Cisco ATA 186 Basic Configuration
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
The Cisco Analog Telephone Adaptor (ATA) 186 is a handset-to-Ethernet adaptor that interfaces regular analog phones with IP-based telephony networks. The Cisco ATA 186 has two voice ports that were designed to support legacy analog touch-tone telephones. Unlike the regular Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports, these cannot be interfaced with a PBX as the Cisco ATA 186 cannot send out digits on these ports. Both voice ports can be used simultaneously as long as they are configured with different telephone numbers.
This document guides you through the initial setup of the Cisco ATA 186 when you use the H.323/SIP/SCCP image for the Cisco ATA. See the Related Information section of this document for configuration information about other protocols.
Prerequisites
Requirements
This configuration requires the Cisco ATA 186 to be at version 2.0 and later, with the H.323 feature set.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco ATA 186 with version 3.1.1 with the H.323 feature set
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure the ATA 186
There are three ways to configure the Cisco ATA 186:
Initial Setup for IP Connectivity
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server is enabled by default from version 2.x and later. When the DHCP field is set to 1, the Cisco ATA 186 contacts the DHCP server to get the IP address, subnet mask, and default route. You can verify which IP address was assigned to the Cisco ATA with the IVR menu. If you are unfamiliar with how to use the IVR system on the Cisco ATA, see the Configure the Cisco ATA 186 through the IVR section of this document. If the Cisco ATA fails to acquire an IP address from the DHCP server, skip to the Troubleshoot IP Connectivity Issues with VLAN Considerations section, as the default settings on the Cisco ATA might prevent it from receiving the proper IP configuration from the DHCP server.
If you wish to configure a static IP address on your Cisco ATA, then you must disable DHCP through the IVR system. You must then configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway also through the IVR. The example in the Configure the Cisco ATA 186 through the IVR section steps you through how to configure an IP address manually. This section also helps you understand how the IVR system is invoked and used.
Troubleshoot IP Connectivity Issues with VLAN Considerations
From version 2.15 and later, the default behavior of the Cisco ATA has changed in regards to the use of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) and 802.1Q VLAN tagging. These changes might affect the way in which the Cisco ATA obtains an IP address from a DHCP server. If your Cisco ATA fails to grab an IP address or it grabs an IP address from your Voice VLAN, then you might need to change the default value in the Opflags field. This can be done if you select IVR menu 323, and then enter in the value 106. If you configure this field through the web interface, then configure the hex value 0x6A. This disables CDP Discovery, 802.1Q tagging, and it prevents the Cisco ATA from requesting option 150 in its DHCP request. Incidentally, some DHCP servers do not respond to a client that requests an Option unknown to them, which can mean that the Cisco ATA is not able to acquire an IP address.
For a detailed discussion on Voice VLANS and how they are used, refer to Configuring Voice VLAN. For a detailed discussion on Auxiliary VLANS and how they are used, refer to the "Configuring Auxiliary VLANs on Catalyst LAN Switches" section of Configuring Voice over IP.
With the new default behavior, the Cisco ATA's traffic is routed to the Voice or Auxiliary VLAN on a Cisco Catalyst Switch that has this feature enabled. This happens because the Cisco ATA sends out its frames with a 802.1Q priority tag. Cisco Catalyst switches that have the Voice or Auxiliary VLAN feature enabled place this traffic in a different VLAN than traffic that comes into that switch port untagged. In addition, when this feature is enabled on a switch, all untagged traffic goes to the Native VLAN of the port. When you change the OpFlags field to 0x6A as described, the traffic from the Cisco ATA is untagged, and then is able to use the Native VLAN of the port.
For the purposes of this document, an Auxiliary or Voice VLAN is a second VLAN that is configured on a Catalyst switch port that enables you to separate your priority tagged traffic from regular traffic on the same switch port. The Native VLAN is the default VLAN where all untagged traffic goes.
Note: Not all Catalyst switches support Auxiliary and Voice VLANS.
Configure the Cisco ATA 186 through the IVR
Complete these steps in order to configure the Cisco ATA 186 through the IVR:
-
Connect an analog touch-tone phone to the port labeled PHONE 1 on the back of the Cisco ATA 186.
-
Pick up the handset on the phone, and then press the Clear function button on top of the Cisco ATA 186.
You should hear the initial IVR prompt.
Note: The IVR cannot be used or heard if your phone is connected to the second port on the Cisco ATA labeled PHONE 2.
