:
------------- Server Config ------------- Product name: Cisco Wireless Location Appliance Version: 1.1.73.0 Use HTTPS: false Port: 8001 Log Modules: 4036 Log Level: TRACE Days to keep events: 2 Keep absent data in mins: 1440 Session timeout in mins: 30 DB backup in days: 0 -------------- Server Monitor -------------- Start time: Tue May 03 10:30:45 PDT 2005 Server current time: Wed May 04 12:10:44 PDT 2005 Server timezone: America/Los_Angeles Restarts: 0 Used Memory: 7849768 Allocated Memory: 17477632 Max Memory: 530907136 DB virtual memory: 14501 DB disk memory: 81952768 Active Sessions: 3 --------------- Active Sessions --------------- Session ID: 25994 Session User ID: 1 Session IP Address: 127.0.0.1 Session start time: Wed May 04 12:10:44 PDT 2005 Session last access time: Wed May 04 12:10:44 PDT 2005 Session ID: 5693 Session User ID: 1 Session IP Address: 1.100.52.13 Session start time: Tue May 03 10:31:15 PDT 2005 Session last access time: Wed May 04 12:06:19 PDT 2005 Session ID: 16228 Session User ID: 1 Session IP Address: 1.100.52.11 Session start time: Tue May 03 10:39:22 PDT 2005 Session last access time: Wed May 04 12:09:59 PDT 2005 #If the Location Appliance is not on, the command output looks like this example:
com.aes.common.util.AesException: Failed to connect to server: http://localhost:8001 at com.aes.client.AesClient.connect(AesClient.java:218) at com.aes.location.test.AesAbstractTest.init(AesAbstractTest.java:181) at com.aes.location.test.admin.AesTestGetServerInfo.main(AesTestGetServerInfo.java:75) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Unknown Source) at com.zerog.lax.LAX.launch(DashoA8113) at com.zerog.lax.LAX.main(DashoA8113) #
Q. No Location is shown for clients or Tags. What should I do?
A. Complete this checklist:
Verify that the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance server is operational. You can perform this from the CLI using the /opt/locserver/bin/getserverinfo command. You see a valid response as shown here:
------------- Server Config ------------- Product name: Cisco Wireless Location Appliance Version: 1.1.73.0 Use HTTPS: false Port: 8001 Log Modules: 4036 Log Level: TRACE Days to keep events: 2 Keep absent data in mins: 1440 Session timeout in mins: 30 DB backup in days: 0 -------------- Server Monitor -------------- Start time: Tue May 03 10:30:45 PDT 2005 Server current time: Wed May 04 12:10:44 PDT 2005 Server timezone: America/Los_Angeles Restarts: 0 Used Memory: 7849768 Allocated Memory: 17477632 Max Memory: 530907136 DB virtual memory: 14501 DB disk memory: 81952768 Active Sessions: 3 --------------- Active Sessions --------------- Session ID: 25994 Session User ID: 1 Session IP Address: 127.0.0.1 Session start time: Wed May 04 12:10:44 PDT 2005 Session last access time: Wed May 04 12:10:44 PDT 2005 Session ID: 5693 Session User ID: 1 Session IP Address: 1.100.52.13 Session start time: Tue May 03 10:31:15 PDT 2005 Session last access time: Wed May 04 12:06:19 PDT 2005 Session ID: 16228 Session User ID: 1 Session IP Address: 1.100.52.11 Session start time: Tue May 03 10:39:22 PDT 2005 Session last access time: Wed May 04 12:09:59 PDT 2005 #Make sure the controller and WCS are reachable using the ping command.
Verify that the SNMP parameters are between the Location Appliance and the controller, and between the Location Appliance and WCS. On the controller, the IP address of both the location server and the WCS must be permitted in WLC Management > SNMP > Communities to be allowed to poll. If any SNMP changes are made in the WLC, a reboot is required.
Verify that the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance polls for Tags and clients. You can see this under the WCS GUI. Go to Location > Location Servers, click on your server, Polling Parameters.
Verify that the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) sees Tags and clients. By default, the WLCs do not have Tag tracking enabled. If you see clients but not Tags, you can verify this if you SSH into the controller and, from the CLI, issue the show rfid config command.
Enable Tag tracking, if necessary, with the config rfid status enable command. Do not forget to click save config.
Verify that you have added the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance into the WCS. In order to perform this, go under Locate > Add Server. The default username and password are both admin.
Verify that you have synchronized the WCS and the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance for both the network designs (maps) and the controllers. This is done through the WCS. Go to Location and choose Synchronize Servers.
Q. Location for Tags are not current. What should I do?
A. Perform these steps:
- Ensure that the location server is synchronized with the WCS and the controller. In order to enable synchronization on the Location Appliance, refer to Keeping Location Servers Synchronized.
- You should have quicker updates from the controller to ensure that the location of devices are most recent. You can do this by reducing the Location Server's polling parameters.
- In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
- Click the name of the server you want to configure.
- Click Administration (left side) to display the administrative configuration options.
- Click Polling Parameters.
- Configure these parameters in the Polling Parameters page:
Parameter Description Retry Count Enter the number of times to retry a polling cycle. Default value is 3. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. Client Stations Check the Enable check box to enable client station polling and enter the polling interval in seconds. Default value is 300. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. Rogues Check the Enable check box to enable rogue access point polling and enter the polling interval in seconds. Default value is 600. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. Asset Tags Check the Enable check box to enable asset tag polling and enter the polling interval in seconds. Default value is 600. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. Note: If you reduce the Polling Parameters too much, this will affect the wireless throughput because the controller's resources are utilized for updating the Location Appliance.
- Ensure that the WCS, location server and WLC are synchronized in time. It is suggested to synchronize them with the NTP server.
- On the controller, it is recommended to have the Tag timeout value to be three times the tag beaconing rate. On the WLC CLI, issue the config rfid timeout 30 command.
Q. Does the location server support port redundancy? Can I configure the two Ethernet ports on the location server and achieve port redundancy?
A. No, redundancy capabilities are not supported on the location server. The only advantage of the second Ethernet interface is when there is a plan to have two WCS servers, with one on each network. Otherwise, just configure one interface. The second interface cannot be utilized in the event that the first goes down.
Q. How do I access the logs in the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance?
A. Complete these steps from the WCS GUI:
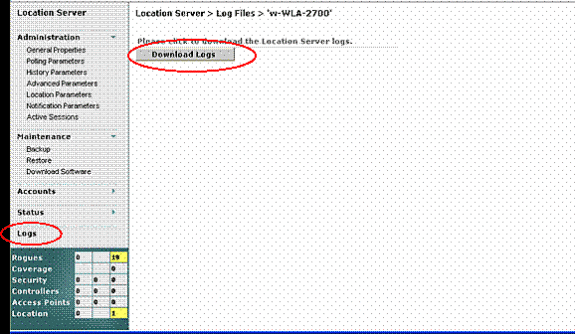
- Go to Location > Location Servers > Logs Location Server > Log Files > ‘w-WLA-2700’.
- Click Download Logs in order to download the location server logs.
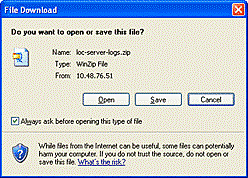
- Click Save in order to save the log files.
Note: For more monitoring options that can be performed on a location server, refer to Monitoring Location Servers.
Q. How do I backup and restore the database in my Cisco Wireless Location Appliance?
A. In WCS GUI, go to Location > Location Servers, click your location appliance, go to Maintenance >Backup, and then go to Maintenance > Restore.
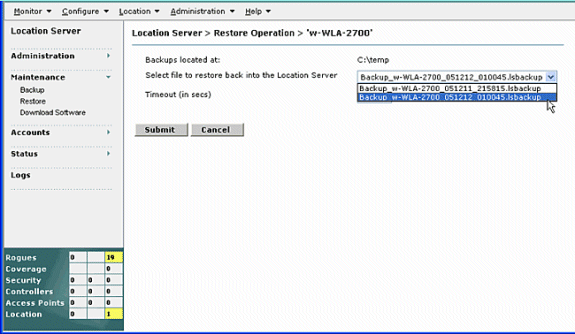
Note: Refer to Performing Maintenance Operations for more options.
Q. I have Version 4 on my WLCs and WCS. I want to upgrade my Location Appliance. When I upgrade, it tells me that the server is still on. “Server is still running, stop the server and try again...” When I attempt to stop the service, it appears that the service is stopped. I try to start the service, but I cannot start the service.
A. In order to work around this problem, some Linux commands at the CLI (telnet/SSH or console) of the Location Appliance can be used. The Linux command ps lists processes that run on the machine. The kill -9 command allows the user to kill off any of those processes by its process ID or PID.
Start with the command ps -ax | grep locserv (without quotation marks) to list all the processes that are on that include locserv in their name. The output of the ps command should show up to three processes that are on. Use the kill -9 <pid> command (again, without quotation marks and substitute the PID from the ps listing for <pid>). After you have killed all the locserv processes, run the ps -ax | grep locserv command again in order to make sure that all are dead. Once they are, you can proceed with the software installation, as documented.
Q. I have recently made some changes to my WLCs and now the Location Appliance is not sending any client data. The logs on the Location Appliance show a lot of THROW errors. I have tried to refresh the configurations from the WLCs in WCS, and synchronize with the location server. However, still no client data is received from the location server.
A. The core problem is not with the Location Appliance, but with the WCS not accurately updating the Location Appliance with the changes that have been made. As a result, the Location Appliance still has the old data about the client. Therefore, the appliance cannot provide the client data.
Cisco bug ID CSCsh40682 ( registered customers only) is related to this issue. The bug is resolved in WCS version 4.2.
Q. Where can I find tips to troubleshoot the Wireless Location Appliance?
A. Tips to troubleshoot the Wireless Location Appliance are available at Troubleshooting Tips Q & A.
More FAQs on Wireless Location Appliance are available in the Frequently Asked Technical Questions section of the document Cisco 2700 Series Wireless Location Appliance Deployment Guide.
Related Information
- Cisco 2700 Series Location Appliance Installation and Configuration Guide
- Cisco Location Appliance Configuration Guide
- Cisco 2700 Series Wireless Location Appliance Deployment Guide
- Troubleshooting Tips Q & A
- Cisco Wireless Control System Configuration Guide, Release 4.0
- Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release 4.0
- Cisco Wireless Location Appliance Data Sheet
- Wireless Product Support
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)









 Feedback
Feedback