- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- Information About Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- How to Deploy Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- Configuration Examples for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense on ISR
- Additional References for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- Feature Information for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense is Cisco's premier network security option. It provides a comprehensive suite of security features such as firewall capabilities, monitoring, alerts, Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
This module describes how to configure and deploy IDS on Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISRs).
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- Information About Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- How to Deploy Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- Configuration Examples for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense on ISR
- Additional References for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- Feature Information for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
Information About Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR Overview
Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense is a premier security solution that provides enhanced inspection for packet flows.
-
Cisco FireSIGHT—A centralized policy and reporting entity that can run anywhere in the network. This can be the Cisco FireSIGHT appliance or a virtual installation on a server class machine.
-
Virtual FirePOWER sensor—Security entities that implement policies, and send events and statistics back to the defense center. The FirePOWER sensor is hosted on Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) E-Series Blade. Both the FireSIGHT and sensor are distributed as virtual packages.
UCS E-Series Blades are general purpose blade servers that are housed within Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISR) Generation 2 (G2) and Cisco ISR 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers. These blades can be deployed either as bare-metal on operating systems or as virtual machines on hypervisors. There are two internal interfaces that connect a router to an UCS E-Series Blade. On ISR G2, Slot0 is a Peripheral Component Interconnet Express (PCIe) internal interface, and UCS E-Series Slot1 is a switched interface connected to the backplane Multi Gigabit Fabric (MGF). In Cisco ISR 4000 Series Routers, both internal interfaces are connected to the MGF.
A hypervisor is installed on the UCS E-Series Blade, and Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense runs as a virtual machine on it. The Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense OVA file is directly installed on the UCS E-Series Blade using the hypervisor operating system. Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense runs as an anonymous inline device with no additional communication with the router. Traffic is diverted from the ingress physical interface to the Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense that runs on the UCS E-Series Blade.
The following figure shows a Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense deployment scenario. In this figure, the traffic lines between sensors and FireSIGHT are control connections. Packets are routed through these connections using router forwarding rules.
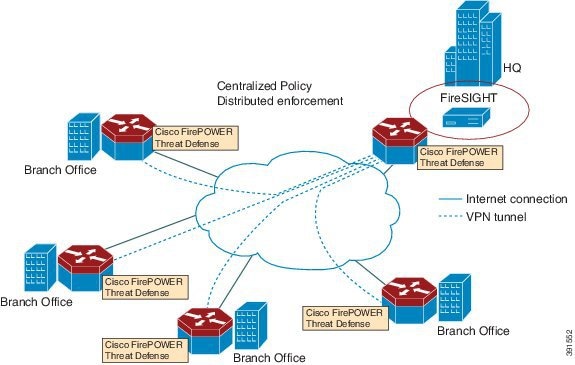
By default, the virtualized Cisco FirePOWER sensor comes with three interfaces, one for management, and two others for traffic analysis. These interfaces must be mapped to the UCS E-Series interfaces.
Hardware and Software Requirements for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense
The following software is required to run the Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense solution:
- UCS-E hypervisor
- ESXi 5.0.0, 5.1.0, or 5.5.0
- Cisco FirePOWER Sensor version Cisco IOS XE Release 3.14S and later releases
- Cisco FireSIGHT version 5.2, 5.3 or 5.4. FireSIGHT only supports the current version and is backward compatible with only the previous version. In case, your Cisco FirePOWER Sensor version is 5.4, then you have to use FireSIGHT version 5.4 or 5.3.
IDS Packet Flow on ISR G2 Routers
IDS monitors the traffic that passes through devices, and generates alerts when intrusions are detected. In IDS mode, traffic is copied to the sensor and is analyzed for threats. IDS mode cannot enforce policies; it can detect and report violations. In IDS mode, traffic is replicated from interfaces and redirected to Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense that runs on the Cisco UCS E-Series Blade.
In Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISR) Generation 2 (G2), Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense uses Router IP Traffic Export (RITE) to copy packets and redirect traffic over a Layer-2 link. RITE allows you to configure routers to export IP packets received on multiple, simultaneous WAN or LAN interfaces. The unaltered IP packets are exported on a single LAN or VLAN interface, thereby, easing the deployment of protocol analyzers and monitoring devices.
-
When IP traffic export is enabled, and packets are captured and transmitted across an interface, a delay occurs on the outbound interface. Performance delays increase with the number of interfaces that are monitored, and the number of destination hosts.
-
The MAC address of the device (device is Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense interface in passive mode) that receives the exported traffic must be on the same VLAN or directly connected to one of the router interfaces.
-
The outgoing interface for exported traffic must be an Ethernet interface. Incoming (or monitored) traffic can traverse any interface.
How to Deploy Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
- Obtaining the FirePOWER Sensor Package
- Installing the FirePOWER Sensor OVA File
- Configuring Traffic Redirect for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense on ISR G2
- Bootstrapping the FirePOWER Sensor
- Enabling IDS Inspection Globally on ISR G2
- Enabling IDS Inspection per Interface on ISR G2
Obtaining the FirePOWER Sensor Package
To deploy the FirePOWER sensor on an Unified Computing System (UCS) E-Series Blade, download and save the OVA file. OVA is an Open Virtualization Archive that contains a compressed and installable version of a virtual machine. Download the OVA file from https://support.sourcefire.com/sections/1/sub_sections/51#5-2-virtual-appliances.
Installing the FirePOWER Sensor OVA File
Install the FirePOWER Sensor OVA on a UCS E-Series Blade, using a hypervisor, such as VMWare VSphere.
Installing Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense on UCS E-Series Blade for Cisco ISR G2 Routers
- Install the card.
- Verify that the card is running by using the show inventory command.
