Analog E&M Troubleshooting Guidelines (Cisco IOS Platforms)
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides step-by-step guidelines to troubleshoot analog recEive and transMit (E&M) issues with Cisco IOS® Software based platforms. Analog E&M is supported on Cisco 1750, 1751, 1760, 26/2700 series, 36/3700 series, VG200, and MC3810 models.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Readers of this document should be knowledgeable of these:
-
Cisco 26/2700, 36/3700, and VG200 platforms require a voice network module (NM-1V, NM-2V) and an E&M Voice Interface Card (VIC).
-
Cisco 1750, 1751, 1760 platforms require the E&M VIC and a suitable Packet Voice Data Module (PVDM) compression unit.
-
Cisco MC3810 platforms require an analog voice module (AVM) with an E&M analog personality module (APM-EM). The MC3810 also requires the high performance voice Compression Module (HCM) or Voice Compression Module (VCM) to process voice calls.
For an overview of Analog E&M, refer to Voice - Analog E&M Signaling Overview.
For more information on the Voice Network Modules and the E&M VIC, refer to Understanding Voice Network Modules, and Understanding E&M Voice Interface Cards.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
All Cisco IOS Software Releases
-
Cisco 1750, 1751, 1760, 26/2700, and 36/3700 series routers
-
VG200 and MC3810
The information presented in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If you are working in a live network, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command before using it.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Step 1: Verify the Analog E&M Hardware is Recognized
To verify that the analog E&M hardware is recognized by the Cisco IOS platform, use these commands:
-
show version - This command displays the configuration of the system hardware, the software version, the names of configuration files, and the boot images. See the sample output.
-
show running-config - The voice ports should appear in the configuration automatically. See the sample output.
Note: Voice requires an IOS Plus feature set.
show version Command on a Cisco 3640 Platform
Cisco-3600#show version Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) 3600 Software (C3640-IS-M), Version 12.1(2), RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Copyright (c) 1986-2000 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Wed 10-May-00 07:20 by linda Image text-base: 0x600088F0, data-base: 0x60E38000 ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.1(20)AA2, EARLY DEPLOYMENT RELEASE SOFTWARE(fc1) Cisco-3600 uptime is 0 minutes System returned to ROM by power-on at 11:16:21 cst Mon Mar 12 2001 System image file is "flash:c3640-is-mz.121-2.bin" cisco 3640 (R4700) processor (revision 0x00) with 126976K/4096K bytes of memory. Processor board ID 16187704 R4700 CPU at 100Mhz, Implementation 33, Rev 1.0 Bridging software. X.25 software, Version 3.0.0. SuperLAT software (copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp). 2 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 2 Voice FXS interface(s) 2 Voice E & M interface(s) DRAM configuration is 64 bits wide with parity disabled. 125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory. 32768K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write) 20480K bytes of processor board PCMCIA Slot0 flash (Read/Write) Configuration register is 0x2102
show version Command on a Cisco MC3810 Platform
Cisco-MC3810#show version Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) MC3810 Software (MC3810-JS-M), Version 12.0(7)T, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc2) Copyright (c) 1986-1999 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Tue 07-Dec-99 10:39 by phanguye Image text-base: 0x00023000, data-base: 0x00C16884 ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.3(1)MA1, MAINTENANCE INTERIM SOFTWARE ROM: MC3810 Software (MC3810-WBOOT-M), Version 11.3(1)MA1, MAINTENANCE INTERIM SOFTWARE Cisco-MC3810 uptime is 2 weeks, 3 days, 15 hours, 44 minutes System returned to ROM by reload System image file is "flash:mc3810-js-mz.120-7.T" Cisco MC3810 (MPC860) processor (revision 06.07) with 28672K/4096K bytes of memory. Processor board ID 09555436 PPC860 PowerQUICC, partnum 0x0000, version A03(0x0013) Channelized E1, Version 1.0. Bridging software. X.25 software, Version 3.0.0. SuperLAT software (copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp). TN3270 