- Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Overview
- Getting Started with Configuring Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow
- Configuring Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow with Predefined Records
- Configuring Data Export for Flexible NetFlow with Flow Exporters
- Customizing Flexible NetFlow Flow Records and Flow Monitors
- Using Flexible NetFlow Flow Sampling
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Restrictions for Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Information About Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Benefit of Emulating Original NetFlow with Flexible NetFlow
- NetFlow Original and NetFlow IPv4 Original Input Predefined Records
- NetFlow IPv4 Original Output Predefined Record
- NetFlow IPv6 Original Input Predefined Record
- NetFlow IPv6 Original Output Predefined Record
- Flexible NetFlow MPLS Egress NetFlow
- How to Get Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Configuration Examples for Emulating Original NetFlow Features with Flexible NetFlow
- Where to Go Next
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Flexible NetFlow
Getting Started with Configuring Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow
This document contains information about and instructions for configuring Flexible NetFlow to emulate the data capture, data analysis, and data export features of original NetFlow. The Flexible NetFlow equivalents of some of the other features that have been added to original NetFlow, such as NetFlow Subinterface Support and Multiple Export Destinations, are described in this document. The purpose of this document is to help you start using Flexible NetFlow as quickly as possible, and explains how to configure certain Flexible NetFlow features but does not explain them in detail. The documents listed in the Getting Started with Configuring Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow contain more detailed information on Flexible NetFlow features.
NetFlow is a Cisco IOS technology that provides statistics on packets flowing through the router. NetFlow is the standard for acquiring IP operational data from IP networks. NetFlow provides data to support network and security monitoring, network planning, traffic analysis, and IP accounting.
Flexible NetFlow improves on original NetFlow by adding the capability to customize the traffic analysis parameters for your specific requirements. Flexible NetFlow facilitates the creation of more complex configurations for traffic analysis and data export through the use of reusable configuration components.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Restrictions for Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Information About Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- How to Get Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Configuration Examples for Emulating Original NetFlow Features with Flexible NetFlow
- Where to Go Next
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Flexible NetFlow
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- You are familiar with the information in the " Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Overview " module.
- The networking device must be running a Cisco IOS release that supports Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow.
IPv4 Traffic
- The networking device must be configured for IPv4 routing.
- One of the following must be enabled on your router and on any interfaces on which you want to enable Flexible NetFlow: Cisco Express Forwarding or distributed Cisco Express Forwarding .
IPv6 Traffic
- The networking device must be configured for IPv6 routing.
- One of the following must be enabled on your router and on any interfaces on which you want to enable Flexible NetFlow: Cisco Express Forwarding IPv6 or distributed Cisco Express Forwarding IPv6.
Restrictions for Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Locally generated traffic (traffic that is generated by the router on which the Flexible NetFlow Output Accounting feature is configured) is not counted as flow traffic for the Output Flexible NetFlow Accounting feature.
- The Flexible NetFlow Output Accounting feature counts CEF-switched packets only. Process- switched transit packets are not counted.
Information About Getting Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Benefit of Emulating Original NetFlow with Flexible NetFlow
- NetFlow Original and NetFlow IPv4 Original Input Predefined Records
- NetFlow IPv4 Original Output Predefined Record
- NetFlow IPv6 Original Input Predefined Record
- NetFlow IPv6 Original Output Predefined Record
- Flexible NetFlow MPLS Egress NetFlow
Benefit of Emulating Original NetFlow with Flexible NetFlow
Emulating original NetFlow with Flexible NetFlow enables to you to deploy Flexible NetFlow quickly because you can use a predefined record instead of designing and configuring a custom user-defined record. You need only configure a flow monitor and apply it to an interface for Flexible NetFlow to start working like original NetFlow. You can add an optional exporter if you want to analyze the data that you collect with an application such as NetFlow collector.
Each flow monitor has a separate cache assigned to it. Each flow monitor requires a record to define the contents and layout of its cache entries. The record format can be one of the predefined record formats, or an advanced user may create his or her own record format using the collect and matchcommands in Flexible NetFlow flow record configuration mode.
Flow exporters are used to send the data that you collect with Flexible NetFlow to a remote system such as a NetFlow Collection Engine. Exporters use UDP as the transport protocol and use the Version 9 export format.
If you are familiar with original NetFlow, you already understand the format and content of the data that you collect and export with Flexible NetFlow when you emulate original NetFlow. You will be able to use the same techniques for analyzing the data.
NetFlow Original and NetFlow IPv4 Original Input Predefined Records
The Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow original" and "NetFlow IPv4 original input" predefined records can be used interchangeably because they have the same key and nonkey fields. The key and nonkey fields and the counters for the Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow original" and "NetFlow IPv4 original input" predefined records are shown in the table below.
| Table 1 | Key and Nonkey Fields Used by the Flexible NetFlow NetFlow Original and NetFlow IPv4 Original Input Predefined Records |
| Field |
Key or Nonkey Field |
Definition |
|---|---|---|
| IP ToS |
Key |
Value in the type of service (ToS) field. |
| IP Protocol |
Key |
Value in the IP protocol field. |
| IP Source Address |
Key |
IP source address. |
| IP Destination Address |
Key |
IP destination address. |
| Transport Source Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer source port field. |
| Transport Destination Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer destination port field. |
| Interface Input |
Key |
Interface on which the traffic is received. |
| Flow Sampler ID |
Key |
ID number of the flow sampler (if flow sampling is enabled). |
| IP Source AS |
Nonkey |
Source autonomous system number. |
| IP Destination AS |
Nonkey |
Destination autonomous system number. |
| IP Next Hop Address |
Nonkey |
IP address of the next hop. |
| IP Source Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP source address. |
| IP Destination Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP destination address. |
| TCP Flags |
Nonkey |
Value in the TCP flag field. |
| Interface Output |
Nonkey |
Interface on which the traffic is transmitted. |
| Counter Bytes |
Nonkey |
Number of bytes seen in the flow. |
| Counter Packets |
Nonkey |
Number of packets seen in the flow. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime First |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the first packet was switched. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime Last |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the last packet was switched. |
The configuration in the How to Get Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow uses the predefined Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow original" record.
NetFlow IPv4 Original Output Predefined Record
The Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow IPv4 original output" predefined record is used to emulate the original NetFlow Egress NetFlow Accounting feature that was released in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T. The key and nonkey fields and the counters for the Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow IPv4 original output" predefined record are shown in the table below.
| Table 2 | Key and Nonkey Fields Used by the Flexible NetFlow NetFlow IPv4 Original Output Predefined Record |
| Field |
Key or Nonkey Field |
Definition |
|---|---|---|
| IP ToS |
Key |
Value in the ToS field. |
| IP Protocol |
Key |
Value in the IP protocol field. |
| IP Source Address |
Key |
IP source address. |
| IP Destination Address |
Key |
IP destination address. |
| Transport Source Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer source port field. |
| Transport Destination Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer destination port field. |
| Interface Output |
Key |
Interface on which the traffic is transmitted. |
| Flow Sampler ID |
Key |
ID number of the flow sampler (if flow sampling is enabled). |
| IP Source AS |
Nonkey |
Source autonomous system number. |
| IP Destination AS |
Nonkey |
Destination autonomous system number. |
| IP Next Hop Address |
Nonkey |
IP address of the next hop. |
| IP Source Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP source address. |
| IP Destination Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP destination address. |
| TCP Flags |
Nonkey |
Value in the TCP flag field. |
| Interface Input |
Nonkey |
Interface on which the traffic is received. |
| Counter Bytes |
Nonkey |
Number of bytes seen in the flow. |
| Counter Packets |
Nonkey |
Number of packets seen in the flow. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime First |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the first packet was switched. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime Last |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the last packet was switched. |
The configuration in the Example: Configuring Flexible NetFlow Egress Accounting for IPv4 and IPv6 Traffic uses the predefined Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow original output" record.
NetFlow IPv6 Original Input Predefined Record
The key and nonkey fields and the counters for the Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow IPv6 original input" predefined record are shown in the table below.
| Table 3 | Key and Nonkey Fields Used by the Flexible NetFlow NetFlow IPv6 Original Input Predefined Record |
| Field |
Key or NonKey Field |
Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Class |
Key |
Value in the traffic class field. |
| Flow Label |
Key |
Flow label. |
| Protocol |
Key |
Value in the protocol field. |
| Extension Map |
Key |
Value in the extension map bitmap. |
| IP Source Address |
Key |
IP source address. |
| IP Destination Address |
Key |
IP destination address. |
| Transport Source Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer source port field. |
| Transport Destination Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer destination port field. |
| Interface Input |
Key |
Interface on which the traffic is received. |
| Flow Direction |
Key |
The direction of the flow. |
| Flow Sampler |
Key |
ID number of the flow sampler (if flow sampling is enabled). |
| Routing Source AS |
Nonkey |
Source autonomous system number. |
| Routing Destination AS |
Nonkey |
Destination autonomous system number. |
| Routing Next-hop Address |
Nonkey |
IP address of the next hop. |
| IP Source Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP source address. |
| IP Destination Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP destination address. |
| Transport TCP Flags |
Nonkey |
Value in the TCP flag field. |
| Interface Output |
Nonkey |
Interface over which the traffic is transmitted. |
| Counter Bytes |
Nonkey |
Number of bytes seen in the flow. |
| Counter Packets |
Nonkey |
Number of packets seen in the flow. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime First |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the first packet was switched. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime Last |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the last packet was switched. |
NetFlow IPv6 Original Output Predefined Record
The key and nonkey fields and the counters for the Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow IPv6 original output" predefined record are shown in the table below.
| Table 4 | Key and Nonkey Fields Used by the Flexible NetFlow NetFlow IPv6 Original Output Predefined Record |
| Field |
Key or Nonkey Field |
Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Class |
Key |
Value in the traffic class field. |
| Flow Label |
Key |
The flow label. |
| Protocol |
Key |
Value in the protocol field. |
| Extension Map |
Key |
Value in the extension map bitmap. |
| IP Source Address |
Key |
IP source address. |
| IP Destination Address |
Key |
IP destination address. |
| Transport Source Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer source port field. |
| Transport Destination Port |
Key |
Value of the transport layer destination port field. |
| Interface Output |
Key |
Interface over which the traffic is transmitted. |
| Flow Direction |
Key |
The direction of the flow. |
| Flow Sampler |
Key |
ID number of the flow sampler (if flow sampling is enabled). |
| Routing Source AS |
Nonkey |
Source autonomous system number. |
| Routing Destination AS |
Nonkey |
Destination autonomous system number. |
| Routing Next-hop Address |
Nonkey |
IP address of the next hop. |
| IP Source Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP source address. |
| IP Destination Mask |
Nonkey |
Mask for the IP destination address. |
| Transport TCP Flags |
Nonkey |
Value in the TCP flag field. |
| Interface Input |
Nonkey |
Interface on which the traffic is received. |
| Counter Bytes |
Nonkey |
Number of bytes seen in the flow. |
| Counter Packets |
Nonkey |
Number of packets seen in the flow. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime First |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the first packet was switched. |
| Time Stamp System Uptime Last |
Nonkey |
System uptime (time, in milliseconds, since this device was first booted) when the last packet was switched. |
Flexible NetFlow MPLS Egress NetFlow
The Flexible NetFlow--MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN. The Flexible NetFlow--MPLS Egress NetFlow feature is enabled by applying a flow monitor in output (egress) mode on the provider edge (PE) to customer edge (CE) interface of the provider's network.
The figure below shows a sample MPLS VPN network topology that includes four VPN 1 sites and two VPN 2 sites. If the Flexible NetFlow--MPLS Egress NetFlow is enabled on an outgoing PE interface by applying a flow monitor in output mode, IP flow information for packets that arrive at the PE as MPLS packets (from an MPLS VPN) and that are transmitted as IP packets to the PE router is captured. For example:
- To capture the flow of traffic going to site 2 of VPN 1 from any remote VPN 1 sites, you enable a flow monitor in output mode on link PE2-CE5 of provider edge router PE2.
- To capture the flow of traffic going to site 1 of VPN 2 from any remote VPN 2 site, you enable a flow monitor in output mode on link PE3-CE4 of the provider edge router PE3.
The flow data is stored in the Flexible NetFlow cache. You can use the show flow monitor monitor-name cachecommand to display the flow data in the cache.
| Figure 1 | Sample MPLS VPN Network Topology with Flexible NetFlow--MPLS Egress NetFlow Feature |
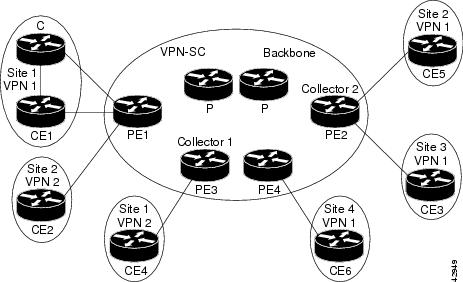
If you configure a Flexible NetFlow exporter for the flow monitors you use for the Flexible NetFlow-- MPLS Egress NetFlow feature, the PE routers will export the captured flows to the configured collector devices in the provider network. Applications such as the Network Data Analyzer or the VPN Solution Center (VPN-SC) can gather information from the captured flows and compute and display site-to-site VPN traffic statistics.
How to Get Started with Configuring Flexible NetFlow
The tasks in this section explain how to configure and verify the emulation of original (ingress) NetFlow data capture with Flexible NetFlow for traffic that is received by the router and how to configure and verify the emulation of original NetFlow data export with Flexible NetFlow.
 Note |
Flexible NetFlow emulation of original NetFlow requires the configuration of a flow monitor and the application of the flow monitor to at least one interface that is receiving the traffic that you want to analyze. |
 Note |
Only the keywords and arguments required for the Flexible NetFlow commands used in these tasks are explained in these tasks. For information on the other keywords and arguments available for these Flexible NetFlow commands, refer to the Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Command Reference . |
- Configuring a Flow Monitor for IPv4 or IPv6 Traffic Using the Predefined Record
- Applying an IPv4 Flow Monitor to an Interface
- Applying an IPv6 Flow Monitor to an Interface
- Configuring a Flow Exporter for the Flow Monitor
Configuring a Flow Monitor for IPv4 or IPv6 Traffic Using the Predefined Record
To configure a flow monitor for IPv4/IPv6 traffic using the Flexible NetFlow "NetFlow IPv4/IPv6 original input" predefined record for the flow monitor, perform the following required task.
Each flow monitor has a separate cache assigned to it. Each flow monitor requires a record to define the contents and layout of its cache entries. The record format can be one of the predefined record formats, or an advanced user may create his or her own record format using the collect and matchcommands in Flexible NetFlow flow record configuration mode.
 Note |
You must remove a flow monitor from all of the interfaces to which you have applied it before you can modify the record format of the flow monitor. |
DETAILED STEPS
Applying an IPv4 Flow Monitor to an Interface
Before it can be activated an IPv4 flow monitor must be applied to at least one interface. To activate an IPv4 flow monitor, perform the following required task.
 Note |
When you specify the "NetFlow original" or the "NetFlow IPv4 original input" predefined record for the flow monitor to emulate original NetFlow, the flow monitor can be used for analyzing only input (ingress) traffic. When you specify the "NetFlow IPv4 original output" predefined record for the flow monitor to emulate the Egress NetFlow Accounting feature, the flow monitor can be used for analyzing only output (egress) traffic. |
DETAILED STEPS
Applying an IPv6 Flow Monitor to an Interface
Before it can be activated an IPv6 flow monitor must be applied to at least one interface. To activate an IPv6 flow monitor, perform the following required task.
 Note |
When you specify the "NetFlow IPv6 original input" predefined record for the flow monitor to emulate original NetFlow, the flow monitor can be used for analyzing only input (ingress) traffic. When you specify the "NetFlow IPv6 original output" predefined record for the flow monitor to emulate the Egress NetFlow Accounting feature, the flow monitor can be used for analyzing only output (egress) traffic. |
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Flow Exporter for the Flow Monitor
To configure a flow exporter for the flow monitor, in order to export the data that is collected by Flexible NetFlow to a remote system for further analysis and storage, perform the following optional task.
Flow exporters are used to send the data that you collect with Flexible NetFlow to a remote system such as a NetFlow Collection Engine. Exporters use UDP as the transport protocol and use the Version 9 export format.
 Note |
Each flow exporter supports only one destination. If you want to export the data to multiple destinations, you must configure multiple flow exporters and assign them to the flow monitor. You can export to a destination using either an IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Emulating Original NetFlow Features with Flexible NetFlow
- Example: Configuring Flexible NetFlow Egress Accounting for IPv4 and IPv6 Traffic
- Example: Configuring Flexible NetFlow Subinterface Support
- Example: Configuring Flexible NetFlow Multiple Export Destinations
Example: Configuring Flexible NetFlow Egress Accounting for IPv4 and IPv6 Traffic
The following example shows how to configure Flexible NetFlow egress accounting for IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
This sample starts in global configuration mode:
! flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1 record netflow ipv4 original-output exit ! ! flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-2 record netflow ipv6 original-output exit ! ip cef ipv6 cef ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.16.6.2 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2:ABCD::2/48 ip flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1 output ipv6 flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-2 output !
Example: Configuring Flexible NetFlow Subinterface Support
The following example shows how to configure Flexible NetFlow subinterface support for IPv4 traffic.
This sample starts in global configuration mode:
! flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1 record netflow ipv4 original-input exit ! ip cef ! interface Ethernet0/0.1 ip address 172.16.6.2 255.255.255.0 ip flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1 input !
The following example shows how to configure Flexible NetFlow to emulate NetFlow subinterface support for IPv6 traffic.
This sample starts in global configuration mode:
! flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-2 record netflow ipv6 original-input exit ! ip cef ipv6 cef ! interface Ethernet0/0.1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2:ABCD::2/48 ipv6 flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-2 input !
Example: Configuring Flexible NetFlow Multiple Export Destinations
The following example shows how to configure Flexible NetFlow multiple export destinations.
This sample starts in global configuration mode:
! flow exporter EXPORTER-1 destination 172.16.10.2 transport udp 90 exit ! flow exporter EXPORTER-2 destination 172.16.10.3 transport udp 90 exit ! flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1 record netflow-original exporter EXPORTER-2 exporter EXPORTER-1 exit ! ip cef ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 172.16.6.2 255.255.255.0 ip flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-1 input !
Where to Go Next
For information on advanced Flexible NetFlow configurations for specific purposes such as quality of service (QoS) and bandwidth monitoring, application and user flow monitoring and profiling, and security analysis, refer to the "Customizing Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Flow Records and Flow Monitors" module.
If you want to configure additional options for data export for Flexible NetFlow, refer to the "Configuring Data Export for Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow with Flow Exporters" module.
If you want to configure flow sampling to reduce the CPU overhead of analyzing traffic, refer to the "Using Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Flow Sampling to Reduce the CPU Overhead of Analyzing Traffic" module.
If you want to configure any of the predefined records for Flexible NetFlow refer, to the "Configuring Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow with Predefined Records" module.