-
You are prompted to enter a menu number followed by the # key. Key in the menu number using the touch-tone pad.
This table lists the menu options that you need in order to configure basic IP connectivity to the Cisco ATA:
IVR Menu Number Feature 1 IP Address (StaticIP) 2 Default Gateway (StaticRoute) 10 Subnet Mask (StaticNetMask) 20 (0 = Disable, 1 = Enable) DHCP (Dhcp) 80 Check IP Address Note: Press the * key to indicate a delimiter (dot). For example, 192*168*3*1 is used to enter an IP address 192.168.3.1 on the touchpad.
Note: When you enter values for a field that is in hexadecimal, you must convert these values to decimals in order to enter it into the IVR system. For example, to enter the hex value 0x6A, key in the number 106 in the IVR.
-
Press the # key after you have entered the value. If you do not press #, the system automatically times out after ten seconds.
You hear a recording of the value you entered, followed by a request to press one of these keys:
-
1—Change your entered value.
-
2—Review your entered value.
-
3—Save your entered value.
-
4—Review the current saved value.
-
-
After you complete the configuration through the IVR, press the # key to exit.
Note: For a complete list of IVR commands, refer to the Voice Menu Codes chapter of Cisco ATA Analog Telephone Adaptor Administrator’s Guides.
Configure the ATA 186 through a Web Server
Complete these steps in order to configure the ATA 186 through a web server:
Note: Once you have IP connectivity from the Cisco ATA 186 to any PC, you are able to perform these additional configurations through the web server.
Note: If you are unable to access the web server, make sure you can ping the Cisco ATA 186 from the PC. If you are unable to ping the Cisco ATA 186, confirm IP connectivity (configured IP address, subnet mask, and network route). In order to confirm that you are using the correct IP address, press 80# on the IVR. For IVR commands, to check the other parameters, refer to the Voice Menu Codes chapter of Cisco ATA Analog Telephone Adaptor Administrator's Guides. Make sure the configured IP address is the one you use for web access.
-
Verify the IP address used by the internal web server on the Cisco ATA 186 through the IVR. In order to do this, select menu number 80#.
-
From the PC, open a Web browser and enter this URL: http://<ipaddress_of_ata>/dev.
This window appears:

-
Select the values for the items that you want to configure.
-
Click apply to save your changes. The Cisco ATA 186 takes ten seconds to reconfigure itself. You need to reload the page before you can make any further changes.
-
Close the web browser.
Configure the ATA 186 through a TFTP Server
This method of provisioning makes it easier to scale large deployments of Cisco ATA 186 adaptors. When the Cisco ATA 186 is powered up, it contacts the TFTP server for a specific profile to download. The Cisco ATA 186 has an internal local nonvolatile cache of the profile so that if the TFTP server is not reachable after three attempts, it uses its own locally cached profile from the previous configuration to continue normal operation. A TFTP server needs to host a profile (configuration) for each Cisco ATA 186.
Create the Profile
Complete these steps in order to create the profile.
-
Modify the example text file (for an H.323 image, the file name is h323_example.txt ) with the required configuration changes and save as a new file, such as h323_example_new.txt.
The configuration changes depend on the network in which the Cisco ATA 186 is used. For more information, refer to the documents listed in the Related Information section.
The example text file is included in the latest Cisco ATA 186 software release zip file located at the Cisco ATA186 Analog Telephone Adaptor Software Download section of Cisco.com.
Note: The Cisco ATA 186 cannot take the configuration directly from the text file. You need to convert the text file into binary format. Use the cfgfmt.exe application to create the binary version of the file.
-
Name the binary profile file.
The binary profile file must be named as "ataxxxxxxxxxxxx ", where each xx is the two-digit lowercase hex representation of each integer in the MAC address of the Cisco ATA 186. For example, if the MAC address of the Cisco ATA 186 is 1.2.3.4.5.6, the file name should be ata010203040506.
Note: The file can be optionally encrypted for security reasons with option e of the cfgfmt.exe application. When you use encryption, the Cisco ATA 186 must be configured with the right key to be able to decrypt the file. The field to be configured is EncryptKey. A value of 0 in this field indicates that no encryption was made on the incoming profile from the TFTP server. In order to specify the key used to encrypt the profile from the TFTP server, type an alphanumeric string (eight characters maximum) in this field.
-
Store the configuration file on the TFTP server.
This example shows the use of the cfgfmt.exe application to create the binary version of the text file:
D:\Documents\My Documents\voice\ata>cfgfmt.exe usage: cfgfmt [-eRc4passwd] [-tPtagFile] input output -eRc4Passwd -- use Rc4Passwd to encrypt or decrypt input -tPtagFile -- specify an alternate PtagFile path D:\Documents\My Documents\voice\ata>cfgfmt.exe h323_example_new.txt ata010203040506
Configure the Cisco ATA 186 to Download its Profile from the TFTP Server
The DHCP server can be configured to provide the TFTP server's URL and file name to the Cisco ATA 186. In the absence of a DHCP server that provides such information, the TFTP server's URL must be manually provisioned either through a web server or IVR. This table lists the fields that need to be provisioned:
| Parameter | Description | IVR Access Code | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| CfgInterval | Specifies the number of seconds (interval) between each configuration update. For example, when you use TFTP for provisioning, the Cisco ATA 186 contacts the TFTP server each time the interval expires to get its configuration file the next time the box is idle. You can set the CfgInterval to a random value to achieve random contact intervals from an individual Cisco ATA 186 to the TFTP server. | 80002 | 3600 (1 hour) |
| EncryptKey | Determines if encryption is to be made on the incoming profile from the TFTP server. An encryption key can be configured which must be the same as the one used for the encryption of the configuration file by the cfgfmt.exe application. This enables the Cisco ATA 186 to decrypt the file. The encryption algorithm used is rc4. | 320 | 0 |
| TFTP URL |
The IP address or URL of the TFTP server to use.
This is needed if the DHCP does not provide the TFTP address.
You can optionally include the path prefix to the TFTP file to download. For
example, if the TFTP server IP address is 192.168.2.170 or www.cisco.com, and
the path to download the TFTP file is in /ata186, then you can specify the URL
as 192.168.2.170/ata186 or
www.cisco.com/ata186.
Note: From the IVR, you can only enter the IP address; from the web server, you can enter the actual URL. |
905 | 0 |
Note: You can also update the Cisco ATA 186 profile from the TFTP server before the CfgInterval expires. To do this, open your Web browser and enter http://<ipaddress>/refresh where ipaddress is the IP address of the Cisco ATA 186 you want to update). The Cisco ATA 186 responds with an OK page if idle; otherwise, the Cisco ATA 186 responds with a later page.
Password Protection
In order to ensure that the Cisco ATA 186 configuration is protected, you can set the password.
Set the Password in Web Configuration Mode
Use this procedure to set your password in Web Configuration mode:
-
Set the value of the UIPassword field to 1, then click the apply button at the bottom of the page.
Note: The "1" entered is NOT a password but only enables the password page. At this time the password is still "0".
-
The "Cisco ATA 186 Password Protected Page" (as shown here) appears and prompts you for the UIPassword. At this point, you are also able to change it to any other alphanumeric password.
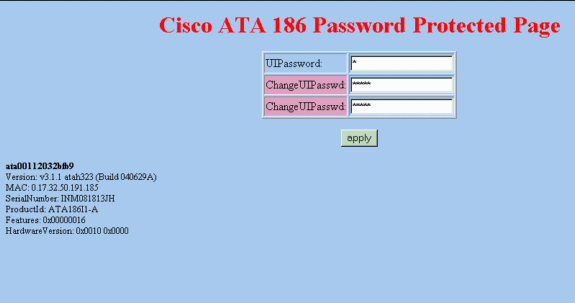
Note: The Password is still "0". You can now change the password to say "12345" on this page.
This is an example of how you can change the password:
-
Start with the UIPassword set to 0.
-
Change the UIPassword to 12345.
-
After you hit the apply button, you now see five periods in the UIPassword field of Web Configuration page.
-
You are now prompted for a password when you try to access the Cisco ATA 186 through the Web Configuration mode.
Set the Password in IVR Mode
Use this procedure to set the password in IVR mode:
-
Pick up the handset on the phone, and then press the Clear function button on top of the Cisco ATA 186.
You should hear the initial IVR prompt.
-
Dial 7387277#, which is the menu option to change the password.
-
Enter the new password followed by the # key.
You are now prompted for a password when you try to access the Cisco ATA 186.
Clear the Password
In order to clear the password, change the Password field to 0.
Note: If you change the UIPassword field in the Web Configuration page, this change prompts you for the "Password" Page. The password is still "12345" or whatever you changed it to. Now, you need to enter 12345 for UIPassword and then change New Password to 0 in order to disable password protection
Complete these steps:
-
Start with the UIPassword set to 12345.
