About FICON
The Cisco MDS 9000 Family supports the Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP), FICON, iSCSI, NVMe, and FCIP capabilities within a single, high-availability platform (see Shared System Storage Network).
The FICON feature is supported only with the following platforms:
-
Cisco MDS 9710 switches
-
Cisco MDS 9706 switches
-
Cisco MDS 9250i switches
-
Cisco MDS 9220i switches
-
Cisco MDS 9148V switches
FCP, NVMe, and FICON are different FC4 protocols and their traffic is independent of each other. Devices using these protocols should be isolated using VSANs.
The fabric binding feature helps prevent unauthorized switches from joining the fabric or disrupting current fabric operations (see the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Security Configuration Guide). The Registered Link Incident Report (RLIR) application provides a method for a switch port to send an LIR to a registered Nx port.
This section includes the following topics:
FICON Requirements
The FICON feature has the following requirements:
-
You can implement FICON features in the following switches:
-
Cisco MDS 9706 and MDS 9710 switches
-
Cisco MDS 9250i and MDS 9220i switches
-
Although in earlier releases the MAINFRAME_PKG license was required to configure FICON, beginning with NX-OS Release 9.4(1a), the FICON feature is a base feature of NX-OS and no special license is required.
MDS-Specific FICON Advantages
This section explains the additional FICON advantages in Cisco MDS switches and includes the following topics:
Fabric Optimization with VSANs
Generally, separate physical fabrics have a high level of switch management and have a higher implementation cost. The ports in each island may also be overprovisioned depending on the fabric configuration.
By using the Cisco MDS-specific VSAN technology, you can have greater efficiency between these physical fabrics by lowering the cost of overprovisioning and reducing the number of switches to be managed. VSANs also help you to move unused ports nondisruptively and provide a common redundant physical infrastructure (see VSAN-Specific Fabric Optimization).
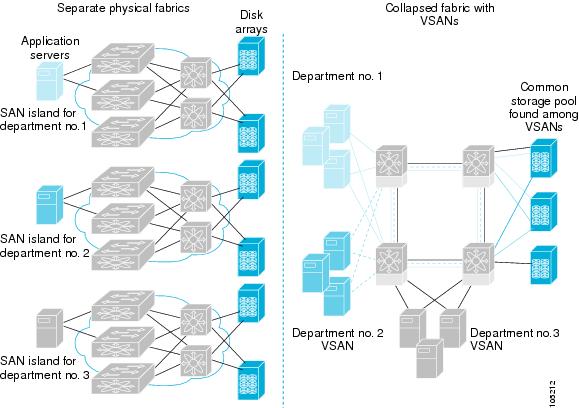
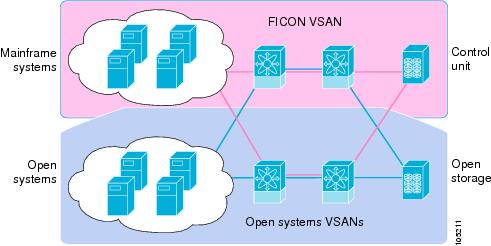
VSANs enable global SAN consolidation by allowing you to convert existing SAN islands into virtual SAN islands on a single physical network. It provides hardware-enforced security and separation between applications or departments to allow coexistence on a single network. It also allows virtual rewiring to consolidate your storage infrastructure. You can move assets between departments or applications without the expense and disruption of physical relocation of equipment.
 Note |
While you can configure VSANs in any Cisco MDS switch, you can only enable FICON in up to eight of these VSANs on switches that support the FICON feature. |
Mainframe users can think of VSANs as being like FICON LPARs in the MDS SAN fabric. You can partition switch resources into FICON LPARs (VSANs) that are isolated from each other, in much the same way that you can partition resources on an IBM Z Systems mainframe server. Each VSAN has its own set of fabric services (such as fabric server, name server, and zone server), FICON CUP, domain ID, Fabric Shortest Path First (FSPF) routing, operating mode, and security profile. FICON VSANs can span line cards and are dynamic in size. For example, one FICON VSAN with 8 ports can span 8 different line cards. FICON VSANs can also include ports on more than one switch in a cascaded configuration. The consistent fairness of the Cisco MDS 9000 switching architecture means that “all ports are created equal,” simplifying provisioning by eliminating the “local switching” issues seen on other vendors’ platforms. Addition of ports to a FICON VSAN is a nondisruptive process. The maximum number of ports for a FICON VSAN is 254 per switch due to FICON addressing limitations.
FCIP Support
The multilayer architecture of the Cisco MDS 9000 Family enables a consistent feature set over protocol-agnostic switch fabric. Cisco MDS 9700 Series and 9200 Series switches transparently integrate FCP, NVMe, FICON, and Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) in one system. The FICON over FCIP feature enables cost-effective access to remotely located mainframe resources. With the Cisco MDS 9000 Family platform, storage replication services such as IBM PPRC can be extended over metro to global distances using ubiquitous IP infrastructure which simplifies business continuance strategies.
For more information, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Series IP Services Configuration Guide.
PortChannel Support
The Cisco MDS implementation of FICON provides support for efficient utilization and increased availability of Inter-Switch Links (ISLs) necessary to build stable large-scale SAN environments. PortChannels ensure an enhanced ISL availability and performance in Cisco MDS switches.
Refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Interfaces Configuration Guide for more information on PortChannels.
VSANs for FICON and FCP Mixing
Cisco MDS 9000 Family FICON-enabled switches simplify deployment of even the most complex mixed environments. Multiple logical FICON, Z-Series Linux/FCP, and Open-Systems Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) fabrics can be overlaid onto a single physical fabric by simply creating VSANs as required for each service. VSANs provide both hardware isolation and protocol-specific fabric services, eliminating the complexity and potential instability of zone-based mixed schemes.
By default, the FICON feature is disabled in all switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family. When the FICON feature is disabled, FC IDs can be allocated seamlessly. Mixed environments are addressed by the Cisco NX-OS software. The challenge of mixing FCP and FICON protocols are addressed by Cisco MDS switches when implementing VSANs.
Switches and directors in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family support FCP and FICON protocol mixing at the port level. If these protocols are mixed in the same switch, you should use VSANs to isolate FCP and FICON ports.
 Tip |
When creating a mixed environment, place all FICON devices in one VSAN (other than the default VSAN) and segregate the FCP switch ports in a separate VSAN (other than the default VSAN). This isolation ensures proper communication for all connected devices. The default VSAN (VSAN 1) should never be used for production services. |
Cisco MDS 9000-Supported FICON Features
The Cisco MDS 9000 Family FICON features include:
-
Flexibility and investment protection — The Cisco MDS 9000 Family shares common switching and service modules across the Cisco MDS 9700 Modular switches.
See the Cisco MDS 9700 Series Multilayer Director Hardware Installation Guide, the Cisco MDS 9250i Multiservice Fabric Switch Hardware Installation Guide, and the Cisco MDS 9220i Fabric Switch Hardware Installation Guide.
-
High-availability FICON-enabled director — Cisco MDS 9700 Series combines nondisruptive software upgrades, stateful process restart and failover, and full redundancy of all major components for a new standard in director-class availability. The Cisco MDS 9710 supports up to 384 autosensing, 64/32/16/10/8/4/2-Gbps Fibre Channel ports for FCP, NVMe, and FICON connections as well as 1/10/25/40 Gbps IP Services ports for FCIP links. The Cisco MDS 9706 supports up to 192 autosensing, 64/32/16/10/8/4/2-Gbps Fibre Channel ports for FCP, NVMe, and FICON connections as well as 1/10/25/40 Gbps IP Services ports for FCIP links. See the Cisco MDS 9000 Series High Availability Configuration Guide.
-
Infrastructure protection — Common software releases provide infrastructure protection across all Cisco MDS 9000 platforms. See the Cisco MDS 9000 NX-OS Software Upgrade and Downgrade Guide.
-
VSAN technology — Cisco MDS 9000 Family provides VSAN technology for hardware-enforced, isolated environments within a single physical fabric for secure sharing of physical infrastructure and enhanced FICON mixed support. See Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
Port-level configurations — There are BB credits, beacon mode, and port security for each port. See the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Interfaces Configuration Guide for information about buffer-to-buffer credits, beacon LEDs, and trunking.
-
Alias name configuration — Provides user-friendly aliases instead of the WWN for switches and attached node devices. See the Configuring and Managing Zones.
-
Comprehensive security framework — Cisco MDS 9000 Family supports RADIUS and TACACS+ authentication, Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMPv3), role-based access control, Secure Shell Protocol (SSH), Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), VSANs, hardware-enforced zoning, ACLs, fabric binding, Fibre Channel Security Protocol (FC-SP), LUN zoning, read-only zones, and VSAN-based access control. See the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Security Configuration Guide for information about RADIUS, TACACS+, FC-SP, and DHCHAP.
-
Traffic encryption — IPSec is supported over FCIP. You can encrypt FICON, FCP, and NVMe traffic that is carried over FCIP. See the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Comprehensive security framework Security Configuration Guide.
-
Local accounting log — View the local accounting log to locate FICON events. For more information about MSCHAP authentication, and local AAA services, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Security Configuration Guide.
-
Unified storage management — Cisco MDS 9000 FICON-enabled switches are fully IBM CUP standard compliant for FICON in-band communications with the IBM Z Systems mainframe server. See the CUP In-Band Management.
-
Port address-based configurations — FICON port name attribute can be configured for ports in FICON VSANs. See the Configuring FICON Ports.
-
You can display the following information:
-
Individual Fibre Channel ports, such as the port name, port number, Fibre Channel address, operational state, type of port, and login data.
-
Nodes attached to ports.
-
Port performance and statistics.
-
-
Configuration files — Store and apply configuration files. See the FICON Configuration Files.
-
FICON and Open Systems Management Server features if installed. —See the VSANs for FICON and FCP Mixing.
-
Enhanced cascading support—See the CUP In-Band Management.
-
Date and time — Enable the IBM Z Systems Server to set the date and time for FICON VSANs on the switch. See the Allowing the Host to Control the Timestamp.
-
Configure SNMP trap recipients and community names — See the Configuring SNMP Control of FICON Parameters.
-
Call Home configurations — Configure the director name, location, description, and contact person. See the Cisco MDS 9000 Series System Management Configuration Guide.
-
Configure preferred domain ID, FC ID persistence, and principal switch priority — For information about configuring domain parameters, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Series System Management Configuration Guide.
-
Sophisticated SPAN diagnostics — Cisco MDS 9000 Family provides industry-first intelligent diagnostics, protocol decoding, and network analysis tools as well as integrated Call Home capability for added reliability, faster problem resolution, and reduced service costs. For information about monitoring network traffic using SPAN, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Series System Management Configuration Guide.
-
Configure R_A_TOV, E_D_TOV — See the “Fibre Channel Time-Out Values” section on page 11-1 .
-
Director-level maintenance tasks—Perform maintenance tasks for the director including maintaining firmware levels, accessing the director logs, and collecting data to support failure analysis. For information about monitoring system processes and logs refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Series System Management Configuration Guide
-
Port-level incident alerts—Display and clear port-level incident alerts. See the Clearing RLIR Information.
FICON Cascading
The Cisco MDS NX-OS software allows multiple switches in a FICON network. To configure multiple switches, you must enable and configure fabric binding in each switch. See the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Security Configuration Guide).
The FICON topologies supported on the Cisco MDS 9000 Series switches are:
-
Single hop/traditional cascade – This topology has two switches with a single hop (or set of ISLs between the switches. This support has been around since the introduction of FICON support in 2004.
-
Multi-hop cascade – This topology allows for up to four (4) switches between the host channels and their associated control units. The ISLs between these switches can be fibre channel ISLs, port channels made of fibre channel ISLs, FCIP ISLs, or port channels made of FCIP ISLs. Multi-hop cascade was introduced in approximately 2017 and begins with the z13 System Z server forward.
FICON VSAN Prerequisites
To ensure that a FICON VSAN is operationally up, be sure to verify the following requirements:
-
Set the default zone to permit, if you are not using the zoning feature or create a zoneset and associated zones for the VSAN. See Configuring zoning for FICON VSANs.
-
Enable in-order delivery on the VSAN. See Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols.
-
Enable (and if required, configure) fabric binding on the VSAN. For more information about Fabric Binding, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Security Configuration Guide.
-
Verify that conflicting FC IDs do not exist in the switch by configuring unique static domain IDs for each FICON VSAN on the switch or in the FICON fabric, if using enhanced FICON cascading. For information about configuring domain parameters, seethe Cisco MDS 9000 Series System Management Configuration Guide.
-
Verify that the configured domain ID and requested domain ID match on the switch and these match what is configured for the switch in the HCD definitions on the IBM Z Systems Server. For information about configuring domain parameters, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Series System Management Configuration Guide.
-
Add the CUP (area FE) to the zone, if you are using zoning. See the CUP In-Band Management.
If any of these requirements are not met, the FICON feature cannot be enabled.

 Feedback
Feedback