Table Of Contents
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Prerequisites for Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Information About Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
GLBP Virtual MAC Address Assignment
GLBP Virtual Gateway Redundancy
GLBP Virtual Forwarder Redundancy
GLBP Gateway Weighting and Tracking
How to Configure Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Configuring GLBP Weighting Values and Object Tracking
GLBP Weighting Configuration Behavior
Sample Output for the show glbp Command
Troubleshooting Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Configuration Examples for Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Customizing GLBP Configuration Example
Configuring GLBP Weighting Example
Enabling GLBP Configuration Example
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), while allowing packet load sharing between a group of redundant routers.
Feature Specifications for the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
•
Information About Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
•
How to Configure Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
•
Configuration Examples for Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Prerequisites for Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Before configuring the GLBP feature, ensure that the routers can support multiple MAC addresses on the physical interfaces. For each GLBP forwarder to be configured, an additional MAC address is used.
Information About Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
To configure GLBP, you need to understand the following concepts:
•
GLBP
•
GLBP Virtual MAC Address Assignment
•
GLBP Virtual Gateway Redundancy
•
GLBP Virtual Forwarder Redundancy
•
GLBP Gateway Weighting and Tracking
GLBP
The Gateway Load Balancing Protocol feature provides automatic router backup for IP hosts configured with a single default gateway on an IEEE 802.3 LAN. Multiple first hop routers on the LAN combine to offer a single virtual first hop IP router while sharing the IP packet forwarding load. Other routers on the LAN may act as redundant GLBP routers that will become active if any of the existing forwarding routers fail.
GLBP performs a similar, but not identical, function for the user as the HSRP and the VRRP. HSRP and VRRP protocols allow multiple routers to participate in a virtual router group configured with a virtual IP address. One member is elected to be the active router to forward packets sent to the virtual IP address for the group. The other routers in the group are redundant until the active router fails. These standby routers have unused bandwidth that the protocol is not using. Although multiple virtual router groups can be configured for the same set of routers, the hosts must be configured for different default gateways, which results in an extra administrative burden. GLBP provides load balancing over multiple routers (gateways) using a single virtual IP address and multiple virtual MAC addresses. Each host is configured with the same virtual IP address, and all routers in the virtual router group participate in forwarding packets. GLBP members communicate between each other through hello messages sent every 3 seconds to the multicast address 224.0.0.102, User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port 3222 (source and destination).
GLBP Active Virtual Gateway
Members of a GLBP group elect one gateway to be the active virtual gateway (AVG) for that group. Other group members provide backup for the AVG in the event that the AVG becomes unavailable. The AVG assigns a virtual MAC address to each member of the GLBP group. Each gateway assumes responsibility for forwarding packets sent to the virtual MAC address assigned to it by the AVG. These gateways are known as active virtual forwarders (AVFs) for their virtual MAC address.
The AVG is responsible for answering Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests for the virtual IP address. Load sharing is achieved by the AVG replying to the ARP requests with different virtual MAC addresses.
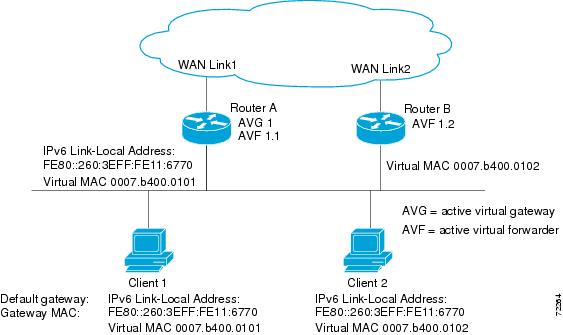
In Figure 1, Router A is the AVG for a GLBP group, and is responsible for the virtual IP address 10.21.8.10. Router A is also an AVF for the virtual MAC address 0007.b400.0101. Router B is a member of the same GLBP group and is designated as the AVF for the virtual MAC address 0007.b400.0102. Client 1 has a default gateway IP address of 10.21.8.10 and a gateway MAC address of 0007.b400.0101. Client 2 shares the same default gateway IP address but receives the gateway MAC address 0007.b400.0102 because Router B is sharing the traffic load with Router A.
Figure 1 GLBP Topology
If Router A becomes unavailable, Client 1 will not lose access to the WAN because Router B will assume responsibility for forwarding packets sent to the virtual MAC address of Router A, and for responding to packets sent to its own virtual MAC address. Router B will also assume the role of the AVG for the entire GLBP group. Communication for the GLBP members continues despite the failure of a router in the GLBP group.
GLBP Virtual MAC Address Assignment
A GLBP group allows up to four virtual MAC addresses per group. The AVG is responsible for assigning the virtual MAC addresses to each member of the group. Other group members request a virtual MAC address after they discover the AVG through hello messages. Gateways are assigned the next MAC address in sequence. A virtual forwarder that is assigned a virtual MAC address by the AVG is known as a primary virtual forwarder. Other members of the GLBP group learn the virtual MAC addresses from hello messages. A virtual forwarder that has learned the virtual MAC address is referred to as a secondary virtual forwarder.
GLBP Virtual Gateway Redundancy
GLBP operates virtual gateway redundancy in the same way as HSRP. One gateway is elected as the AVG, another gateway is elected as the standby virtual gateway, and the remaining gateways are placed in a listen state.
If an AVG fails, the standby virtual gateway will assume responsibility for the virtual IP address. A new standby virtual gateway is then elected from the gateways in the listen state.
GLBP Virtual Forwarder Redundancy
Virtual forwarder redundancy is similar to virtual gateway redundancy with an AVF. If the AVF fails, one of the secondary virtual forwarders in the listen state assumes responsibility for the virtual MAC address.
The new AVF is also a primary virtual forwarder for a different forwarder number. GLBP migrates hosts away from the old forwarder number using two timers that start as soon as the gateway changes to the active virtual forwarder state. GLBP uses the hello messages to communicate the current state of the timers.
The redirect time is the interval during which the AVG continues to redirect hosts to the old virtual forwarder MAC address. When the redirect time expires, the AVG stops redirecting hosts to the virtual forwarder, although the virtual forwarder will continue to forward packets that were sent to the old virtual forwarder MAC address.
The secondary holdtime is the interval during which the virtual forwarder is valid. When the secondary holdtime expires, the virtual forwarder is removed from all gateways in the GLBP group. The expired virtual forwarder number becomes eligible for reassignment by the AVG.
GLBP Gateway Priority
GLBP gateway priority determines the role that each GLBP gateway plays and what happens if the AVG fails.
Priority also determines if a GLBP router functions as a backup virtual gateway and the order of ascendancy to becoming an AVG if the current AVG fails. You can configure the priority of each backup virtual gateway with a value of 1 through 255 using the glbp priority command.
In Figure 1, if Router A, the AVG in a LAN topology, fails, an election process takes place to determine which backup virtual gateway should take over. In this example, Router B is the only other member in the group so it will automatically become the new AVG. If another router existed in the same GLBP group with a higher priority, then the router with the highest priority would be elected. If both routers have the same priority, the backup virtual gateway with the higher IP address would be elected to become the active virtual gateway.
By default, the GLBP gateway preemptive scheme is disabled. A backup virtual gateway can become the AVG only if the current AVG fails, regardless of the priorities assigned to the virtual gateways. You can enable the GLBP preemptive scheme using the glbp preempt command. Preemption allows a backup virtual gateway to become the AVG, if the backup virtual gateway is assigned a higher priority than the current AVG.
GLBP Gateway Weighting and Tracking
GLBP uses a weighting scheme to determine the forwarding capacity of each router in the GLBP group. The weighting assigned to a router in the GLBP group determines whether it will forward packets and, if so, the proportion of hosts in the LAN for which it will forward packets. Thresholds can be set to disable forwarding when the weighting falls below a certain value, and when it rises above another threshold, forwarding is automatically reenabled.
The GLBP group weighting can be automatically adjusted by tracking the state of an interface within the router. If a tracked interface goes down, the GLBP group weighting is reduced by a specified value. Different interfaces can be tracked to decrement the GLBP weighting by varying amounts.
GLBP Benefits
Load Sharing
You can configure GLBP in such a way that traffic from LAN clients can be shared by multiple routers, thereby sharing the traffic load more equitably among available routers.
Multiple Virtual Routers
GLBP supports up to 1024 virtual routers (GLBP groups) on each physical interface of a router, and up to 4 virtual forwarders per group.