Emulation software. Primary Rate ISDN software, Version 1.1. MC3810 SCB board (v05.A1) 1 Multiflex E1(slot 3) RJ45 interface(v02.C0) 1 Six-Slot Analog Voice Module (v03.K0) 1 Analog FXS voice interface (v03.K0) port 1/1 1 Analog FXS voice interface (v03.A0) port 1/2 1 Analog FXO voice interface (v04.A0) port 1/3 1 Analog FXO voice interface (v04.A0) port 1/4 1 Analog E&M voice interface (v05.B0) port 1/5 1 Analog E&M voice interface (v05.B0) port 1/6 1 6-DSP(slot2) Voice Compression Module(v02.C0) 1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 2 Serial(sync/async) network interface(s) 2 Channelized E1/PRI port(s) 256K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory. 8192K bytes of processor board System flash (AMD29F016) Configuration register is 0x2102
show running-config Command on a Cisco 3640 Platform
Cisco-3600#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! !--- Some output is omitted. version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime ! hostname Cisco-3600 ! voice-port 3/0/0 ! voice-port 3/0/1 ! voice-port 3/1/0 ! voice-port 3/1/1 ! end
Step 2: Confirm the PBX E&M Configuration Parameters
The Cisco router/gateway needs to match the PBX configuration. One of the challenges of configuring and troubleshooting analog E&M circuits is the amount of configuration variables that are present. These guidelines help to determine the information to be gathered from the PBX.
-
E&M Signaling Type ( I, II, III, V)
-
Audio Implementation (2-wire / 4-wire)
-
Start Dial Supervision (wink-start, immediate, delay-dial)
-
Dial Method (dtmf, pulse)
-
Call Progress Tones (Standardized within geographic regions)
-
PBX Port Impedance
Note: E&M Type IV is not supported by Cisco router/ gateways. E&M Type V is the most common interface type used outside of North America. The term Type V is not commonly used outside of North America. From the viewpoint of many PBX operators there is only one E&M type (Type V).
For more information about these parameters, refer to Voice - Analog E&M Signaling Overview.
Step 3: Confirm the Cisco IOS Router/Gateway Configuration
The Cisco router / gateway configuration should match the connected PBX configuration. Use these commands to verify the Cisco IOS platform configuration:
-
show running-config - This command displays the running configuration of the router/ gateway.
Note: The default configuration on E&M voice ports is Type I, wink-start, operation 2-wire, dial method dual tone multifrequency (DTMF). Default E&M voice port parameters are not displayed with the show running-config command.
-
show voice-port - For E&M voice ports, this command displays specific configuration data such as E&M voice port, interface type, impedance, dial-supervision signal, audio operation, and dial method. For detailed information see the sample output here.
Sample Output of show voice port Command
Cisco-3600#show voice port 1/0/0 recEive And transMit 1/0/0 Slot is 1, Sub-unit is 0, Port is 0 Type of VoicePort is E&M Operation State is DORMANT Administrative State is UP The Last Interface Down Failure Cause is Administrative Shutdown Description is not set Noise Regeneration is enabled Non Linear Processing is enabled Music On Hold Threshold is Set to -38 dBm In Gain is Set to 0 dB Out Attenuation is Set to 0 dB Echo Cancellation is enabled Echo Cancel Coverage is set to 8 ms Connection Mode is normal Connection Number is not set Initial Time Out is set to 10 s Interdigit Time Out is set to 10 s Call-Disconnect Time Out is set to 60 s Region Tone is set for US Analog Info Follows: Currently processing none Maintenance Mode Set to None (not in mtc mode) Number of signaling protocol errors are 0 Impedance is set to 600r Ohm Voice card specific Info Follows: Signal Type is immediate Operation Type is 2-wire E&M Type is 5 Dial Type is dtmf In Seizure is inactive Out Seizure is inactive Digit Duration Timing is set to 100 ms InterDigit Duration Timing is set to 100 ms Pulse Rate Timing is set to 10 pulses/second InterDigit Pulse Duration Timing is set to 500 ms Clear Wait Duration Timing is set to 400 ms Wink Wait Duration Timing is set to 200 ms Wink Duration Timing is set to 200 ms Delay Start Timing is set to 300 ms Delay Duration Timing is set to 2000 ms Dial Pulse Min. Delay is set to 140 ms
For more information on configuring analog E&M voice ports, refer to Configuring Voice Ports.
Step 4: Verify the Wiring Arrangement Between the PBX and the Cisco Router/Gateway
Physical wiring is often the primary source for analog E&M problems. Verify that the cable/wiring you use is appropriate for the E&M setup in place. Consider these:
-
E&M Type I and Type V use two leads for Supervisory Signaling (on-hook /off-hook signaling) - E (ear, earth) and M (mouth, magnet). Cisco router/ gateways expect to see off-hook conditions on the M-lead and signal off-hook to the remote device on the E-lead.
-
E&M Type II and Type III use four leads for Supervisory Signaling (on/off hook signaling) - E (ear, earth), M (mouth, magnet), SG (Signal Ground), SB (Signal Battery). Cisco router/gateways expect to see off-hook conditions on the M-lead and signal off-hook to remote device on E-lead.
-
Audio Operation - The 2-wire / 4-wire operation is independent of the signaling type. For example, a 4-wire audio operation E&M circuit has six physical wires if configured for Type I or Type V. It has eight physical wires if configured for Type II or Type III.
-
Audio Path Wiring - In the 4-wire audio mode, some PBX and key system products reverse the normal usage of the T&R and T1&R1 pairs. In that case, to match up the audio pairs with the Cisco E&M audio pairs, it may be necessary to connect T&R on the PBX side to T1&R1 on the Cisco side, and T1&R1 on the PBX side to T&R on the Cisco side.
For more information and diagrams of the different E&M types, pinouts, and wiring arrangements, refer to Voice - Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Interface Types and Wiring Arrangements.
For more information about Analog E&M parameters, refer to Voice - Analog E&M Signaling Overview.
Step 5: Verify Supervision Signaling
This step explains how to verify that on-hook /off-hook signals are transmitted between the PBX and the router/gateway. Use this diagram as a reference scenario for the show and debug command output.
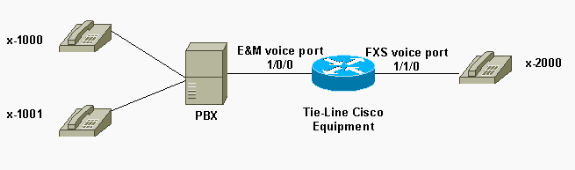
Before you attempt any debug commands, refer to Important Information on Debug Commands. If you access the router through the console port, enter the command terminal monitor. Otherwise no debug output is displayed.
Perform these steps to verify supervision signaling.
-
Turn on the command debug vpm signal on the Cisco router/gateway. This command is used to collect debug information for signaling events (on-hook/ off-hook transitions).
-
Place a call from the PBX to the router/gateway. With this, you want the PBX to seize the E&M trunk and send the on-hook -> off-hook signal transition to the router/gateway. This output displays a successful reception of these signals.
In this example, PBX seizes the router trunk. The router E&M voice port transitions from on-hook to off-hook state. This shows that on-hook, off-hook signaling is received from the PBX.
maui-gwy-01#debug vpm signal Voice Port Module signaling debugging is enabled *Mar 2 05:54:43.996: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.4 , 34] em_onhook_offhookhtsp_setup_ind *Mar 2 05:54:44.000: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 8] *Mar 2 05:54:44.784: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 10] *Mar 2 05:54:44.784: htsp_process_event: [1/1/0, 1.2 , 5] fxsls_onhook_setuphtsp_alerthtsp_alert_notify *Mar 2 05:54:44.788: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 11] *Mar 2 05:54:44.788: htsp_process_event: [1/1/0, 1.5 , 11] fxsls_waitoff_voice
If no output is displayed, then there is probably a problem with the E&M supervision signaling. This list describes some possible problems and the corresponding solutions:
-
Problem: The PBX is not configured to seize the E&M port connected to the Cisco equipment.
-
Solution: Configure the PBX to seize the trunk.
-
Problem: There is an E&M Type (I, II, III or V) mistmatch between the PBX and the router/gateway.
-
Solution: Verify (and change if necessary) the E&M type configured on the Cisco equipment. See the Confirm the Cisco IOS Router/Gateway Configuration section of this document.
-
Problem: Incorrect wiring arrangement (cabling) for the supervisory signaling leads (E and M leads for Type I and V; E,M, SB, SG leads for Type II and III).
-
Solution: Wiring issues are usually the primary source of analog E&M problems. Make sure that the cable used corresponds to the required PBX and Cisco router/gateway pinout, interface type and audio operation setup. For more information, refer to Voice - Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Interface Types and Wiring Arrangements.
-
Problem: The Cisco router/gateway configuration changes are not enabled.
-
Solution: Issue the shutdown/no shutdown command sequence on the E&M voice port after configuration changes.
Note: There can be cases where on-hook/off-hook signals have only been sent one way. This is probably an indication of a defective cable where one path of the signaling leads is wired correctly and the other side is not.
Step 6: Verify the Cisco Equipment Sends and Receives Digits to/from the PBX
After you confirm the successful supervisory (on-hook/off-hook) signaling between the PBX and the router/gateway, verify that address information (DTMF digits or Pulse Dial) is passed between both ends.
Note: DTMF digits are sent on the audio path. Pulse Dial address information is sent by pulsing on the E or M lead.
There are three start dial supervision line protocols (immediate start, wink start, and delay dial) that analog E&M uses to define how the equipment passes address information. Make sure that both the Cisco router/gateway and PBX are configured with the same start dial supervision protocol.
-
Turn on the commands debug vpm signal and debug vtsp dsp on the Cisco router/gateway. The command debug vtsp dsp displays the digits received/sent by the voice digital signal processors (DSPs).
-
Place a call from the PBX to the router/gateway. This output displays a successful reception of the expected digits. In this example the router receives a call from the PBX to extension x2000.
maui-gwy-01#show debugging Voice Port Module signaling debugging is on Voice Telephony dsp debugging is on maui-gwy-01# *Mar 1 03:16:19.207: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.4 , 34] em_onhook_offhookhtsp_setup_ind *Mar 1 03:16:19.207: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 8] *Mar 1 03:16:19.339: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=2,rtp_timestamp =0x9961CF03 *Mar 1 03:16:19.399: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=2,duration=110 *Mar 1 03:16:19.539: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=0,rtp_timestamp =0x9961CF03 *Mar 1 03:16:19.599: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=0,duration=110 *Mar 1 03:16:19.739: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=0,rtp_timestamp =0x9961CF03 *Mar 1 03:16:19.799: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=0,duration=110 *Mar 1 03:16:19.939: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=0,=rtp_timestamp =0x9961CF03 *Mar 1 03:16:19.999: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=0,duration=110 *Mar 1 03:16:19.999: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 10] *Mar 1 03:16:19.999: htsp_process_event: [1/1/0, 1.2 , 5] fxsls_onhook_setuphtsp_alerthtsp_alert_notify *Mar 1 03:16:20.003: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 11] *Mar 1 03:16:20.003: htsp_process_event: [1/1/0, 1.5 , 11] fxsls_waitoff_voice *Mar 1 03:16:27.527: htsp_process_event: [1/1/0, 1.5 , 34] fxsls_waitoff_offhook *Mar 1 03:16:27.531: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 6] em_offhook_connectem_stop_timers em_offhook
-
Place a call from the router/gateway to the PBX. This output displays the digits that the Cisco equipment sends. In this example, PBX receives a call from the router to extension x1000.
Log Buffer (1000000 bytes): *Mar 1 03:45:31.287: htsp_process_event: [1/1/1, 1.2 , 34] fxsls_onhook_offhook htsp_setup_ind *Mar 1 03:45:31.291: htsp_process_event: [1/1/1, 1.3 , 8] *Mar 1 03:45:33.123: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=1, rtp_timestamp=0xCD4365D8 *Mar 1 03:45:33.283: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=1,duration=205 *Mar 1 03:45:33.463: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=0, rtp_timestamp=0xCD4365D8 *Mar 1 03:45:33.643: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=0,duration=225 *Mar 1 03:45:33.823: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=0, rtp_timestamp=0xCD4365F0 *Mar 1 03:45:34.003: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=0,duration=222 *Mar 1 03:45:34.203: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_BEGIN: digit=0, rtp_timestamp=0xCD4365F0 *Mar 1 03:45:34.411: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DTMF_DIGIT_OFF: digit=0,duration=252 *Mar 1 03:45:34.415: htsp_process_event: [1/1/1, 1.3 , 10] *Mar 1 03:45:34.415: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.4 , 5] em_onhook_setup em_offhook *Mar 1 03:45:34.415: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.13 , 43] em_start_timer: 1200 ms *Mar 1 03:45:34.715: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.10 , 34] em_wink_offhookem_stop_timers em_start_timer: 1200 ms *Mar 1 03:45:34.923: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.11 , 22] em_wink_onhook em_stop_timers em_send_digit htsp_dial *Mar 1 03:45:34.923: digit=1, components=2, freq_of_first=697, freq_of_second=1209, amp_of_first=16384, amp_of_second=16384 *Mar 1 03:45:34.923: digit=0, components=2, freq_of_first=941, freq_of_second=1336, amp_of_first=16384, amp_of_second=16384 *Mar 1 03:45:34.923: digit=0, components=2, freq_of_first=941, freq_of_second=1336, amp_of_first=16384, amp_of_second=16384 *Mar 1 03:45:34.923: digit=0, components=2, freq_of_first=941, freq_of_second=1336, amp_of_first=16384, amp_of_second=16384 *Mar 1 03:45:35.727: vtsp_process_dsp_message: MSG_TX_DIALING_DONE *Mar 1 03:45:35.727: htsp_process_event: [1/0/0, 1.7 , 19] em_offhook_digit_donehtsp_alerthtsp_alert_notify
This list describes some possible problems and the corresponding solutions:
-
Problem: Start dial supervision mismatch or timing issues between the PBX and router/gateway.
-
Solution: Make sure that both end systems are configured with the same start dial protocol. For more information, refer to Voice - Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Start Dial Supervision Signaling.
-
Problem: Audio Operation mismatch (for example, one side configured for 2-wire, the other for 4-wire) or wiring problems on the audio path.
-
Solution: Verify the router/gateway and PBX configuration and the wiring arrangement. For more information, refer to Voice - Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Interface Types and Wiring Arrangements.
Note: DTMF digits are passed on the audio path. Even if the line supervision signaling operates correctly, DTMF digits are not passed if the audio path is broken.
-
Problem: Wiring problems in the audio path.
-
Solution: Verify the wiring arrangement. For more information, refer to Voice - Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Interface Types and Wiring Arrangements.
In the 4-wire audio mode, some PBX and key system products reverse the normal usage of the T&R and T1&R1 pairs. In that case, to match up the audio pairs with the Cisco E&M audio pairs, you may need to connect T&R on the PBX side to T1&R1 on the Cisco side, and T1&R1 on the PBX side to T&R on the Cisco side. If the audio pairs are not correctly matched up in 4-wire mode, there is no end-to-end audio path in either direction.
If the E&M interface is configured to send dial strings as Dial Pulse (which works by pulsing on the E or M lead), it is possible to establish a call even with the 4-wire audio pairs reversed. However, there is no audio path in either direction after the call is established (or there might be some low level transmission of audio, but the sound levels are far too low for comfort). If you use DTMF to send dial strings, the E&M interface goes off-hook at the start of the call. However, the call is not completed, as one end sends the DTMF tones on the wrong audio pair, and the other end does not receive these DTMF tones.
Step 7: Verify the Router/Gateway Sends to the PBX the Expected Digits
Once the two end devices are able to successfully send supervision and address signaling (on-hook, off-hook, digits), the troubleshooting process is complete., Now it is in the dial plan domain. If incomplete or incorrect digits are sent by the Cisco equipment, then the Telco switch (CO or PBX) is not able to ring the correct station.
Note: On plain old telephone service (POTS) dial peers, the only digits that are sent to the other end are the ones specified with the wild card character (".") with the command destination-pattern string . The POTS dial peer command prefix string is used to include a dial-out prefix that the system enters automatically instead of people dialing it. See this output for a better explanation of this issue.
hostname maui-gwy-01 ! !--- Some output is omitted. ! !--- E&M Voice Port. ! voice-port 1/0/0 type 2 signal immediate ! !--- FXS Voice Port. voice-port 1/1/0 ! dial-peer voice 1 pots destination-pattern 2000 port 1/1/0 ! !--- Dial peer 2 is in charge of forwarding !--- calls to the E&M voiceport 1/0/0. !--- In this case the digit "1" in the destination pattern !--- is dropped. The system !--- transmits the 3 digits matched by the "." wildcard. !--- Since the PBX expects the "1000" string, !--- the prefix command is used. ! dial-peer voice 2 pots destination-pattern 1... port 1/0/0 prefix 1 !
For more information on voice dial peers, refer to Configuring Voice over IP.
Step 8: Verify the Router/Gateway Receives from the PBX the Expected Digits
Verify that the digits received from the PBX match a dial peer in the router/gateway. If incomplete or incorrect digits are sent by the PBX, a dial-peer is not matched in the Cisco router/gateway. Use the command debug vtsp dsp to view the digits received in the analog E&M voice port. For sample output. see Step 6 in this document.
To verify which dial peers match a specific string, use the command show dialplan number string . See this sample output:
maui-vgw-01#show dialplan number 1000
Macro Exp.: 1000
VoiceEncapPeer2
information type = voice,
tag = 2, destination-pattern = `1...',
answer-address = `', preference=0,
group = 2, Admin state is up, Operation state is up,
incoming called-number = `', connections/maximum = 0/unlimited,
application associated:
type = pots, prefix = `1',
session-target = `', voice-port = `1/0/0',
direct-inward-dial = disabled,
register E.164 number with GK = TRUE
Connect Time = 19644, Charged Units = 0,
Successful Calls = 63, Failed Calls = 2,
Accepted Calls = 65, Refused Calls = 0,
Last Disconnect Cause is "10 ",
Last Disconnect Text is "normal call clearing.",
Last Setup Time = 28424467.
Matched: 1000 Digits: 1
Target:
maui-vgw-01#show dialplan number 2000
Macro Exp.: 2000
VoiceEncapPeer1
information type = voice,
tag = 1, destination-pattern = `2000',
answer-address = `', preference=0,
group = 1, Admin state is up, Operation state is up,
incoming called-number = `', connections/maximum = 0/unlimited,
application associated:
type = pots, prefix = `',
session-target = `', voice-port = `1/1/1',
direct-inward-dial = disabled,
register E.164 number with GK = TRUE
Connect Time = 19357, Charged Units = 0,
Successful Calls = 68, Failed Calls = 8,
Accepted Calls = 76, Refused Calls = 0,
Last Disconnect Cause is "10 ",
Last Disconnect Text is "normal call clearing.",
Last Setup Time = 28424186.
Matched: 2000 Digits: 4
Target:
Test Equipment Suitable for Working on Analog Voice Ports
While not required for every installation, it is sometimes necessary to use test equipment to isolate problems with analogue E&M ports. The most useful equipment is a digital multimeter and a technician's line test set (sometimes called a 'buttinski' or 'butt set'). These allow measurements to be made of signaling states and voltages, as well as monitoring the audio signals.
The Digital Multimeter is used to measure the DC loop voltage and AC ringing voltage on FXS ports, E or M lead signaling transitions, voltages on E or M leads, and DC resistance of E&M signaling leads. This picture shows a typical Digital Multimeter.

The Technician's Line Test set is often referred to as a 'Buttinski' or 'Butt Set'. In the terminating mode of operation, it acts like a normal telephone handset when connected to a loopstart trunk. It allows telephone numbers to be dialed on the inbuilt keypad. When switched to the monitoring mode (bridging mode), the unit presents a high impedance to the TX or RX audio pairs of the E&M port., This allows the audio signals and tones to be heard on the inbuilt loudspeaker. This helps to find issues with one way audio, incorrect digits sent or received, distortion and level problems, and possible sources of noise and echo. This picture shows a typical Technician's (Butt) Test set.

PBX Interconnection
The majority of PBXs that interface with peripheral equipment use cable Distribution Frames (DFs). Multi-pair cables are run from the PBX equipment cabinet to the distribution frame which are then 'jumpered' (cross connected) to the external devices. These DFs have various names., The most common terms are 110 block, 66 block, or Krone frame. The DF is generally the place where all connections are made between the router voice port and the PBX., It is where most wiring errors are made. Therefore, it is the best place to perform testing and troubleshooting. The picture here shows a typical '110' DF.
Use Rollover Cable for E&M Port-to-Port Testing
The majority of faults with E&M ports are due to incorrect wiring or PBX port programming. However, convincing the customer or the PBX technicians that this is the case can be difficult. To determine if the fault is external to the router, you can use the standard 'rollover' console cable that is supplied with every Cisco router as an E&M cross over. This cross over connects the signaling output of one port to the input of the other port. It maintains an audio path between the two ports. The configured dial peers send a test call out one port. This is then looped back into the second port, proving the operation of the router.
The 'Rollover' console cable has this RJ45 connector wiring:
1-------8
2-------7
3-------6
4-------5
5-------4
6-------3
7-------2
8-------1
The signaling cross over occurs as pins 2 (M lead) and 7 (E lead) on one port are connected to pins 7 (E lead) and 2 (M lead) on the other port. The two ports share a common internal ground. The crossover on pins 4 and 5 (audio pair) has no effect on the audio signal. By setting both voice ports to 2 wire, type 5 operation, the E&M ports become symmetrical. An outwards seizure on one port is seen as an incoming seizure on the second port. Any DTMF digits sent out immediately come back in. It is then matched on another dial peer. If the test calls are successful, the router voice ports operate properly.
In this example, it is assumed that there are working devices on the IP network that can originate and accept VoIP calls.
The voice ports and dial peers are configured like this:
voice-port 1/0/0 !--- First port is under test. operation 2-wire signal-type wink type 5 ! voice-port 1/0/1 !--- Second port is under test. operation 2-wire signal-type wink type 5 ! dial-peer voice 100 pots !--- Send call out to port 1/0/0, strip the !--- 100 and prefix with a called !--- number 200. destination-pattern 100 port 1/0/0 prefix 200 ! dial-peer voice 200 voip !--- Incoming test call for 200 comes !--- in on port 1/0/1. It is sent to 1.1.1.1 as VoIP call. destination-pattern 200 session-target ipv4:1.1.1.1 !
When a VoIP call comes into the router with a called number of 100, it is sent out to port 1/0/0. By default, any explicitly matched digits on a POTS dial peer are assumed as an access code. They are stripped off before the call is made. To route the call correctly, they need to be replaced. In this case, the prefix command prepends the digits '200' as the called number. This call is immediately looped back in on port 1/0/1. The digits match on dial-peer 200 and make the new call to the designated IP address. The devices that originate and accept the VoIP calls should then have an audio connection which is across the IP network and goes out and back in the E&M ports. This proves that the router works properly. This also isolates the fault as being external to the router. The majority of faults are due to incorrect cabling or PBX port programming issues.
Related Information
- Voice - Analog E&M Signaling Overview
- Voice - Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Interface Types and Wiring Arrangements
- Voice - Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Start Dial Supervision Signaling
- Understanding Voice Network Modules
- Understanding E&M Voice Interface Cards
- Voice Technology Support
- Voice and IP Communications Product Support
- Troubleshooting Cisco IP Telephony

- Technical Support - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
02-Feb-2006 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback