Migrate Standalone Catalyst 6500 Switch to Catalyst 6500 VSS
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides information about the procedure for migrating a standalone Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch to a Cisco Catalyst 6500 Virtual Switching System.
Note: This document provides the common steps that are required for the migration. Exact steps are based on the current switch configuration and can vary slightly from the mentioned procedure.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
-
Knowledge of Virtual Switching Systems (VSS) concepts. For more information, refer to Understanding Virtual Switching Systems.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches with Supervisor VS-S720-10G-3C/XL that runs Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.2(33)SXH1 or later.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
The Virtual Switching System (VSS) is a new and innovative feature on Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches that effectively allows clustering of two physical chassis together into a single logical entity. Such a technology allows for new enhancements in all areas of enterprise campus and data center deployment, which includes High Availability, Scalability / Performance, Management and Maintenance.
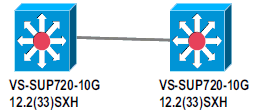
Current implementation of VSS allows you to merge two physical Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches together into a single logically-managed entity. This figure provides a graphical representation of this concept where two 6509 chassis can be managed as a single 18-slot chassis once VSS is enabled:
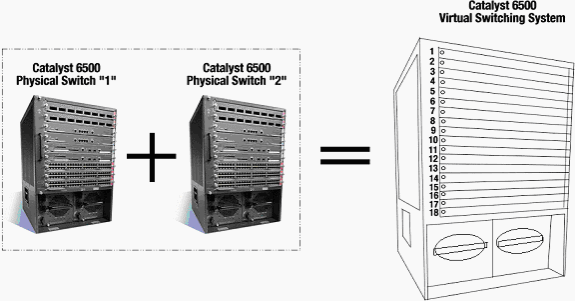
Migration Process
Hardware and Software Support
VSS is a software feature available only with the Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches. In order to enable and configure this feature, this is required:
| Hardware | VS-S720-10G-3C/XL |
| Software | Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(33)SXH1 or later |
| Model Number | Description |
| WS-C6503-E | E-Series 3-slot chassis |
| WS-C6504-E | E-Series 4-slot chassis |
| WS-C6506 | 6-slot chassis |
| WS-C6506-E | E-Series 6-slot chassis |
| WS-C6509 | 9-slot chassis |
| WS-C6509-E | E-Series 9-slot chassis |
| WS-C6509-NEB-A | 9-slot vertical Network Equipment Building Standards (NEBS) chassis |
| WS-C6509-V-E | E-Series 9-slot vertical chassis |
| WS-C6513 | 13-slot chassis |
This table gives a complete list of the chassis supported with the initial release of Cisco Virtual Switching System. For more information, refer to Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Virtual Switching System (VSS) 1440.
Migration Paths
The table lists some of the possible migration paths to the VSS. This list is only suggestive and not comprehensive.
| Initial Setup | Upgrade Required | Final Setup |
|---|---|---|
| Two Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches with WS-SUP720-3B supervisors. |
Hardware Upgrade - Supervisors VS-S720-10G-3C/XL Software Upgrade - Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SXH1 or later | VSS |
| Two Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches with VS-S720-10G-3C/XL supervisors. |
Software Upgrade - Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SXH1 or later | VSS |
Migration Overview
Common Configuration in Standalone Environment
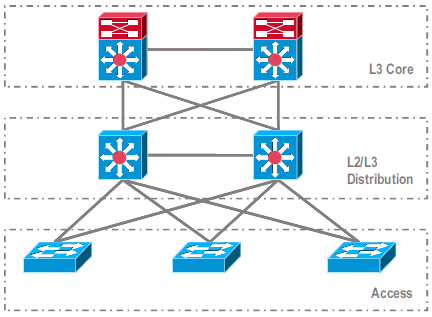
Features or Protocols that run between Layer 3 (L3) Core and L2/L3 Distribution:
-
IP Routing Protocols
-
L3 Port Channels or EqualCost MultiPath feature of IP Routing
Features or Protocols that run between L2/L3 Distribution and Access Layer:
-
Spanning Tree Protocol
-
First Hop Routing Protocols (FHRP)
-
Policies: QoS, ACL
-
L2 Trunks, VLANs, Port Channels
Migration to VSS
This is a multi-step process, and each step is explained in this section.