Preemption
The redundancy scheme of GLBP enables you to preempt an active virtual gateway with a higher priority backup virtual gateway that has become available. Forwarder preemption works in a similar way, except that forwarder preemption uses weighting instead of priority and is enabled by default.
Authentication
You can use a simple text password authentication scheme between GLBP group members to detect configuration errors. A router within a GLBP group with a different authentication string than other routers will be ignored by other group members.
How to Configure Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
This section contains the following procedures:
•
Customizing GLBP (optional)
•
Configuring GLBP Weighting Values and Object Tracking (optional)
•
Enabling and Verifying GLBP (required)
•
Troubleshooting Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (optional)
Customizing GLBP
This task explains how to customize your GLBP configuration.
GLBP Customizing Behavior
Customizing the behavior of GLBP is optional. Be aware that as soon as you enable a GLBP group, that group is operating. It is possible that if you first enable a GLBP group before customizing GLBP, the router could take over control of the group and become the AVG before you have finished customizing the feature. Therefore, if you plan to customize GLBP, it is a good idea to do so before enabling GLBP.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface type number
4.
ip address ip-address mask [secondary]
5.
glbp group authentication text string
6.
glbp group forwarder preempt [delay minimum seconds]
7.
glbp group load-balancing [host-dependent | round-robin | weighted]
8.
glbp group preempt [delay minimum seconds]
9.
glbp group priority level
10.
glbp group timers [msec] hellotime [msec] holdtime
11.
glbp group timers redirect redirect timeout
12.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
What to Do Next
If you do not need to configure GLBP weighting values and object tracking, proceed to the "Enabling and Verifying GLBP" section.
Configuring GLBP Weighting Values and Object Tracking
This task explains how to configure GLBP weighting values and object tracking.
GLBP Weighting Configuration Behavior
GLBP weighting is used to determine whether a router can act as a virtual forwarder. Initial weighting values can be set and optional thresholds specified. Interface states can be tracked and a decrement value set to reduce the weighting value if the interface goes down. When the GLBP router weighting drops below a specified value, the router will no longer be an active virtual forwarder. When the weighting rises above a specified value, the router can resume its role as an active virtual forwarder.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
track object-number interface type number {line-protocol | ip routing}
4.
interface type number
5.
glbp group weighting maximum [lower lower] [upper upper]
6.
glbp group weighting track object-number [decrement value]
7.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling and Verifying GLBP
This task explains how to enable GLBP on an interface and verify its configuration and operation. GLBP is designed to be easy to configure. Each gateway in a GLBP group must be configured with the same group number, and at least one gateway in the GLBP group must be configured with the virtual IP address to be used by the group. All other required parameters can be learned.
Prerequisites
If VLANs are in use on an interface, the GLBP group number must be different for each VLAN.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface type number
4.
ip address ip-address mask [secondary]
5.
glbp group ip [ip-address [secondary]]
6.
exit
7.
show glbp [interface-type interface-number] [group] [state] [brief]
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
This section provides the following output example:
•
Sample Output for the show glbp Command
Sample Output for the show glbp Command
In the following example, output information is displayed about the status of the GLBP group, named 10, on the router:
Router# show glbp 10FastEthernet0/0 - Group 10State is Active2 state changes, last state change 23:50:33Virtual IP address is 10.21.8.10Hello time 5 sec, hold time 18 secNext hello sent in 4.300 secsRedirect time 1800 sec, forwarder time-out 28800 secAuthentication text "stringabc"Preemption enabled, min delay 60 secActive is localStandby is unknownPriority 254 (configured)Weighting 105 (configured 110), thresholds: lower 95, upper 105Track object 2 state Down decrement 5Load balancing: host-dependentThere is 1 forwarder (1 active)Forwarder 1State is Active1 state change, last state change 23:50:15MAC address is 0007.b400.0101 (default)Owner ID is 0005.0050.6c08Redirection enabledPreemption enabled, min delay 60 secActive is local, weighting 105Troubleshooting Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
The Gateway Load Balancing Protocol feature introduces five privileged EXEC mode commands to enable diagnostic output concerning various events relating to the operation of GLBP to be displayed on a console. The debug condition glbp, debug glbp errors, debug glbp events, debug glbp packets, and debug glbp terse commands are intended only for troubleshooting purposes because the volume of output generated by the software can result in severe performance degradation on the router. Perform this task to minimize the impact of using the debug glbp commands.
This procedure will minimize the load on the router created by the debug condition glbp or debug glbp command because the console port is no longer generating character-by-character processor interrupts. If you cannot connect to a console directly, you can run this procedure via a terminal server. If you must break the Telnet connection, however, you may not be able to reconnect because the router may be unable to respond due to the processor load of generating the debugging output.
Prerequisites
This task requires a router running GLBP to be attached directly to a console.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
no logging console
4.
Use Telnet to access a router port and repeat Steps 1 and 2.
5.
terminal monitor
6.
end
7.
debug condition glbp interface-type interface-number group [forwarder]
8.
configure terminal
9.
no terminal monitor
10.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
This section contains the following configuration examples:
•
Customizing GLBP Configuration Example
•
Configuring GLBP Weighting Example
•
Enabling GLBP Configuration Example
Customizing GLBP Configuration Example
In the following example, Router A, shown in Figure 1, is configured with a number of GLBP commands:
interface fastethernet 0/0ip address 10.21.8.32 255.255.255.0glbp 10 authentication text stringxyzglbp 10 forwarder preempt delay minimum 60glbp 10 load-balancing host-dependentglbp 10 preempt delay minimum 60glbp 10 priority 254glbp 10 timers 5 18glbp 10 timers redirect 1800 28800Configuring GLBP Weighting Example
In the following example, Router A, shown in Figure 1, is configured to track the IP routing state of the POS interface 6/0, an initial GLBP weighting with upper and lower thresholds is set, and a weighting decrement value of 5 is set. If POS interface 6/0 goes down, the weighting value of the router is reduced.
track 2 interface POS 6/0 ip routinginterface fastethernet 0/0glbp 10 weighting 110 lower 95 upper 105glbp 10 weighting track 2 decrement 5Enabling GLBP Configuration Example
In the following example, Router A, shown in Figure 1, is configured to enable GLBP, and the virtual IP address of 10.21.8.10 is specified for GLBP group 10:
interface fastethernet 0/0ip address 10.21.8.32 255.255.255.0glbp 10 ip 10.21.8.10Additional References
For additional information related to GLBP, see the following sections:
•
MIBs
•
RFCs
Related Documents
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature.
—
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs has not been modified by this feature.
To obtain lists of supported MIBs by platform and Cisco IOS release, and to download MIB modules, go to the Cisco MIB website on Cisco.com at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/ITDIT/MIBS/servlet/index
If Cisco MIB Locator does not support the MIB information that you need, you can also obtain a list of supported MIBs and download MIBs from the Cisco MIBs page at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
To access Cisco MIB Locator, you must have an account on Cisco.com. If you have forgotten or lost your account information, send a blank e-mail to cco-locksmith@cisco.com. An automatic check will verify that your e-mail address is registered with Cisco.com. If the check is successful, account details with a new random password will be e-mailed to you. Qualified users can establish an account on Cisco.com by following the directions found at this URL:
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature.
—
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents new commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T command reference publications.
debug condition glbp
To display debugging messages about Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) conditions, use the debug condition glbp command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging output, use the no form of this command.
debug condition glbp interface-type interface-number group [forwarder]
no debug condition glbp type number group [forwarder]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Examples
The following is sample output from the debug condition glbp command:
Router# debug condition glbp fastethernet 0/0 10 1Condition 1 set5d23h: Fa0/0 GLBP10.1 Debug: Condition 1, glbp Fa0/0 GLBP10.1 triggered, count 1Related Commands
debug glbp errors
To display debugging messages about Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) error conditions, use the debug glbp errors command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging output, use the no form of this command.
debug glbp errors
no debug glbp errors
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Examples
The following is sample output from the debug glbp errors command:
Router# debug glbp errorsGLBP Errors debugging is on1d19h: GLBP: Fa0/0 API active virtual address 10.21.8.32 not found1d19h: GLBP: Fa0/0 API active virtual address 10.21.8.32 not found1d19h: GLBP: Fa0/0 API active virtual address 10.21.8.32 not foundRelated Commands
debug glbp events
To display debugging messages about Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) events that are occurring, use the debug glbp events command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging output, use the no form of this command.
debug glbp events [all | detail | terse]
no debug glbp events [all | detail | terse]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Examples
The following is sample output from the debug glbp events command when the terse keyword is specified:
Router# debug glbp events terseGLBP Events debugging is on(protocol, redundancy, track)Related Commands
debug glbp packets
To display summary information about Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) packets being sent or received, use the debug glbp packets command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging output, use the no form of this command.
debug glbp packets [all | detail | hello | reply | request | terse]
no debug glbp packets [all | detail | hello | reply | request | terse]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Examples
The following is sample output from the debug glbp packets command:
Router# debug glbp packets helloGLBP Packets debugging is on(Hello)1d19h: GLBP: Fa0/0 Grp 10 Hello out 10.21.8.32 VG Active pri 254 vIP 10.21.8.10 11d19h: GLBP: Fa0/0 Grp 10 Hello out 10.21.8.32 VG Active pri 254 vIP 10.21.8.10 11d19h: GLBP: Fa0/0 Grp 10 Hello out 10.21.8.32 VG Active pri 254 vIP 10.21.8.10 11d19h: GLBP: Fa0/0 Grp 10 Hello out 10.21.8.32 VG Active pri 254 vIP 10.21.8.10 1Related Commands
debug glbp terse
To display a limited range of debug messages about Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) errors, events, and packets, use the debug glbp terse command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging output, use the no form of this command.
debug glbp terse
no debug glbp terse
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Examples
The following is sample output from the debug glbp terse command:
Router# debug glbp terseGLBP:GLBP Errors debugging is onGLBP Events debugging is on(protocol, redundancy, track)GLBP Packets debugging is on(Request, Reply)Related Commands
glbp authentication
To configure an authentication string for the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP), use the glbp authentication command in interface configuration mode. To delete an authentication string, use the no form of this command.
glbp group authentication text string
no glbp group authentication text string
Syntax Description
group
GLBP group number in the range from 0 to 1023.
text string
Specifies an authentication string. The number of characters in the command plus the text string must not exceed 255 characters.
Defaults
No authentication of GLBP messages occurs.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
The authentication string is sent in plain text in all GLBP messages. The same authentication string must be configured on all the routers that are configured to be members of the same GLBP group, to ensure interoperation. A router will ignore all GLBP messages that contain the wrong authentication string.
Examples
The following example configures stringxyz as the authentication string required to allow GLBP routers in group 10 to interoperate:
interface fastethernet 0/0glbp 10 authentication text stringxyzRelated Commands
glbp forwarder preempt
To configure a router to take over as active virtual forwarder (AVF) for a Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) group if it has higher priority than the current AVF, use the glbp forwarder preempt command in interface configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
glbp group forwarder preempt [delay minimum seconds]
no glbp group forwarder preempt [delay minimum]
Syntax Description
Defaults
Forwarder preemption is enabled with a default delay of 30 seconds.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Examples
The following example shows a router being configured to preempt the current AVF when its priority is higher than that of the current AVF. If the router preempts the current AVF, it waits 60 seconds before taking over the role of the AVF.
glbp 10 forwarder preempt delay minimum 60Related Commands
glbp ip
To activate the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP), use the glbp ip command in interface configuration mode. To disable GLBP, use the no form of this command.
glbp group ip [ip-address [secondary]]
no glbp group ip [ip-address [secondary]]
Syntax Description
Defaults
GLBP is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
The glbp ip command activates GLBP on the configured interface. If an IP address is specified, that address is used as the designated virtual IP address for the GLBP group. If no IP address is specified, the designated address is learned from another router configured to be in the same GLBP group. For GLBP to elect an active virtual gateway (AVG), at least one router on the cable must have been configured with the designated address. A router must be configured with, or have learned, the virtual IP address of the GLBP group before assuming the role of a GLBP gateway or forwarder. Configuring the designated address on the AVG always overrides a designated address that is currently in use.
When the glbp ip command is enabled on an interface, the handling of proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests is changed (unless proxy ARP was disabled). ARP requests are sent by hosts to map an IP address to a MAC address. The GLBP gateway intercepts the ARP requests and replies to the ARP on behalf of the connected nodes. If a forwarder in the GLBP group is active, proxy ARP requests are answered using the MAC address of the first active forwarder in the group. If no forwarder is active, proxy ARP responses are suppressed.
