Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Content Switching Module with SSL (CSM-S) Installation Note
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Content Switching Module with SSL Installation Note
Environmental and System Requirements
Preparing to Install the CSM-S
Installing and Removing the Module
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support Website
Definitions of Service Request Severity
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Content Switching Module with SSL Installation Note
Product Number: WS-X6066-SLB-S-K9
This publication describes how to install the Content Switching Module with SSL (CSM-S) in the Catalyst 6500 series switches, including the software and hardware requirements for each.

Note
The term SSL daughter card refers to an SSL termination daughter card for the Except where specifically differentiated, the term "Content Switching Module" and its acronym "CSM" includes both the Content Switching Module and the Content Switching Module with SSL.
The term "Content Switching Module with SSL" and its acronym "CSM-S" are used only where the information presented is specific to the CSM-S.
that accelerates Secure Socket Layer (SSL) transactions.
Contents
This publication contains these sections:
•
Environmental and System Requirements
•
Obtaining Technical Assistance
•
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Safety Overview
Front Panel Description
This section describes the physical attributes of the Content Switching Module with SSL.
Figure 1 shows the CSM-S front panel.
Figure 1 Content Switching Module with SSL Front Panel


Note
The RJ-45 connector is covered by a removable plate.

Note
You are required to make SSL daughter card configurations through a direct connection to the CSM-S SSL connector console port. After the configurations, you can establish an SSH or Telnet connection to further configure the module. See Chapter 5 in the Catalyst 6500 Series Content Switching Module with SSL Installation and Configuration Note.
Status LED
At startup, the CSM-S initializes various hardware components and communicates with the supervisor engine. The Status LED indicates the supervisor engine operations and the initialization results. During the normal initialization sequence, the status LED changes from off to red, orange, and green.

Note
For more information on the supervisor engine LEDs, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Module Installation Guide.
Table 1 describes the Status LED operation.
Table 1 Content Switching Module with SSL Status LED
Off
•
The module is waiting for the supervisor engine to provide power.
•
The module is not online.
•
The module is not receiving power, which could be caused by the following:
–
Power is not available to the CSM-S.
–
Module temperature is over the limit1 .
Red
•
The module is released from reset by the supervisor engine and is booting.
•
If the boot code fails to run, the LED stays red after startup.
Orange
•
The module is initializing hardware or communicating with the supervisor engine.
•
A fault occurred during the initialization sequence.
•
The module has failed to download its Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) on startup but continues with the remainder of the initialization sequence and provides the module online status from the supervisor engine.
•
The module has not received module online status from the supervisor engine. This problem could be caused by the supervisor engine detecting a failure in an external loopback test that it issued to the CSM-S.
Green
•
The module is operational; the supervisor engine has provided module online status.
Green to orange
•
The module is disabled through the supervisor engine CLI 2 using the set module disable mod command.
Color here.
•
FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standard) indicator. OK, I'll bite. What is this indicator used for and what does it tell a user?
1 Enter the show environment temperature mod command to display the temperature of each of four sensors on the CSM-S.
2 CLI = command-line interface.
RJ-45 Connectors
The RJ-45 connector, covered by a removable plate, is used to connect a management station device or a test device. This connector is used by field engineers to perform testing and to obtain dump information
The SSL console port is available to make the necessary connection to the SSL daughter card for configuration purposes. After the configurations, you can make an SSH or Telnet connection to further configure the module. See Chapter 5 in the Catalyst 6500 Series Content Switching Module with SSL Installation and Configuration Note.
Environmental and System Requirements
This section describes the environmental and system requirements.
Environmental Requirements
Table 2 lists the environmental requirements for the CSM-S.
System Requirements
Before you install the CSM-S in the Catalyst 6500 series switch, make sure that the switch meets the hardware and software requirements listed in this section.

CautionYou can use the Multilayer Switch Feature Card (MSFC), which is internal to the Catalyst 6500 series switch, to route traffic on either the client side or the server side of the CSM-S, but not both simultaneously (unless policy-based routing is used).
Memory Requirements
The CSM-S memory is not configurable.
Supported Hardware
Before you can use the Catalyst 6500 series CSM-S, you must have a Supervisor Engine 1A with an MSFC, a Policy Feature Card (PFC), a Supervisor Engine 2 with an MSFC, and any module that has ports to connect server and client networks. The PFC is required for the VLAN access control list (VACL) capture functionality.

CautionThe WS-X6066-SLB-S-K9 CSM-S are not fabric enabled, but the module can operate in a fabric-enabled chassis like any other nonfabric module.
Table 3 lists the supported hardware and software for the CSM-S.
Power Supply
You can place the CSM-S in any slot in the Catalyst 6500 series chassis except for the slots that are occupied by the supervisor engine and the standby supervisor engine. The CSM-S operates on power that is supplied by the chassis. Up to four CSM-S modules can be supported by each switch chassis.
Software Requirements

CautionThe CSM-S release is not supported by the Catalyst operating system. The CSM-S cannot be used in a Catalyst 6500 series switch with a Catalyst operating system software release earlier than release 7.5 .
Table 4 lists the software versions for the CSM-S:
Software Compatibility
Software release 1.1(1)requires Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(8a)EX or higher. However, the features new toCSM-S release 1.1(1) are only available with Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(18)SXD and subsequent releases.
Table 5 and Table 6 list the CSM-S software release compatibility.
Installing the CSM-S
These sections describe how to install the and:
•
Preparing to Install the CSM-S
•
Installing and Removing the Module

CautionThe WS-X6066-SLB-S-K9 Content Switching Module with SSL are not fabric enabled.
Preparing to Install the CSM-S
Before installing the CSM-S, make sure that the following items are available:
•
Catalyst 6500 series switch chassis
•
Management station that is available through a Telnet or a console connection to perform configuration tasks
Required Tools
These tools are required to install the CSM-S in the Catalyst 6500 series switches:
•
Flat-blade screwdriver
•
Phillips-head screwdriver
•
Wrist strap or other grounding device
•
Antistatic mat or antistatic foam
Whenever you handle the CSM-S, always use a wrist strap or other grounding device to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Installing and Removing the Module

CautionDuring this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool, or you could shock yourself.
All Catalyst 6500 series switches support hot swapping, which allows you to install, remove, replace, and rearrange modules without turning off the system power. For more information on removing the CSM-S from a switch, see the "Removing the Module" section.
When the system detects that a module has been installed or removed, the system automatically runs diagnostic and discovery routines, acknowledges the presence or absence of the module, and resumes system operation.
These sections describe how to install and verify the operation of the CSM-S in the Catalyst 6500 series switches:
Slot Assignments
The Catalyst 6006 and 6506 switch chassis have 6 slots, the Catalyst 6009 and 6509 switch chassis have 9 slots, and the Catalyst 6513 switch chassis has 13 slots.

Note
The Catalyst 6509-NEB switch has vertical slots, which are numbered 1 to 9 from right to left. Install the modules with the component side facing to the right.
•
Slot 1 is reserved for the supervisor engine.
•
Slot 2 can be used for a redundant supervisor engine if the supervisor engine in slot 1 fails.
•
If a redundant supervisor engine is not required, slots 2 through 6 on the 6-slot chassis, slots 2 through 9 on the 9-slot chassis, and slots 2 through 13 on the 13-slot chassis are available for switching modules, such as the CSM-S.
•
The empty slots require filler plates, which are blank switching-module carriers that maintain consistent airflow through the switch chassis.
Removing the Module
This section describes how to remove an existing module from a Catalyst 6500 series switch chassis slot.

CautionDuring this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool, or you could shock yourself.

Warning
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments.
To remove a supervisor engine or module from the chassis, perform these steps:
Step 1
Disconnect any network interface cables that are attached to the supervisor engine or module.
Step 2
Verify that the captive installation screws on all of the modules in the chassis are tight.
This step assures that the space that is created by the removed module is maintained.

Note
If the captive installation screws are loose, the electromagnetic interference (EMI) gaskets on the installed modules will push the modules toward the open slot, reducing the opening size and making it difficult to install the replacement module.
Step 3
Loosen the two captive installation screws on the supervisor engine or module.
Step 4
Depending on the orientation of the slots in the chassis (horizontal or vertical), perform one of the following sets of substeps:
Horizontal slots
a.
Place your thumbs on the left and right ejector levers, and simultaneously rotate the levers outward to unseat the module from the backplane connector.
b.
Grasp the front edge of the module, and slide the module part of the way out of the slot. Place your other hand under the module to support the weight of the module. Do not touch the module circuitry.
Vertical slots
a.
Place your thumbs on the ejector levers that are located at the top and bottom of the module, and simultaneously rotate the levers outward to unseat the module from the backplane connector.
b.
Grasp the edges of the module, and slide the module straight out of the slot. Do not touch the module circuitry.
Step 5
Place the module on an antistatic mat or antistatic foam, or immediately reinstall it in another slot.
Step 6
If the slot from which you removed the module is to remain empty, install a module filler plate to keep dust out of the chassis and to maintain proper airflow through the chassis.

Warning
Blank faceplates (filler panels) serve three important functions: they prevent exposure to hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic interference (EMI) that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all cards and faceplates are in place.
Installing a Module
This section describes how to install a supervisor engine or module in the Catalyst 6500 series switches.

CautionTo prevent ESD damage, handle modules by the carrier edges only.

CautionDuring this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool, or you could shock yourself.

Warning
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments.
To install a supervisor engine or module in the chassis, perform these steps:
Step 1
Choose a slot for the supervisor engine or module.
Step 2
Verify that there is enough clearance to accommodate any interface equipment that you will connect directly to the supervisor engine or module ports. If possible, place modules between empty slots that contain only module filler plates.
Step 3
Verify that the captive installation screws are tightened on all modules installed in the chassis.
This action ensures that the EMI gaskets on all modules are fully compressed to maximize the opening space for the replacement module.

Note
If the captive installation screws are loose, the EMI gaskets on the installed modules will push adjacent modules toward the open slot, reducing the opening size and making it difficult to install the replacement module.
Step 4
Remove the module filler plate by removing the two Phillips pan-head screws from the filler plate. (To remove a module, refer to the "Removing the Module" section.)
Step 5
Fully open both ejector levers on the new or replacement module. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 2 Positioning the Module in a Horizontal Slot Chassis

Step 6
Depending on the orientation of the slots in the chassis (horizontal or vertical), perform one of the following sets of substeps:
Horizontal slots
a.
Position the supervisor engine or module in the slot. Make sure that you align the sides of the module carrier with the slot guides on each side of the slot. (See Figure 2.)
b.
Carefully slide the supervisor engine or module into the slot until the EMI gasket along the top edge of the module makes contact with the module in the slot above it and both ejector levers have closed to approximately 45 degrees with respect to the module faceplate. (See Figure 3.)
Figure 3 Clearing the EMI Gasket in a Horizontal Slot Chassis

c.
Using the thumb and forefinger of each hand, grasp the two ejector levers and press down to create a small (0.040 inch [1 mm]) gap between the modules EMI gasket and the module above it. (See Figure 3.)

CautionPressing down too firmly on the levers will bend and damage them.
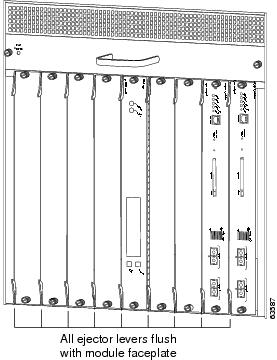
d.
While pressing down, simultaneously close the left and right ejector levers to fully seat the supervisor engine or module in the backplane connector. The ejector levers are fully closed when they are flush with the module faceplate. (See Figure 4.)
Figure 4 Ejector Lever Closure in a Horizontal Slot Chassis


Note
Failure to fully seat the module in the backplane connector can result in error messages.
e.
Tighten the two captive installation screws on the supervisor engine or module.

Note
Make sure that the ejector levers are fully closed before tightening the captive installation screws.
Vertical slots
a.
Position the supervisor engine or switching module in the slot. (See Figure 5.) Make sure that you align the sides of the switching-module carrier with the slot guides on the top and bottom of the slot.
Figure 5 Positioning the Module in a Vertical Slot Chassis
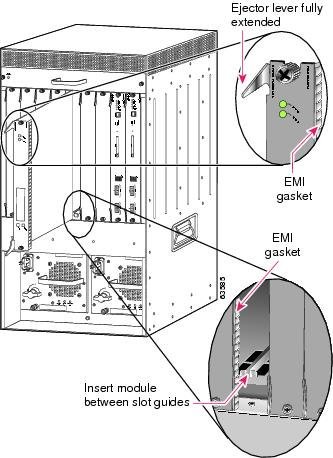
b.
Carefully slide the supervisor engine or module into the slot until the EMI gasket along the right edge of the module makes contact with the module in the slot adjacent to it and both ejector levers have closed to approximately 45 degrees with respect to the module faceplate. (See Figure 6.)
c.
Using the thumb and forefinger of each hand, grasp the two ejector levers and exert a slight pressure to the left, deflecting the module approximately 0.040 inches (1 mm) to create a small gap between the modules EMI gasket and the module adjacent to it. (See Figure 6.)
Figure 6 Clearing the EMI Gasket in a Vertical Slot Chassis


CautionExerting too much pressure on the ejector levers will bend and damage them.
d.
While pressing on the ejector levers, simultaneously close them to fully seat the supervisor engine or module in the backplane connector. The ejector levers are fully closed when they are flush with the module faceplate. (See Figure 7.)
Figure 7 Ejector Lever Closure in a Vertical Slot Chassis
e.
Tighten the two captive installation screws on the module.

Note
Make sure that the ejector levers are fully closed before tightening the captive installation screws.
This completes the CSM-S installation procedure.
Verifying the Installation
When you install the CSM-S into the Catalyst 6500 series switch, the module goes through a startup sequence that requires no intervention. At the successful conclusion of the startup sequence, the green Status LED will light and remain on. If the Status LED does not show green, or if it shows a different color, refer to Table 1 to determine the modules status.
Using the CLI
The software interface for the module is the Cisco IOS and the Catalyst operating system command-line interface accessed through a Telnet connection to the switch or through the switch console interface. Refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide and the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Software Configuration Guide for details.
To understand the Cisco IOS command-line interface and Cisco IOS command modes, refer to Chapter 2, "Command-Line Interfaces," in the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide.
To understand the Catalyst operating system command-line interface and Catalyst operating system command modes, refer to Chapter 2, "Command-Line Interfaces," in the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Configuration Guide.
Unless your switch is located in a fully trusted environment, we recommend that you configure the module through a Telnet connection using Secure Shell (SSH) encryption.
You can session into the module from the switch console and configure the CSM-S. The session is a Telnet interface through the Ethernet out-of-band channel (EOBC) of the switch backplane.
You can also make a Telnet connection into the module from a specified host and on a specific interface. Telnet support for this host should be configured or enabled from the module console.
Console output is redirected to all active Telnet sessions. When no Telnet session is available, the output is saved to a buffer. The buffer output can be subsequently examined when you make a Telnet connection into the module.
Related Documentation
For more detailed installation and configuration information for the Content Switching Module with SSL, refer to the following publications:
•
Release Notes for the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Content Switching Module with SSL
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Content Switching Module with SSL Installation Note
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Content Switching Module with SSL Command Reference
•
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Catalyst 6500 Series Switches
For more detailed installation and configuration information for SSL services, refer to the following publications:
•
Release Notes for Catalyst 6500 Series SSL Services Module Software Release 2.x
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch SSL Services Module Installation and Verification Note
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch SSL Services Module Command Reference
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch SSL Services Module System Messages
Translated Safety Warnings
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/home/home.htm
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Ordering Documentation
You can find instructions for ordering documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/es_inpck/pdi.htm
You can order Cisco documentation in these ways:
•
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order Cisco product documentation from the Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/index.shtml
•
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in North America, by calling 800 553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
You can send comments about technical documentation to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit comments by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
For all customers, partners, resellers, and distributors who hold valid Cisco service contracts, Cisco Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day, award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical Support Website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not hold a valid Cisco service contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support Website
The Cisco Technical Support Website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support Website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3 and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool automatically provides recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service request will be assigned to a Cisco TAC engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone. (S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.) Cisco TAC engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553 2447For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is "down," or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your business operation are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired, but most business operations remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service to satisfactory levels.
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online and printed sources.
•
Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, and logo merchandise. Visit Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
•
The Cisco Product Catalog describes the networking products offered by Cisco Systems, as well as ordering and customer support services. Access the Cisco Product Catalog at this URL:
http://cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/pcat/
•
Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
•
Packet magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends, technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at this URL:
•
iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to help growing companies learn how they can use technology to increase revenue, streamline their business, and expand services. The publication identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to help solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help readers make sound technology investment decisions. You can access iQ Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
•
Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
•
World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.

Copyright © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)























 Feedback
Feedback