|
1
|
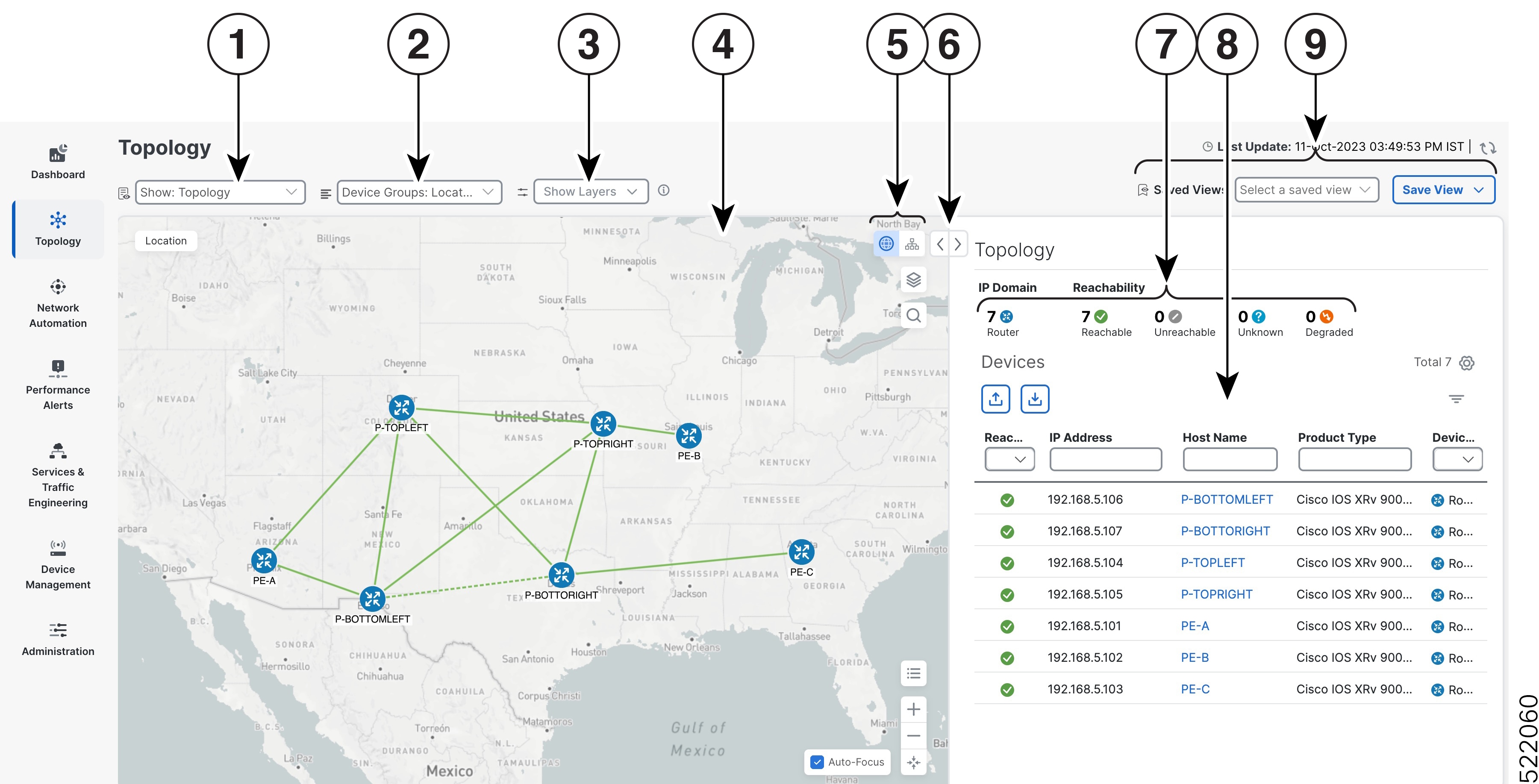
Topology Map View: From the Show drop-down list, click the option that displays the data that you would like to see on the map.
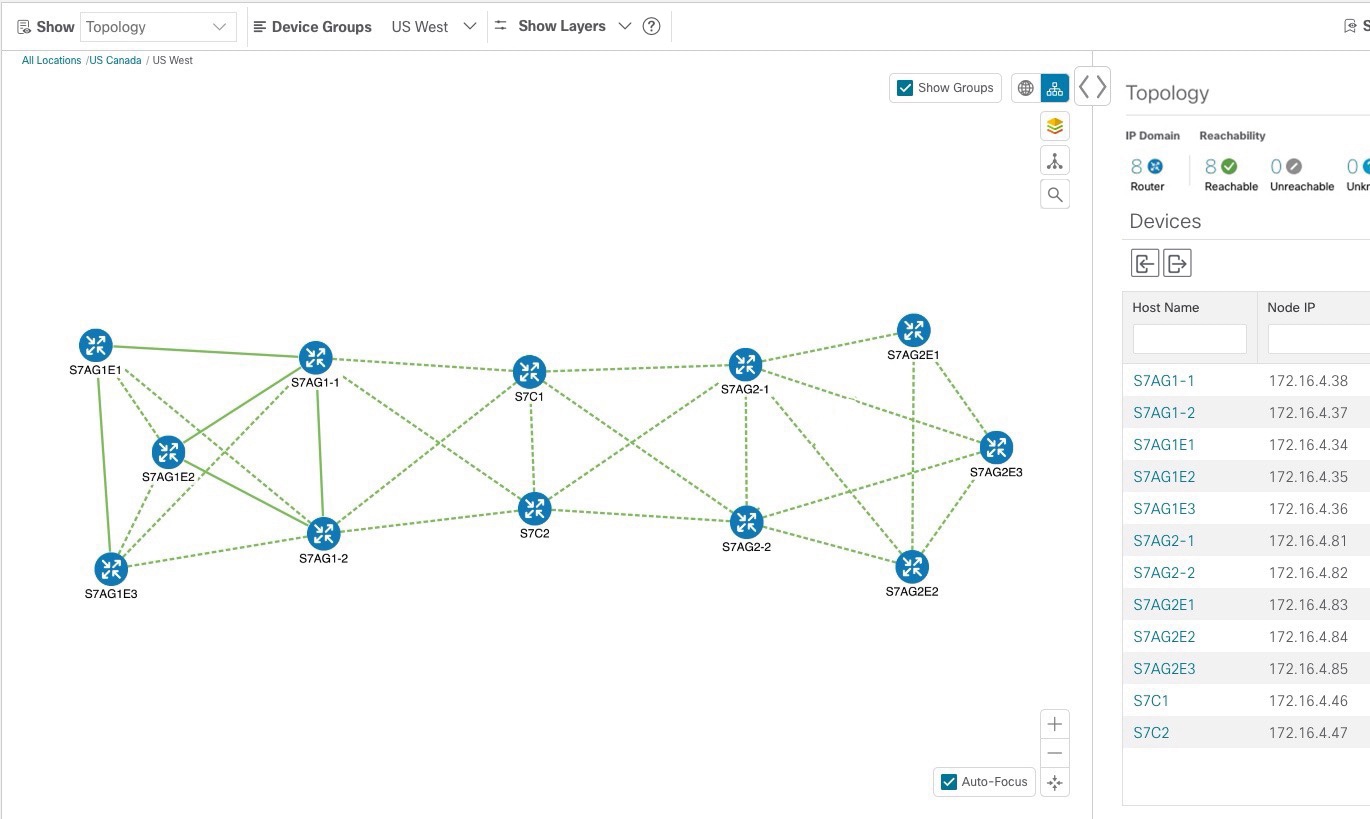
If Topology is selected, devices and links in the network are displayed.
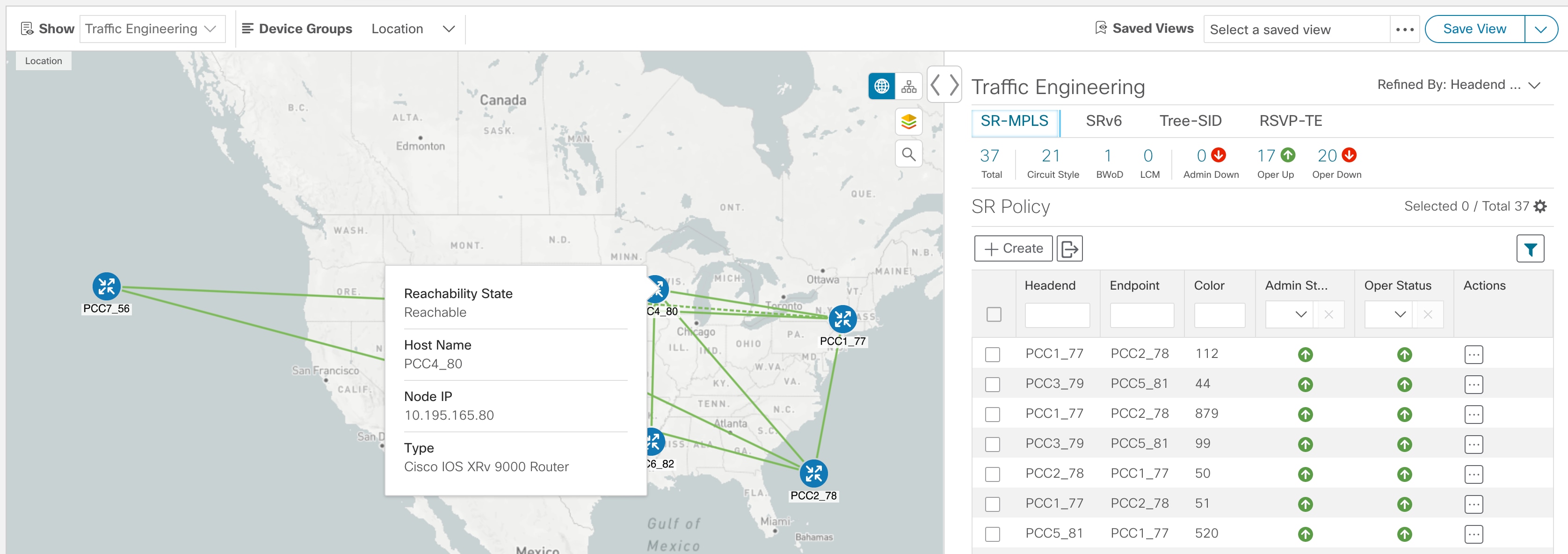
If Traffic Engineering is selected, TE tunnel information is displayed. For more information on the Traffic Engineering topology map, see View SR-MPLS and SRv6 Policies on the Topology Map and View RSVP-TE Tunnels on the Topology Map.
|
|
2
|
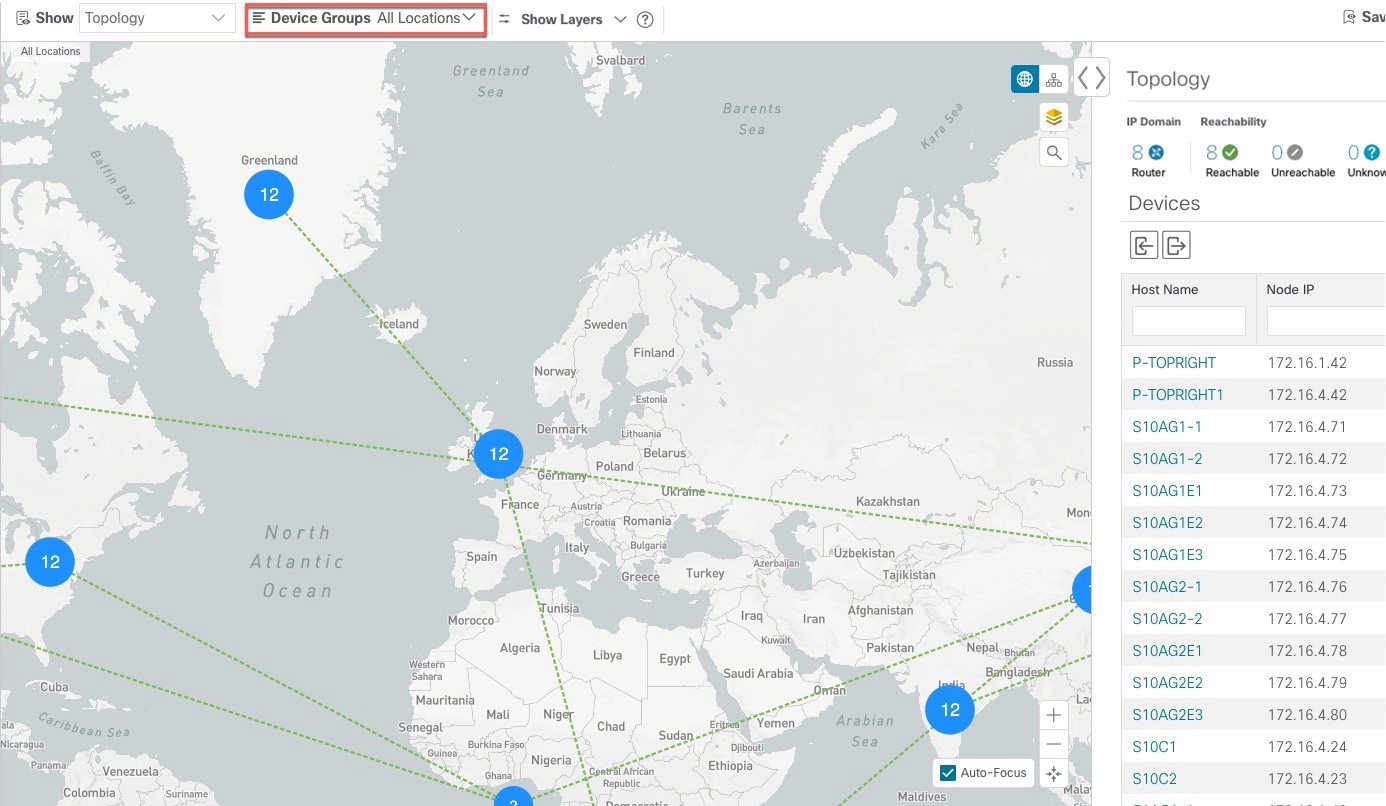
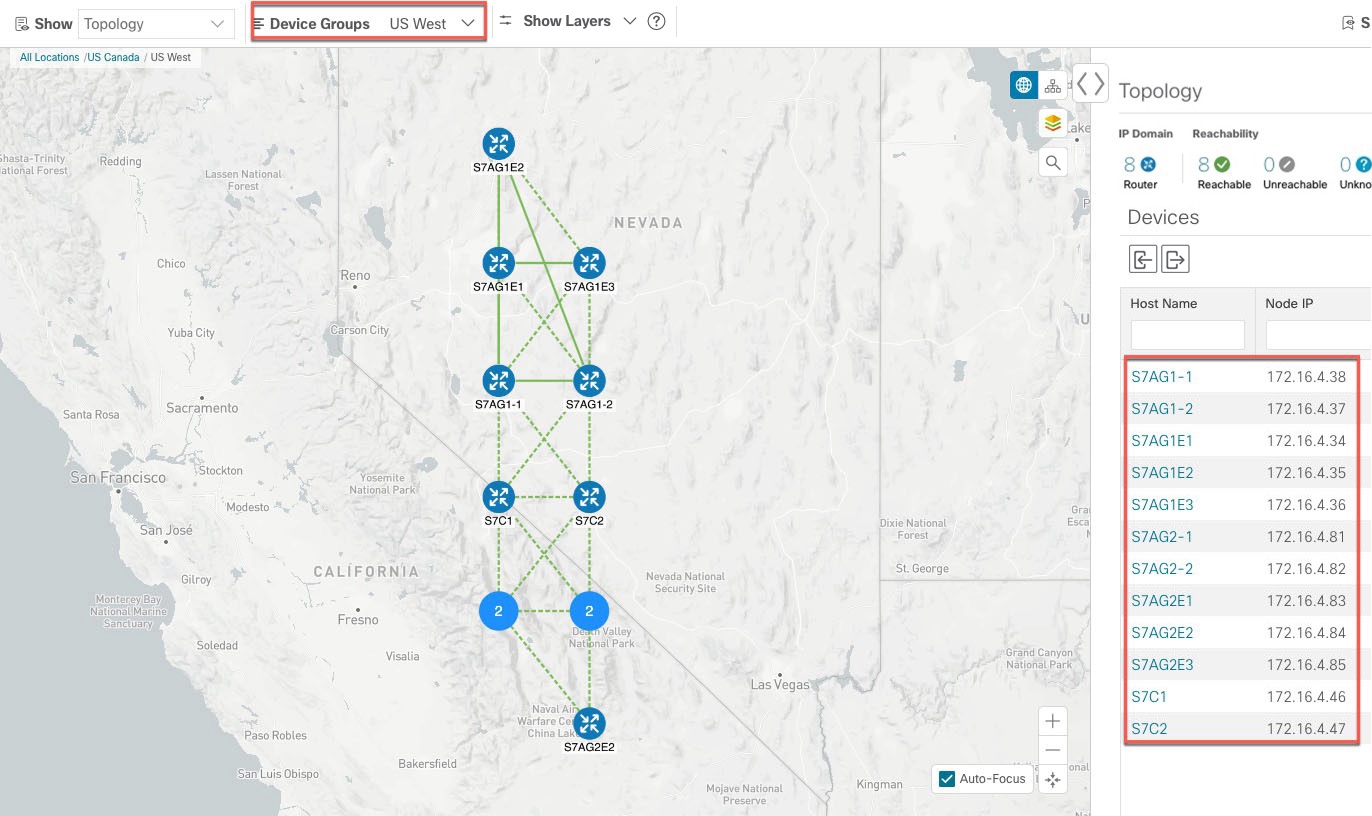
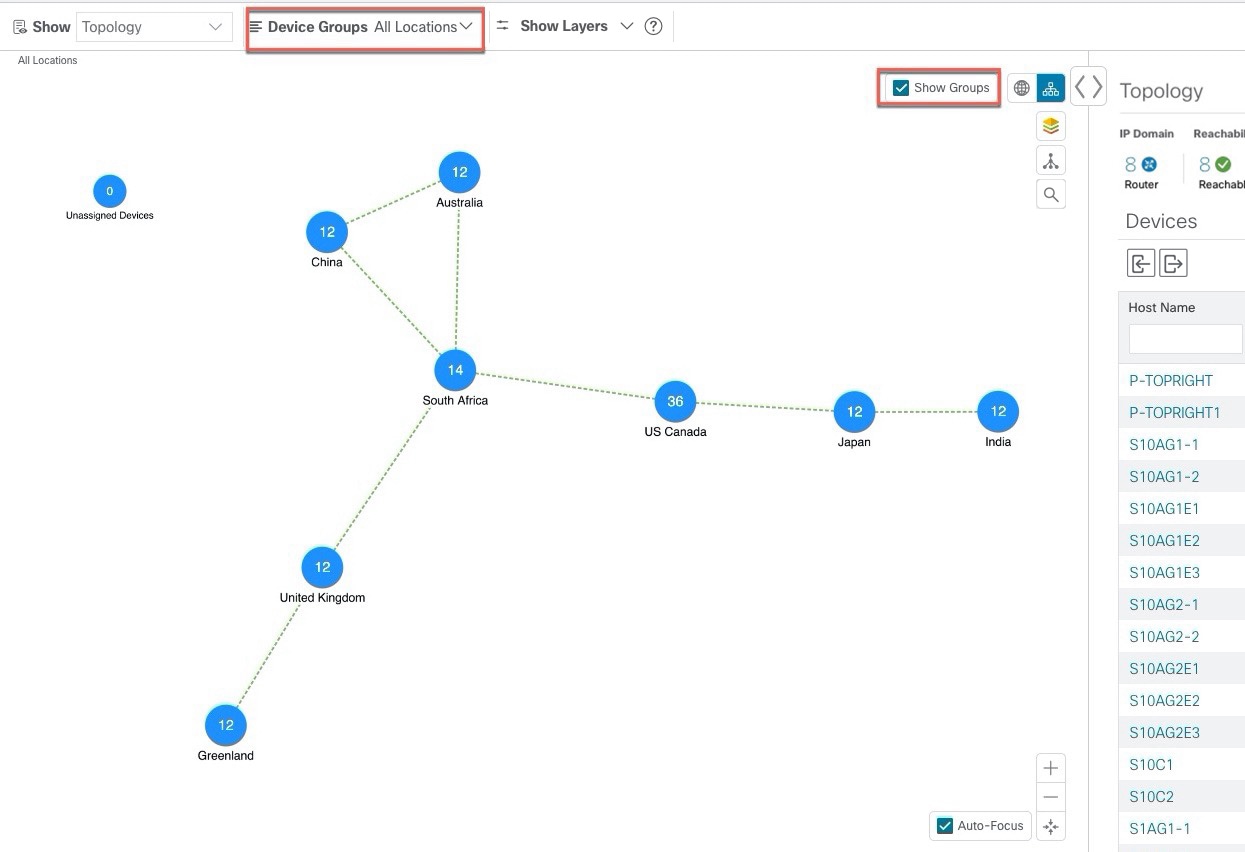
Device Groups: From the drop-down list, click the group of devices you want displayed on the map. All other device groups will be hidden.
|
|
3
|
Show Hide: From the drop-down list, click the network layers you want displayed on the map. All devices and links that belong to the
selected layers are then displayed. By default, all layers are displayed.
|
|
4
|
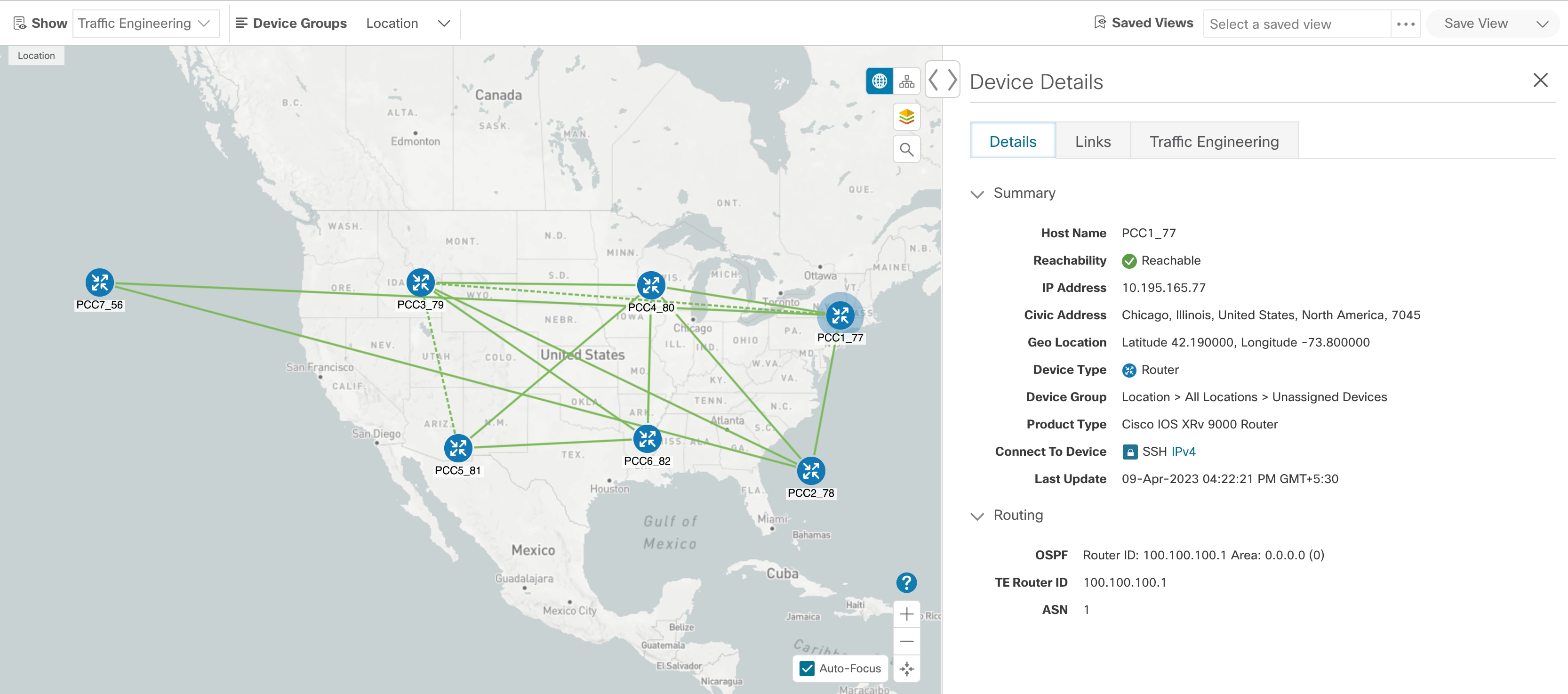
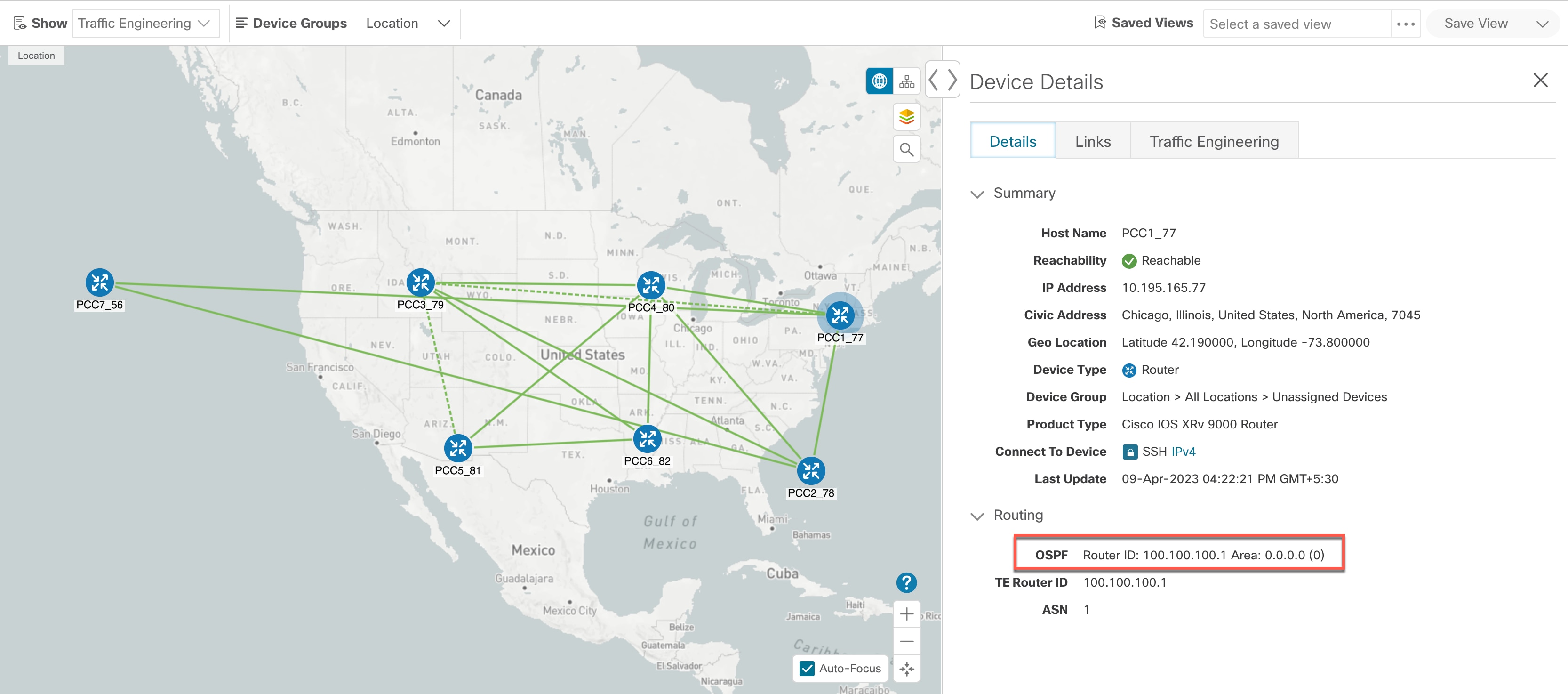
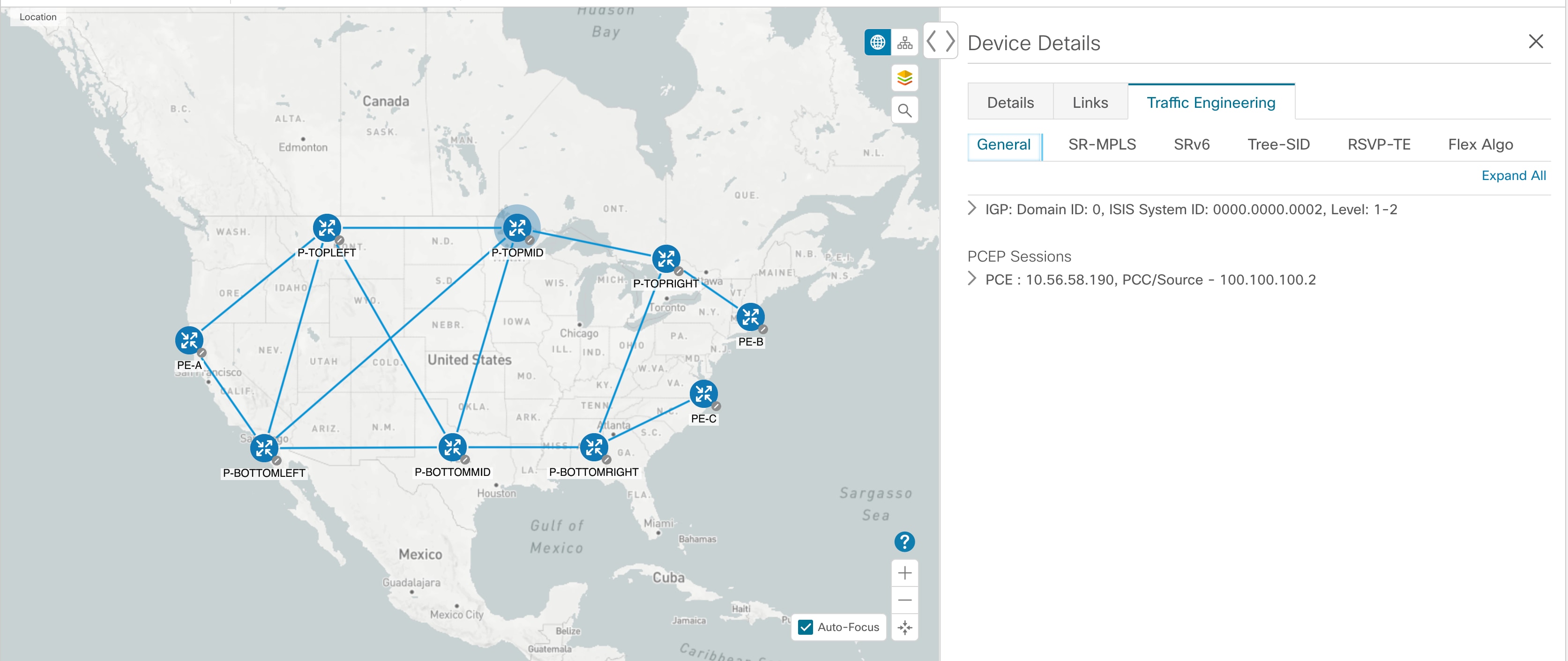
Topology Map: The network topology can be displayed on a logical map or a geographical map, where the devices and links are shown in their
geographic context. From the map, you can drill down to get detailed information about devices and links.
Devices:
-
To view a device configuration summary, hover the mouse pointer over the device icon. A pop up window displaying the host
name, state, node ID, and device type appears.
-
To view device details, click on the device icon.
-
If devices are in close physical proximity, the geographical map shows them as a cluster. The number in a blue circle ( ) indicates the number of devices in the cluster. Displaying devices in this manner helps prevent overlap and clutter on the
map. ) indicates the number of devices in the cluster. Displaying devices in this manner helps prevent overlap and clutter on the
map.
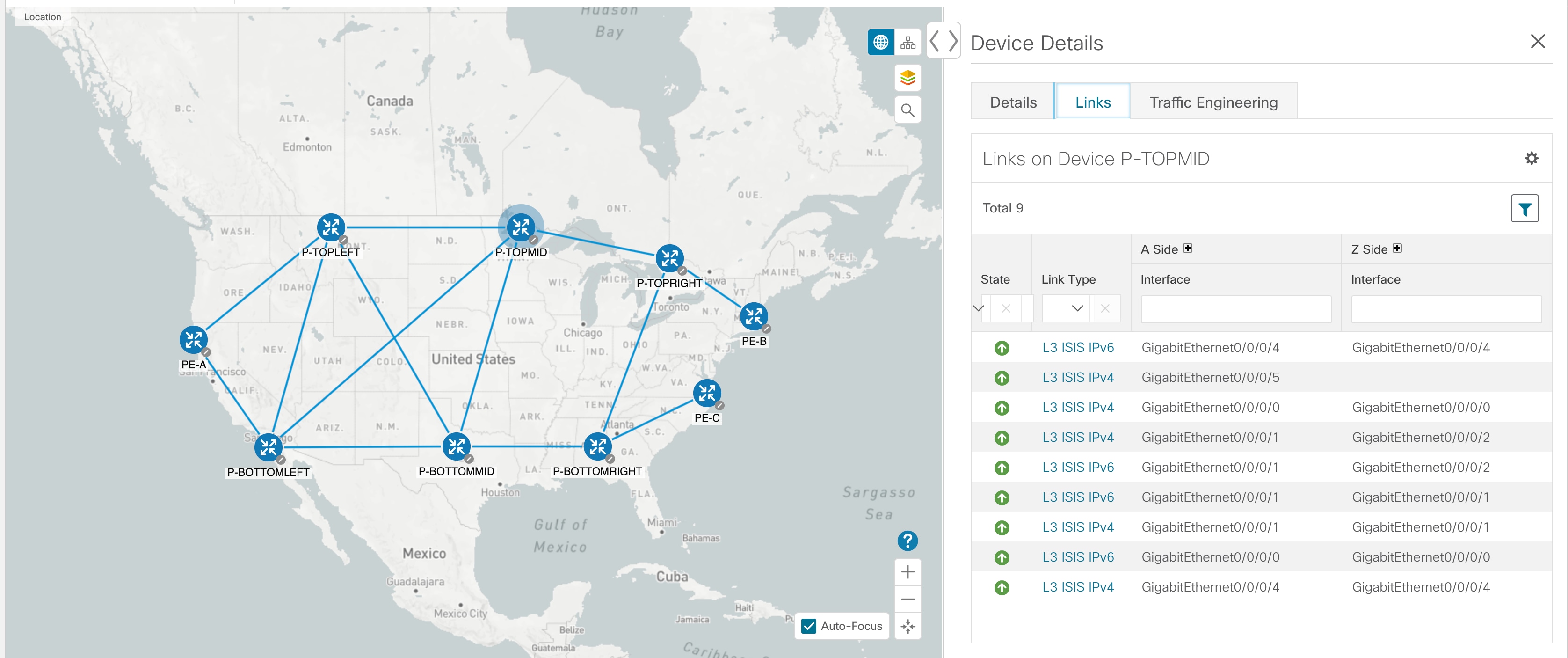
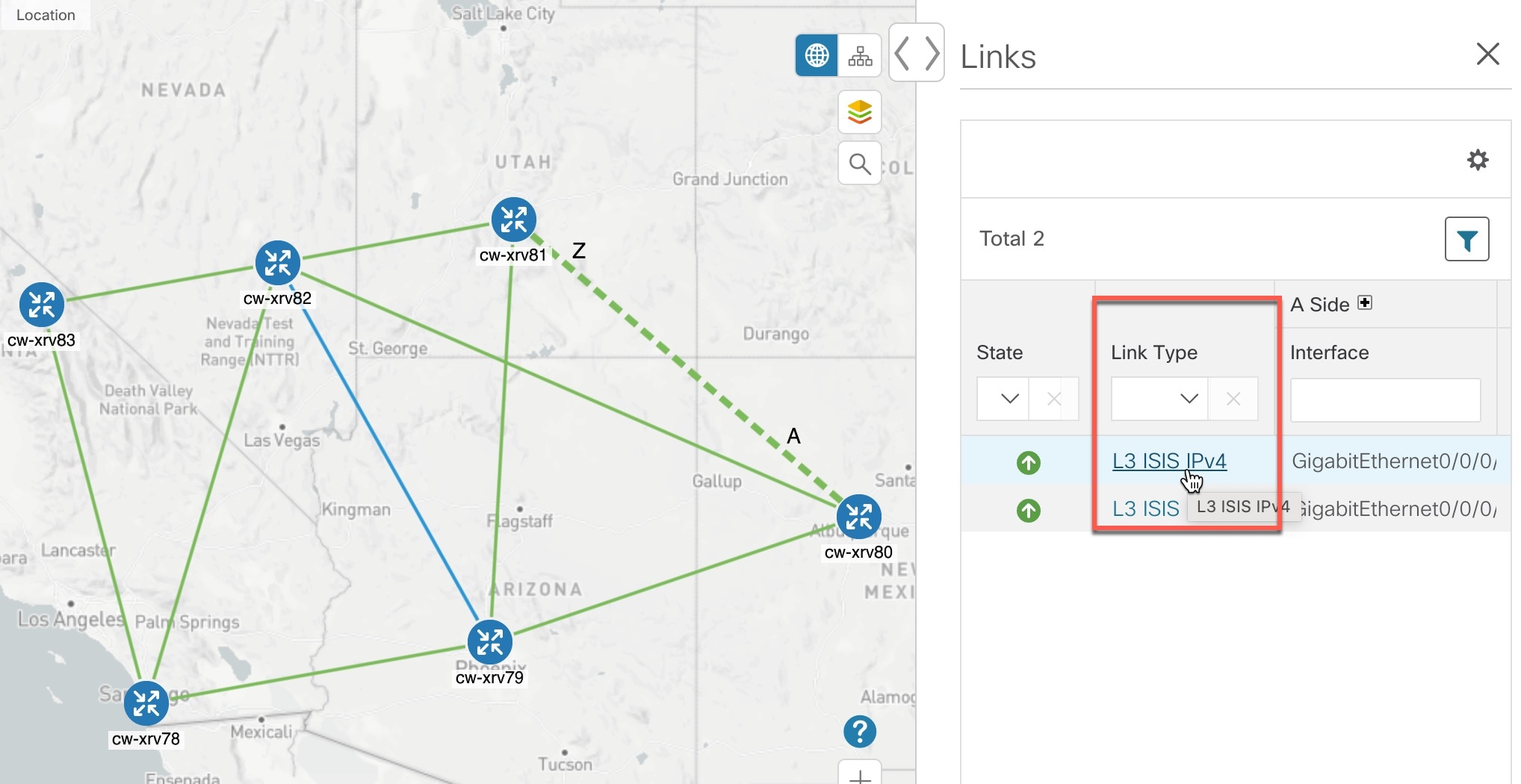
Links:
-
A solid line indicates a single link between two devices. If there is more than one link between two devices, or between a device and a cluster of devices, the
line is shown dashed instead. A dashed line indicates an aggregated link that represents more than one link, or the use of multiple protocols (for example, IPv4 and IPv6) on the same physical
link.
-
A and Z indicates headend and endpoint, respectively.
-
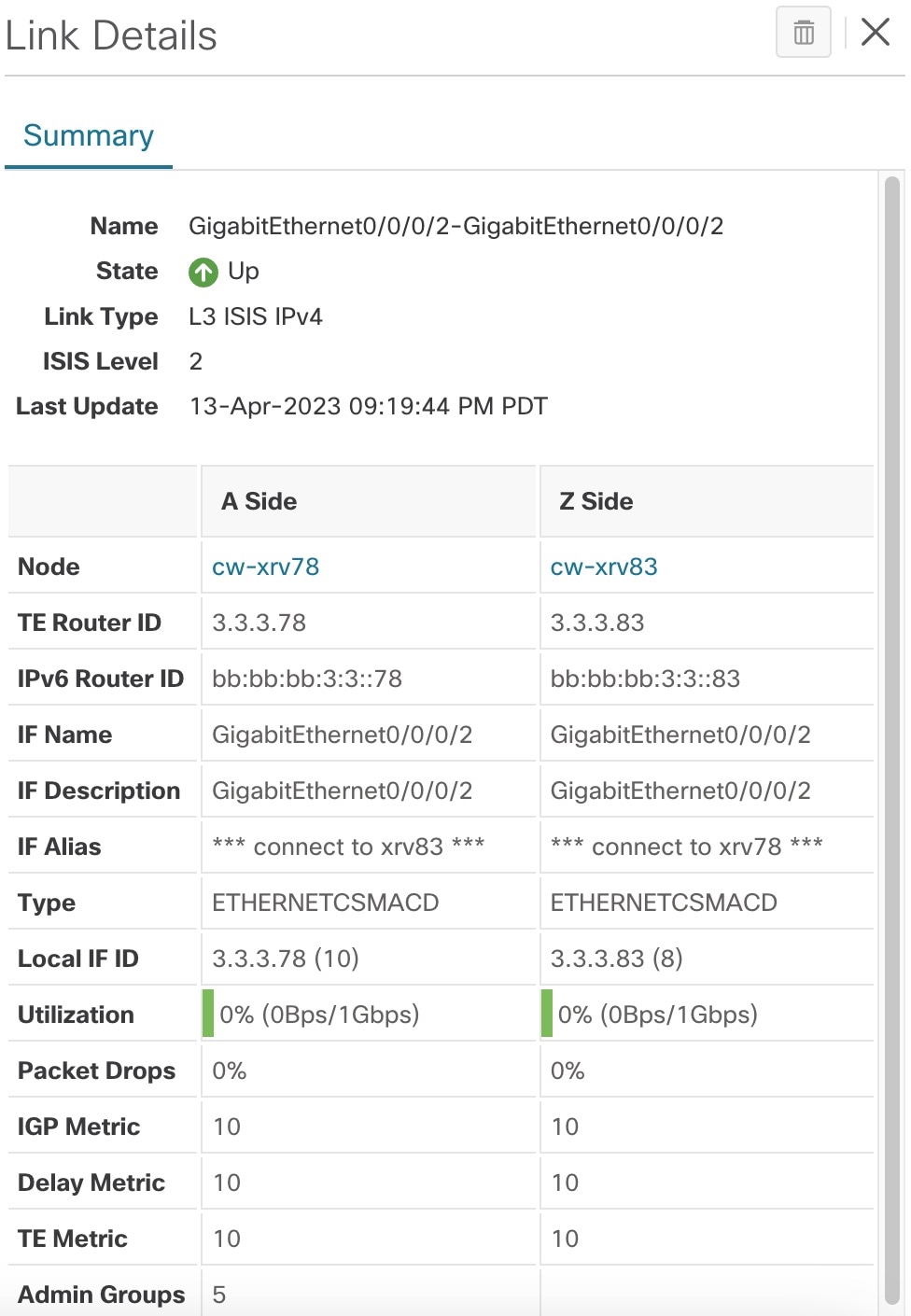
To view link information details, click on the link.
|
Note
|
Although aggregated, dual stack links show as one single line.
|
|
|
5
|
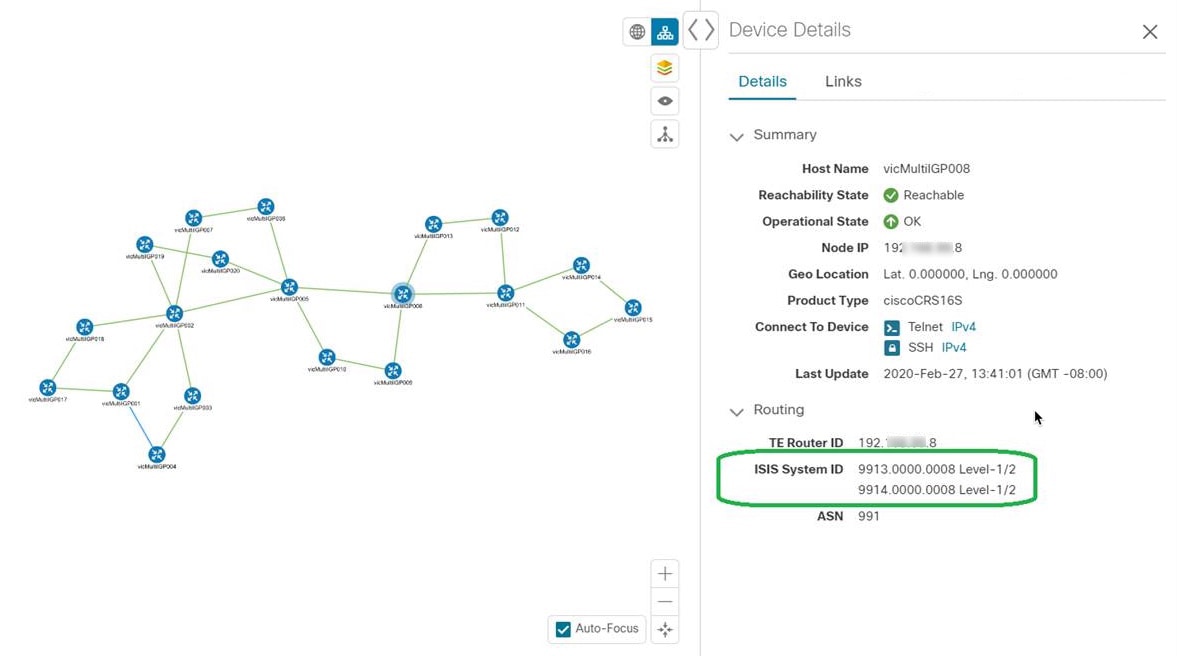
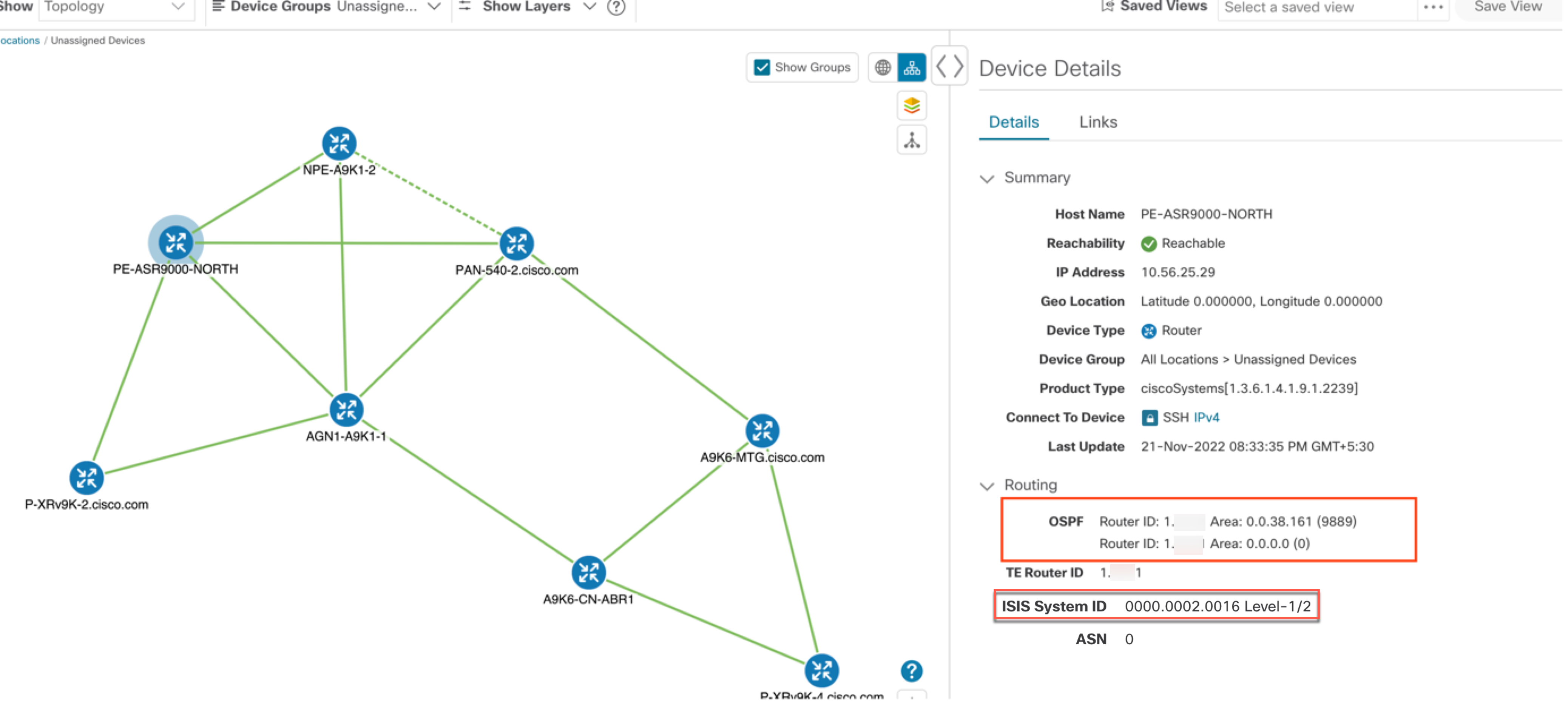
 : The logical map shows devices and their links, positioned according to an automatic layout algorithm, ignoring their geographical
location. You can change the layout algorithm. : The logical map shows devices and their links, positioned according to an automatic layout algorithm, ignoring their geographical
location. You can change the layout algorithm.
 : The geographical map shows single devices, device clusters, links, and tunnels, superimposed on a map of the world. Each
device location on the map reflects the device's GPS coordinates (longitude and latitude) as defined in the device inventory. : The geographical map shows single devices, device clusters, links, and tunnels, superimposed on a map of the world. Each
device location on the map reflects the device's GPS coordinates (longitude and latitude) as defined in the device inventory.
 : The Display Preferences window allows you to change display settings for devices, links, utilization, Flexible Algorithms, and TE tunnel metrics. : The Display Preferences window allows you to change display settings for devices, links, utilization, Flexible Algorithms, and TE tunnel metrics.
 : The global search allows you to search the topology using device names, location or the device civic location. : The global search allows you to search the topology using device names, location or the device civic location.
 : Export to KML allows you to export the geo localised objects using a KML format. KML is an XML base file format used to
display information in a geographic context, such as Google Earth. : Export to KML allows you to export the geo localised objects using a KML format. KML is an XML base file format used to
display information in a geographic context, such as Google Earth.
|
|
6
|
Expand/Collapse/Hide Side Panel: Expand or collapse the contents of the side panel. Close the side panel to get a larger view of the topology map.
|
|
7
|
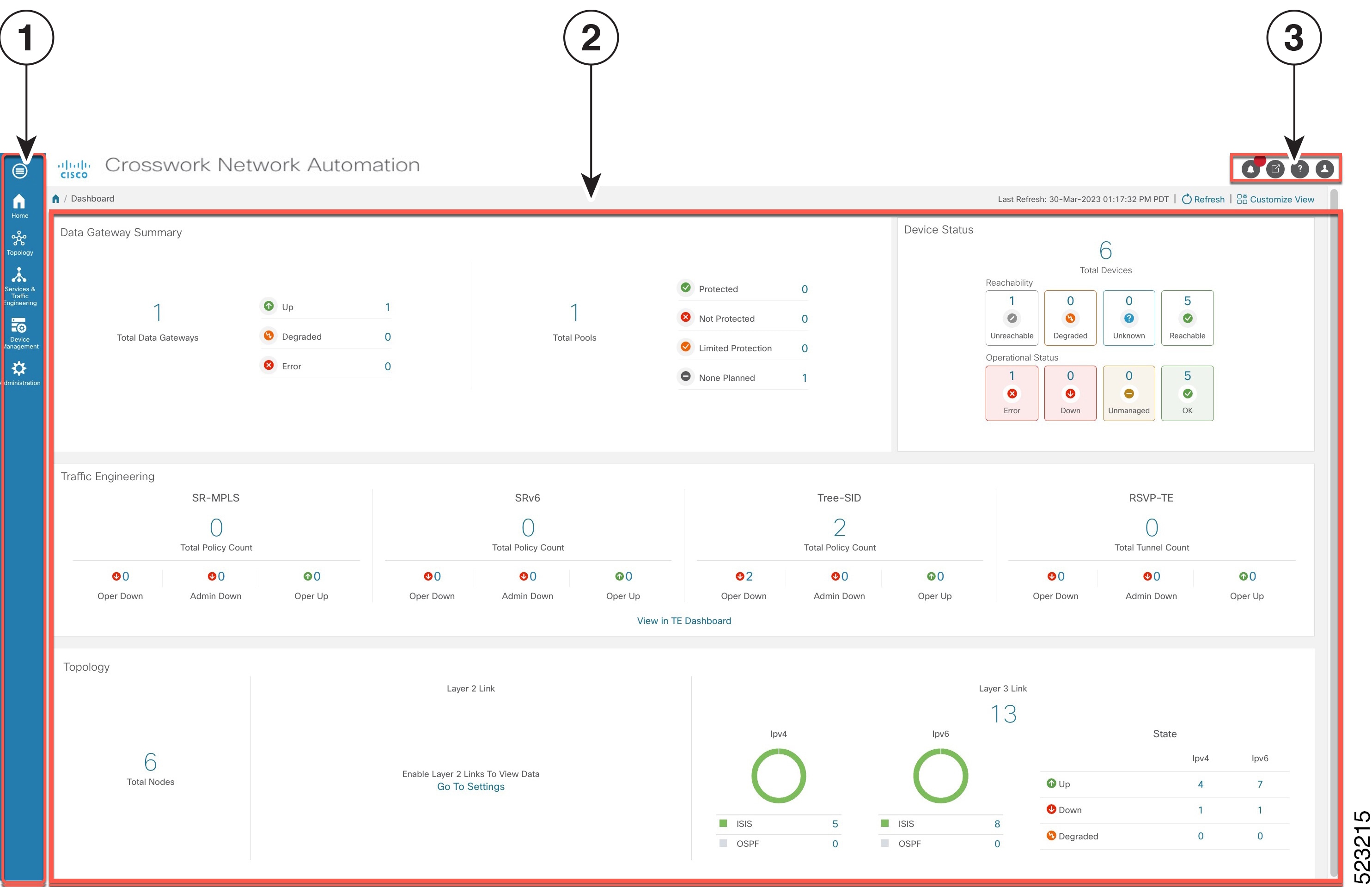
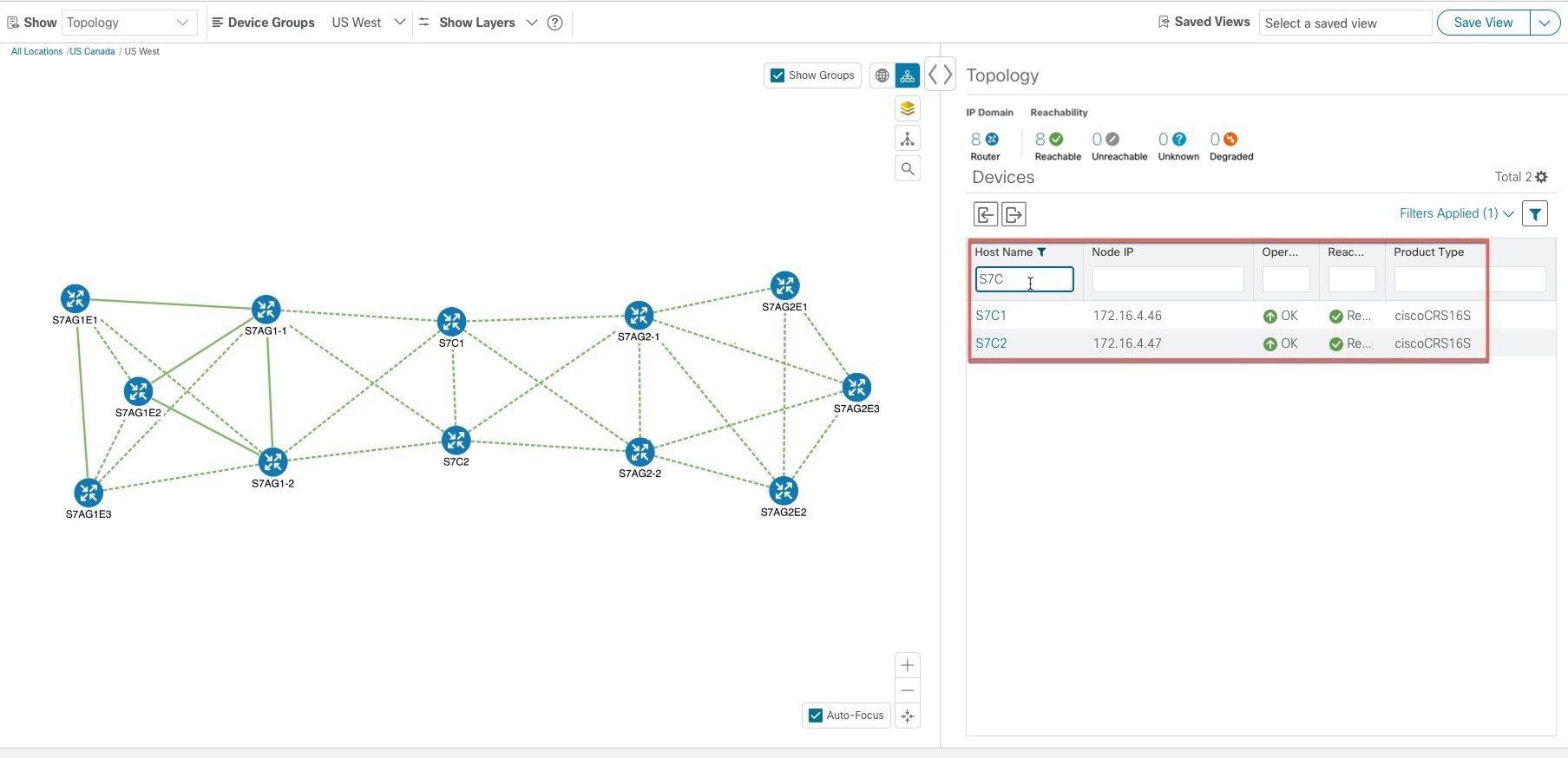
The Mini Dashboard provides a summary of the IP Domain and device reachability status. If filters are applied, the Mini Dashboard is updated to reflect what is displayed in the Devices table.
|
|
8
|
The content of this window changes depending on what applications you have installed, what Show is set to for the Topology Map and if you have selected to view more information on the device, link, SR-MPLS policy, SRv6 policy, or RSVP-TE tunnel..
|
|
9
|
Saved Custom Map Views: Lets you create a named custom view using the settings and layout for your current map, settings of the tables saved in
the saved views, or display a custom view you have created previously. It also saves any filters applied to the Devices and Traffic Engineering tables.
|







 Feedback
Feedback