Examples
The following example activates GLBP for group 10 on Fast Ethernet interface 0/0. The virtual IP address to be used by the GLBP group is set to 10.21.8.10.
interface fastethernet 0/0ip address 10.21.8.32 255.255.255.0glbp 10 ip 10.21.8.10The following example activates GLBP for group 10 on Fast Ethernet interface 0/0. The virtual IP address used by the GLBP group will be learned from another router configured to be in the same GLBP group.
interface fastethernet 0/0glbp 10 ipRelated Commands
glbp load-balancing
To specify the load-balancing method used by the active virtual gateway (AVG) of the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP), use the glbp load-balancing command in interface configuration mode. To disable load balancing, use the no form of this command.
glbp group load-balancing [host-dependent | round-robin | weighted]
no glbp group load-balancing
Syntax Description
Defaults
The round-robin method is the default.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
Use the host-dependent method of GLBP load balancing when you need each host to always use the same router. Use the weighted method of GLBP load balancing when you need unequal load balancing because routers in the GLBP group have different forwarding capacities.
Examples
The following example shows the host-dependent load-balancing method being configured for the AVG of the GLBP group 10:
interface fastethernet 0/0glbp 10 ip 10.21.8.10glbp 10 load-balancing host-dependentRelated Commands
glbp preempt
To configure the gateway to take over as active virtual gateway (AVG) for a Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) group if it has higher priority than the current AVG, use the glbp preempt command in interface configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
glbp group preempt [delay minimum seconds]
no glbp group preempt [delay minimum]
Syntax Description
Defaults
A GLBP router with a higher priority than the current AVG cannot assume the role of AVG.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Examples
The following example shows a router being configured to preempt the current AVG when its priority of 254 is higher than that of the current AVG. If the router preempts the current AVG, it waits 60 seconds before assuming the role of AVG.
glbp 10 preempt delay minimum 60glbp 10 priority 254Related Commands
glbp priority
To set the priority level of the gateway within a Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) group, use the glbp priority command in interface configuration mode. To remove the priority level of the gateway, use the no form of this command.
glbp group priority level
no glbp group priority level
Syntax Description
group
GLBP group number in the range from 0 to 1023.
level
Priority of the gateway within the GLBP group. The range is from 1 to 255. The default is 100.
Defaults
level: 100
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to control which virtual gateway becomes the active virtual gateway (AVG). After the priorities of several different virtual gateways are compared, the gateway with the numerically higher priority is elected as the AVG. If two virtual gateways have equal priority, the gateway with the higher IP address is selected.
Examples
The following example shows a virtual gateway being configured with a priority of 254:
glbp 10 priority 254Related Commands
Enables GLBP.
Configures a router to take over as the AVG for a GLBP group if it has higher priority than the current AVG.
glbp timers
To configure the time between hello packets sent by the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) gateway and the time that the virtual gateway and virtual forwarder information is considered valid, use the glbp timers command in interface configuration mode. To restore the timers to their default values, use the no form of this command.
glbp group timers [msec] hellotime [msec] holdtime
no glbp group timers
Syntax Description
Defaults
hellotime: 3 seconds
holdtime: 10 secondsCommand Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
Routers on which timer values are not configured can learn timer values from the active virtual gateway (AVG). The timers configured on the AVG always override any other timer settings. All routers in a GLBP group should use the same timer values. If a GLBP gateway sends a hello message, the information should be considered valid for one holdtime. Normally, holdtime is greater than three times the value of hello time, (holdtime > 3 * hellotime). The range of values for holdtime force the holdtime to be greater than the hello time.
Examples
The following example shows the GLBP group 10 on Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 timers being configured for an interval of 5 seconds between hello packets, and the time after which virtual gateway and virtual forwarder information is considered to be invalid to 18 seconds:
interface fastethernet 0/0glbp 10 ipglbp 10 timers 5 18glbp timers redirect
To configure the time during which the active virtual gateway (AVG) for a Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) group continues to redirect clients to a secondary active virtual forwarder (AVF), use the glbp timers redirect command in interface configuration mode. To restore the redirect timers to their default values, use the no form of this command.
glbp group timers redirect redirect timeout
no glbp group timers redirect redirect timeout
Syntax Description
Defaults
redirect: 600 seconds
timeout: 14,400 secondsCommand Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
A virtual forwarder that is assigned a virtual MAC address by the AVG is known as a primary virtual forwarder. If the virtual forwarder has learned the virtual MAC address from hello messages, it is referred to as a secondary virtual forwarder.
The redirect timer sets the time delay between a forwarder failing on the network and the AVG assuming that the forwarder will not return. The virtual MAC address that the forwarder was responsible for replying to is still given out in Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) replies, but the forwarding task is handled by another router in the GLBP group.
Note
The zero value for the redirect argument cannot be removed from the range of acceptable values because preexisting configurations of Cisco IOS software already using the zero value could be negatively affected during an upgrade. However, be advised that a zero setting is not recommended and, if used, results in a redirect timer that never expires. If the redirect timer does not expire, then when a router fails, new hosts continue to be assigned to the failed router instead of being redirected to the backup.
The timeout interval is the time delay between a forwarder failing on the network and the MAC address for which the forwarder was responsible becoming inactive on all of the routers in the GLBP group. After the timeout interval, packets sent to this virtual MAC address will be lost. The timeout interval must be long enough to allow all hosts to refresh their ARP cache entry that contained the virtual MAC address.
Examples
The following example shows the commands used to configure GLBP group 1 on Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 with a redirect timer of 1800 seconds (30 minutes) and timeout interval of 28,800 seconds (8 hours):
Router# config terminalRouter(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0Router(config-if)# glbp 1 timers redirect 1800 28800glbp weighting
To specify the initial weighting value of the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) gateway, use the glbp weighting command in interface configuration mode. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
glbp group weighting maximum [lower lower] [upper upper]
no glbp group weighting
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default gateway weighting value is 100 and the default lower weighting value is 1.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
The weighting value of a virtual gateway is a measure of the forwarding capacity of the gateway. If a tracked interface on the router fails, the weighting value of the router may fall from the maximum value to below the lower threshold, causing the router to give up its role as a virtual forwarder. When the weighting value of the router rises above the upper threshold, the router can resume its active virtual forwarder role.
Use the glbp weighting track and track commands to configure parameters for an interface to be tracked. If an interface on a router goes down, the weighting for the router can be reduced by a specified value.
Examples
The following example shows the weighting of the gateway for GLBP group 10 being set to a maximum of 110 with a lower weighting limit of 95 and an upper weighting limit of 105:
interface fastethernet 0/0ip address 10.21.8.32 255.255.255.0glbp 10 weighting 110 lower 95 upper 105Related Commands
glbp weighting track
To specify a tracking object where the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) weighting changes based on the availability of the object being tracked, use the glbp weighting track command in interface configuration mode. To remove the tracking, use the no form of this command.
glbp group weighting track object-number [decrement value]
no glbp group weighting track object-number [decrement value]
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default decrement value is 10.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
This command ties the weighting of the GLBP gateway to the availability of its interfaces. It is useful for tracking interfaces that are not configured for GLBP.
When a tracked interface goes down, the GLBP gateway weighting decreases by 10. If an interface is not tracked, its state changes do not affect the GLBP gateway weighting. For each GLBP group, you can configure a separate list of interfaces to be tracked.
The optional value argument specifies by how much to decrement the GLBP gateway weighting when a tracked interface goes down. When the tracked interface comes back up, the weighting is incremented by the same amount.
When multiple tracked interfaces are down, the configured weighting decrements are cumulative.
Use the track command to configure each interface to be tracked.
Examples
In the following example, Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 tracks two interfaces represented by the numbers 1 and 2. If interface 1 goes down, the GLBP gateway weighting decreases by the default value of 10. If interface 2 goes down, the GLBP gateway weighting decreases by 5.
interface fastethernet 0/0ip address 10.21.8.32 255.255.255.0glbp 10 weighting track 1glbp 10 weighting track 2 decrement 5Related Commands
Specifies the initial weighting value of a GLBP gateway.
Configures an interface to be tracked where changes in the state of the interface affect the weighting of a GLBP gateway.
show glbp
To display Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) information, use the show glbp command in privileged EXEC mode.
show glbp [interface-type interface-number] [group] [state] [brief]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
Use the show glbp command to display information about GLBP groups on a router. The brief keyword displays a single line of information about each virtual gateway or virtual forwarder.
Examples
The following is sample output from the show glbp command:
Router# show glbpFastEthernet0/0 - Group 10State is Active2 state changes, last state change 23:50:33Virtual IP address is 10.21.8.10Hello time 5 sec, hold time 18 secNext hello sent in 4.300 secsRedirect time 1800 sec, forwarder time-out 28800 secAuthentication text "stringabc"Preemption enabled, min delay 60 secActive is localStandby is unknownPriority 254 (configured)Weighting 105 (configured 110), thresholds: lower 95, upper 105Track object 2 state Down decrement 5Load balancing: host-dependentThere is 1 forwarder (1 active)Forwarder 1State is Active1 state change, last state change 23:50:15MAC address is 0007.b400.0101 (default)Owner ID is 0005.0050.6c08Redirection enabledPreemption enabled, min delay 60 secActive is local, weighting 105The following is sample output from the show glbp command with the brief keyword specified:
Router# show glbp briefInterface Grp Fwd Pri State Address Active router Standby routerFa0/0 10 - 254 Active 10.21.8.10 local unknownFa0/0 10 1 7 Active 0007.b400.0101 local -Table 1 describes the significant fields shown in the displays.
Related Commands
track
To configure an interface to be tracked where the Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) weighting changes based on the state of the interface, use the track command in global configuration mode. To remove the tracking, use the no form of this command.
track object-number interface type number {line-protocol | ip routing}
no track object-number interface type number {line-protocol | ip routing}
Syntax Description
Defaults
The state of the interfaces is not tracked.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.2(14)S
This command was introduced.
12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
Usage Guidelines
Use the track command in conjunction with the glbp weighting and glbp weighting track commands to configure parameters for an interface to be tracked. If a tracked interface on a GLBP router goes down, the weighting for that router is reduced. If the weighting falls below a specified minimum, the router will lose its ability to act as an active GLBP virtual forwarder.
Examples
In the following example, Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 tracks whether serial interfaces 2/0 and 3/0 are up. If either serial interface goes down, the GLBP weighting is reduced by the default value of 10. If both serial interfaces go down, the GLBP weighting will fall below the lower threshold and the router will no longer be an active forwarder. To resume its role as an active forwarder, the router must have both tracked interfaces back up, and the weighting must rise above the upper threshold.
track 1 interface serial 2/0 line-protocoltrack 2 interface serial 3/0 line-protocolinterface fastethernet 0/0ip address 10.21.8.32 255.255.255.0glbp 10 weighting 110 lower 95 upper 105glbp 10 weighting track 1glbp 10 weighting track 2In the following example, Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 tracks whether serial interface 2/0 is enabled for IP routing, whether it is configured with an IP address, and whether the state of the interface is up. If serial interface 2/0 goes down, the GLBP weighting is reduced by a value of 20.
track 2 interface serial 2/0 ip routinginterface fastethernet 0/0ip address 10.21.8.32 255.255.255.0glbp 10 weighting 110 lower 95 upper 105glbp 10 weighting track 2 decrement 20Related Commands
Specifies the initial weighting value of a GLBP gateway.
Specifies an object to be tracked that affects the weighting of a GLBP gateway.
Glossary
AVF—active virtual forwarder. One virtual forwarder within a GLBP group is elected as active virtual forwarder for a specified virtual MAC address, and is responsible for forwarding packets sent to that MAC address. Multiple active virtual forwarders can exist for each GLBP group.
AVG—active virtual gateway. One virtual gateway within a GLBP group is elected as the active virtual gateway, and is responsible for the operation of the protocol.
GLBP gateway—Gateway Load Balancing Protocol gateway. A router or gateway running GLBP. Each GLBP gateway may participate in one or more GLBP groups.
GLBP group—Gateway Load Balancing Protocol group. One or more GLBP gateways configured with the same GLBP group number on connected Ethernet interfaces.
vIP—virtual IP address. An IPv4 address. There must be only one virtual IP address for each configured GLBP group. The virtual IP address must be configured on at least one GLBP group member. Other GLBP group members can learn the virtual IP address from hello messages.
Note
Refer to the Internetworking Terms and Acronyms for terms not included in this glossary.