AV
pairs —Attribute-value pairs.
CEF —Cisco Express Forwarding. The Layer 3 IP switching technology that optimizes network performance and scalability for networks
with large and dynamic traffic patterns.
data-link
control
layer —Layer 2 in the SNA architectural model. Responsible for the transmission of data over a particular physical link. Corresponds
approximately to the data link layer of the OSI model.
DCE —Data circuit-terminating equipment (ITU-T expansion). Devices and connections of a communications network that comprise the
network end of the user-to-network interface.
DF
bit —Don’t Fragment bit. The bit in the IP header that can be set to indicate that the packet should not be fragmented.
DTE —Data terminal equipment. The device at the user end of a user-network interface that serves as a data source, destination,
or both.
HDLC —High-Level Data Link Control. A generic link-level communications protocol developed by the ISO. HDLC manages synchronous,
code-transparent, serial information transfer over a link connection.
ICMP —Internet Control Message Protocol. A network protocol that handles network errors and error messages.
IDB — Interface descriptor block.
IS-IS —Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System. The OSI link-state hierarchical routing protocol based on DECnet Phase V routing,
whereby ISs (devices) exchange routing information based on a single metric to determine network topology.
L2TP —An extension to PPP that merges features of two tunneling protocols: Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) from Cisco Systems and Point-to-Point
Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) from Microsoft. L2TP is an IETF standard endorsed by Cisco Systems and other networking industry
leaders.
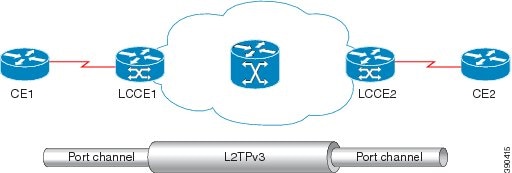
L2TPv3 —The draft version of L2TP that enhances functionality in RFC 2661 (L2TP).
LMI —Local Management Interface.
MPLS —Multiprotocol Label Switching. A switching method that forwards IP traffic using a label. This label instructs the devices
in the network where to forward packets based on preestablished IP routing information.
MQC —Modular quality of service CLI.
MTU —Maximum Transmission Unit. The maximum packet size, in bytes, that a particular interface can handle.
PMTU —Path MTU.
PVC —Permanent virtual circuit. A virtual circuit that is permanently established. A Frame Relay logical link, whose endpoints
and class of service are defined by network management. Analogous to an X.25 permanent virtual circuit, a PVC consists of
the originating Frame Relay network element address, originating data-link control identifier, terminating Frame Relay network
element address, and termination data-link control identifier. Originating refers to the access interface from which the PVC
is initiated. Terminating refers to the access interface at which the PVC stops. Many data network customers require a PVC
between two points. PVCs save the bandwidth associated with circuit establishment and tear down in situations where certain
virtual circuits must exist all the time. Data terminating equipment with a need for continuous communication uses PVCs.
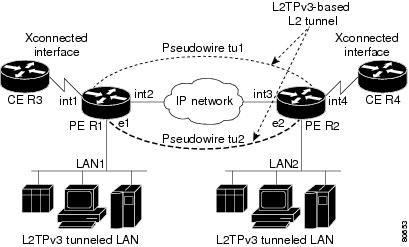
PW —Pseudowire.
SNMP —Simple Network Management Protocol. The network management protocol used almost exclusively in TCP/IP networks. SNMP provides
a means to monitor and control network devices and manage configurations, statistics collection, performance, and security.
tunneling —Architecture that is designed to provide the services necessary to implement any standard point-to-point encapsulation scheme.
UNI —User-Network Interface.
VPDN —Virtual private dialup network. A network that allows separate and autonomous protocol domains to share common access infrastructure,
including modems, access servers, and ISDN devices. A VPDN enables users to configure secure networks that take advantage
of ISPs that tunnel remote access traffic through the ISP cloud.



 Feedback
Feedback