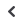
51
Cybersecurity in ASEAN: An Urgent Call to Action
AppendixB: ASEANCountriesCybersecurity
PolicyDevelopments
Notes: CERT is computer emergency response team; CII is critical information infrastructure; CNII is critical national information infrastructure;
CICC is the Cybercrime Investigation and Coordinating Center; VNISA is the Vietnam Information Security Association; NCIRT is National Cyber Incident
Response Teams; MAS is Monetary Authority of Singapore; MOUs are memorandums of understanding; BSSN is Badan Siber dan Sandi Negara;
MIC is Ministry of Information and Communications; AIS is American International School.
Source: A.T. Kearney analysis
ASEAN
Singapore
Malaysia
Thailand
Indonesia
Philippines
Vietnam
Rest of
ASEAN
No overarching
unifying strategy
in place
Strategy
No ASEAN-wide laws
in place
Legislation
No ASEAN-wide
governing bodies;
Annual ASEAN
Ministerial Conference
gathers key
stakeholders to
discuss cybersecurity
Governance and
operational
entities
Annual ASEAN CERT
Incident Drill to
enhance cooperation
and coordination
among ASEAN CERTs;
ASEAN Cybersecurity
Industrial Attachment
Programme
Sector-speci ic
and international
cooperation
ASEAN Cyber
Capacity Programme
(launched 2017) to
develop technical,
policy and strategy
building capabilities;
no collaborative
education strategy
National Cybersecurity
Strategy in place (2016)
with de inition of CII
sectors
Cybersecurity Bill
drafted (2017);
Computer Misuse and
Cybersecurity Act
(1993, amended 2017);
Personal Data
Protection Act
Cyber Security
Agency of Singapore;
NCIRT in place;
MAS for inancial
services
Singapore “soft lead”
for ASEAN cooperation;
multiple bilateral
agreements and MoUs;
MAS coordinates
inancial sector
collaboration
Comprehensive
awareness strategy
part of National
Cybercrime Action
Plan (2016); holistic
capacity-building
strategy in place;
professionalizing data
protection oicers
National Cybersecurity
Policy launched (2016)
with de inition of CNII
sectors
New cybersecurity law
being drafted (2017);
Computer Crime Act
(1997); Personal Data
Protection regulation
MDEC; Cybersecurity
Malaysia; entities
under Cybersecurity
Malaysia include
MyCERT, MyCC,
MyCSC, etc.
Multiple international
bilateral agreements
and MoUs;
public–private and
sector-speci ic
cooperation under
NCSP
CyberSAFE (public
awareness) and
CyberGuru (technical
knowledge); MDEC’s
strategic talent
development;
Cybersecurity
Malaysia’s local vendor
development
National cybersecurity
strategy drafted
National Cybersecurity
Bill proposed (2017);
Computer Crimes Act
(2007, amended 2017);
Personal Data
Protection Act
National Cybersecurity
Committee (proposed),
aims to protect CNII
sectors; ThaiCERT
No overarching
strategy in place;
Digital Forensics
Center coordinates
international training
cooperation
Digital Forensics Center
provides services and
training; MDES currently
promotes awareness;
no overarching strategy
in place
No national
cybersecurity strategy
No speciic
cybersecurity laws;
electronic information
and transactions law;
data protection
regulation
BSSN recently
launched (2017) to
consolidate activities,
not yet fully formed;
GOV CSIRT and
IDCERT; IDSIRTII/CC
Part of BSSN’s agenda,
no overarching strategy
in place; few bilateral
partnerships, for
example with Japan
Part of BSSN’s agenda,
no overarching strategy
in place; fragmented
training and awareness
by IDSIRTII/CC and
IDCERT
National Cybersecurity
Plan 2022 launched
(2017) with deinition
of CII sectors
No cybersecurity-
speciic laws;
Cybercrime Prevention
Act (2012); Data
Privacy Act (2012)
DICT is leading agency;
CICC monitors
cybercrime and
oversees CERT
Protection and
management of CII
under NCP 2022;
CICC to facilitate
international and
business-sector
cooperation
Under NCP 2022
agenda, no current
strategy in place;
plan to establish
CISO program in
government agencies
No national
cybersecurity strategy
Law on cybersecurity
drafted (2017);
no cybercrime or data
protection laws in place
MIC leads; AIS leads
activities on
information security;
VNCERT; VNISA
investigations, trainings,
and coordination
No strategy in place;
VNCERT and VNISA
work with private
sector
No overarching
strategy in place;
VNISA organizes info
security seminars,
events; MIC coordinates
awareness and training
No strategy in place
Largely absent; some
countries such as
Laos are drafting
cybercrime laws
Largely no governance
bodies; CERTs typically
act as national
cybersecurity agency:
response, awareness,
etc.
No public–private or
sector-speciic focus,
except Cambodia’s
emphasis on inancial
sector; fragmented
international
cooperation
No education strategy;
CERTs responsible for
general awareness
Awareness
and capacity-
building
Absent
Initiated or proposed
Established and operational