Using Telnet to Run Utilities on Remote Cisco ICM Terminals
Contents
Introduction
This document explains how to connect to and exit from Telnet, a standard terminal emulation protocol in the TCP/IP protocol stack. Telnet is loaded on your computer when you install Cisco Intelligent Contact Management (ICM). You can use Telnet to connect to and run utilities on remote ICM terminals, such as dumplog , OPCTest , and rttest . You can also use Telnet to start and stop ICM services and to review ICM log files.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of this topic:
-
Telnet
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Connect to a Remote ICM System
Complete these steps to access Telnet:
-
Start Telnet in one of two ways:
-
Select Start > Run and enter Telnet.
-
Select Start > Programs > Accessories and click Telnet.
-
-
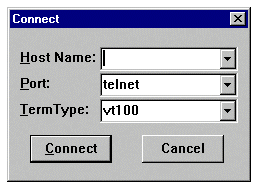
In Telnet, select Connect > Remote System. This Connect dialog box displays:
-
In the Host Name field, enter the name or IP address of the remote system you want to connect to. For example, geociscortra or 179.x.x.x.
-
Select Telnet in the Port field.
-
Select vt100 in the TermType field.
-
Click Connect.
-
When a connection is made, the title bar of the Telnet window displays the host name or IP address of the system to which you are connected.
-
Log in with a valid account name and password. Typically, this is your customer username. Refer to Cisco ICM Hand-off documents for the correct account name.
-
Enter n for no when prompted if you want to use advanced features.
-
Enter exit to quit Telnet when you are finished using the remote system.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback