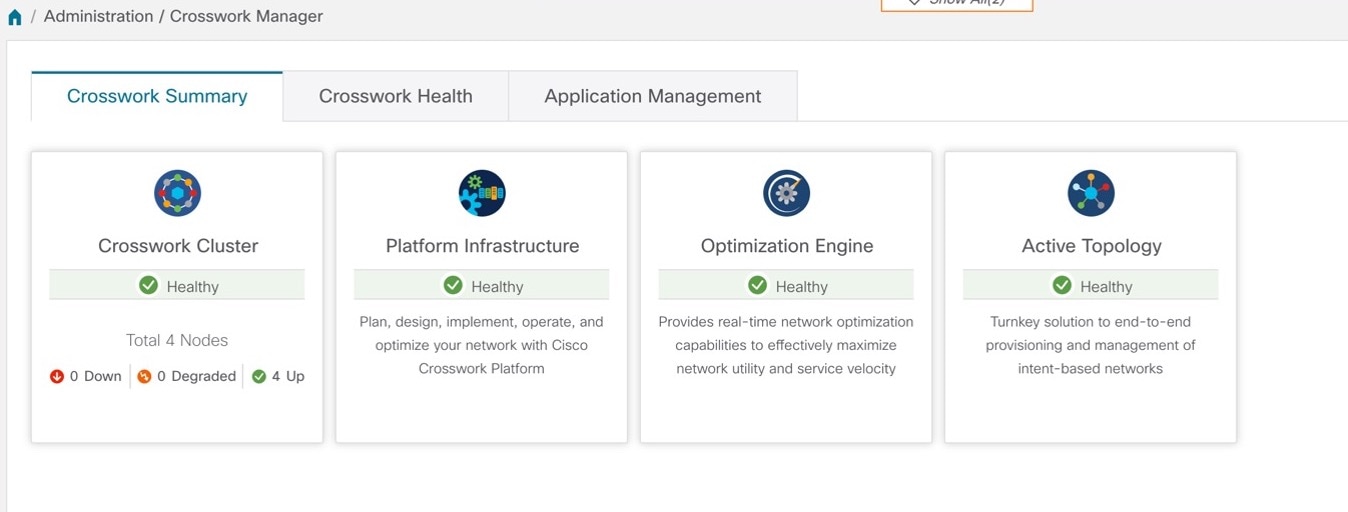
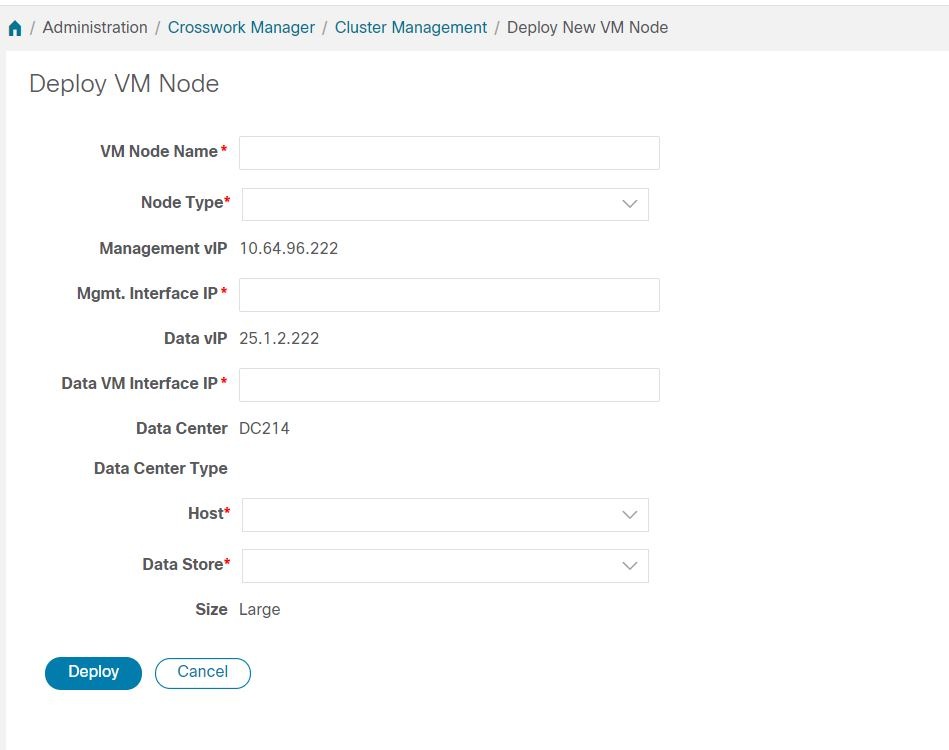
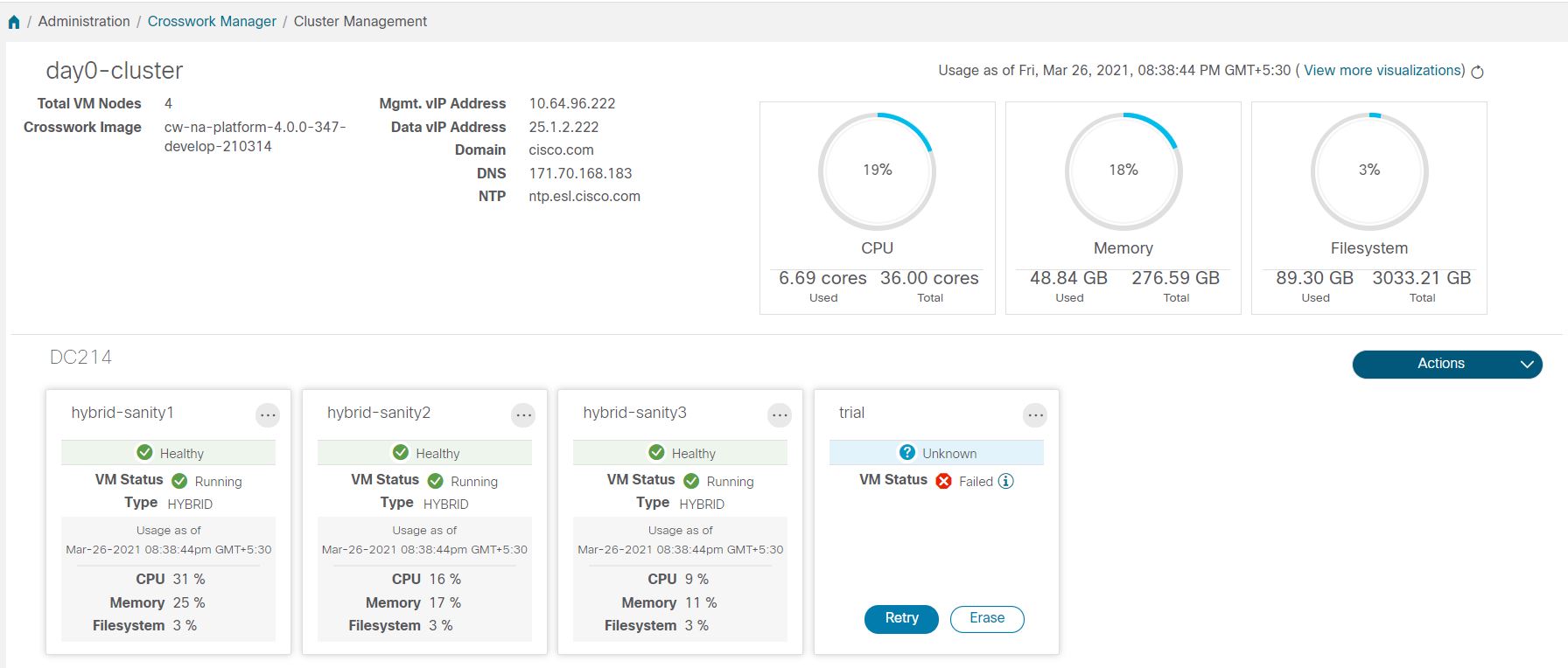
Cluster Management Overview
The Cisco Crosswork platform uses a cluster architecture. The cluster distributes platform services across a unified group of virtual machine (VM) hosts, called nodes. The underlying software architecture distributes processing and traffic loads across the nodes automatically and dynamically. This architecture helps Cisco Crosswork respond to how you actually use the system, allowing it to perform in a scalable, available, and extensible manner.
For the 4.0 release, a single cluster consists of a minimum of three nodes, all operating in a hybrid configuration. These three hybrid nodes are mandatory for all Cisco Crosswork deployments. If you have more demanding scale requirements, you can add up to three more nodes, all operating in a worker configuration.
As a Cisco Crosswork administrator, you have full access to all cluster configuration and monitoring functions.



 Feedback
Feedback