About RADIUS
The RADIUS distributed client/server system allows you to secure networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS clients run on Cisco NX-OS devices and send authentication and accounting requests to a central RADIUS server that contains all user authentication and network service access information.
RADIUS Network Environments
RADIUS can be implemented in a variety of network environments that require high levels of security while maintaining network access for remote users.
You can use RADIUS in the following network environments that require access security:
-
Networks with multiple-vendor network devices, each supporting RADIUS. For example, network devices from several vendors can use a single RADIUS server-based security database.
-
Networks already using RADIUS. You can add a Cisco NX-OS device with RADIUS to the network. This action might be the first step when you make a transition to a AAA server.
-
Networks that require resource accounting. You can use RADIUS accounting independent of RADIUS authentication or authorization. The RADIUS accounting functions allow data to be sent at the start and end of services, indicating the amount of resources (such as time, packets, bytes, and so on) used during the session. An Internet service provider (ISP) might use a freeware-based version of the RADIUS access control and accounting software to meet special security and billing needs.
-
Networks that support authentication profiles. Using the RADIUS server in your network, you can configure AAA authentication and set up per-user profiles. Per-user profiles enable the Cisco NX-OS device to better manage ports using their existing RADIUS solutions and to efficiently manage shared resources to offer different service-level agreements.
RADIUS Operation
When a user attempts to log in and authenticate to a Cisco NX-OS device using RADIUS, the following process occurs:
-
The user is prompted for and enters a username and password.
-
The username and encrypted password are sent over the network to the RADIUS server.
-
The user receives one of the following responses from the RADIUS server:
- ACCEPT
- The user is authenticated.
- REJECT
- The user is not authenticated and is prompted to reenter the username and password, or access is denied.
- CHALLENGE
- A challenge is issued by the RADIUS server. The challenge collects additional data from the user.
- CHANGE PASSWORD
- A request is issued by the RADIUS server, asking the user to select a new password.
The ACCEPT or REJECT response is bundled with additional data that is used for EXEC or network authorization. You must first complete RADIUS authentication before using RADIUS authorization. The additional data included with the ACCEPT or REJECT packets consists of the following:
-
Services that the user can access, including Telnet, rlogin, or local-area transport (LAT) connections, and Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP), or EXEC services.
-
Connection parameters, including the host or client IPv4 or IPv6 address, access list, and user timeouts.
RADIUS Server Monitoring
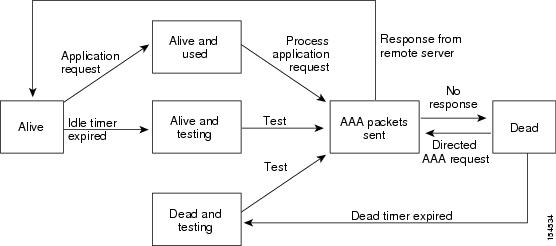
An unresponsive RADIUS server can cause a delay in processing AAA requests. You can configure the Cisco NX-OS device to periodically monitor a RADIUS server to check whether it is responding (or alive) to save time in processing AAA requests. The Cisco NX-OS device marks unresponsive RADIUS servers as dead and does not send AAA requests to any dead RADIUS servers. The Cisco NX-OS device periodically monitors the dead RADIUS servers and brings them to the alive state once they respond. This monitoring process verifies that a RADIUS server is in a working state before real AAA requests are sent its way. Whenever a RADIUS server changes to the dead or alive state, a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap is generated and the Cisco NX-OS device displays an error message that a failure is taking place.
 Note |
The monitoring interval for alive servers and dead servers are different and can be configured by the user. The RADIUS server monitoring is performed by sending a test authentication request to the RADIUS server. |
Vendor-Specific Attributes
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft standard specifies a method for communicating VSAs between the network access server and the RADIUS server. The IETF uses attribute 26. VSAs allow vendors to support their own extended attributes that are not suitable for general use. The Cisco RADIUS implementation supports one vendor-specific option using the format recommended in the specification. The Cisco vendor ID is 9, and the supported option is vendor type 1, which is named cisco-av-pair. The value is a string with the following format:
protocol : attribute separator value *
The protocol is a Cisco attribute for a particular type of authorization, the separator is = (equal sign) for mandatory attributes, and * (asterisk) indicates optional attributes.
When you use RADIUS servers for authentication on a Cisco NX-OS device, the RADIUS protocol directs the RADIUS server to return user attributes, such as authorization information, with authentication results. This authorization information is specified through VSAs.
The following VSA protocol options are supported by the Cisco NX-OS software:
- Shell
- Protocol used in access-accept packets to provide user profile information.
- Accounting
- Protocol used in accounting-request packets. If a value contains any white spaces, you should enclose the value within double quotation marks.
The Cisco NX-OS software supports the following attributes:
- roles
- Lists all the
roles to which the user belongs. The value field is a string that lists the
role names delimited by white space. For example, if the user belongs to roles
network-operator and network-admin, the value field would be network-operator
network-admin. This subattribute, which the RADIUS server sends in the VSA
portion of the Access-Accept frames, can only be used with the shell protocol
value. The following examples show the roles attribute that is supported by the
Cisco Access Control Server (ACS):
shell:roles=network-operator network-admin shell:roles*“network-operator network-adminThe following examples show the roles attribute that is supported by FreeRADIUS:
Cisco-AVPair = shell:roles=\network-operator network-admin\ Cisco-AVPair = shell:roles*\network-operator network-admin\
Note
When you specify a VSA as shell:roles*"network-operator network-admin" or "shell:roles*\"network-operator network-admin\"", this VSA is flagged as an optional attribute and other Cisco devices ignore this attribute.
- accountinginfo
- Stores accounting information in addition to the attributes covered by a standard RADIUS accounting protocol. This attribute is sent only in the VSA portion of the Account-Request frames from the RADIUS client on the switch. It can be used only with the accounting protocol data units (PDUs).
 Feedback
Feedback