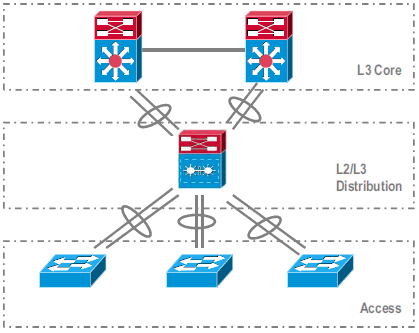
Migration steps between Core and Distribution Layer:
-
Configuring MultiChassis EtherChannel (MEC)
-
Modifying IP Routing configuration and removing commands, which are no more required
Migration steps between Distribution and Access Layer:
-
Configuring MEC
-
Keeping Spanning Tree Protocol enabled
-
Modifying FHRP commands
-
Moving QoS and ACL policies to MEC (if required)
-
Moving L2 Trunks configuration to MEC
Step By Step Migration Process
Complete these steps:
-
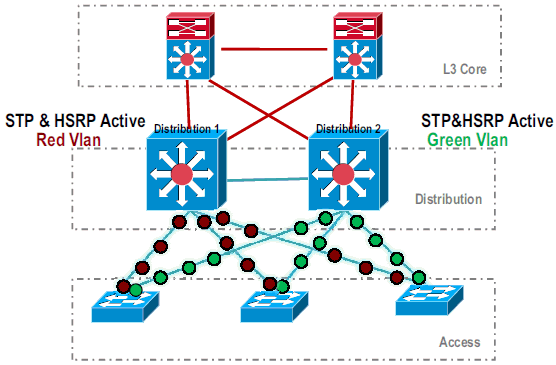
In the initial standalone setup, traffic is commonly load-balanced among Distribution switches using VLAN load sharing and HSRP configuration.
-
Modify the HSRP and STP configuration so that Distribution-1 is active for all flows, and neighboring devices detect this change and send all traffic to Distribution-1.
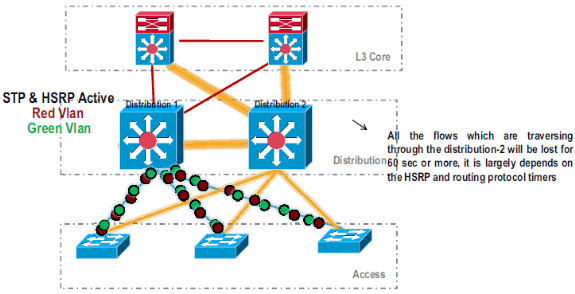
-
Shut down the physical interfaces of Distribution-2, so that it is isolated from the network.
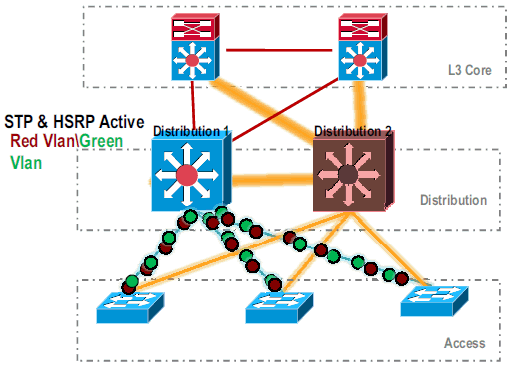
.
Once the Distribution-2 is completely removed from the network, it can be converted to VSS mode without disrupting production traffic.
-
If not previously installed, install the new supervisor (VS-SUP720-10G) and verify the status.
Distribution-2#show module Mod Ports Card Type Model Serial No. --- ----- -------------------------------------- ------------------ ----------- 5 5 Supervisor Engine 720 10GE (Active) VS-S720-10G SAD104707BB 9 48 CEF 720 48 port 10/100/1000mb Ethernet WS-X6748-GE-TX SAL1020NGY3
-
Copy VSS compatible Cisco IOS software to the sup-bootdisk:
Distribution-2#copy ftp: sup-bootdisk: Address or name of remote host []? 172.16.85.150 Source filename []? s72033-ipservices_wan_vz.122-33.SXH1.bin Destination filename [s72033-ipservices_wan_vz.122-33.SXH1.bin]? Accessing ftp://172.16.85.150/s72033-ipservices_wan_vz.122-33.SXH1.bin...
-
Update the bootvar to load Cisco IOS software copied to the sup-bootdisk:
Distribution-2(config)#boot system flash sup-bootdisk:s72033-ipservices_wan_vz.122-33.SXH1.bin -
For the Distribution-2 switch to run in VSS mode, a Virtual Switch Link (VSL) is required. The current Port Channel link between Distribution-1 and Distribution-2 can be utilized to form the VSL.
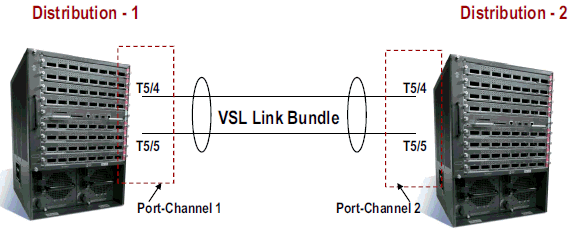
-
Configure the Virtual Switch attributes:
-
Virtual Switch Domain Number (unique within the network)
-
Virtual Switch Number (unique within the domain)
-
Virtual Switch Link (VSL)
Distribution-2(config)#hostname VSS VSS(config)#switch virtual domain 100 VSS(config-vs-domain)#switch 1 !--- After conversion Distribution-2 will be noted !--- as Switch 1 in VSS mode. VSS(config-vs-domain)# exit VSS(config)#interface port-channel 1 VSS(config-if)#switch virtual link 1 VSS(config-if)#interface TenG 5/4 VSS(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode on VSS(config-if)#interface TenG 5/5 VSS(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode on VSS(config-if)# ^Z VSS#
-
-
Convert the Distribution-2 switch to VSS mode.
Note: Issue this command via the switch's console:
VSS#switch convert mode virtual This command will convert all interface names to naming convention "interface-type switch-number/slot/port", save the running config to startup-config and reload the switch. Do you want to proceed? [yes/no]: yes Converting interface names Building configuration... !--- At this point the switch will reboot !--- snippet of the console output System detected Virtual Switch configuration... Interface TenGigabitEthernet 1/5/4 is member of PortChannel 1 Interface TenGigabitEthernet 1/5/5 is member of PortChannel 1 !--- snippet of the console output 00:00:23: %PFREDUN-6-ACTIVE: Initializing as ACTIVE processor for this switch !--- snippet of the console output 00:00:28: %VSL_BRINGUP-6-MODULE_UP: VSL module in slot 5 switch 1 brought up Initializing as Virtual Switch Active
-
Verify the conversion of the Distribution-2 switch to VSS mode.
VSS#show switch virtual role Switch Switch Status Preempt Priority Role Session ID Number Oper(Conf) Oper(Conf) Local Remote ------------------------------------------------------------------- LOCAL 1 UP FALSE(N) 110(110) ACTIVE 0 0 In dual-active recovery mode: NoThe Distribution-2 switch is successfully converted and is operating in VSS mode. Pre-configuration steps can also be performed after converting the Distribution-1 switch. However, pre-configuration helps to reduce the amount of packet loss during migration.
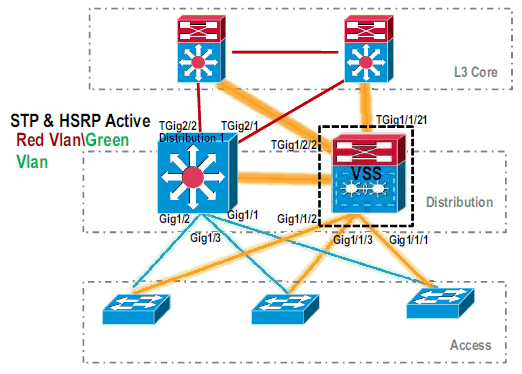
-
Complete these steps to pre-configure VSS Switch 1:
-
Configure MEC using Switch-1's local interfaces. Interfaces of Switch-2 (currently Distribution-1) can be added to MEC after converting it to VSS mode.
-
Configure MEC.
-
Move interface configuration to MEC.
-
Move QoS and ACL policies to MEC.
Configuration Changesinterface TenGigabitEthernet1/2/1 ip address 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20
Configure Neighboring Devices to accommodate Port Channel!--- MEC to Core layer VSS(config)# int ten 1/2/1 VSS(config-if)# no ip address VSS(config-if)# interface po20 VSS(config-if)# ip address 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.0 VSS(config-if)# no shut VSS(config-if)# interface ten1/2/1 VSS(config-if)# channel-group 20 mode desirable !--- MEC to Access layer VSS(config-if)# interface po10 VSS(config-if)# switchport VSS(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q VSS(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 VSS(config-if)# no shut VSS(config-if)# interface gig1/1/2 VSS(config-if)# switchport VSS(config-if)# channel-group 10 mode desirable
Connection between VSS Switch-1 and its neighboring devices are down at this moment. Therefore, a port channel is configured without interfering traffic flow through Distribution-1.
!--- In Core layer devices Core(config)# int gig 1/1 Core(config-if)# no ip address Core(config-if)# int po20 Core(config-if)# ip address 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0 Core(config-if)# no shut Core(config-if)# int gig 1/1 Core(config-if)# channel-group 20 mode desirable
!--- In Access layer devices Access(config)# int po10 Access(config-if)# switchport Access(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q Access(config-if)# switchport trunk Access(config-if)# no shut Access(config-if)# int gig 1/1 Access(config-if)# channel-group 10 mode desirable
-
-
In VSS, both active and standby chassis use active chassis burnt-in MAC address and VLAN IP address. HSRP is no longer required.
-
Move HSRP virtual IP addresses to the VLAN interfaces.
-
Remove HSRP configuration from the VLAN interfaces.
Configuration Changesinterface Vlan10 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 standby 10 ip 10.1.1.1 standby 10 priority 110 ! interface Vlan20 ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 standby 20 ip 20.1.1.1 standby 20 priority 110 !
VSS(config)# interface Vlan10 VSS(config-if)# no standby 10 ip 10.1.1.1 VSS(config-if)# no standby 10 priority 110 VSS(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 VSS(config-if)# interface Vlan20 VSS(config-if)# no standby 20 ip 20.1.1.1 VSS(config-if)# no standby 20 priority 110 VSS(config-if)# ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
Note: End devices would be still pointing their ARP entries to initial HSRP MAC address. Until these entries time out or another ARP is sent to update their cache, there is some connectivity loss.
-
-
Enable the NSF-SSO feature for the IP Routing protocols used. VSS simplifies the routing configuration, so some of the network statements are no longer required. Therefore, they can be removed.
VSS Switch-1
CoreVSS#show running-config | begin ospf router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 !--- rest of output elided !--- Previous L3 interfaces are merged as MEC, hence some routing statements are no longer required. VSS(config)# router ospf 1 VSS(config-router)# nsf VSS(config-router)# no network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Core#show running-config | begin ospf router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 !--- rest of output elided !--- Previous L3 interfaces are merged as MEC, hence some routing statements are no longer required. Core(config)# router ospf 1 Core(config-router)# nsf Core(config-router)# no network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
-
Modify STP configuration so that VSS Switch-1 becomes the root for all VLANs.
-
-
Verify VSS Switch-1 configuration and connectivity.
-
Enable VSS Switch-1 interfaces.
-
Verify L2 connectivity to Access layer devices.
-
Verify L3 connectivity to Core layer devices.
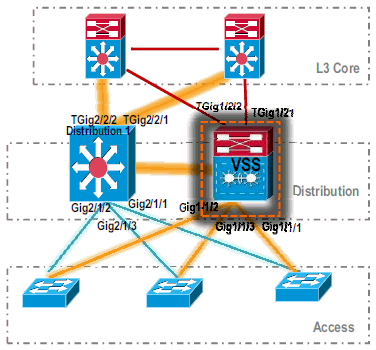
-
-
After VSS Switch-1 connectivity is verified, shut down the interfaces of Distribution-1 to switch the traffic over to VSS.
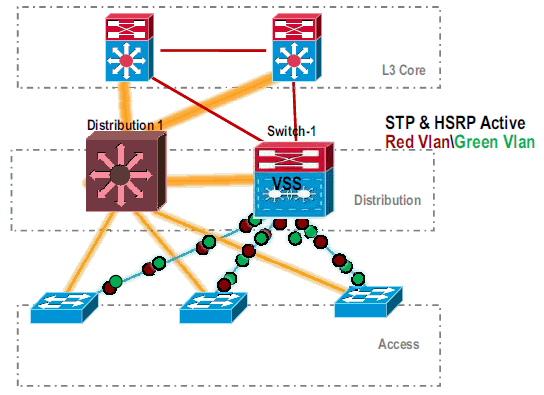
-
Repeat the conversion steps on the Distribution-1 switch to bring that in preferred VSS standby mode.