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| Overview of Flexible NetFlow |
"Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Overview" |
| Configuring flow exporters to export Flexible NetFlow data |
"Configuring Data Export for Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow with Flow Exporters" |
| Customizing Flexible NetFlow |
"Customizing Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Flow Records and Flow Monitors" |
| Configuring flow sampling to reduce the overhead of monitoring traffic with Flexible NetFlow |
"Using Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Flow Sampling to Reduce the CPU Overhead of Analyzing Traffic" |
| Configuring Flexible NetFlow using predefined records |
"Configuring Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow with Predefined Records" |
| Using Flexible NetFlow Top N Talkers to analyze network traffic |
"Using Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Top N Talkers to Analyze Network Traffic" |
| Configuring IPv4 multicast statistics support for Flexible NetFlow |
"Configuring IPv4 Multicast Statistics Support for Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow" |
| Configuration commands for Flexible NetFlow |
Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Command Reference |
Standards
| Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
| None |
-- |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| RFC 3954 |
Cisco Systems NetFlow Services Export Version 9 |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password |
Feature Information for Flexible NetFlow
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 5 | Feature Information for Flexible NetFlow |
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| Flexible NetFlow |
12.2(33)SRC 12.2(50)SY 12.4(9)T 15.0(1)SY 15.0(1)SY1 |
Flexible NetFlow is introduced. Support for this feature was added for Cisco 7200 series routers in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC. The following commands were introduced or modified: cache (Flexible NetFlow), clear flow exporter, clear flow monitor, clear sampler, collect counter, collect flow, collect interface, collect ipv4, collect ipv4 destination, collect ipv4 fragmentation, collect ipv4 section, collect ipv4 source, collect ipv4 total-length, collect ipv4 ttl, collect routing, collect timestamp sys-uptime, collect transport, collect transport icmp ipv4, collect transport tcp, collect transport udp, debug flow exporter, debug flow monitor, debug flow record, debug sampler, description (Flexible NetFlow), destination, dscp (Flexible NetFlow), exporter, flow exporter, flow monitor, flow platform, flow record, ip flow monitor, match flow, match interface (Flexible NetFlow), match ipv4, match ipv4 destination, match ipv4 fragmentation, match ipv4 section, match ipv4 source, match ipv4 total-length, match ipv4 ttl, match routing, match transport, match transport icmp ipv4, match transport tcp, match transport udp, mode (Flexible NetFlow), option (Flexible NetFlow), record, sampler, show flow exporter, show flow interface, show flow monitor, show flow record, show sampler, source (Flexible NetFlow), statistics packet, template data timeout, transport (Flexible NetFlow). |
| Flexible NetFlow--IPv6 Unicast Flows |
12.2(33)SRE 12.2(50)SY 12.4(20)T 15.0(1)SY 15.0(1)SY1 |
Enables Flexible NetFlow to monitor IPv6 traffic. Support for this feature was added for Cisco 7200 and 7300 NPE series routers in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRE. The following commands were introduced or modified: collect routing, debug flow record, match routing, record, show flow monitor, show flow record, collect ipv6, collect ipv6 destination, collect ipv6 extension map, collect ipv6 fragmentation, collect ipv6 hop-limit, collect ipv6 length, collect ipv6 section, collect ipv6 source, collect transport icmp ipv6, ipv6 flow monitor, match ipv6, match ipv6 destination, match ipv6 extension map, match ipv6 fragmentation, match ipv6 hop-limit, match ipv6 length, match ipv6 section, match ipv6 source, match transport icmp ipv6. |
| Flexible NetFlow--MPLS Egress NetFlow |
12.2(33)SRE 12.2(50)SY 12.4(22)T 15.0(1)SY 15.0(1)SY1 |
The Flexible NetFlow--MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets undergoing MPLS label disposition; that is, packets that arrive on a router as MPLS packets and are transmitted as IP packets. Support for this feature was added for Cisco 7200 and 7300 NPE series routers in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRE. No commands were introduced or modified by this feature. |
| Flexible NetFlow: Export to an IPv6 Address |
15.2(2)T |
This feature enables Flexible NetFlow to export data to a destination using an IPv6 address. The following commands were introduced or modified: destination |
| Flexible NetFlow: IPFIX Export Format |
15.2(4)M |
Enables sending export packets using the IPFIX export protocol. The export of extracted fields from NBAR is only supported over IPFIX. Support for this feature was added for Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services routers in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S. The following command was introduced: export-protocol. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback