Feedback Feedback
|
Contents
- Configuring IP SLAs DNS Operations
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About IP SLAs DNS Operations
- DNS Operation
- How to Configure IP SLAs DNS Operations
- Configuring an IP SLAs DNS Operation on the Source Device
- Configuring a Basic DNS Operation on the Source Device
- Configuring a DNS Operation with Optional Parameters on the Source Device
- Scheduling IP SLAs Operations
- Troubleshooting Tips
- What to Do Next
- Configuration Examples for IP SLAs DNS Operations
- Example Configuring a DNS Operation
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Configuring IP SLAs DNS Operation
Configuring IP SLAs DNS Operations
This module describes how to configure the IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Domain Name System (DNS) operation to measure the difference between the time taken to send a DNS request and receive a reply. This module also demonstrates how the results of the DNS operation can be displayed and analyzed to determine the DNS lookup time which is a critical element for determining the performance of a DNS or web server.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About IP SLAs DNS Operations
DNS Operation
The DNS operation measures the difference between the time taken to send a DNS request and receive a reply. DNS is used in the Internet for translating names of network nodes into addresses. The IP SLAs DNS operation queries for an IP address if you specify a host name, or queries for a host name if you specify an IP address.
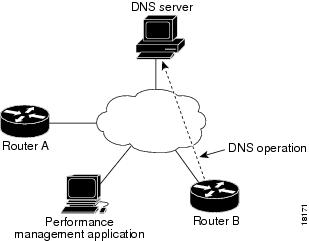
In the figure below Device B is configured as the source IP SLAs device and a DNS operation is configured with the DNS server as the destination device.
Connection response time is computed by measuring the difference between the time taken to send a request to the DNS server and the time a reply is received by Device B. The resulting DNS lookup time can help you analyze your DNS performance. Faster DNS lookup times translate to a faster web server access experience.
How to Configure IP SLAs DNS Operations
Configuring an IP SLAs DNS Operation on the Source Device
 Note | There is no need to configure an IP SLAs responder on the destination device. |
Perform one of the following tasks:
- Configuring a Basic DNS Operation on the Source Device
- Configuring a DNS Operation with Optional Parameters on the Source Device
Configuring a Basic DNS Operation on the Source Device
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a DNS Operation with Optional Parameters on the Source Device
DETAILED STEPS
Scheduling IP SLAs Operations
- ip sla schedule operation-number [life {forever | seconds}] [start-time {[hh:mm:ss] [month day | day month] | pending | now | after hh:mm:ss}] [ageout seconds] [recurring]
- ip sla group schedule group-operation-number operation-id-numbers schedule-period schedule-period-range [ageout seconds] [frequency group-operation-frequency] [life {forever | seconds}] [start-time{hh:mm[:ss] [month day | day month] | pending | now | after hh:mm[:ss]}]
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
- If the IP SLAs operation is not running and not generating statistics, add the verify-data command to the configuration of the operation (while configuring in IP SLA configuration mode) to enable data verification. When data verification is enabled, each operation response is checked for corruption. Use the verify-data command with caution during normal operations because it generates unnecessary overhead.
- Use the debug ip sla trace and debug ip sla error commands to help troubleshoot issues with an IP SLAs operation.
What to Do Next
To add proactive threshold conditions and reactive triggering for generating traps (or for starting another operation) to an IP SLAs operation, see the "Configuring Proactive Threshold Monitoring" section.
operation)
To display and interpret the results of an IP SLAs operation, use the show ip sla statistics command. Check the output for fields that correspond to criteria in your service level agreement to determine whether the service metrics are acceptable.
Configuration Examples for IP SLAs DNS Operations
Example Configuring a DNS Operation
The following example shows how to configure a DNS operation from Device B to the DNS server (IP address 172.20.2.132) as shown in the "DNS Operation" figure in the "DNS Operation" section. The operation is scheduled to start immediately. In this example, the target address is a hostname and the DNS operation will query the DNS server for the IP address associated with the hostname host1. No configuration is required at the DNS server.
Additional References
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Cisco IOS IP SLAs commands |
|
|
Cisco IOS IP SLAs: general information |
"Cisco IOS IP SLAs Overview" module of the Cisco IOS IP SLAs Configuration Guide. |
|
Multioperation scheduling for IP SLAs |
"Configuring Multioperation Scheduling of IP SLAs Operations" module of the Cisco IOS P SLAs Configuration Guide |
|
Proactive threshold monitoring for IP SLAs |
"Configuring Proactive Threshold Monitoring of IP SLAs Operations" module of the Cisco IOS IP SLAs Configuration Guide |
MIBs
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Configuring IP SLAs DNS Operation
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for the IP SLAs - DNS Operation |
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
IP SLAs - DNS Operation |
12.2(31)SB2 12.2(33)SRB1 12.2(33)SXH 12.3(14)T Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1 15.0(1)S Cisco IOS XE 3.1.0SG |
The IP SLAs Domain Name System (DNS) Operation feature allows you to measure the difference between the time taken to send a DNS request and receive a reply. |
|
IPSLA 4.0 - IP v6 phase2 |
15.2(3)T Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S 15.1(2)SG Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4SG |
Support was added for operability in IPv6 networks. The following commands are introduced or modified: dns (IP SLA), show ip sla configuration, show ip sla summary. |
|
IP SLAs VRF Aware 2.0 |
12.4(2)T 15.1(1)S 15.1(1)SY Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8S |
Support was added for IP SLAs VRF-aware capabilities for TCP connect, FTP, HTTP and DNS client operation types. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.