Distribution-1(config)#hostname VSS VSS(config)#switch virtual domain 100 VSS(config-vs-domain)#switch 2 !--- After conversion Distribution-1 will be noted !--- as Switch 2 in VSS mode. VSS(config-vs-domain)# exit VSS(config)#interface port-channel 2 VSS(config-if)#switch virtual link 2 VSS(config-if)#interface TenG 5/4 VSS(config-if)#channel-group 2 mode on VSS(config-if)#interface TenG 5/5 VSS(config-if)#channel-group 2 mode on VSS(config-if)# ^Z VSS# VSS#switch convert mode virtual This command will convert all interface names to naming convention "interface-type switch-number/slot/port", save the running config to startup-config and reload the switch. Do you want to proceed? [yes/no]: yes Converting interface names Building configuration... !--- At this point the switch will reboot !--- snippet of the console output System detected Virtual Switch configuration... Interface TenGigabitEthernet 2/5/4 is member of PortChannel 2 Interface TenGigabitEthernet 2/5/5 is member of PortChannel 2 !--- snippet of the console output 00:00:23: %PFREDUN-6-ACTIVE: Initializing as ACTIVE processor for this switch !--- snippet of the console output 00:00:28: %VSL_BRINGUP-6-MODULE_UP: VSL module in slot 5 switch 2 brought up Initializing as Virtual Switch Standby
-
After the VSS standby switch boots up, the VSS active configuration is automatically synchronized to VSS standby. On boot up, interfaces of VSS standby (Switch-2) are in shutdown state.
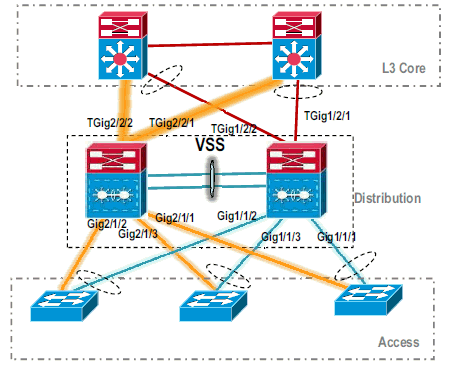
-
Finalize the virtual switch configuration.
Note: This final, critical step is applicable only for a first-time conversion. If the switch has been converted or partially converted already, you cannot use this command. An error message is generated if the switch is converted or partially converted:
11:27:30: %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: channel-misconfig error detected on Po110, putting Gi9/2 in err-disable state
You can issue this command to automatically configure the standby virtual switch configuration on the active virtual switch:
VSS#switch accept mode virtual This command will bring in all VSL configurations from the standby switch and populate it into the running configuration. In addition the startup configurations will be updated with the new merged configurations. Do you want proceed? [yes/no]: yes Merging the standby VSL configuration. . . Building configuration...
Note: Be aware that the switch accept mode virtual command is no longer needed in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2 SXI as the configurations are merged automatically.
-
Add the Switch-2 interfaces to MEC.
- VSS
!--- To Core layer VSS(config)# interface range tengig 1/2/1, tengig2/2/1 VSS(config-if-range)# channel-group 20 mode desirable VSS(config-if-range)# no shut !--- To Access layer VSS(config)# interface range gig 1/1/2, gig 2/1/2 VSS(config-if-range)# switchport VSS(config-if-range)# channel-group 10 mode desirable VSS(config-if-range)# no shut
- VSS Neighbor - Core
Core(config)# interface range gig 1/1, gig 1/2 Core(config-if-range)# channel-group 20 mode desirable Core(config-if-range)# no shut
- VSS Neighbor - Access
Access(config)# interface range gig 1/1, gig 1/2 Access(config-if-range)# channel-group 10 mode desirable Access(config-if-range)# no shut
Migration to VSS is complete. At this point, both switches of VSS are running and traffic is load-balanced on all uplink interfaces.
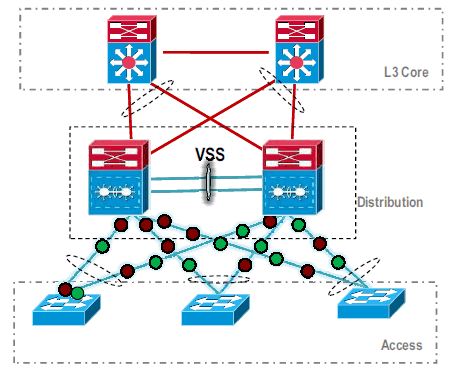
- VSS
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2013 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)











 Feedback
Feedback