- Configure the Cisco Integrated Management
Controller (CIMC) port.
The CIMC GUI is a web-based management interface for E-Series Servers. You can launch the CIMC GUI to manage the server from any remote host that meets the following minimum requirements: The CMIC runs on the port that is named management. To bootstrap this port with an IP address, use the following configuration: interface ucse2/0 imc access-port dedicated imc ip-address 10.66.152.158 255.255.255.0 !
Connect to the CMIC through the browser by using the default login and password, which are admin and password, respectively. Based on the configuration example, the browser here is https://10.66.152.158.
- Install ESXi.
Download the ESXi image for your Cisco UCS E-Series Blade from https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/ details?downloadGroup=CISCO-ESXI-5.1.0-GA-25SEP2012&productId=284.
- Install FirePOWER Sensor by using a hypervisor, such as VMWare VSphere on the Cisco UCS E-Series Blade.
- Configure traffic redirect. For more information, see the section “Configuring Traffic Redirect for Firepower Threat Defense on Cisco ISR G2 Routers”.
- Configure the VMWare
vSwitch. The Virtual Machine Network Interface Card (VMNIC) mapping is as
follows:
- VMNIC0—Router Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) interface (UCS 1/0/0)
- VMNIC1—Router Multi-Gigabit Fabric (MGF) VLAN interface (UCS 1/0/1)
- VMNIC2—Front panel GigabitEthernet port
- VMNIC3—Front panel GigabitEthernet port.

Note
VMNIC3 is only available on UCS E-Series 140D, 160Dm and 180D.
Configuring Traffic Redirect for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense on ISR G2
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ip
vrf
vrf-name
4.
rd
route-distinguisher
5.
exit
6.
interface
type
number
7.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
8.
exit
9.
interface
type
number
10.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
11.
exit
12.
interface
type
number
13.
ip
vrf
forwarding
name
14.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
15.
exit
16.
interface
type
number
17.
description
string
18.
switchport
mode
{access
|
trunk}
19.
no
ip
address
20.
exit
21.
interface
type
number
22.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
23.
exit
24.
interface
type
number
25.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
26.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Bootstrapping the FirePOWER Sensor
You must configure the FirePOWER Sensor manually. Perform this task to configure a FirePOWER sensor to communicate with FireSIGHT. For more information, see https://support.sourcefire.com/sections/10.
A sensor running on a Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) E-Series Blade is bootstrapped by logging into the console of the FirePOWER Sensor virtual machine through VSphere.
 Note | FirePOWER Sensor must be installed and deployed before bootstrapping it. |
1. Provide the default username and password to login.
2.
configure
network
ipv4
manual
ip-address
network-mask
default-gateway
3.
configure
network
dns
servers
dns-server
4.
configure
network
dns
searchdomains
domain-name
5.
configure
manager
add
dc-hostname
registration-key
DETAILED STEPS
Example
The following is sample output from the show network command that displays the configured network settings of the FirePOWER Sensor:
Device# show network ---------------------------------------------------- IPv4 Configuration : manual Address : 10.66.152.137 Netmask : 255.255.255.0 Gateway : 10.66.152.1 MAC Address : 44:03:A7:43:05:AD Management port : 8305 ---------------------------------------------------- IPv6 Configuration : disabled Management port : 8305 ----------------------------------------------------
The following is sample output from the show dns command that displays the configured DNS settings:
Device# show dns search cisco.com nameserver 192.10.26.10
The following is sample output from the show managers command that displays the configured management settings:
Device# show managers Host : sourcefire-dc.cisco.com Registration Key : cisco-sf Registration : pending RPC Status :
Enabling IDS Inspection Globally on ISR G2
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
utd
4.
mode
ids-global
5.
ids
mac-address
6.
ids
redirect
interface
interface -type
interface-number
7.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling IDS Inspection per Interface on ISR G2
Based on your requirements, you can configure unified threat defense (UTD) Intrusion Detection System (IDS) inspection at a global level or at an interface level.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
utd
4.
ids
mac-address
5.
ids
redirect
interface
interface -type
interface-number
6.
exit
7.
interface
type
number
8.
utd
ids
9.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense on ISR
Example: Configuring Traffic Redirect for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense on ISR G2
Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ip vrf vrf1 Router(config-vrf)# rd 100:1 Router(config-vrf)# exit Router(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit Router(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/1 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit Router(config)# interface ucse 2/0 Router(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding vrf1 Router(config-if)# ip address 192.0.2.2 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit Router(config)# interface ucse 2/1 Router(config-if)# description internal switch module connected to a Service Module Router(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Router(config-if)# no ip address Router(config-if)# exit Router(config)# interface vlan 1 Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit Router(config)# iinterface vlan 10 Router(config-if)# ip address 192.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# end
Example: Enabling IDS Inspection Globally on ISR G2
Router# configure terminal Router(config)# utd Router(config-utd)# mode ids-global Router(config-utd)# ids 000b.3456.234b Router(config-utd)# ids redirect ucse 2/0 Router(config-utd)# end
Example: Enabling IDS Inspection per Interface on ISR G2
Router# configure terminal Router(config)# utd Router(config-utd)# ids 12ab.47dd.ff89 Router(config-utd)# ids redirect ucse 2/0 Router(config-utd)# exit Router(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)# utd ids Router(config-if)# end
Additional References for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
|
IOS commands |
|
|
Security commands |
|
|
UCS E-Series Servers |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense for ISR |
Cisco IOS Release 15.5(1)T |
Cisco FirePOWER Threat Defense is a premier network security option. It provides a comprehensive suite of Security features such as firewall capabilities, monitoring, alerts, Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS). The following command was introduced or modified: ids, utd. |
 Feedback
Feedback