-
Change the UIPassword to 0.
-
After you hit the Apply button, you now see one period in the UIPassword field of the Web Configuration page, and the password page is disabled.
Recover Forgotten Password
The only way to recover a forgotten password is to reset the entire configuration of the Cisco ATA 186
There are two codes to reset the Cisco ATA 186, depending on the software version:
For software versions earlier than 2.xx, use code 444.
For software versions 2.xx and later, use code 322873738 (FACTRESET).
Note: If the ATA does not reset to the factory default settings, make sure you have turned off the use of the TFTP server for provisioning. If you use a TFTP server for provisioning, follow all of these steps to reset the Cisco ATA 186 to the factory default settings. If you do not use a TFTP server for provisioning, follow only steps 2 through 5 in this procedure to reset the Cisco ATA 186 to the factory default settings.
Note: This reset procedure does not work if the ATA is configured to prompt the user for the UIPassword when the user attempts to perform a factory reset or upgrade using the Voice Configuration menu. (The OpFlags Parameter Bits 28-31 have been set to a value of 6.) In this event, you need the original password in order to reset the ATA. For more information on the OpFlags Parameter settings, refer to the OpFlags section of Cisco ATA 186 and Cisco ATA 188 Analog Telephone Adaptor Administrator's Guide (H.323)(2.15).
Perform these steps:
-
Unplug the Ethernet cable.
-
Pick up the telephone handset.
-
Press the Function button on top of the ATA.
-
Enter 322873738#* for release 2.xx or 444#* for other releases.
-
Hang-up.
-
Pick up the telephone handset.
-
Press the Function button on top of the ATA.
-
Enter 305# in order to disable the use of TFTP.
-
When prompted to enter a value, enter 0#.
-
When prompted with the option to save, enter 3.
-
Hang-up.
-
Reconnect the Ethernet cable.
For more information, refer to the "Resetting the Cisco ATA to Factory Default Values" section of Configuring the Cisco ATA for SCCP. For all Cisco ATA releases before build 020514a, refer to Cisco Security Advisory: ATA-186 Password Disclosure Vulnerability.
Set up the Cisco ATA 186 for Collecting Debugs
In order to collect the debug output from the Cisco ATA 186, you must configure the ATA 186 to send debug information to the PC as shown here:
-
In the NPrintf field, enter the IP address and port number of the PC to which debug messages are to be sent. Use this syntax to do so: IP_Address.Port Number where port is 9001. If another process on your PC already uses port 9001, you can use some other value (legal values are from 1024 to 65535). If no port value is entered, the default value is 9001.
For example, 192.168.2.159.9001.
Note: If this field is set to 0 or 0.0.0.0.0, the Cisco ATA 186 does not send any debug messages.
-
On the PC, execute prserv.exe from the DOS prompt, and debugs should begin to show up.
This executable file is included in the latest Cisco ATA 186 software release zip file located at the Cisco ATA186 Analog Telephone Adaptor Software Download section of Cisco.com.
Upgrade the Software
You can upgrade the software image of your Cisco ATA 186 remotely. In order to upgrade the software, two methods are available:
-
Use the Executable file method
-
Use the TFTP server method
For detailed information on how to upgrade your Cisco ATA image, refer to Upgrading Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs).
Verify
In order to verify your Cisco ATA configuration with the web server, see the Configure the Cisco ATA 186 through a Web Server section of this document. You can also verify the configuration using the IVR. For the IVR menu numbers used for verification, refer to the Voice Menu Codes chapter of Cisco ATA Analog Telephone Adaptor Administrator's Guides.
Troubleshoot
For troubleshooting the Cisco ATA configuration or upgrade, you can use the prserv.exe tool. For more information on this, see the Set up the Cisco ATA 186 for Collecting Debugs section of this document. Additionally, some of the common issues and frequently asked questions on Cisco ATA 186 are discussed in Cisco ATA 186 FAQ and Common Issues.
Related Information
- Configuring and Troubleshooting an ATA 186 with Cisco IOS Gatekeepers
- Configuring and Troubleshooting Cisco ATA 186 with an IOS Gateway
- Cisco ATA 186 and Cisco ATA 188 Analog Telephone Adaptor At A Glance
- Upgrading Analog Telephone Adaptors (ATAs)
- Unified Communications Support
- Troubleshooting Cisco IP Telephony
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
02-Jan-2020 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback