Installation Workflow
To set up Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine and Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway complete the below installation tasks in the order of their listing:
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
This section contains the following topics:
To set up Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine and Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway complete the below installation tasks in the order of their listing:
This section explains the procedure to install using vCenter.
Before you begin, ensure that:
You are creating the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM on VMware ESXi 6.5 (Update 2 or later), and using the VMware vCenter Server 6.5 (Update 2d or later) or 6.7 (Update 3b).
 Note |
VMware vCenter supports vSphere Web Client (flash mode) and vSphere Client (HTML5 mode), however vSphere Web Client (flash mode) is recommended for the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM deployment and is explained in this procedure. The vSphere Client (HTML5 mode) is supported only on VMware vCenter Server 6.7 Update 3b. |
You have a public IP address (IPv4) to assign to the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM's management network virtual interface. The default gateway must be reachable via this IP address.
 Note |
It is preferred that the DNS and NTP servers are reachable via the Management Network Interface. However, it is not mandatory. The only requirement is that they are reachable on one of the network interfaces connected to the server. |
You have a public or private IP address (IPv4) to assign to the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM's data network virtual interface. This IP address must be able to reach the gateway address for the network where Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway will be installed.
The NTP server you will use to synchronize the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM clock is reachable on the network.
 Note |
During the installation and first-time booting of the VM, the links to the specified gateways will be validated. VM configuration will fail if the links are inaccessible. |
Also during installation, Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine creates two special administrative IDs:
The virtual machine (VM) administrator, with the username cw-admin, and the default password cw-admin. Data center administrators use this ID to log in to and troubleshoot the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM. You will use it to verify that the VM has been properly set up (see Verify the VM Configuration).
The Crosswork administrator, with the username admin and the default password admin. Product administrators use this ID to log in to and configure the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine user interface, and to perform special operations, such as stopping and restarting services.
While this section describes installation, you must also set up Cisco SR-PCE in order to use Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. Refer to the appropriate device configuration guide (for example, Segment Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers).
| Step 1 |
Download the latest available Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine image file (*.ova) to your system.
|
||
| Step 2 |
With VMware ESXi running, log in to the VMware vSphere Web Client. On the left side, choose the ESXi host on which you want to deploy the VM, then select , similar to the following figure. 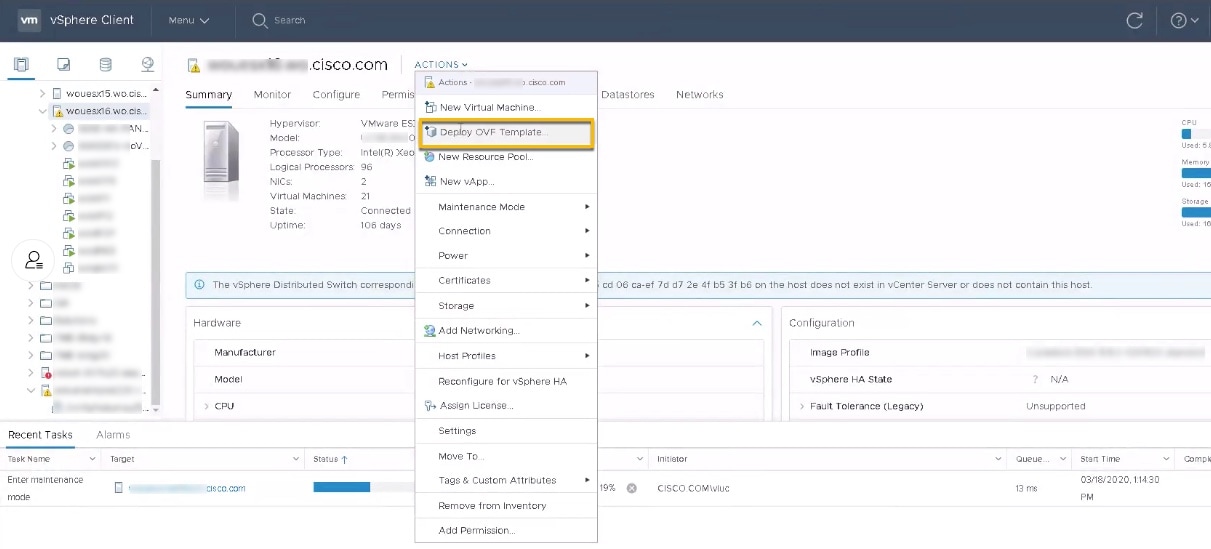 |
||
| Step 3 |
The VMware Deploy OVF Template wizard appears and highlights the first step, 1 - Select template, similar to the following figure. Click Browse to navigate to the location where you downloaded the OVA image file and select it. Once selected, the file name is displayed in the window. 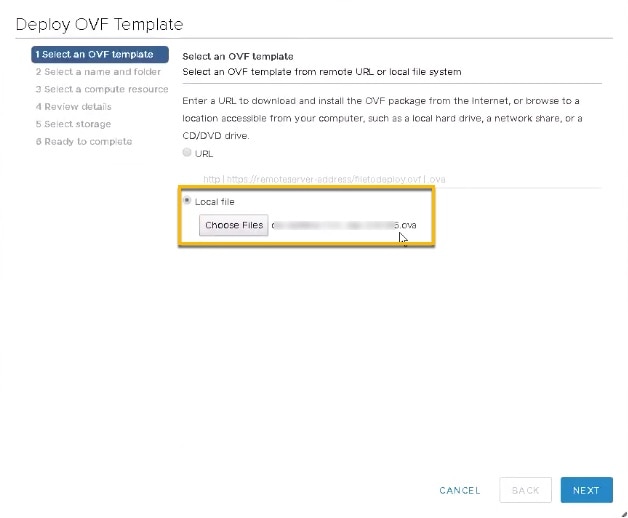 |
||
| Step 4 |
Click Next to go to 2 - Select name and location, as shown in the following figure. Enter a name for the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM you are creating. Cisco recommends that you include the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine version and build number in the name (for example: CW Optimization Engine 1.1 Build 123). 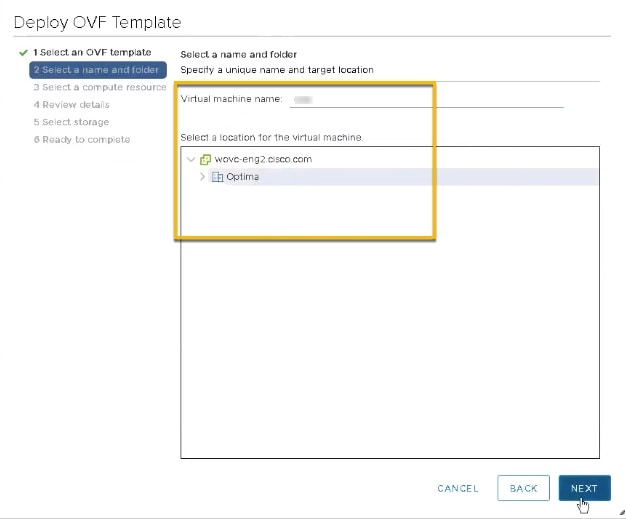 |
||
| Step 5 |
Click Next to go to 3 - Select a resource, similar to the following figure. Choose the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM’s host. 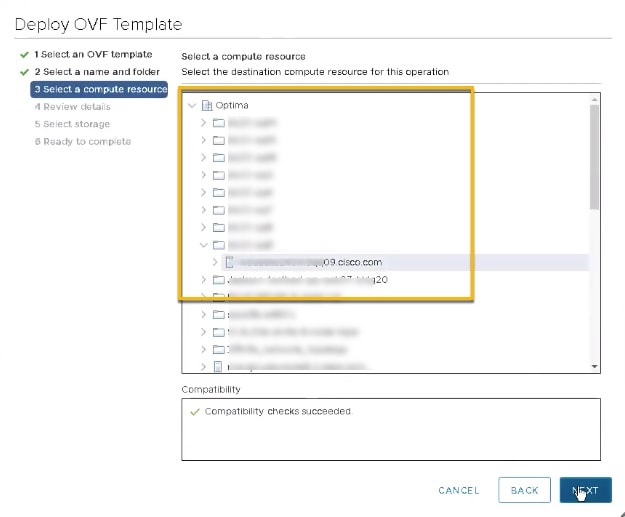 |
||
| Step 6 |
Click Next. The VMware vCenter Server validates the OVA. Network speed will determine how long validation takes. When validation is complete, the wizard moves to 4 - Review details, similar to the following figure. Take a moment to review the OVF template you are deploying. Note that this information is gathered from the OVF and cannot be modified. 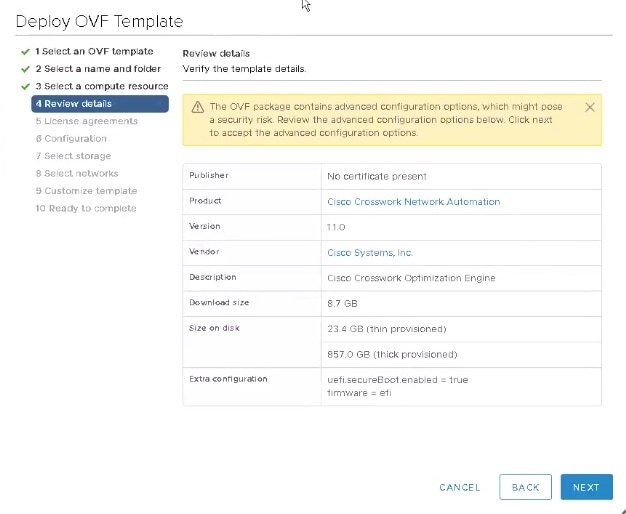 |
||
| Step 7 |
Click Next to go to 5 - Accept license agreements. Review the End User License Agreement and click on Accept before you continue. |
||
| Step 8 |
Click Next to go to 6 - Select configuration, similar to the following figure. Select the desired deployment configuration (IPv4). IPv6 or an IPv4 network on a single interface is not currently supported. |
||
| Step 9 |
Click Next to go to 7 - Select Storage, similar to the following figure. Select the relevant option from the Select virtual disk format drop-down list. From the table, choose the datastore you want to use and review its properties to ensure there is enough available storage.
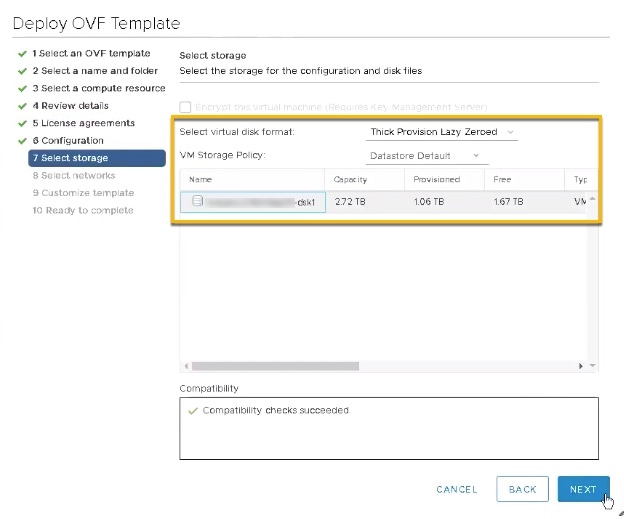 |
||
| Step 10 |
Click Next to go to 8 - Select networks, similar to the following figure. In the dropdown table at the top of the page, choose the appropriate destination network for the source Data Network and Management Network, respectively. 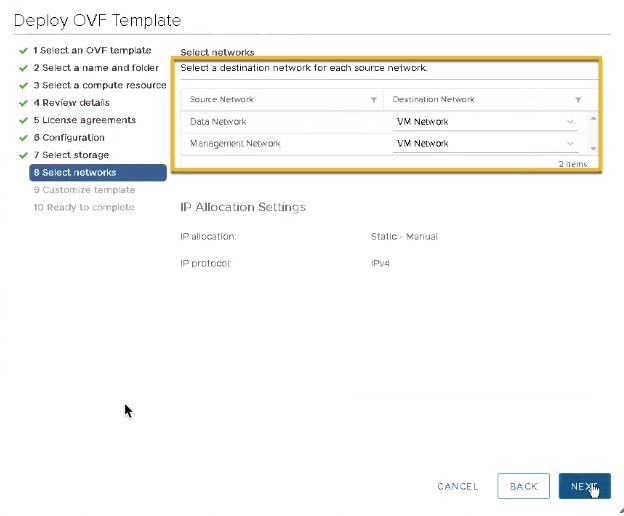 |
||
| Step 11 |
Click Next to go to 9 - Customize template. |
||
| Step 12 |
Expand the Management Network settings. According to your deployment configuration, the fields displayed are different, similar to the following figures. Make relevant entries for IPv4 deployment (Management IPv4 Address, Management IPv4 Gateway, and Management IPv4 Netmask fields). 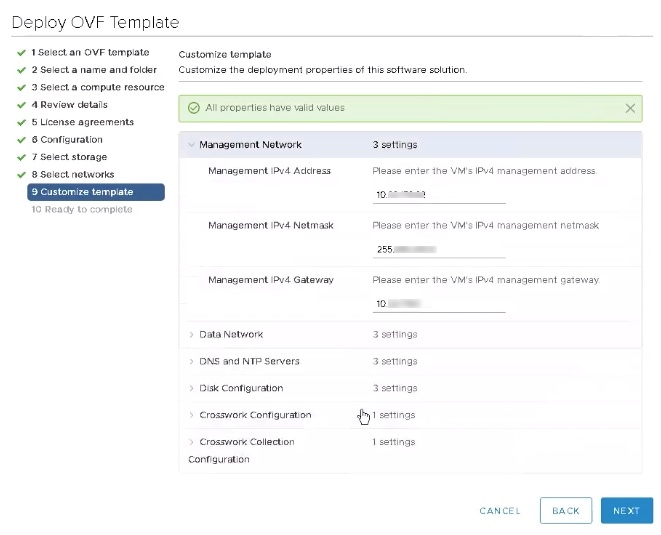 |
||
| Step 13 |
Expand the Data Network settings. According to your deployment configuration, the fields displayed are different, similar to the following figures. Make relevant entries for IPv4 deployment (Data IPv4 Address, Data IPv4 Gateway, and Data IPv4 Netmask fields) respectively. 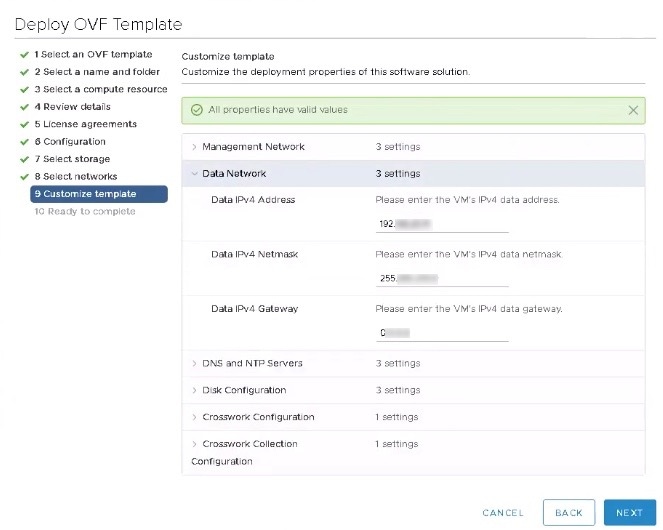 |
||
| Step 14 |
Expand the DNS and NTP Servers settings, similar to the following figure. According to your deployment configuration (IPv4), the fields displayed are different. Make entries in three fields:
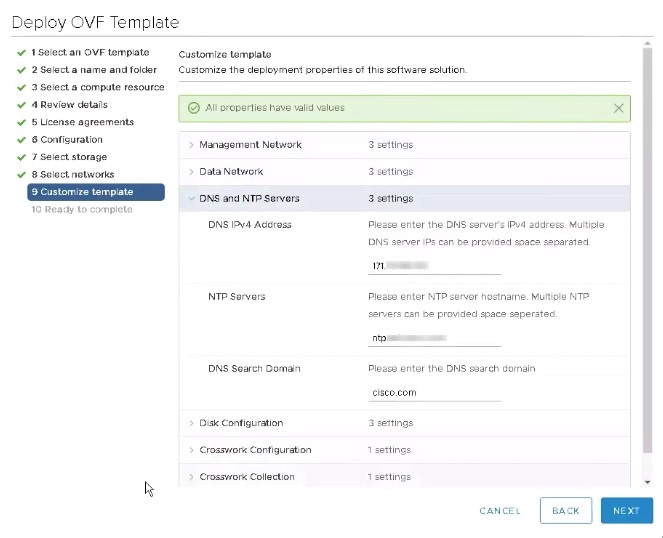 |
||
| Step 15 |
Disk Configuration settings allows you to adjust the amount of storage space available to Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. The default settings should work for most environments. For assistance in adding additional storage, contact the Cisco Customer Experience team.  |
||
| Step 16 |
Expand the Crosswork Configuration and enter any legal disclaimer text (users will see this text if they log into the CLI). |
||
| Step 17 |
Expand the Crosswork Collection Configuration settings, similar to the following figure.  |
||
| Step 18 |
Click Next to go to 10 - Ready to Complete, similar to the following figure (template name will depend on the version you are installing). Review your settings and then click Finish if you are ready to begin deployment.  |
||
| Step 19 |
Wait for the deployment to finish before continuing. To check on the deployment status:
|
||
| Step 20 |
After the deployment tasks are complete, check the host's VM settings to permit boot from EFI Firmware: |
||
| Step 21 |
You can now power on the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM to complete the deployment process. Expand the host’s entry so you can click the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM and then choose , similar to the following figure. 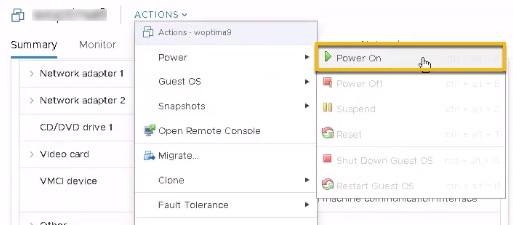 From this point, it will take 20 minutes for the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine VM to become operational. Please wait for the process to finish before continuing. |
Before trying to log in to the new installation, verify that the VM is properly configured. You will be prompted to change the VM administrator's password during first login via the console.
| Step 1 |
After the VM is powered on, wait for 20 minutes, and then launch the console. |
| Step 2 |
In the password prompt, enter the default cw-admin user password, cw-admin. When prompted to change the cw-admin user's password, enter the default password again for verification. Then enter and confirm the new password as prompted. |
| Step 3 |
If you see instructions to check
|
To log in to the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine web-based user interface from a browser, perform these steps. If you are unable to display the user interface, see Troubleshoot the Installation.
| Step 1 |
Launch one of the supported browsers (see Supported Web Browsers). |
| Step 2 |
In the browser's address bar, enter: The Log In window opens. When you access Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine for the first time, some browsers display a warning that the site is untrusted. When this happens, follow the prompts to add a security exception and download the self-signed certificate from the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine server. After you add a security exception, the browser accepts the server as a trusted site in all future login attempts. If you want to use a CA signed certificate, see the "Manage Certificates"section in the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine User Guide. |
| Step 3 |
Log into Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine as follows:
|
| Step 4 |
To exit the web GUI, close the browser window or click |
The following table lists common problems experienced while installing Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, and approaches to identifying the source of the problem and solving it.
 Note |
You need to login as a super user to perform the troubleshooting. |
|
Issue |
Action |
|---|---|
|
Cannot Connect to the VM |
|
|
VM cannot be reached by the provided gateways due to IP misconfiguration |
1. You will see error messages in the login banner indicating this problem when you try to connect to the VM via SSH following the steps in as explained in Verify the VM Configuration. 2. Redeploy the VM from scratch, using the correct IP configuration. |
|
Configure NTP after installation |
|
|
User wants to configure NTP after the VM deployment, in the scenario of giving the wrong NTP address, or the server being down. |
1. You need to edit the /etc/chrony/chrony.conf file. Add the pool line at the bottom of the file with relevant NTP server details. 2. Restart the chronyd service ( 3. Please verify that the NTP server has been configured ( |
|
Cannot Display the User Interface |
|
|
Browser does not display the login screen. |
1. Make sure you are using a supported browser (see Supported Web Browsers and that you entered the correct IP address in the browser (this should be the same as the management IP4 address and port number (30603) you entered during installation). 2. Log in to the VM using SSH, as explained in Verify the VM Configuration. 3. At the prompt, enter the command collect. This generates a file. 4. Open a ticket with the Cisco Customer Experience team and attach the file to the ticket. |
|
Unable to resolve other network addresses on the local network. |
1. While connected to the VM, open the file /etc/resolv.conf file and check that it contains the correct DNS name server and search domain. 2. If it does not, redeploy the VM using the correct DNS name server and search domain configuration. |
|
Running |
1. While connected to the VM, open the file /etc/hosts file and check if the IP address assigned to the VM is correct. 2. If the address is wrong, redeploy the VM using the correct management IP address. |
|
Running |
1. While connected to the VM, check the login banner for any error messages. 2. If there are error messages in the login banner, they will be recorded in /var/log/firstBoot.log file, along with recommended remediation steps. Open the log and follow the steps given for the error message found in the banner. 3. If this does not help, run |
|
Running |
1. Check for user input errors in the /var/log/boot.log file and perform the log's recommended remediation steps. 2. If this does not help, please contact the Cisco Customer Experience team. |
|
Running |
Please contact the Cisco Customer Experience team. |
|
Able to Display the User Interface |
|
|
I cannot log in. |
1. Make sure you are using the Crosswork administrator default user ID and password (admin and admin). 2. If the Crosswork administrator default password has already been changed, use the new password. |
|
I can log in but cannot access some features. |
Make sure all the applications and their underlying services are up and running by selecting and checking the status of the applications and services. See the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine User Guide topic "Monitor Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure and Resources". |
|
Crosswork Manager shows one or more applications or their underlying services are not running. |
1. In Crosswork Manager, check the description of the application or service issue and, if possible, try restarting the application or service. See the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine User Guide topic "Monitor Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure and Resources". 2. Gather log and metric information about the application or service with issues. See the User Guide topic "View, Control and Log Cisco Crosswork Applications and Services". 3. Contact Cisco Customer Experience team. |
|
CPU Overcommitment |
|
|
CPU/memory overcommitment occurs when the vCPUs are running on a host are more than the total number of physical processor cores in that host. VMware vCenter/ESXi allows this for the flexibility in deploying and running the VMs on physical hosts. It is natural to assume that the vCenter users will try to maximize the physical resources usage by deploying and running a reasonably high amount of VMs on a specific ESXi host. However, it can lead to a problem manifested in a "soft lockup" situation, where a VM will not be able to get a vCPU allocated in a reasonable amount of time. |
|
Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway is initially deployed as a VM called Base VM (containing only enough software to register itself with Crosswork).
Before installing Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway, it is helpful to be familiar with Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway OVF Parameters and Deployment Scenarios.
You can use either of the following two ways to install Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway:
Before you begin installing Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway, read below about OVF parameters and possible deployment scenarios.
 Note |
|
|
OVF Parameter |
Description |
Deployment Scenario |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Host Information |
||||||||
|
Hostname* |
Hostname of the server specified as a fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
|
|||||||
|
Description* |
A detailed description of the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance. |
|||||||
|
Label |
Label used by Crosswork to categorize and group multiple Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instances. |
|||||||
|
Private Key URI |
SCP URI to private key file for session key signing. You can retrieve this using SCP (user@host:path/to/file). |
Crosswork uses self-signed certificates for handshake with Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway. These certificates are generated upon installation. However, if you want to use third-party or your own certificate files, then you must input these three parameters.
|
||||||
|
Certificate File URI |
SCP URI to PEM formatted signing certificate chain for this VM. You can retrieve this using SCP (user@host:path/to/file). |
|||||||
|
Certificate File and Key Passphrase |
SCP user passphrase to retrieve the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway PEM formatted certificate file and private key. |
|||||||
|
Passphrases |
||||||||
|
dg-admin Password* |
The password you have chosen for the dg-admin user. |
|||||||
|
dg-oper Password* |
The password you have chosen for the dg-oper user. |
|||||||
|
||||||||
|
1Management IPv4 Address |
||||||||
|
Management IPv4 Method* |
How the management interface gets its IPv4 address. |
|||||||
|
Management IPv4 Address |
IPv4 address of the management interface. |
|||||||
|
Management IPv4 Netmask |
IPv4 netmask of the management interface in dotted quad format. |
|||||||
|
Management IPv4 Gateway |
IPv4 address of the management gateway. |
|||||||
|
1Management IPv6 Address |
||||||||
|
Management IPv6 Method* |
How the Management interface gets its IPv6 address. |
|||||||
|
Management IPv6 Address |
IPv6 address of the management interface. |
|||||||
|
Management IPv6 Netmask |
IPv6 prefix of the management interface. |
|||||||
|
Management IPv6 Gateway |
IPv6 address of the management gateway. |
|||||||
|
1Southbound Data IPv4 Address |
||||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv4 Method* |
How the southbound data interface gets its IPv4 address. |
|||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv4 Address |
IPv4 address of the southbound data interface. |
|||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv4 Netmask |
IPv4 netmask of the southbound data interface in dotted quad format. |
|||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv4 Gateway |
IPv4 address of the southbound Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway. |
|||||||
|
1Southbound Data IPv6 Address |
||||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv6 Method* |
How the southbound data interface gets its IPv6 address. |
|||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv6 Address |
IPv6 address of the southbound data interface. |
|||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv6 Netmask |
IPv6 netmask of the southbound data interface in dotted quad format. |
|||||||
|
Southbound Data IPv6 Gateway |
IPv6 address of the southbound data gateway. |
|||||||
|
1Northbound Data IPv4 Address |
||||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv4 Method* |
How the Northbound data interface gets its IPv4 address. |
|||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv4 Address |
IPv4 address of the Northbound data interface. |
|||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv4 Netmask |
IPv4 netmask of the Northbound data interface in dotted quad format. |
|||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv4 Gateway |
IPv4 address of the Northbound data gateway. |
|||||||
|
1Northbound Data IPv6 Address |
||||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv6 Method* |
How the Northbound data interface gets its IPv6 address. |
|||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv6 Address |
IPv6 address of the Northbound data interface. |
|||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv6 Netmask |
IPv6 netmask of the Northbound data interface in dotted quad format. |
|||||||
|
Northbound Data IPv6 Gateway |
IPv6 address of the Northbound data gateway. |
|||||||
|
DNS and NTP |
||||||||
|
DNS Address* |
Space-delimited list of IPv4/IPv6 addresses of the DNS server accesible from the management interface. |
|||||||
|
DNS Search Domain* |
DNS search domain |
|||||||
|
NTP Servers* |
Space-delimited list of IPv4/IPv6 addresses or hostnames of the NTP servers accessible from the management interface. |
You must enter a value here, such as pool.ntp.org. NTP server is important for time synchronization between Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM and Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. Using a non-functional or dummy address may cause issues when Crosswork and Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway try to communicate with each other. If you are not using an NTP server, ensure that time gap between Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway and Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine is not more than 10 minutes. Else, Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway will fail to pull images. |
||||||
|
Syslog Servers |
||||||||
|
Server Address |
IPv4 or IPv6 address of a syslog server accessible from the management interface.
|
If you want to use an external syslog server, you must specify these 7 settings.
|
||||||
|
Syslog Port |
Port number of the syslog server. |
|||||||
|
Syslog Protocol |
Use UDP, TCP, or RELP when sending syslog. |
|||||||
|
Use Syslog over TLS? |
Use TLS to encrypt syslog traffic. |
|||||||
|
TLS Peer Name |
Syslog server's hostname exactly as entered in the server certificate SubjectAltName or subject common name. |
|||||||
|
Syslog Root Certificate File URI |
PEM formatted root cert of syslog server retrieved using SCP. |
|||||||
|
Syslog Certificate File Passphrase |
Password of SCP user to retrieve Syslog certificate chain. |
|||||||
|
Controller Settings |
||||||||
|
Controller IP* |
IP address of the Crosswork controller i.e., Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine.
|
|||||||
|
Controller Port* |
Port of the Crosswork controller i.e., Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. |
|||||||
|
Controller Signing Certificate File URI |
PEM formatted root cert of Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine to validate signing certs retrived using SCP. PEM file is generated by Crosswork and is available at the following location:
|
|||||||
|
SSL/TLS Certificate File URI |
Crosswork controller PEM formatted SSL/TLS certificate file retrieved using SCP. |
|||||||
|
Controller Certificate File Passphrase |
Password of SCP user to retrieve Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine certificate chain. |
|||||||
|
Proxy Server URL |
URL of management network proxy server. |
If you want to use a proxy server, you must specify these parameters. |
||||||
|
Proxy Server Bypass List |
Space-delimited list of subnets and domains that will not be sent to the proxy server. |
|||||||
|
Authenticated Proxy Username |
Username for authenticated proxy servers. |
|||||||
|
Authenticated Proxy Passphrase |
Passphrase for authenticated proxy servers. |
|||||||
|
HTTPS Proxy SSL/TLS Certificate File URI |
HTTPS proxy PEM formatted SSL/TLS certificate file retrieved using SCP. |
|||||||
|
HTTPS Proxy SSL/TLS Certificate File passphrase |
Password of SCP user to retrieve proxy certificate chain. |
|||||||
|
Auto Enrollment Package |
||||||||
|
Enrollment Destination Host and Path |
SCP host and path to transfer the enrollment package using SCP (user@host:/path/to/file ). |
Enrollment package is required for enrolling Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway with Crosswork. The enrollment package is automatically transferred once Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway boots up for the first time if you specify these parameters during the installation. If you do not specify these parameters during installation, then you must export enrollment package manually following the procedure Export Enrollment Package. Note:
|
||||||
|
Enrollment Passphrase |
SCP user passphrase to transfer enrollment package. |
|||||||
1Either an IPv4 or IPv6 address must be specified. Selecting None for both will result in a non-functional deployment.
 Note |
Although Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway supports both IPv6 and IPv4, it is recommended to use IPv4 as Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine supports only IPv4. |
Ensure the following:
You are creating the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM on a recommended VMware version (See Virtual Machine (VM) Requirements for supported versions). To know which vCenter build you have, check on the vSphere web client under Help menu.
The Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM has allocated to it a minimum of 32 GB of RAM, 8 vCPUs, and 50 GB of hard drive space.
You have a public/private IPv4/IPv6 address to assign to the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM's management network virtual interface. The DNS servers, NTP servers, and the Crosswork application must be reachable via this IP address.
You have two public or private IPv4/IPv6 addresses to assign to the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM's Northbound and Southbound data network virtual interfaces. Your managed devices must be reachable via the Southbound data network interface and your output destinations (either Crosswork, external Kafka, or gRPC server) must be reachable via the Northbound data network interface.
During installation, Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway creates two default accounts:
A Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway administrator, with the username dg-admin and password set during installation. The product administrator uses this ID to log in to and troubleshoot the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway.
A Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway operator, with the username dg-oper and password set during installation. This is a read-only user and has permissions to perform all ‘read’ operations and some limited ‘action’ commands. To know what operations can an operator perform, see Table: Permissions Per Role in the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 1.1 User Guide.
 Note |
These two pre-defined usernames are reserved and cannot be changed. Change of password would be allowed from the console for both the accounts. In case of lost or forgotten passwords, the user would have to create a new VM, destroy the current VM, and re-enroll the new one on the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. |
| Step 1 |
Download the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway 1.1.0 image file from CCO (*.ova).
|
||||
| Step 2 |
Connect to vCenter vSphere Client. Then select Actions > Deploy OVF Template, as shown in the following figure:  |
||||
| Step 3 |
The VMware Deploy OVF Template wizard appears and highlights the first step, 1 Select template, as shown in the following figure.  |
||||
| Step 4 |
Click Next to go to 2 Select name and location, as shown in the following figure. |
||||
| Step 5 |
Click Next to go to 3 Select a resource, as shown in the following figure. Choose the VM’s host.  |
||||
| Step 6 |
Click Next. The VMware vCenter Server validates the OVA. Network speed will determine how long validation takes. When the validation is complete, the wizard moves to 4 Review details, as shown in the following figure. Review the OVA’s information and then click Next. Take a moment to review the OVF template you are deploying.
 |
||||
| Step 7 |
Click Next to go to 5 accept license agreements. Review the End User License Agreement and click Accept.  |
||||
| Step 8 |
Click Next to go to 6 Select configuration, as shown in the following figure. To install Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway for Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, you must select Crosswork On Premise from the Configuration dropdown.  |
||||
| Step 9 |
Click Next to go to 7 Select storage, as shown in the following figure.
 |
||||
| Step 10 |
Click Next to go to 8 Select networks, as shown in the following figure. In the dropdown table at the top of the page, choose the appropriate destination network for the source Management Network, Northbound Data Network, and Southbound Data Network respectively.  |
||||
| Step 11 |
Click Next to go to 9 Customize template, with the Host Information Settings already expanded. As per the deployment scenario chosen by you in Section: Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway OVF Parameters and Deployment Scenarios, enter the information for the parameters:
|
||||
| Step 12 |
Click Next to go to 10 Ready to complete, as shown in the following figure. Review your settings and then click Finish if you are ready to begin deployment.  |
||||
| Step 13 |
Wait for the deployment to finish before continuing. To check the deployment status:
 Wait for the deployment status to become 100%.
|
||||
| Step 14 |
Once the deployment status is 100%, power on the VM to complete the deployment process. Expand the host’s entry so you can click the VM and then choose Actions > Power > Power On, as shown in the following figure:  Wait for at least 5 minutes for the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM to come up and then login via vCenter or SSH as explained in the Section Log In and Log Out. |
This is an alternative way to install Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway. You can modify mandatory/optional parameters in the script as per your requirement and run the OVF Tool.
Below is a sample script for installing using this method:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# robot.ova path
ROBOT_OVA_PATH="<mention the orchestrator path>"
# Download robot.ova
# Change the path to a convenient location for download
ova_path=<mention the ova path>
mkdir -p $ova_path
echo "Delete ova image if exists"
rm -rf $ova_path/*.ova
# Download robot.ova
cd $ova_path
echo "Downloading ova image"
wget -d --proxy=off -r -l1 -H -t1 -nd -N -np -A.ova -erobots=off ${ROBOT_OVA_PATH}
filename=`find $ova_path -name \*.ova`
VM_NAME="dg-42"
DM="thin"
Deployment="onpremise"
Hostname="Hostname"
ManagementIPv4Address="<management_ipv4_address>"
ManagementIPv4Gateway="<management_ipv4_gateway>"
ManagementIPv4Netmask="<management_ipv4_netmask>"
ManagementIPv4Method="Static"
SouthDataIPv4Address="<southdata_ipv4_address>"
SouthDataIPv4Gateway="<southdata_ipv4_gateway>"
SouthDataIPv4Netmask="<southdata_ipv4_netmask>"
SouthDataIPv4Method="Static"
NorthDataIPv4Address="<northdata_ipv4_address>"
NorthDataIPv4Gateway="<northdata_ipv4_gateway>"
NorthDataIPv4Netmask="<northdata_ipv4_netmask>"
NorthDataIPv4Method="Static"
DNS="<DNS_ip_address>"
NTP="<NTP Server>"
Domain="cisco.com"
ControllerIP="<controller_ipv4_address>"
ControllerPort="<controller_port>"
ControllerSignCertChain="cw-admin@<management_ip_address>:/home/cw-admin/controller.pem"
ControllerCertChainPwd="<Password>"
Description="Description for Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway for 42"
Label="Label for Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway dg-42"
dg_adminPassword="<dg-admin_password>"
dg_operPassword="<dg-oper_password>"
EnrollmentURI="<enrollment_package_URI>"
EnrollmentPassphrase="<password>"
# Please replace this information according to your vcenter setup
VCENTER_LOGIN="<vCenter login details>"
VCENTER_PATH="<vCenter path>"
DS="<DS details>"
ovftool --acceptAllEulas --X:injectOvfEnv --skipManifestCheck --overwrite --noSSLVerify --powerOffTarget --powerOn \
--allowExtraConfig --extraConfig:firmware=efi --extraConfig:uefi.secureBoot.enabled=true \
--datastore="$DS" --diskMode="$DM" \
--name=$VM_NAME \
--net:"Management=VM Network" \
--net:"SouthData=DPortGroupVC-1" \
--net:"NorthData=DPortGroupVC-2" \
--deploymentOption=$Deployment \
--prop:"ControllerIP=$ControllerIP" \
--prop:"ControllerPort=$ControllerPort" \
--prop:"ControllerSignCertChain=$ControllerSignCertChain" \
--prop:"ControllerCertChainPwd=$ControllerCertChainPwd" \
--prop:"EnrollmentURI=$EnrollmentURI" \
--prop:"EnrollmentPassphrase=$EnrollmentPassphrase" \
--prop:"Hostname=$Hostname" \
--prop:"Description=$Description" \
--prop:"Label=$Label" \
--prop:"ManagementIPv4Address=$ManagementIPv4Address" \
--prop:"ManagementIPv4Gateway=$ManagementIPv4Gateway" \
--prop:"ManagementIPv4Netmask=$ManagementIPv4Netmask" \
--prop:"ManagementIPv4Method=$ManagementIPv4Method" \
--prop:"SouthDataIPv4Address=$SouthDataIPv4Address" \
--prop:"SouthDataIPv4Gateway=$SouthDataIPv4Gateway" \
--prop:"SouthDataIPv4Netmask=$SouthDataIPv4Netmask" \
--prop:"SouthDataIPv4Method=$SouthDataIPv4Method" \
--prop:"NorthDataIPv4Address=$NorthDataIPv4Address" \
--prop:"NorthDataIPv4Gateway=$NorthDataIPv4Gateway" \
--prop:"NorthDataIPv4Netmask=$NorthDataIPv4Netmask" \
--prop:"NorthDataIPv4Method=$NorthDataIPv4Method" \
--prop:"DNS=$DNS" \
--prop:"NTP=$NTP" \
--prop:"dg-adminPassword=$dg_adminPassword" \
--prop:"dg-operPassword=$dg_operPassword" \
--prop:"Domain=$Domain" $ROBOT_OVA_PATH "vi://$VCENTER_LOGIN/$VCENTER_PATH"
| Step 1 |
Open a command prompt. |
| Step 2 |
Navigate to the location where you installed the OVF Tool. |
| Step 3 |
Run the OVF Tool using the following command:
For example, |
Once the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway is installed, complete the following tasks in the order of their listing:
You can use either of the following two ways to access Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway:
Follow these steps to log in via vCenter:
| Step 1 |
Locate the VM in vCenter and then right click and select Open Console. The Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway flash screen comes up. |
| Step 2 |
Enter username (  |
 Note |
The SSH process is protected from brute force attacks by blocking the client IP after a number of login failures. Failures such as incorrect username or password, connection disconnect, or algorithm mismatch are counted against the IP. Up to 4 failures within a 20 minute window will cause the client IP to be blocked for at least 7 minutes. Continuing to accumulate failures will cause the blocked time to be increased. Each client IP is tracked separately. |
Follow these steps to login via SSH.
| Step 1 |
Run the following command: ssh <username>@<ManagementNetworkIP> where ManagementNetworkIP is the management network IP address. For example, To login as adminstrator user: ssh dg-admin@<ManagementNetworkIP> To login as operator user: ssh dg-oper@<ManagementNetworkIP> The following Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway flash screen opens prompting for password:  |
| Step 2 |
Input the corresponding password (the one that you created during installation process) and press Enter. |
To log out, select option l Logout from the Main Menu and press Enter or click OK.

This image is not available in preview/cisco.com
Every Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance must be identified by means of an immutable identifier. This requires generation of a Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway enrollment package. The enrollment package can be generated during installation by supplying OVF parameters or by using the Export Enrollment Package option from the interactive menu in the console.
The enrollment package is a JSON document created from the information obtained through the OVF template populated by the user during installation. It includes the all necessary information about Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway required for registering, such as Certificate, UUID of the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance, and metadata like Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance name, creation time, version info, and so on.
If you opted not to export the enrollment package during install, then you must export it before you can enroll the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance with Crosswork. The steps to do so are described in Export Enrollment Package.
 Note |
The enrollment package is unique to each Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance. |
A sample enrollment package JSON file is shown below:
{
"name": "dg116.cisco.com",
"description": "CDG Base VM for Automation",
"profile": {
"cpu": 8,
"memory": 31,
"nics": 3
},
"interfaces": [
{
"name": "eth0",
"mac": "00:50:56:9e:09:7a",
"ipv4Address": "<ip_address>/24"
},
{
"name": "eth1",
"mac": "00:50:56:9e:67:c3",
"ipv4Address": "<ip_address>/16"
},
{
"name": "eth2",
"mac": "00:50:56:9e:83:83",
"ipv4Address": "<ip_address>/16"
}
],
"certChain": [
"MIIFezCCA2OgAwIBAgIJAIP1aTyDBd/MMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBDQUAMFQxCzAJBgNVBAYTAlVTMQswCQYDVQQIDAJDQTERMA8GA1UEBwwIU2FuIEpvc2UxCzAJBgNVBAoMAkRHMRgwFgYDVQQDDA9kZzExNi5jaXNjby5jb20wHhcNMTkxMDI4MTQwMDE0WhcNMzkxMDIzMTQwMDE0WjBUMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzELMAkGA1UECAwCQ0ExETAPBgNVBAcMCFNhbiBKb3NlMQswCQYDVQQKDAJERzEYMBYGA1UEAwwPZGcxMTYuY2lzY28uY29tMIICIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAg8AMIICCgKCAgEAuizEa5R/BERI5G7mc0XD23NKFg6y8YzL1IFn7r1xUwP13mmOZq1WjNowhCecVSV9X+a2Ozcs69S2zJe6lsV8hV9g7+maTiE1KPrsyO6oAGvyA5RE/BfbR2LgR5mnsYK/GqInfqnR0/W6C038Godp2gRo6V+C3cgdtcGBaTegQuHpDqzQFLOxmV25+XFAyWlorb6PLDXU1nihs1kOYZbAZrqsBod+CVBVaj9ne809T6SfaiFiOiZ7pPDMotcDnivfQl+/n2/JvqS0SRcFbua5yirwKqCdRoK1JRnMZS1TR6aA9eex24Dc/xzKK+PBI+vNstX1u3JyoisNayc3GgFBgHXP/TqmEF2+EhuxnonY0FG37eYz0AWjbzc57VApeZuHd4pC2jwwe7ln8NxnVqnGqHUSa3Lsz6/NLsCKs89qyvg+0GqMiB8bjWdjP+/I7LOCpaUFK+NaiIoDrHGy2JtbbpHtWqPWH80TM1hYbd8osznr4+CvAeHp3xB69alBrM/QNYHP7wmI8z7Ok4sAFIcprLS9Vhw9dT+EYL2jTfADA/g2vhUKc4Ip9NTdaQfMUyDhMp85Rliu4XvCOS6EjYfB92VouYnKRtA/vAgImTYkCVxifZ2CKPfyaI1SA6VaHDx2APVLFC9TjEWTkAvYU6tIAsIj0JMAPaWFZiBdsym4aN8CAwEAAaNQME4wHQYDVR0OBBYEFBTwQocZxTkwKsMrdrotzAk/ztZgMB8GA1UdIwQYMBaAFBTwQocZxTkwKsMrdrotzAk/ztZgMAwGA1UdEwQFMAMBAf8wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQENBQADggIBACRJEeEO6zpbpV16O/pEDBmxz6KmM1XTLyNtnJrhtJ7EVcWDPWut6NgxsuETVDT+0BSr+/br2IVK1Gz8mi2PcGSuJKG3pATeg8XrdCYcnyWN2f7U3WXBQrX9a4GYNE0NPTjLmcm0+1zahQi2mNE6UHcf7R+CTP/CJYspcwWGqT127m2kWYyWBZX544dI+tX/InWnkMNP0AAXAOTJrGyNV+DRqoLD8/gjl1Zu+J6tkajenJv/RuS8FBqdXBUlCmPeaHgATsROYI+ZtFeBZC3051xNnSDFY+M4/6h+h2c6KTrQERLVZx15yRCZHZ/B3q/SLPiaMOkVuwn1SwMXvR+V67x2cxbmM1lgeKmAcyKeP4RMJmcpvZYQEaCJxKSoLh9Fp03wxLJbJS18w2J8l+hi7eYQ3PMKKhCGEepZslRCKRvW/ecIvV37EPI1g9Ecr1ea9q5tmrjqpdXbD0OMms057HY0/UQggLd939BuwWE1ryy6QDEc7I1edfvmovE9Sw+vdGGvikWONfsI4vCbBd6QCRl+f5pbOwYanln5YUnI3fRhVQ5OsrhstVkCzAMtQxr88Q4junWrduzFyHn36cE7qDBk7A1umeh04Pv1jZMrduBT2J9mD2A4VyGo2YE0VWvrd/m8R7QsLPBYfRZzYKJNSBeLlxl3V4j37aGGblL7uZFD"
],
"version": "1.1.0 (branch dg110dev - build number 152)",
"duuid": "d58fe482-fdca-468b-a7ad-dfbfa916e58b"
}
Before enrolling Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway with Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, you must export the enrollment package.
 Note |
This is needed only if you have not specified Auto Enrollment Package Transfer settings in the OVF template. Otherwise, the file will be at the SCP URI destination after the VM boots. |
Follow these steps:
| Step 1 |
Log into the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway Base VM as explained in Section Log In and Log Out. |
||
| Step 2 |
From the Main Menu, select 1 Export Enrollment Package and click OK.  |
||
| Step 3 |
Enter the SCP URI for exporting the enrollment package and click OK.
 |
||
| Step 4 |
Enter the SCP passphrase (the SCP user password) and click OK.  The enrollment package is exported. |
||
| Step 5 |
Manually copy the enrollment package from the above SCP server to your local computer, to be used in the next task to enroll Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway with Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. |
| Step 1 |
Log into Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine as described in Section Log In to the UI From a Browser. |
||
| Step 2 |
From the Main Menu, select Admin > Data Gateway Management. The Data Gateway Management page opens. |
||
| Step 3 |
Click the Add button.  The Enroll New Data Gateway dialog opens. |
||
| Step 4 |
Click Browse and navigate to the folder to which you copied the enrollment package and select it.  |
||
| Step 5 |
Select the Data gateway admin state in which you want to bring up the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway:
 The Enroll New Data Gateway dialog displays a summary of the selected enrollment package:
It also displays additional details:
|
||
| Step 6 |
Click Enroll.Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway displays the following message upon successful enrollment:  Once you click Enroll, a dialog pops up asking if you want to attach devices now or later. It is recommended to choose Later as devices must only be attached once the operational state of the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance is Up.
 |
The Operational Status of a Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance is shown as "Degraded" until it establishes a connection with Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine and downloads collector binary files. While it depends on the bandwidth between the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance and Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, this operation typically takes less than 5 minutes. Click the ![]() icon in the Data Gateways pane to refresh the pane to reflect the latest operational status of the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance and wait for it to become Up. If the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance fails to enroll, contact Cisco CX for assistance.
icon in the Data Gateways pane to refresh the pane to reflect the latest operational status of the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance and wait for it to become Up. If the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance fails to enroll, contact Cisco CX for assistance.
During the enrollment process, the enrollment package is uploaded to the controller application, i.e., Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, which then instantiates a new Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance in its database and waits for a "first-sign-of-life" from the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway.
Session Establishment
Once the connectivity is established, the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance confirms the identity of the controller and offers its own proof of identity via signed certificates during this initial connection.
Download of Configuration Files
Once the session is established, Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway downloads the following configuration files:
|
boot-config |
A json response created by Crosswork that contains a list of services (docker containers) and functional images should be downloaded on that particular Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance. |
|
docker-compose |
A YAML file that contains instructions and order to start up the right set of services and functional images. |
Download of Functional Images
A functional image represents a collection profile for a protocol, i.e., CLI, SNMP, or MDT. Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway downloads the following functional images:
|
CLI Collection |
To connect to a device using SSH/Telnet, collect show commands output, and send it to the designated output destination. |
|
SNMP Collection |
To connect to a device using SNMP protocol, collect SNMP responses, receive SNMP traps, and send them to a designated output destination. |
|
MDT Collection |
To connect to a device and collect model-driven telemetry or event-driven telemetry events, and send them to a designated output destination. |
After the downloads, Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway boots the containers.
Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway is now ready to collect data.
The following table lists common problems that might be experienced while installing or enrolling Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway, and provides approaches to identifying the source of the problem and solving it.
|
Issue |
Action |
|---|---|
|
1. Cannot enroll Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway with Crosswork |
|
|
Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway cannot be enrolled with Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine due to an NTP issue, i.e., there is a clock-drift between the two. The clock-drift might be with either Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway or Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. Also, on the NTP servers for Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine and Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway, the initial time is set to the ESXi server. For this reason, the ESXi server must also have NTP configured. Sync the clock time on the host and retry. |
1. Log into the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM. 2. From the main menu, go to 5 Troubleshooting > Run show-tech. Enter the destination to save the tarball containing logs and vitals and click OK. In the show-tech logs (in file 3. From the main menu, go to 3 Change Current System Settings > 1 Configure NTP. Configure NTP to sync with the clock time on the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine server and try re-enrolling Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway. It is also possible that the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine's NTP server might be down or its address might be incorrect. To configure NTP on the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine side, see Configure NTP after installation. |
|
2. Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway remains in degraded state for more than 10 minutes with reason stated as "Could not collect vitals" |
|
|
Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway remains in degraded state for more than 10 minutes with reason stated as "Could not collect vitals" due to certificate errors. |
1. Log into the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM. 2. From the main menu, select 5 Troubleshooting > Run show-tech. Enter the destination to save the tarball containing logs and vitals and click OK. In the show-tech logs (in file 1. From the main menu, select 3 Change Current System Settings > 7 Import Certification. 2. From the Import Certificates menu, select 1 Controller Signing Certificate File and click OK. 3. Enter the SCP URI for the certificate file and click OK. |
|
3. Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway remains in degraded state for more than 10 minutes with reason stated as "gRPC connection cannot be established" |
|
|
Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway remains in degraded state for more than 10 minutes with reason stated as "gRPC connection cannot be established" due to certificate errors. |
1. Re-upload the certificate file as explained in the troubleshooting scenario 2. above. 2. Reboot the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM following the steps below: a. From the main menu, select 5 Troubleshooting and click OK. b. From the Troubleshooting menu, select 7 Reboot VM and click OK. c. Once the reboot is complete, check if the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway's operational status is Up. |
| Step 1 |
Log in to Crosswork UI as desribed in Log In to the UI From a Browser. |
| Step 2 |
From the navigation panel, select Admin > Data Gateway Management. The Data Gateway Management page opens. |
| Step 3 |
In the Data Gateways panel, select the Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM you want to remove and click Delete button.  |
| Step 4 |
A Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway instance must be in maintenance mode to be deleted. Click Switch & Continue when prompted to switch to maintenance mode. 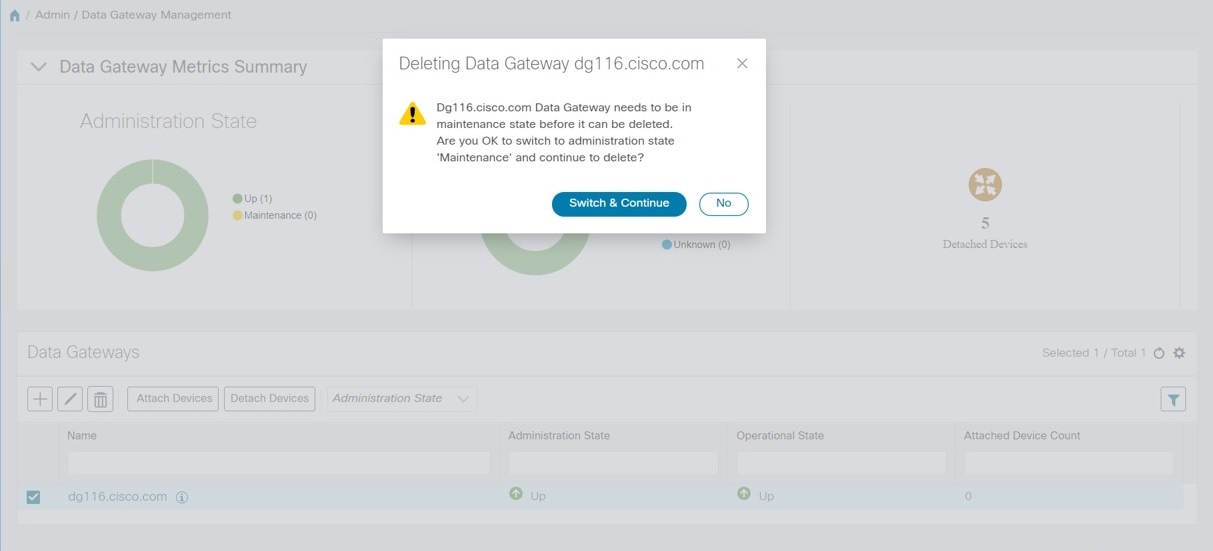 The selected Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway VM is deleted.  |